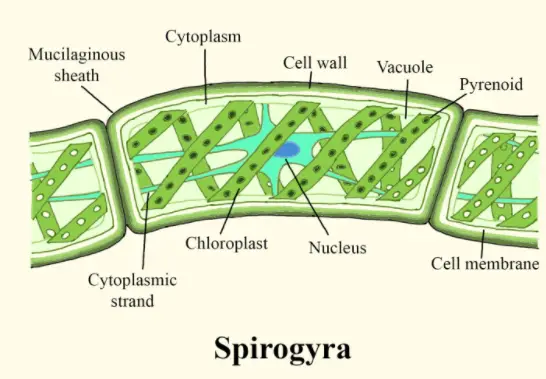
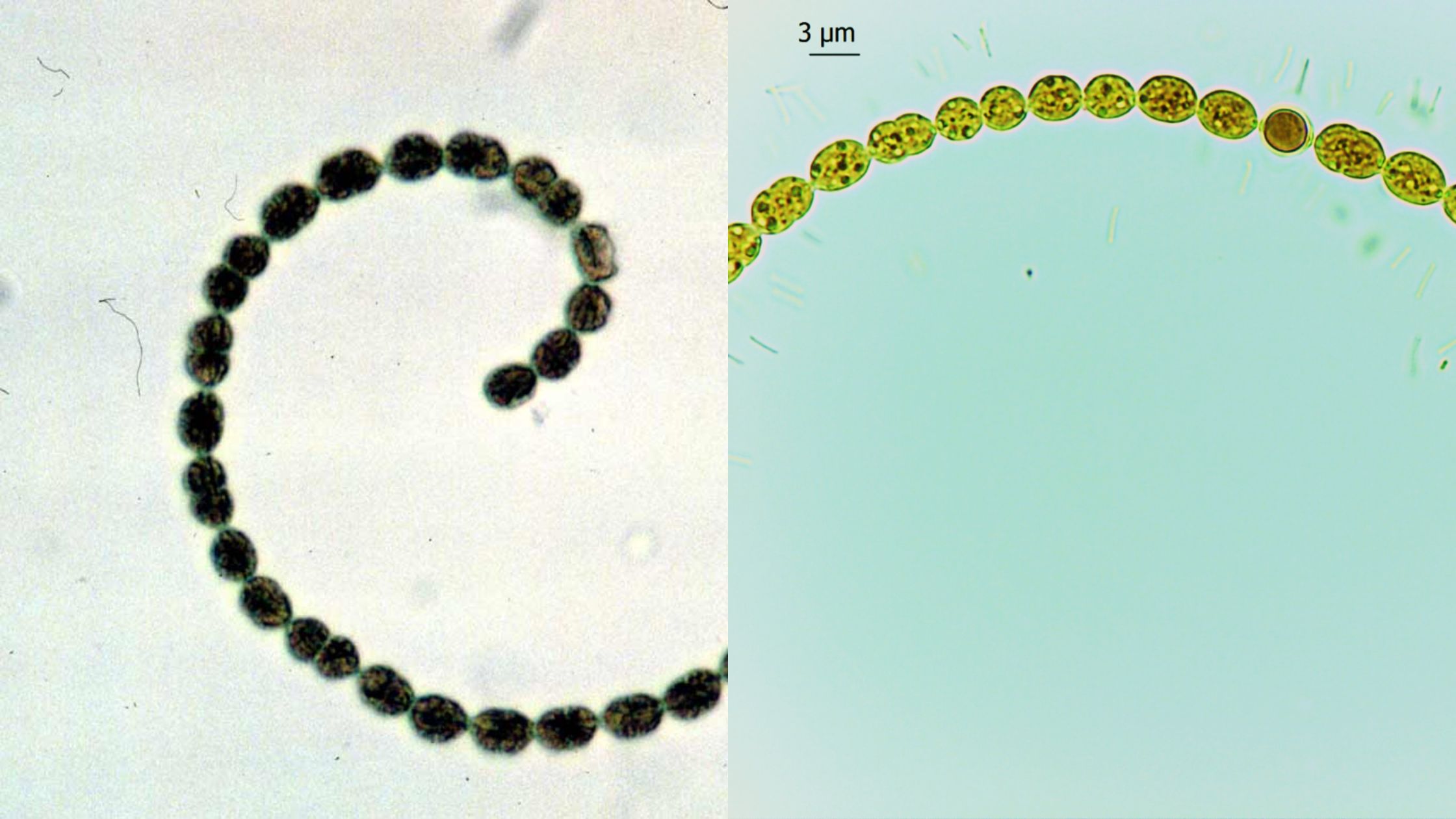
Spirogyra – Definition, Structure, Life Cycle, Diagram, Reproduction
Spirogyra is a genus of filamentous green algae that belongs to the Chlorophyta phylum. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats and is known for its spiral chloroplasts that give it its distinctive appearance. In this article, you will learn about the definition and structure of Spirogyra, as well as its reproduction process. A detailed … Read more