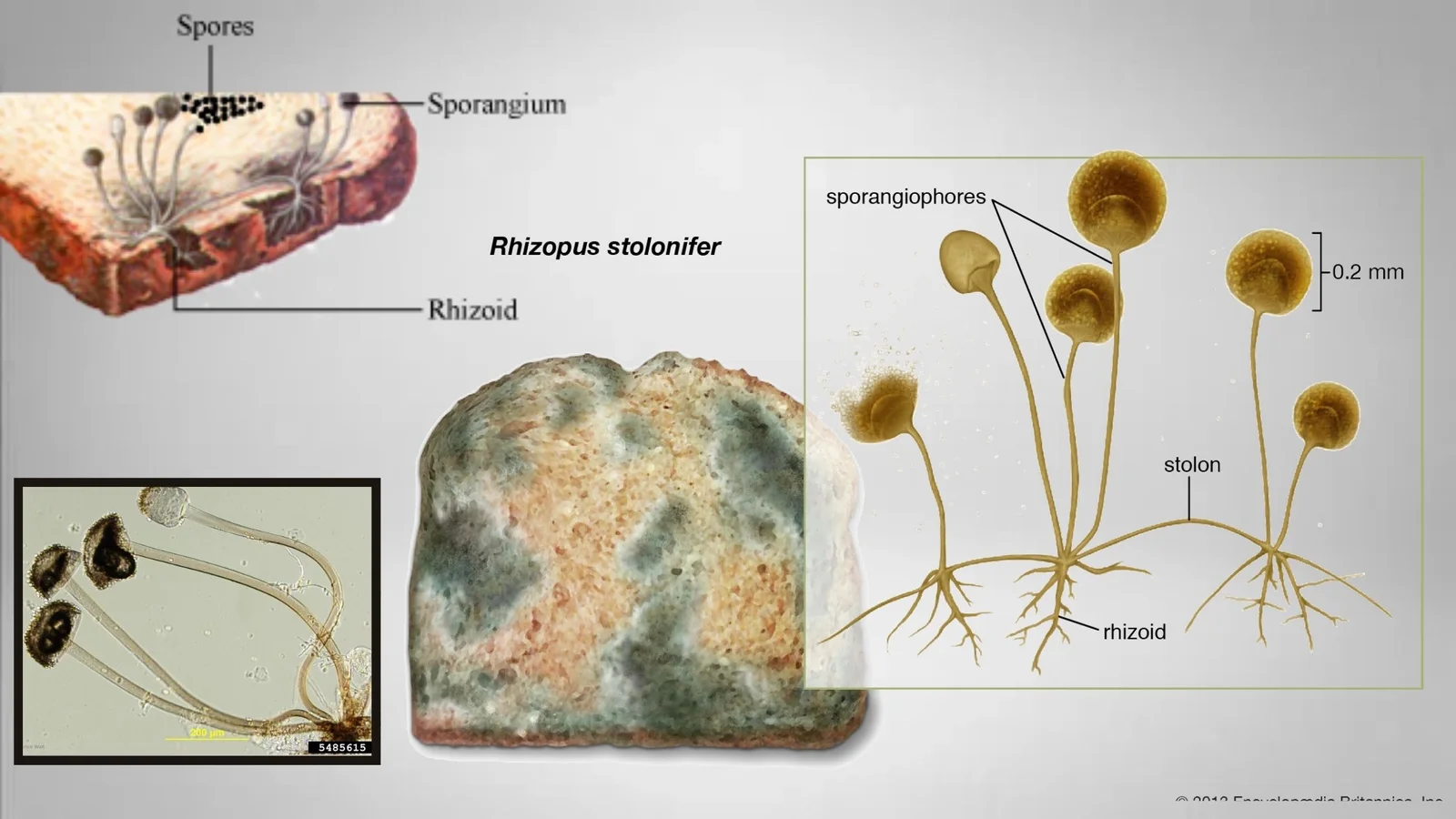
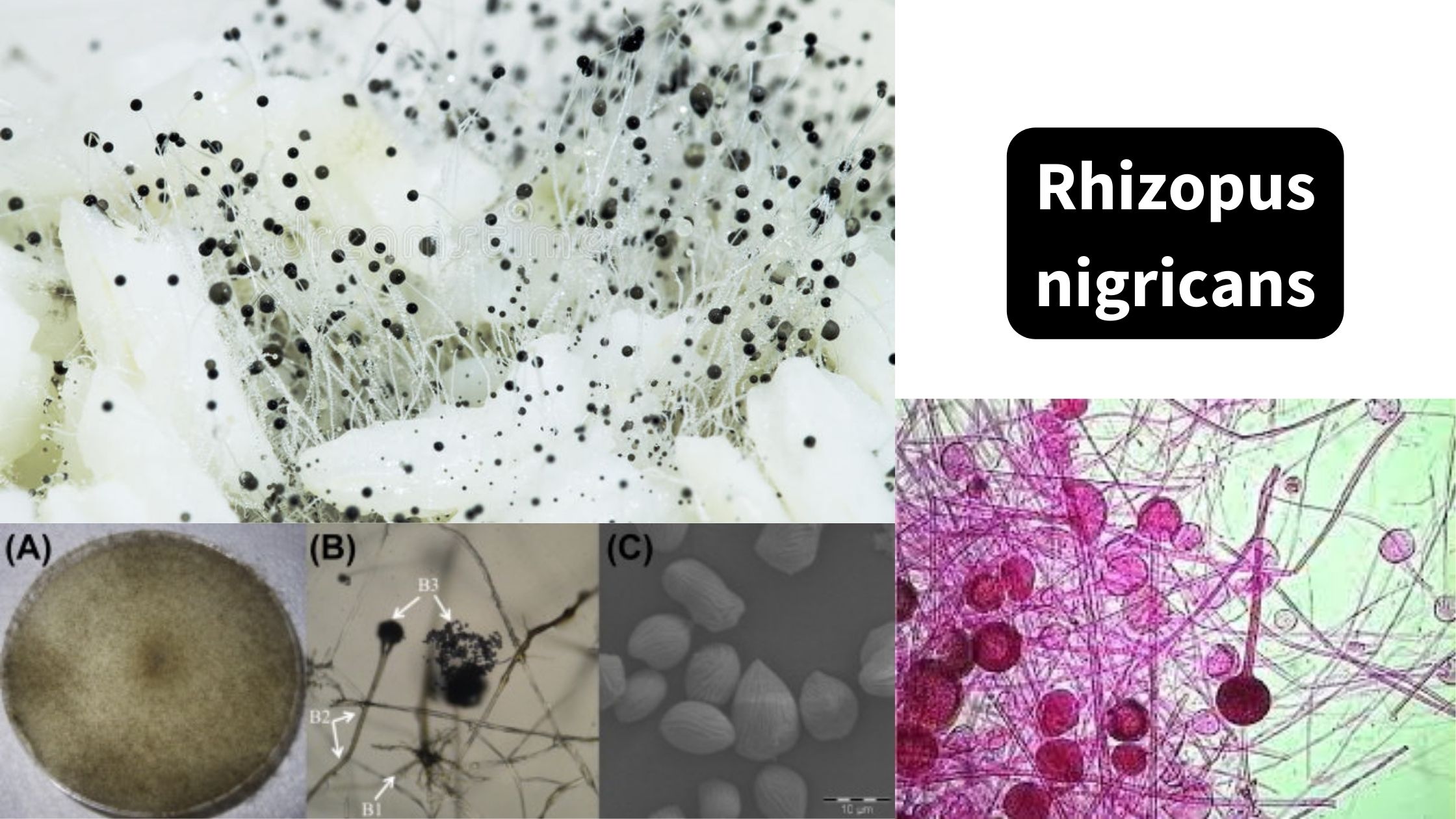
Blastomyces dermatitidis – Morphology, Transmission, Treatment
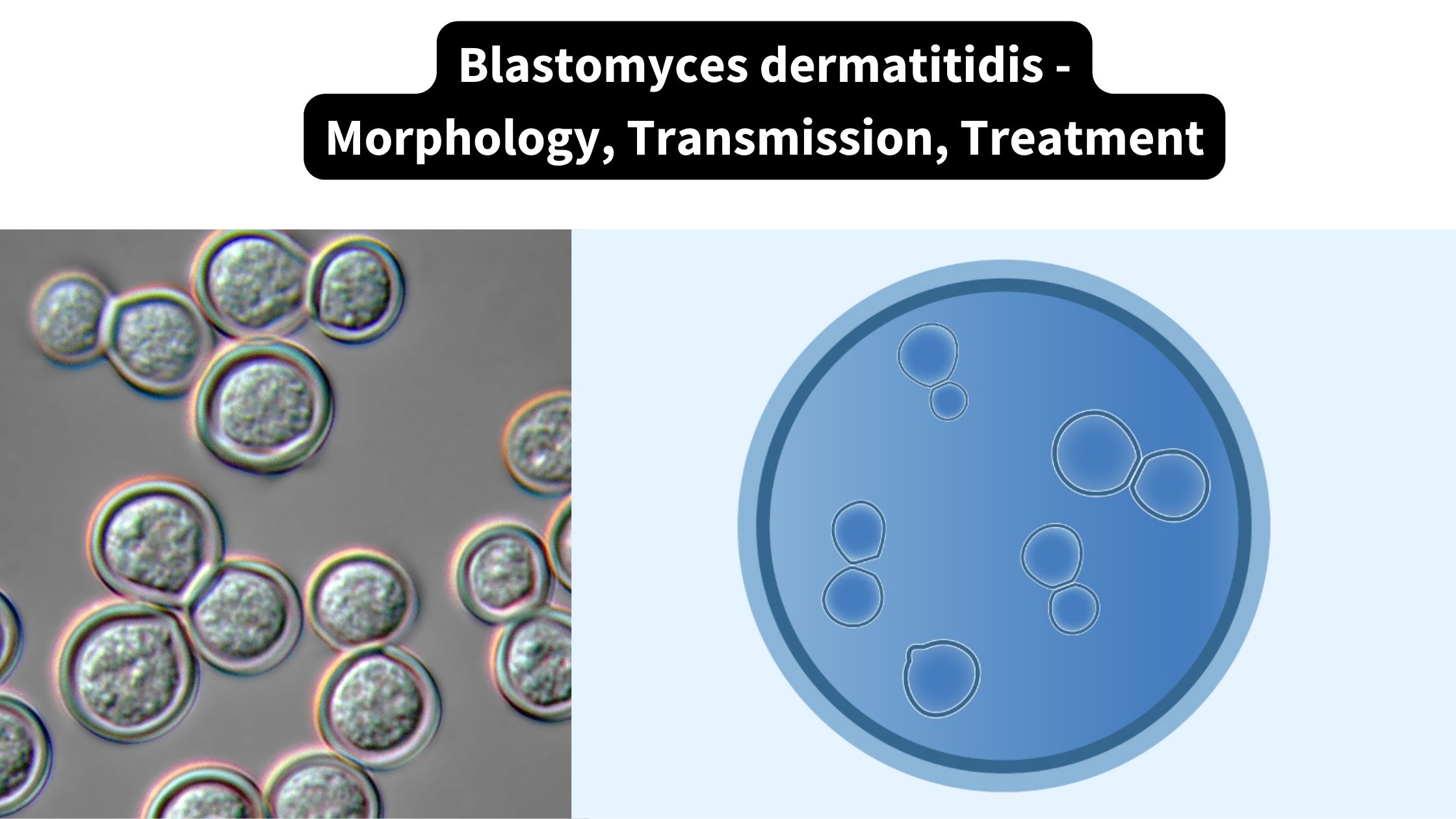
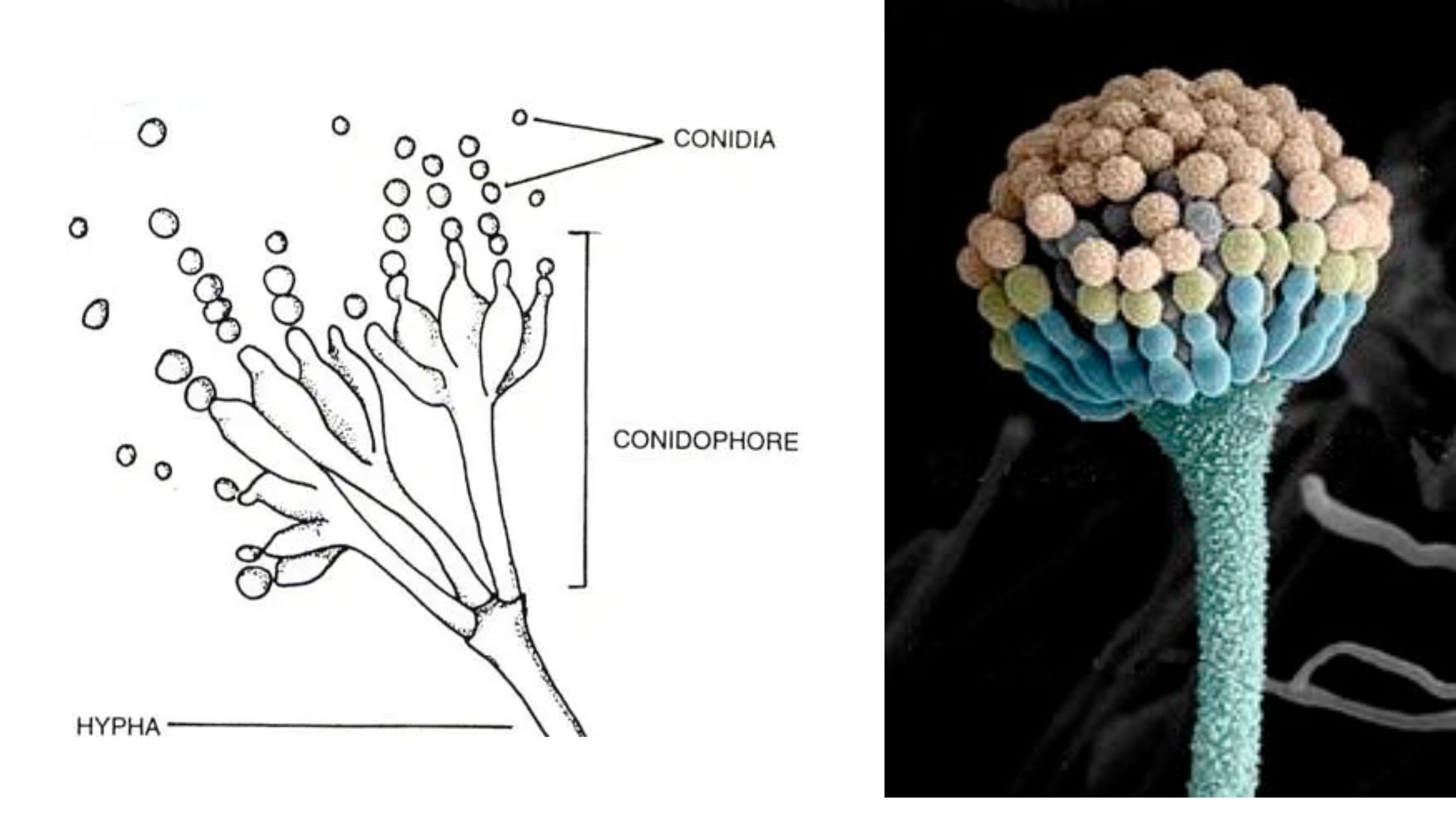
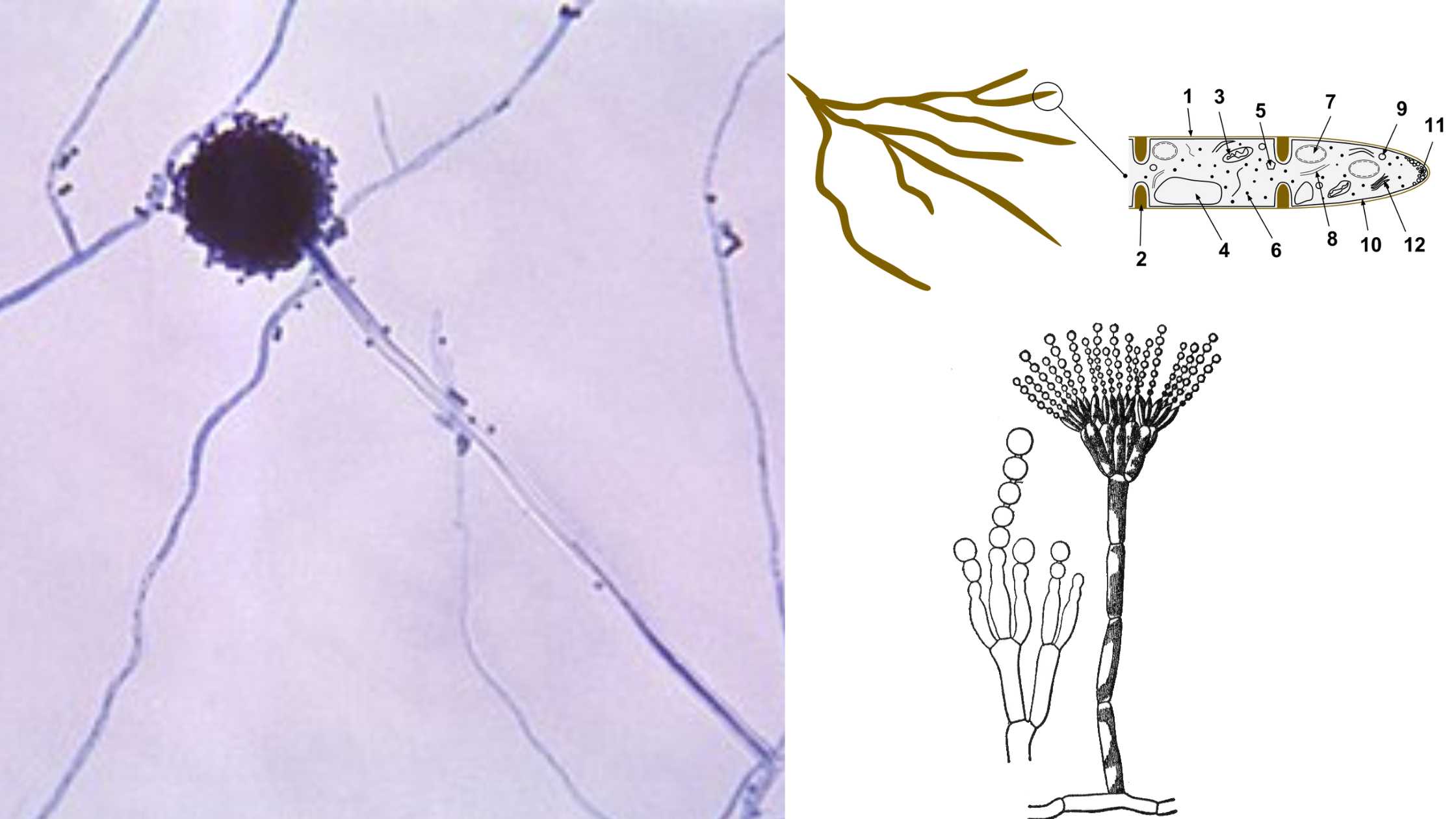
Kingdom: Fungi Division: Ascomycota Class: Eurotiomycetes Order: Onygenales Family: Ajellomycetaceae Genus: Blastomyces Species: B. dermatitidis Morphology of Blastomyces dermatitidis Blastomyces dermatitidis is a dimorphic fungus that causes blastomycosis, a fungal infection in humans and animals. The fungus exists in two different morphological forms, the yeast phase, and the mold phase. Overall, the morphology of Blastomyces dermatitidis … Read more