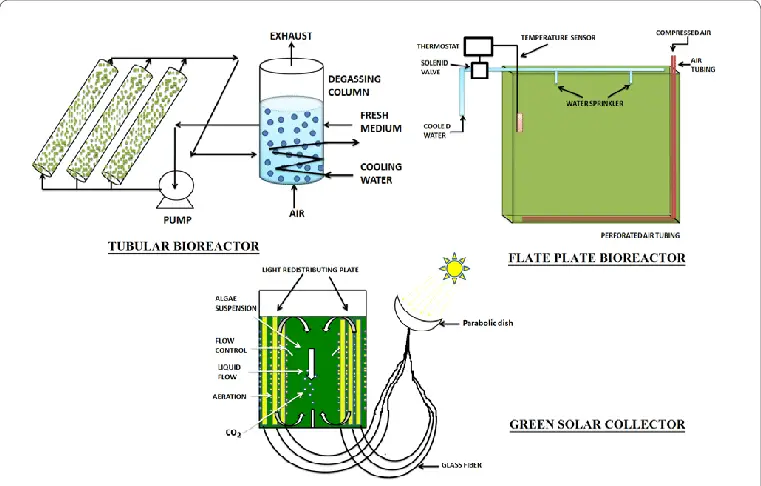
Algae Bioreactor – Definition, Types, Feature, Uses
The Algae Bioreactor is a closed system that treats wastewater and produces biofuels using algae. The earliest commercial applications of algae bioreactors occurred in the 1960s for wastewater treatment. With the increasing global demand for alternative energy sources, the usage of algae bioreactors for biofuel production has risen to prominence in the 21st century. The … Read more