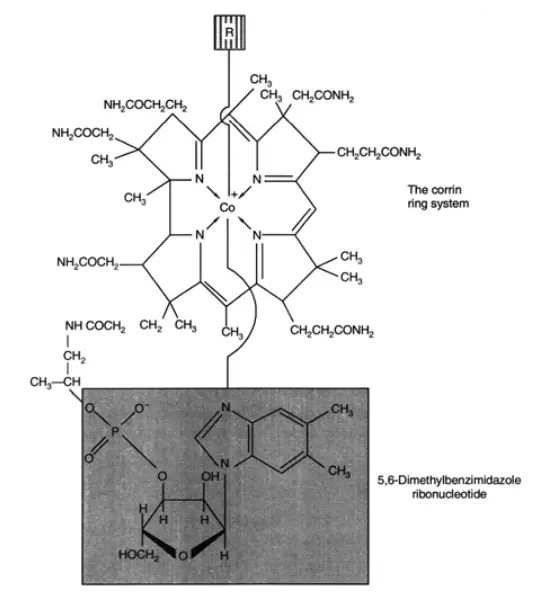
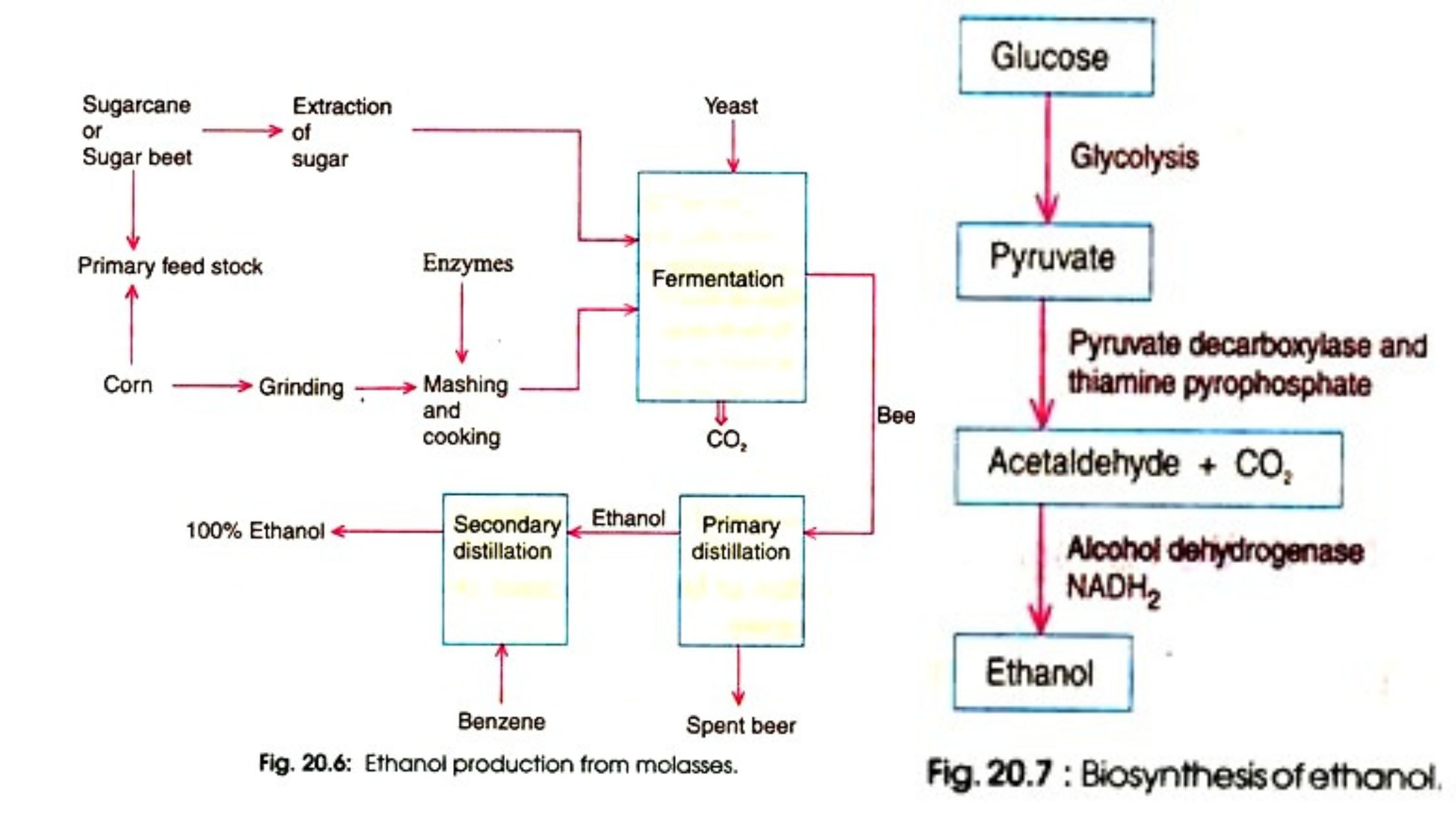
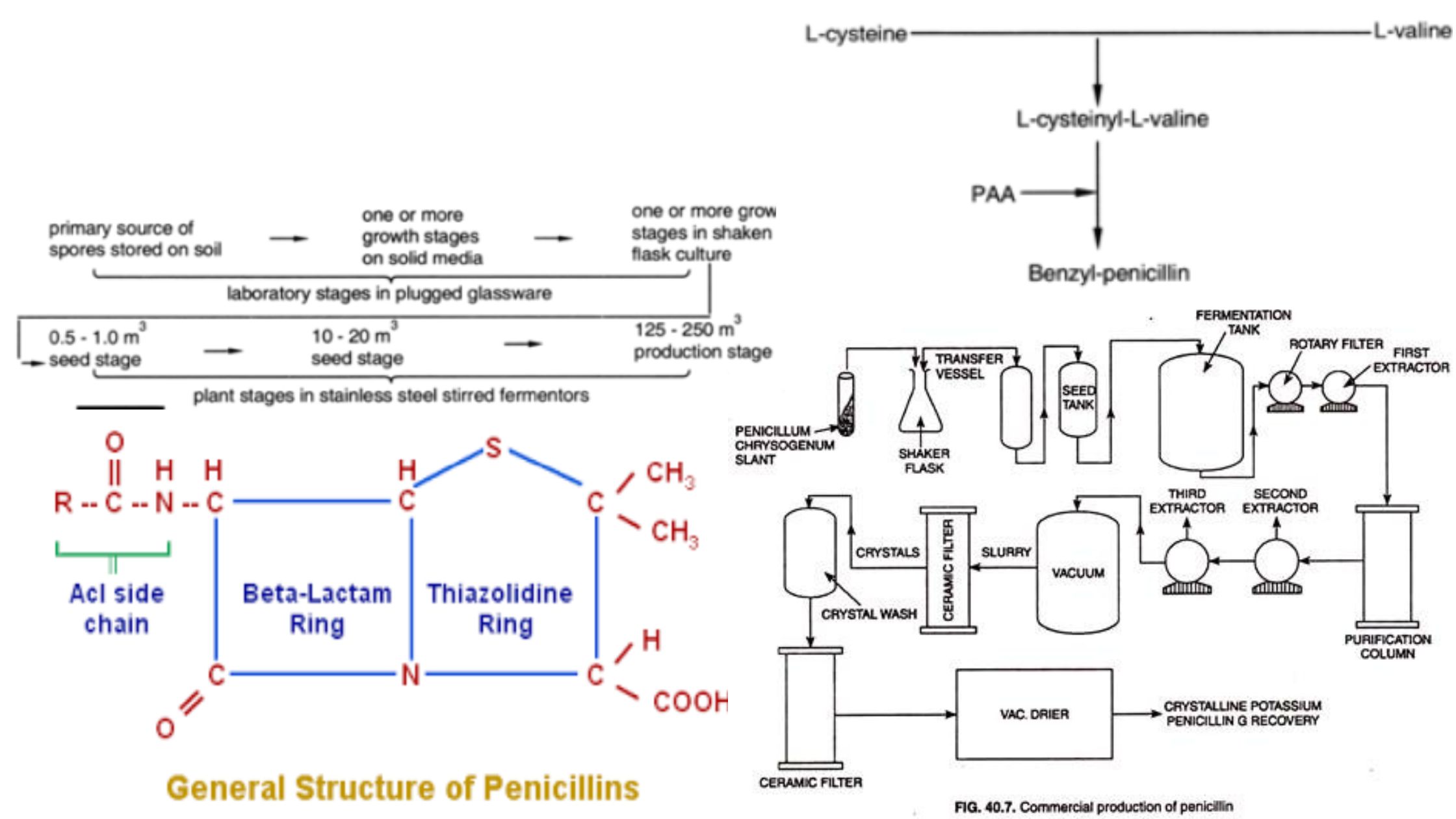
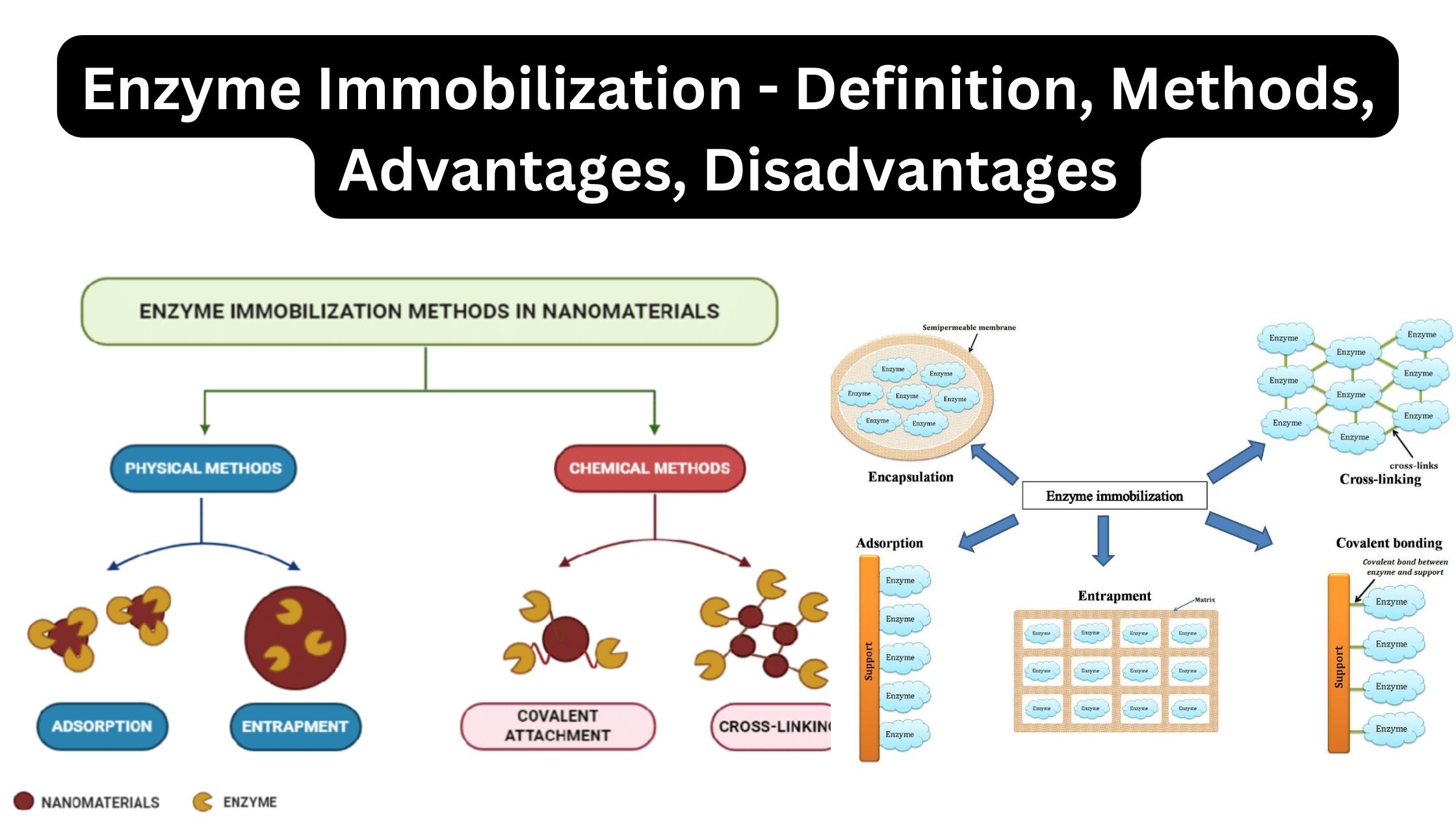
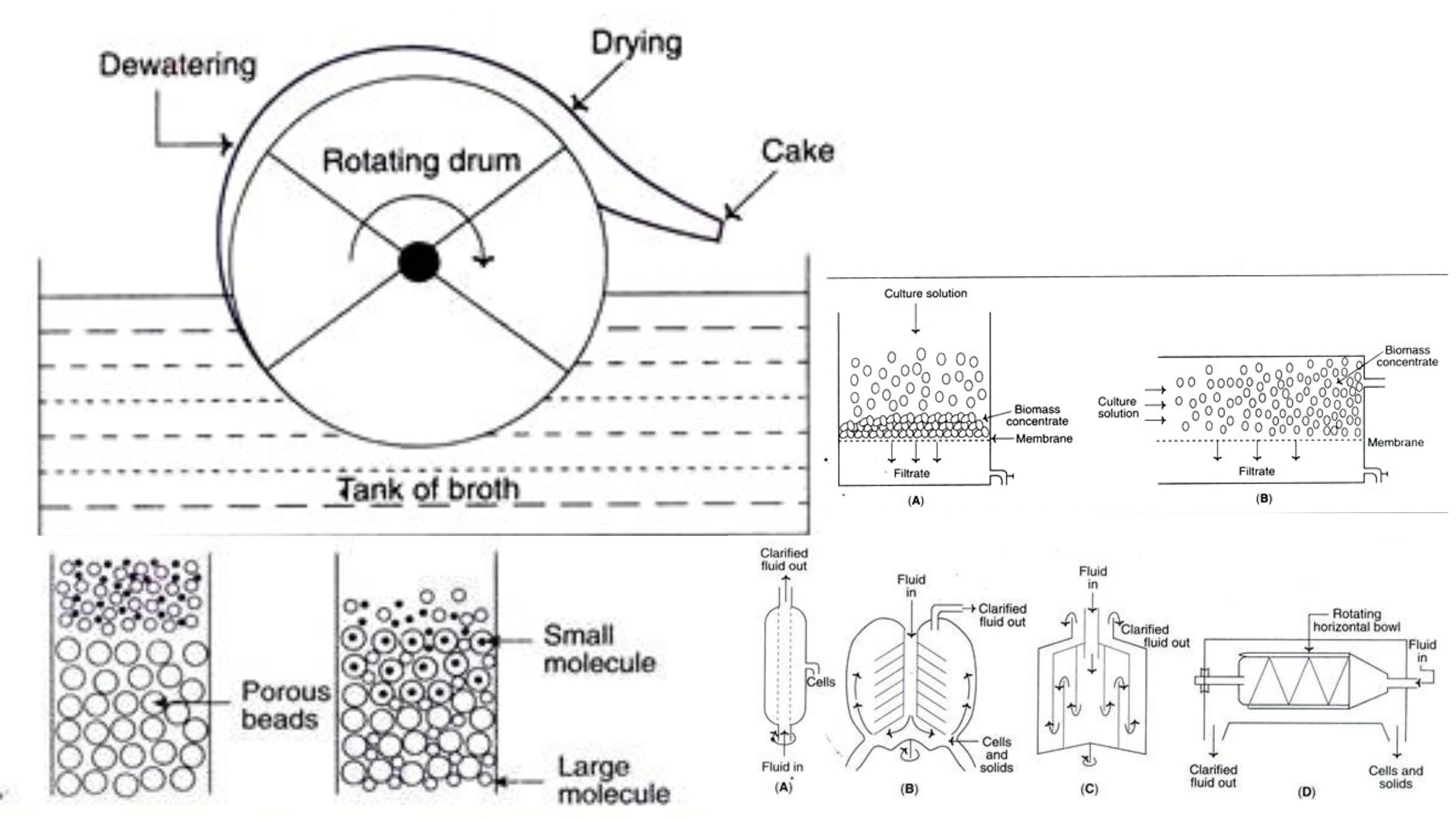
Vitamin B12 Production
What is Vitamin B12? Microorganisms used for B12 Productions Streptomyces griseus, S. olivaceus, Bacillus megaterium, B. coagulans, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Propionibacterium freudenreichi, P. shermani, and a mixed fermentation of a Proteus spp. and a Pseudomonas spp. may be used in the industrial manufacture of vitamin B12. Typically, Vitamin By is produced via the submerged-culture method. The … Read more