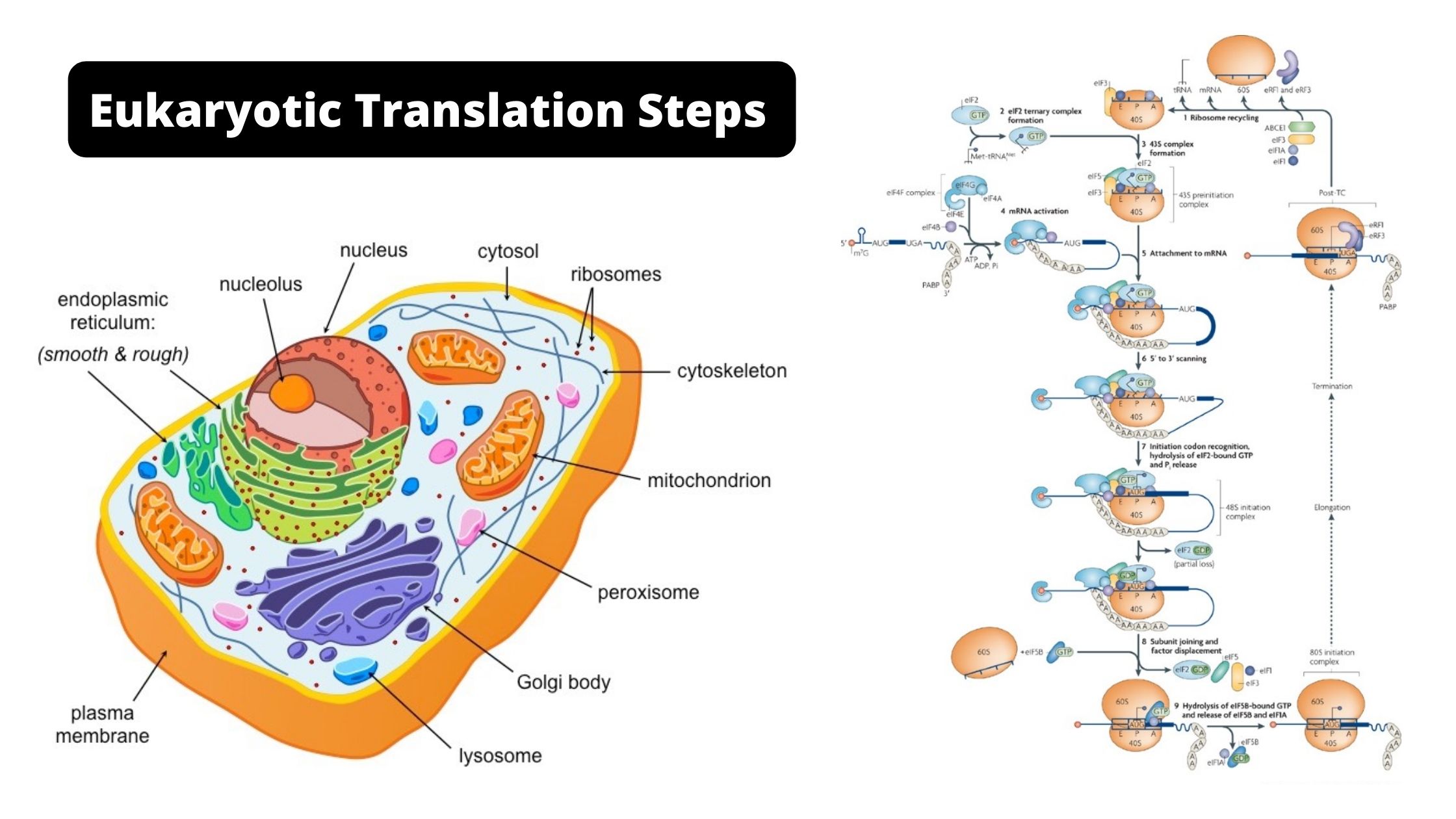
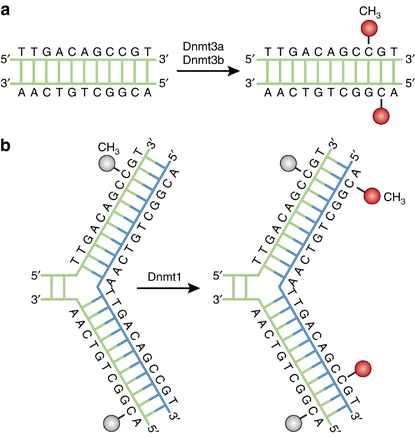
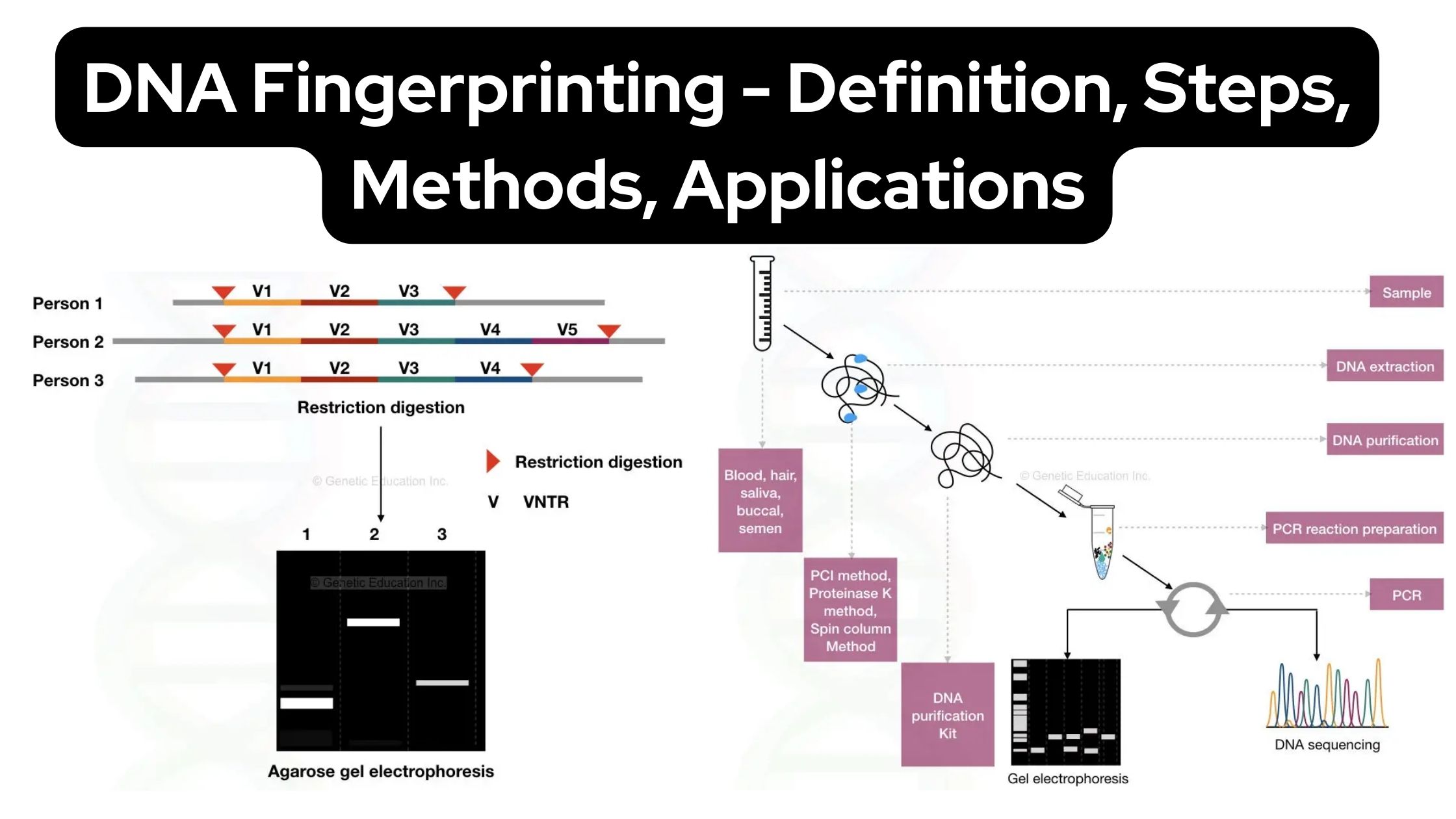
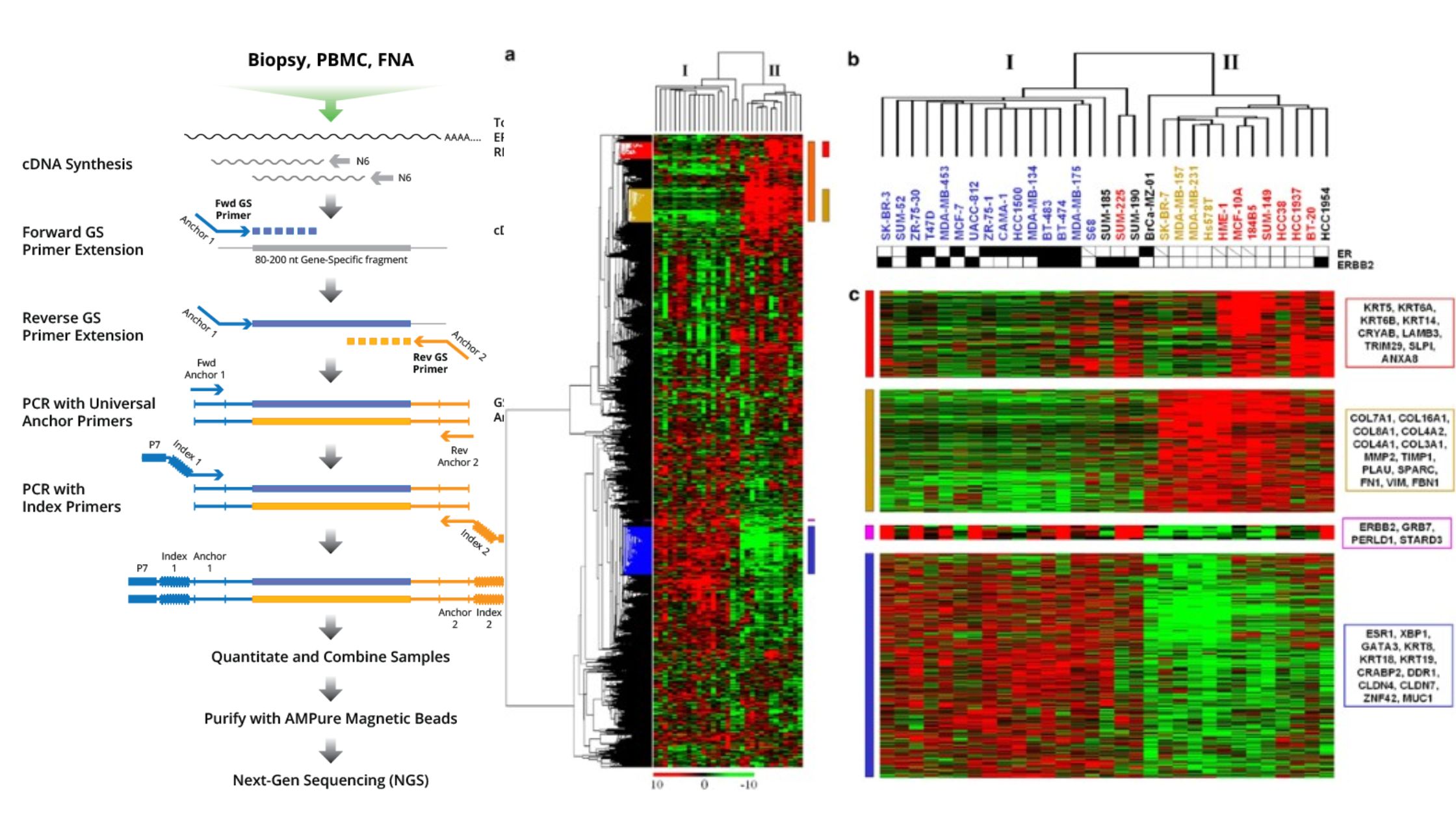
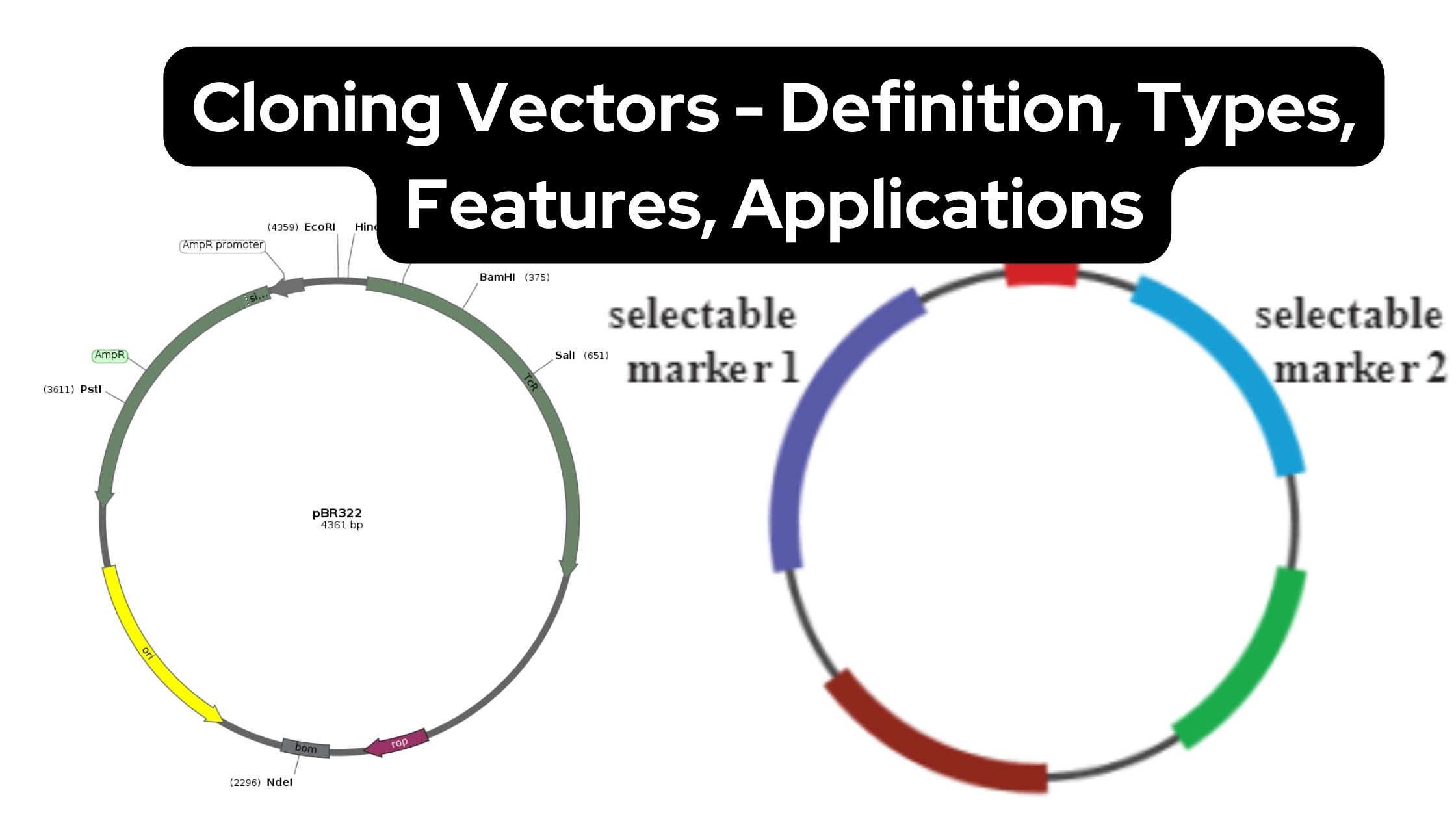
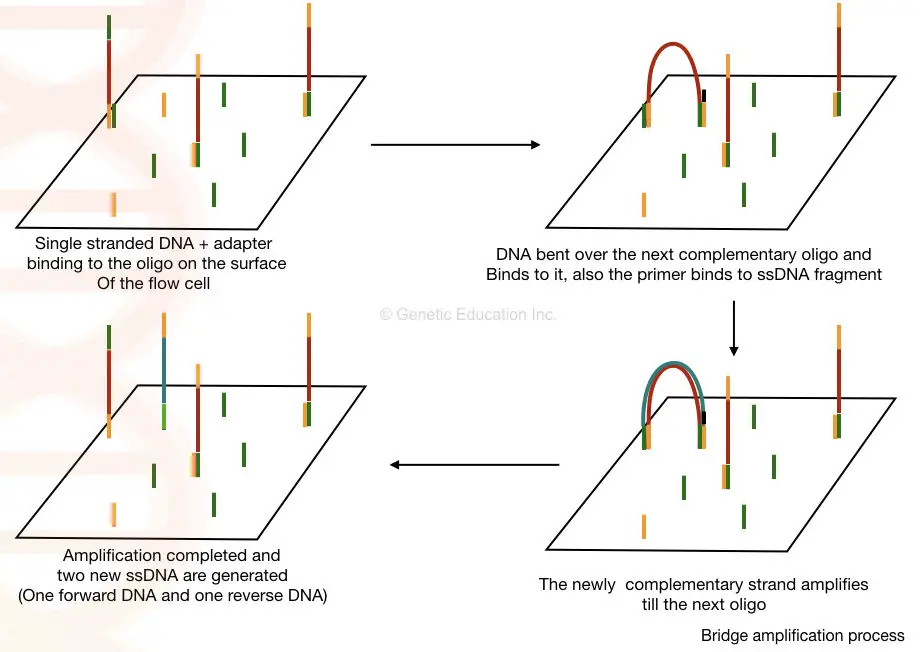
General Protocol for Western Blotting
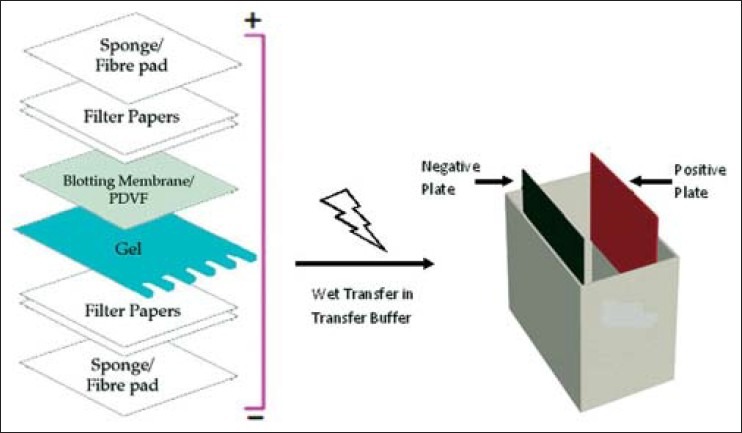
Principle of Western blotting The principle of Western blotting involves the separation of proteins based on their size through gel electrophoresis, followed by the transfer of the separated proteins onto a solid support (blotting), and the detection of the target protein using specific antibodies (detection). In the first step, gel electrophoresis, proteins are separated based on … Read more