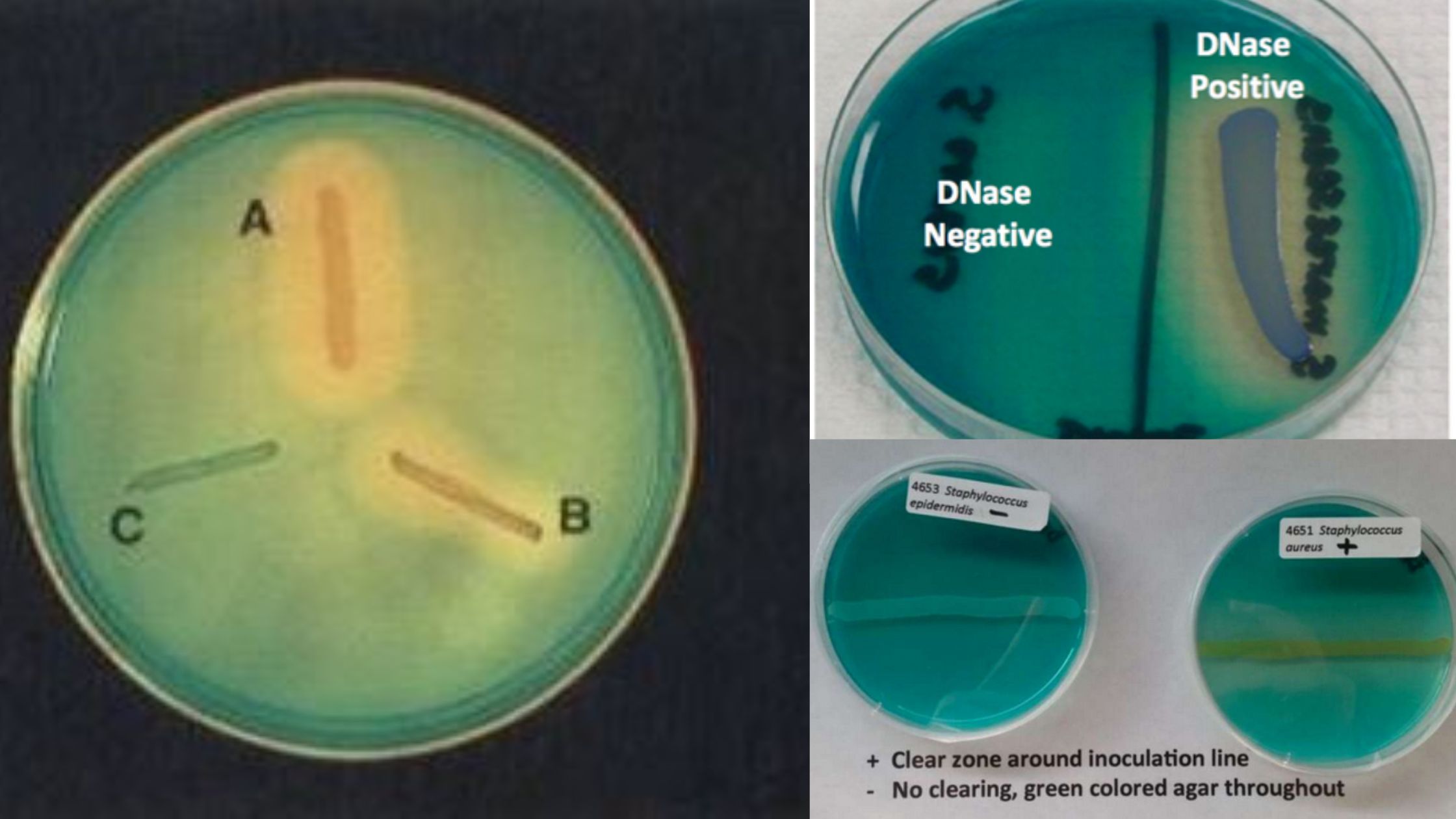
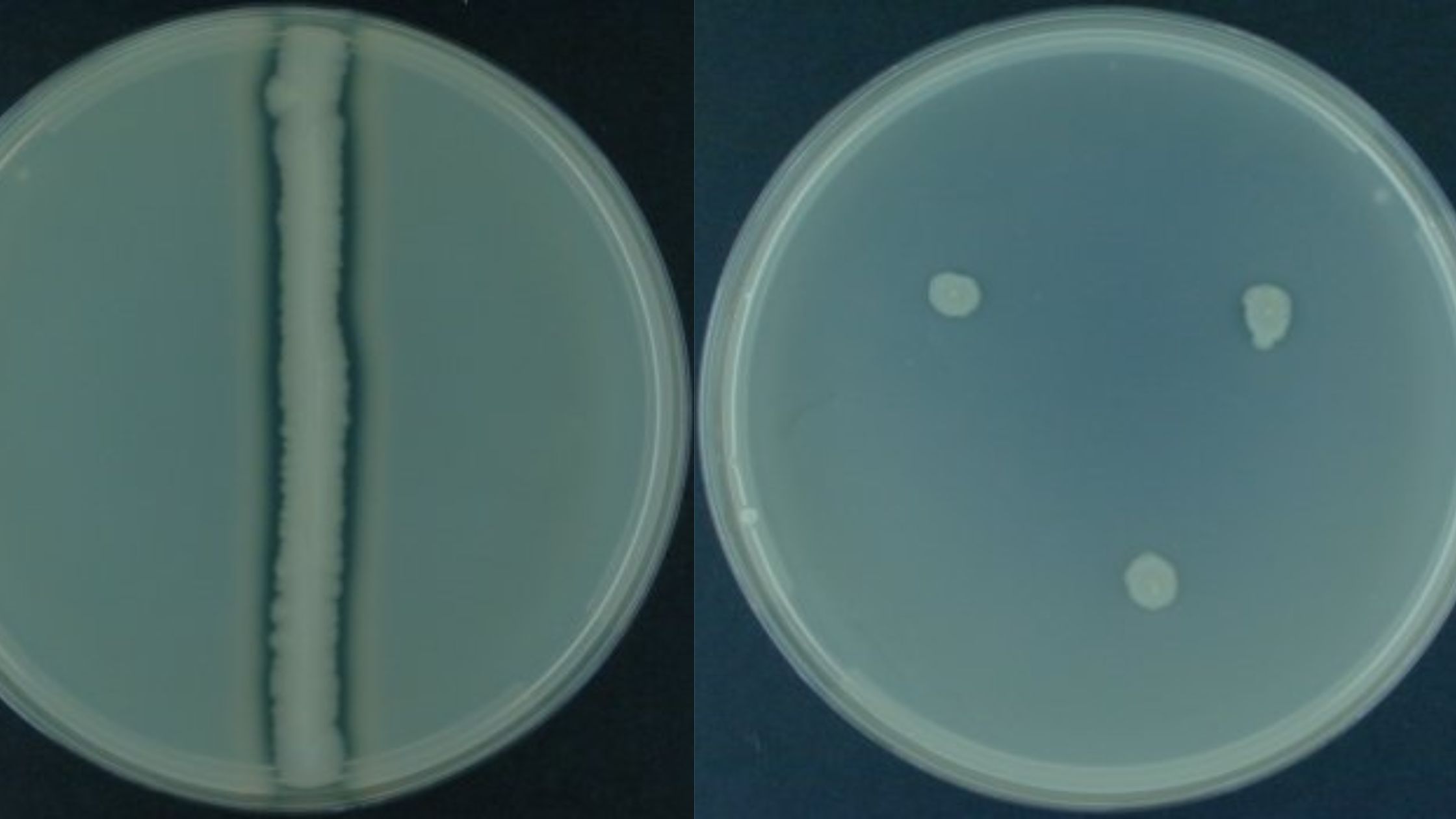
Cetrimide Agar Test – Principle, Purpose, Procedure, Results
Cetrimide Selective Agar is a solid medium that is recommended for use in qualitative procedures for selective isolation and presumed identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other nonfermenting, gram-negative bacilli.