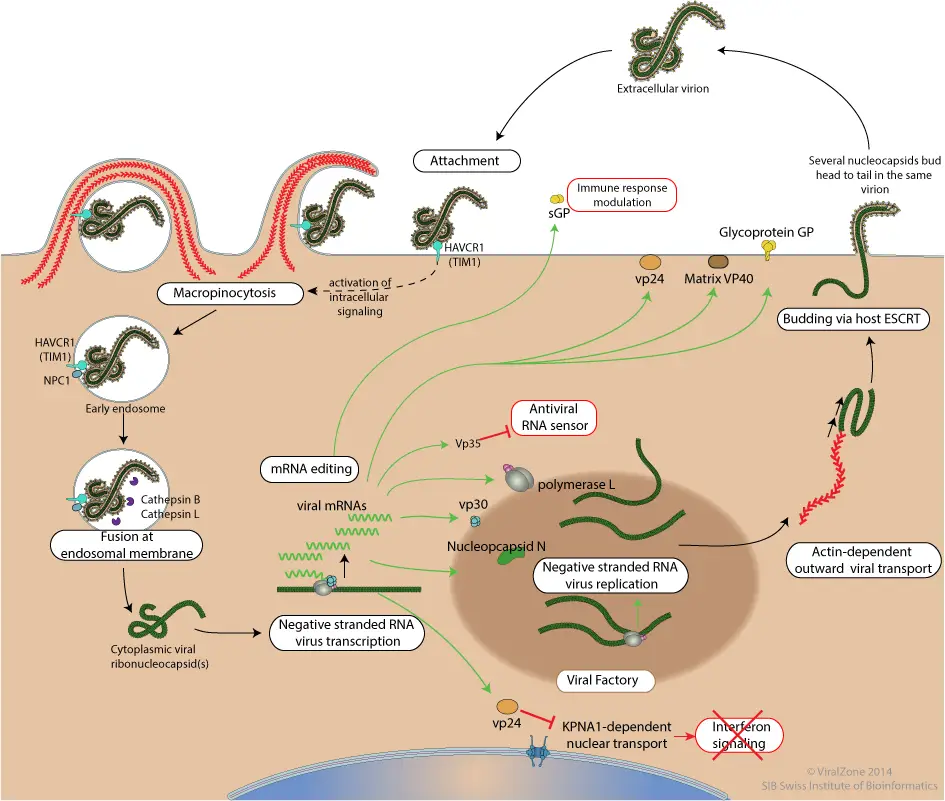
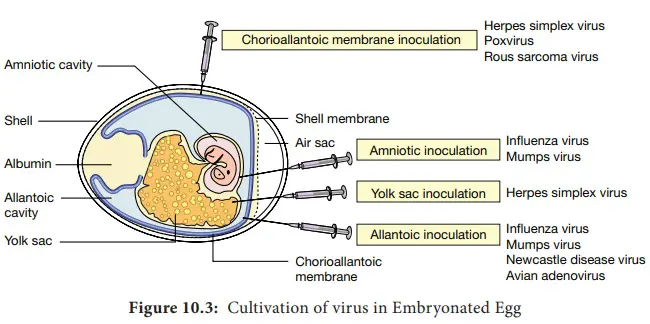
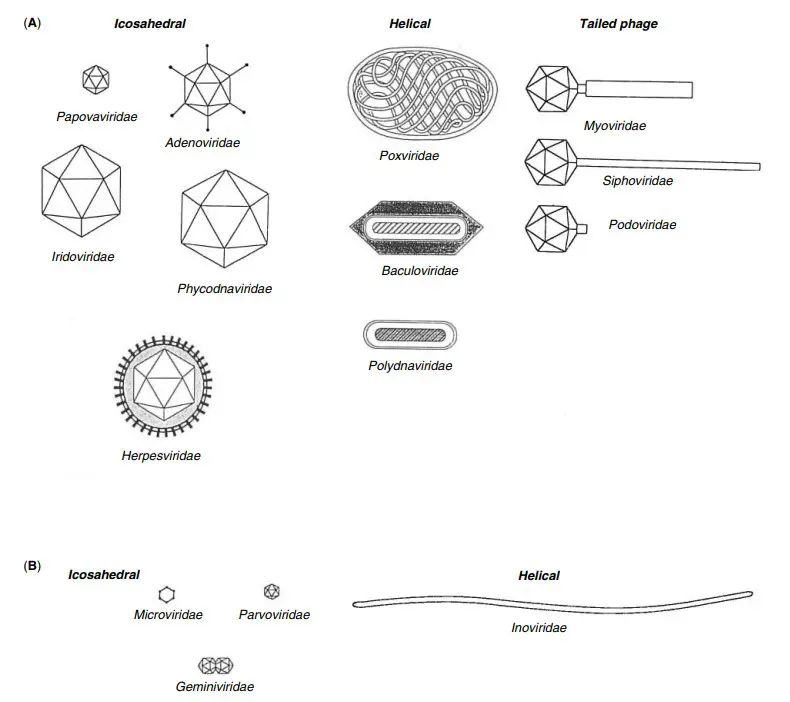
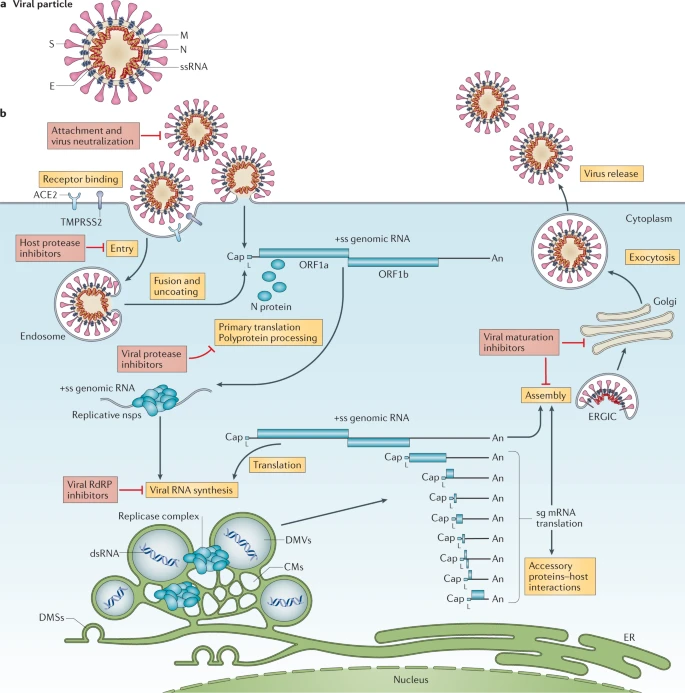
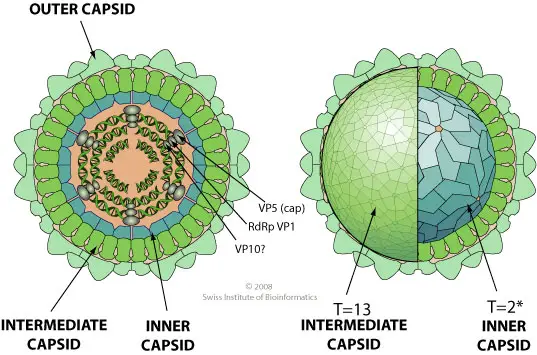
Ebola Virus – Structure, Genome, Replication, Pathogenesis
Ebola Virus Ebola Virus Classification Hosts of Ebola Virus Structure of Ebola Virus Genome of Ebola Virus The genome is composed of a single strand of negative RNA and measures around 18–19 kilobases in length. There are seven proteins in all that are encoded by the genome. Neither the 3′ nor the 5′ end is polyadenylated or … Read more