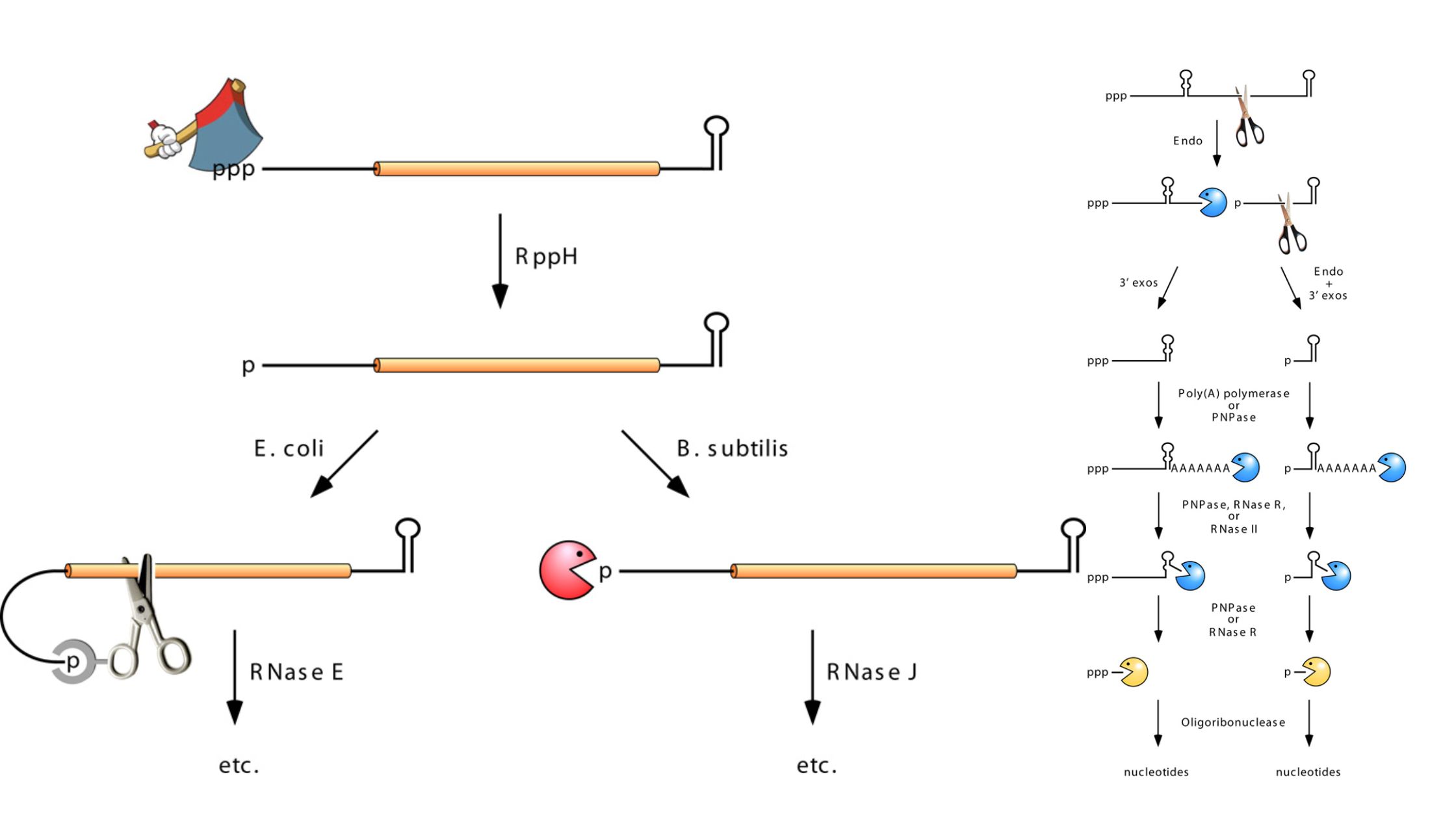
Heterogeneous Nuclear RNA (hnRNA)
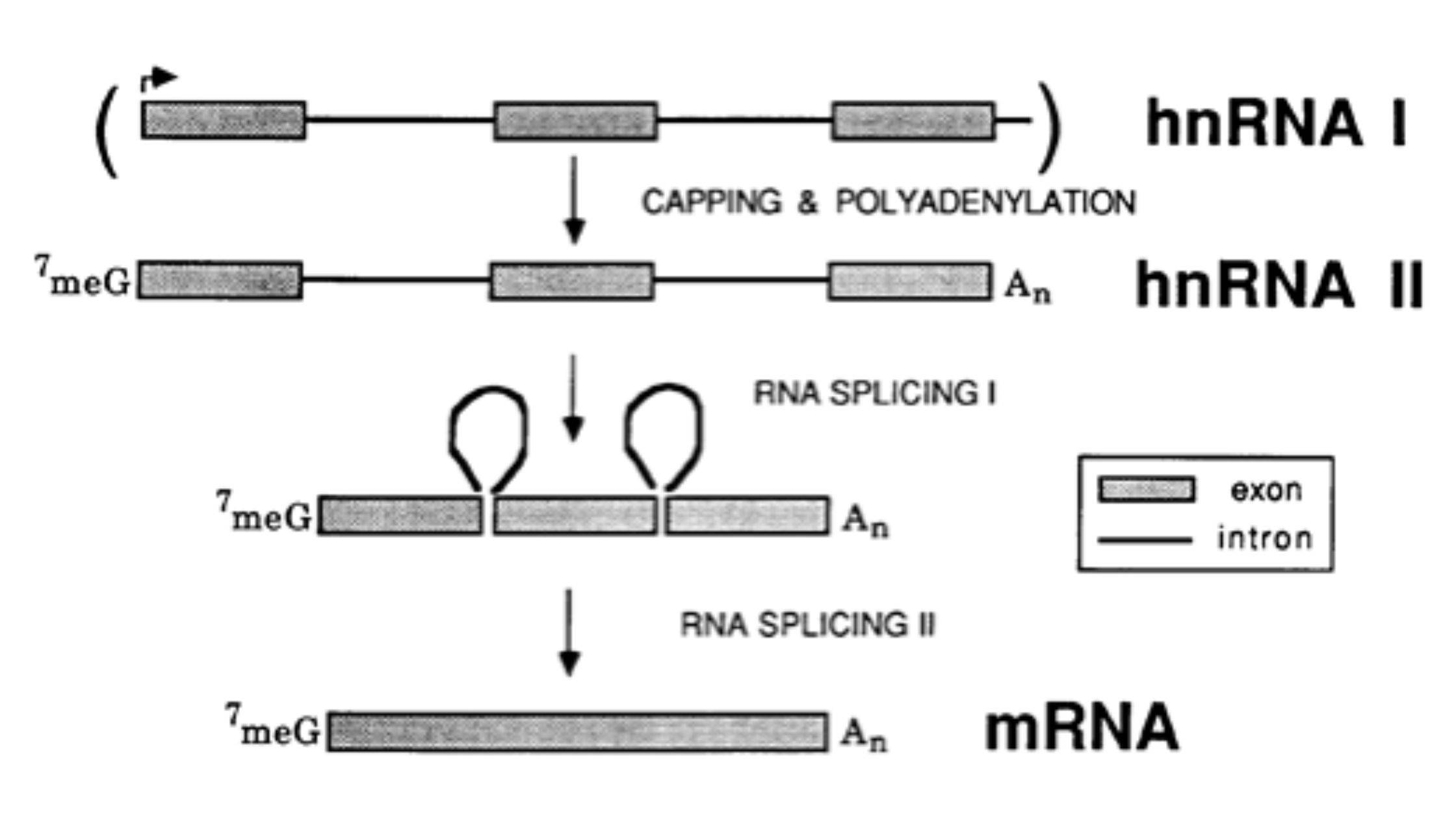
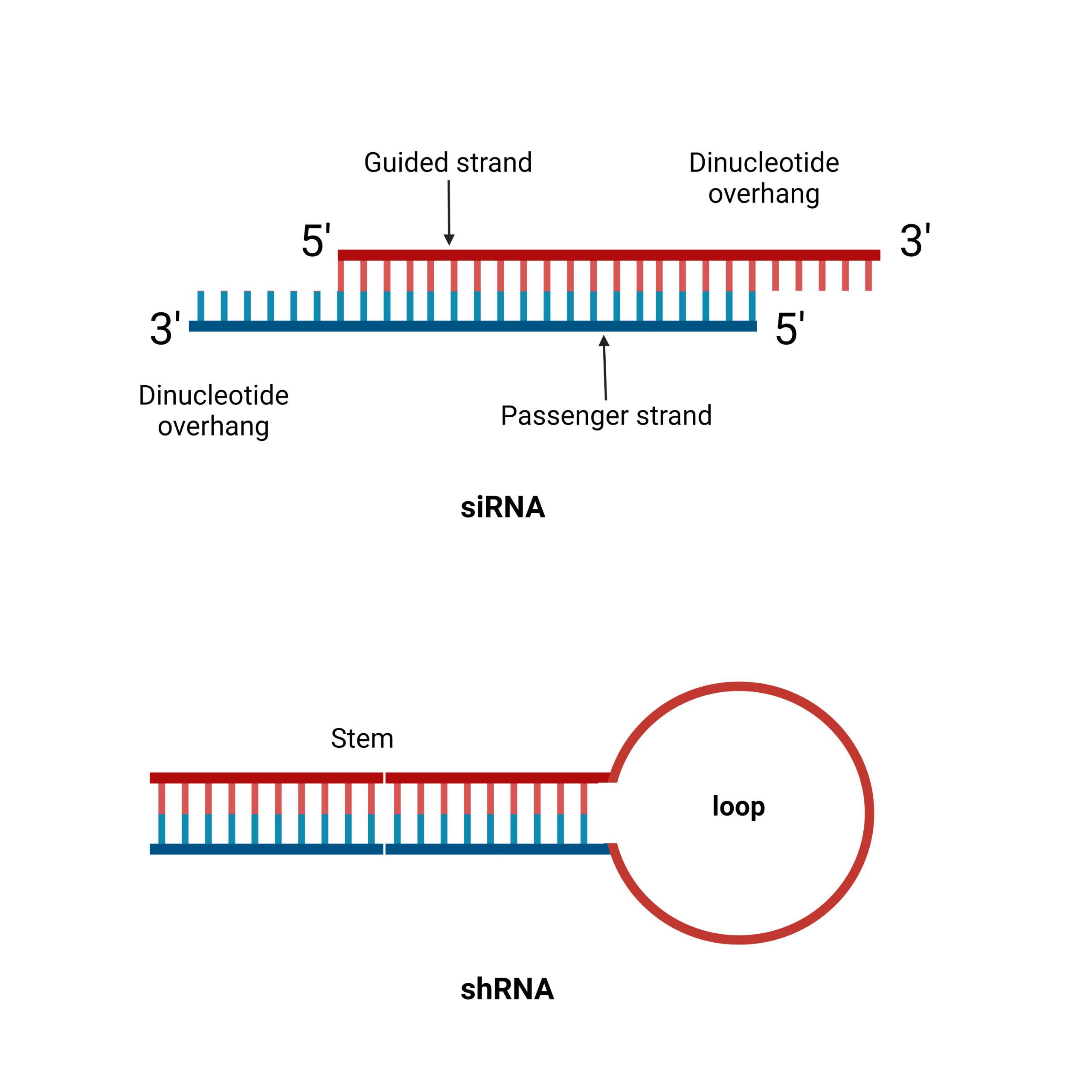
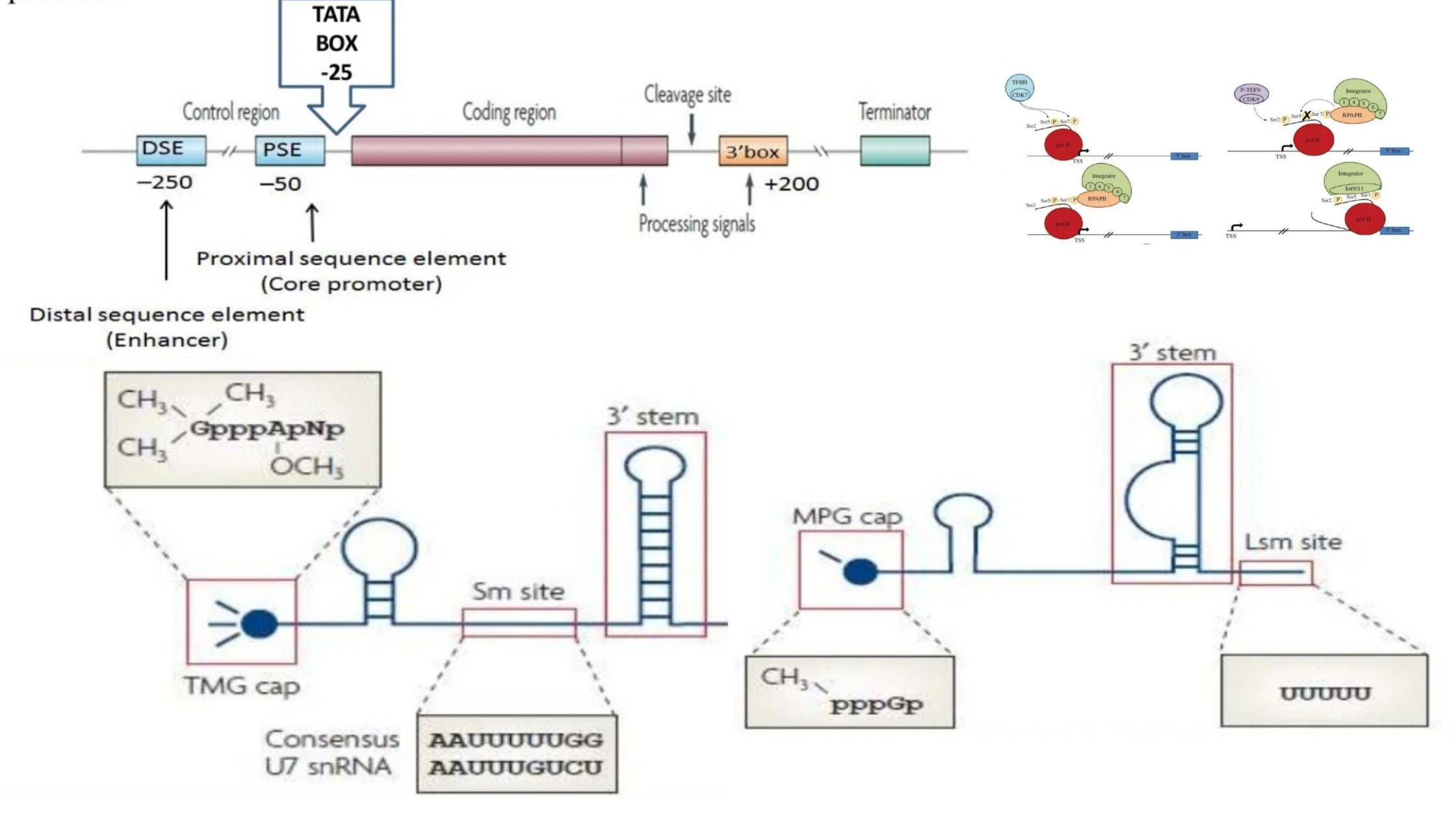
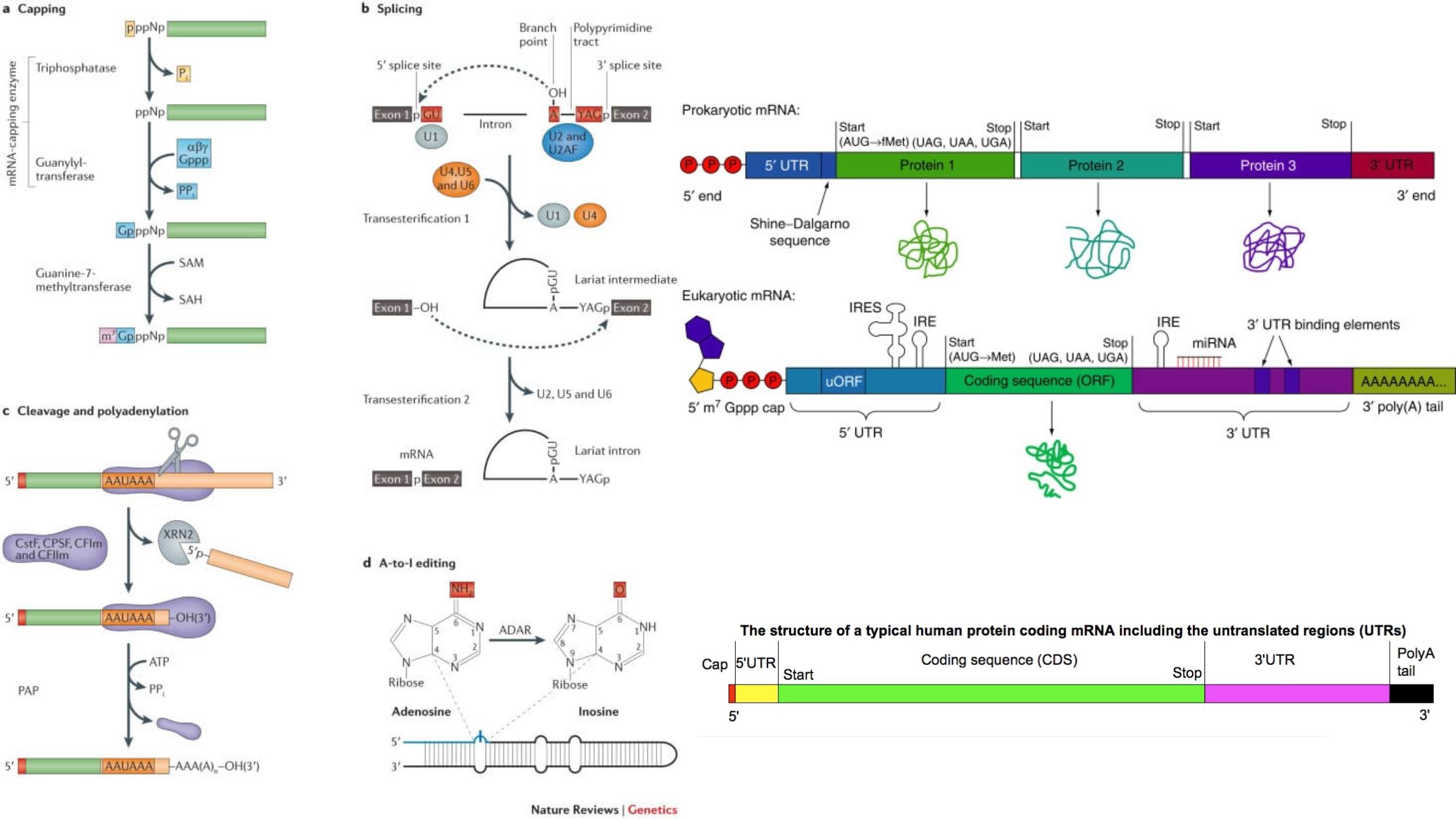
What is Heterogeneous Nuclear RNA (hnRNA)? Properties of hnRNA Processing of hnRNA During processing, the hnRNA undergoes the following chemical modifications: 1. Packaging of hnRNA with protein 2. Polyadenylation or Poly (A) tail formation 3. RNA splicing 4. 5′ Capping Mature mRNA One central coding segment, two untranslated segments, one on either side of the … Read more