Biological Macromolecules – Types, Structure, Functions, Examples
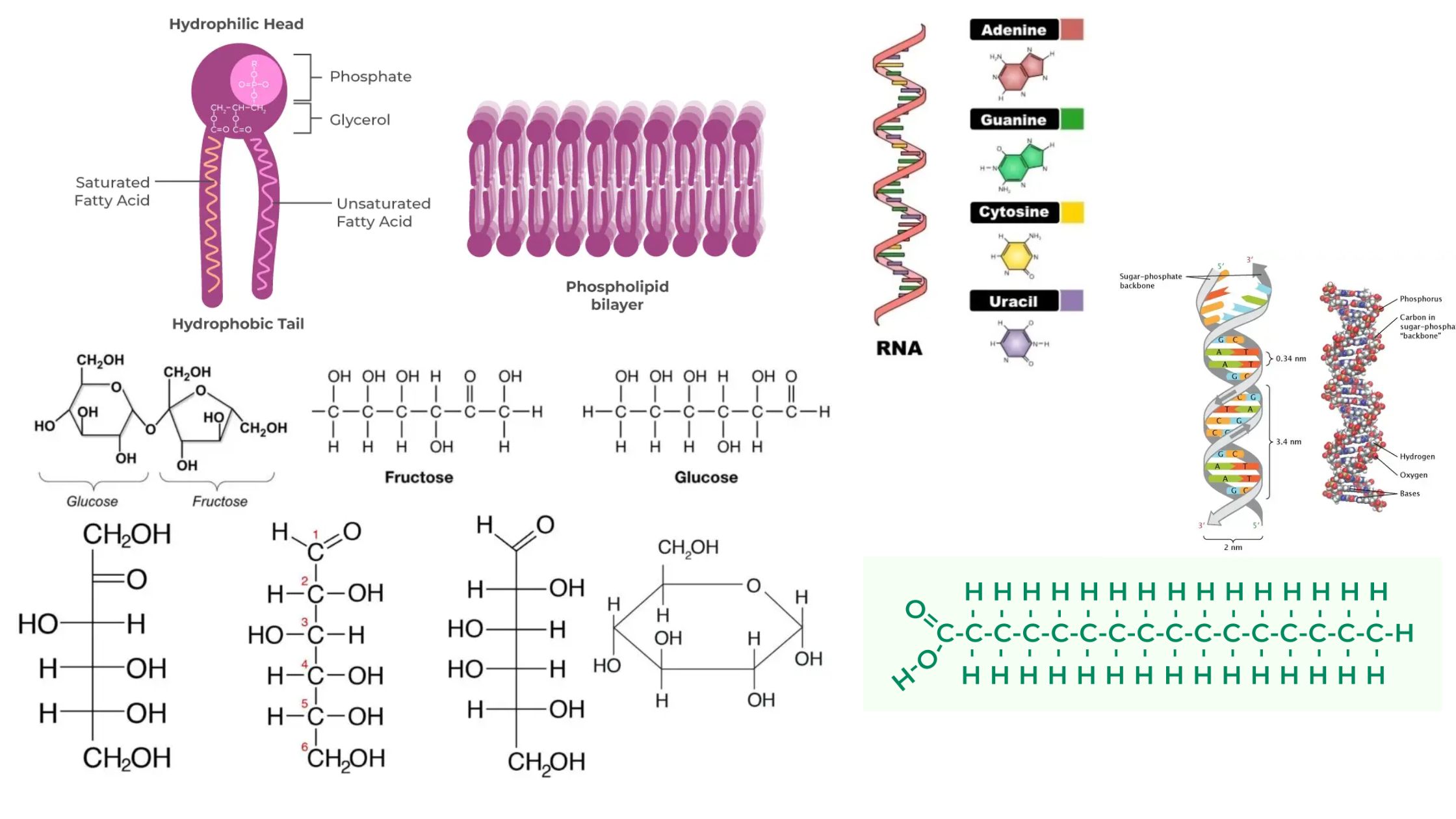
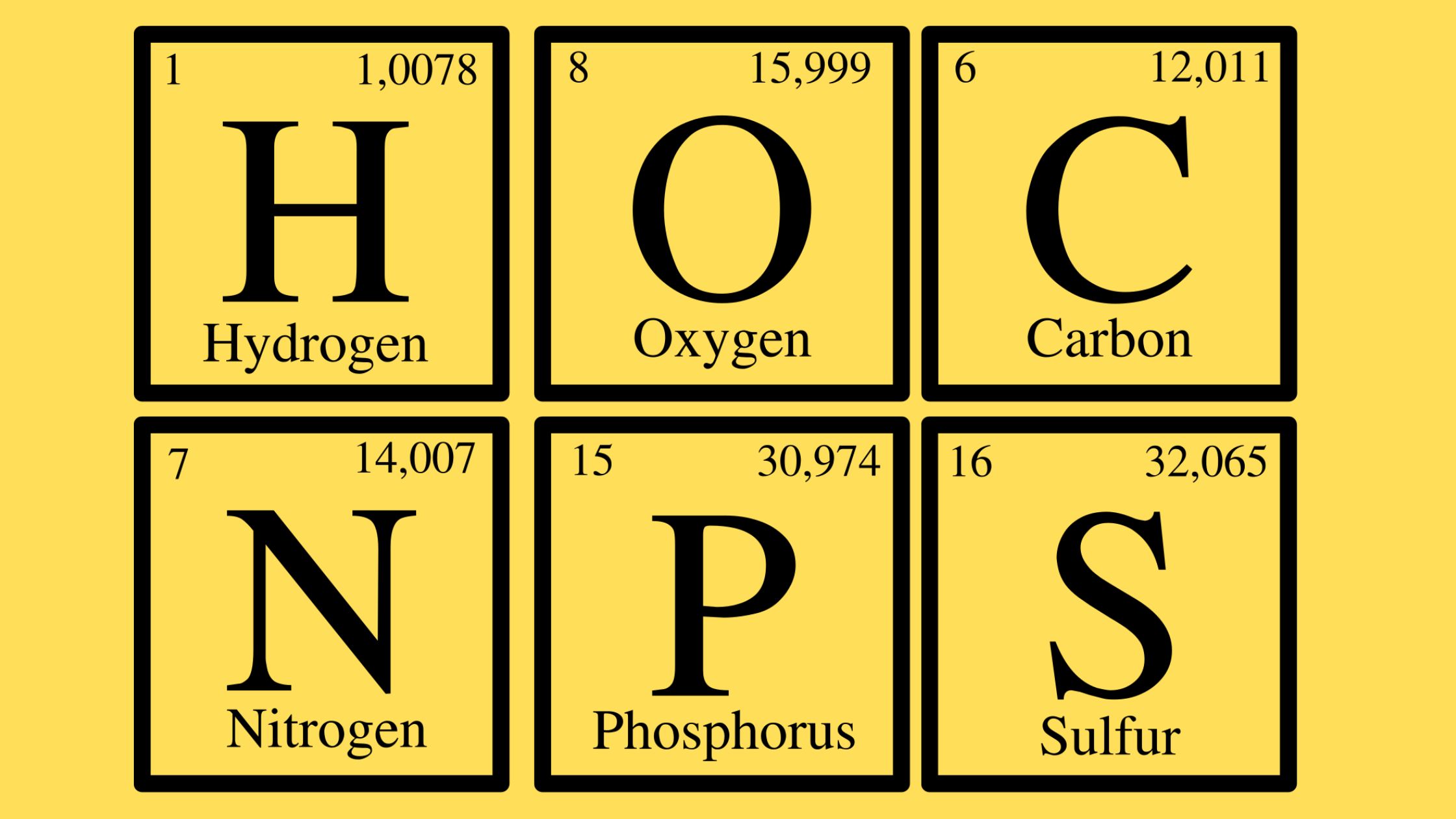
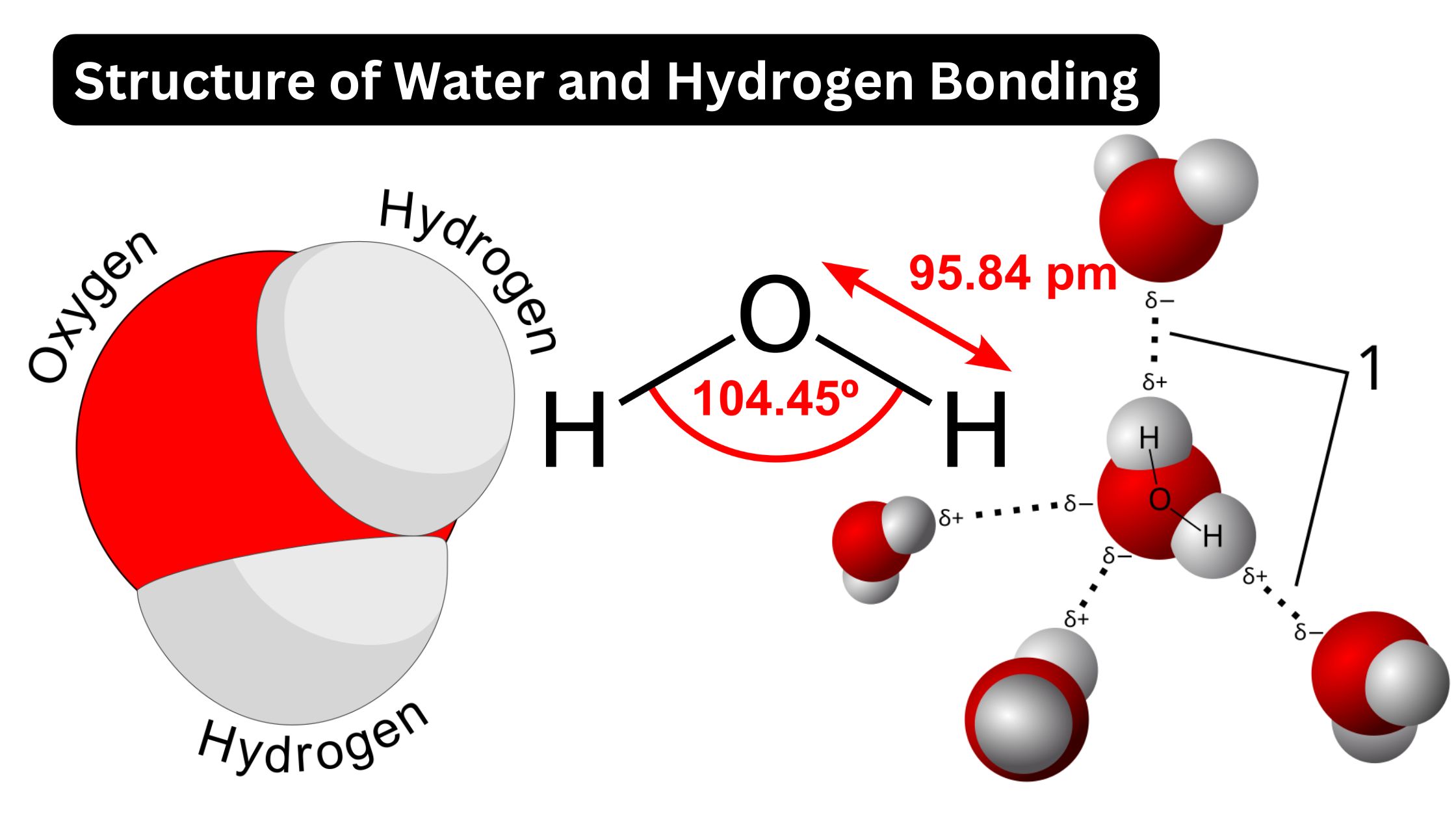
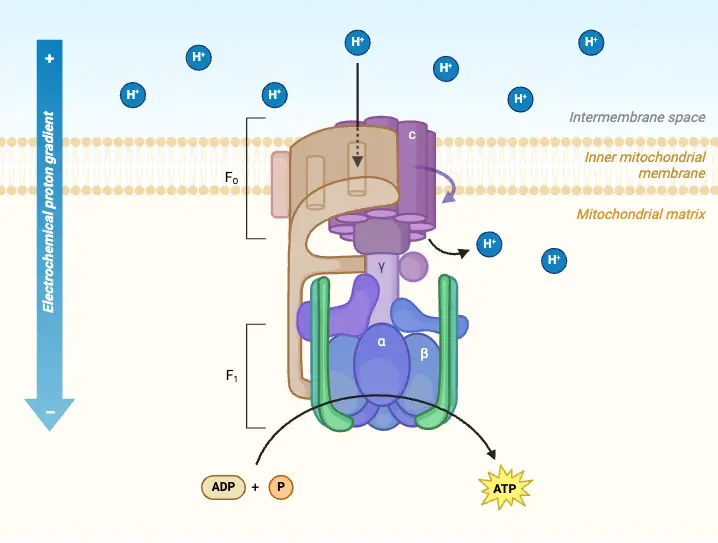
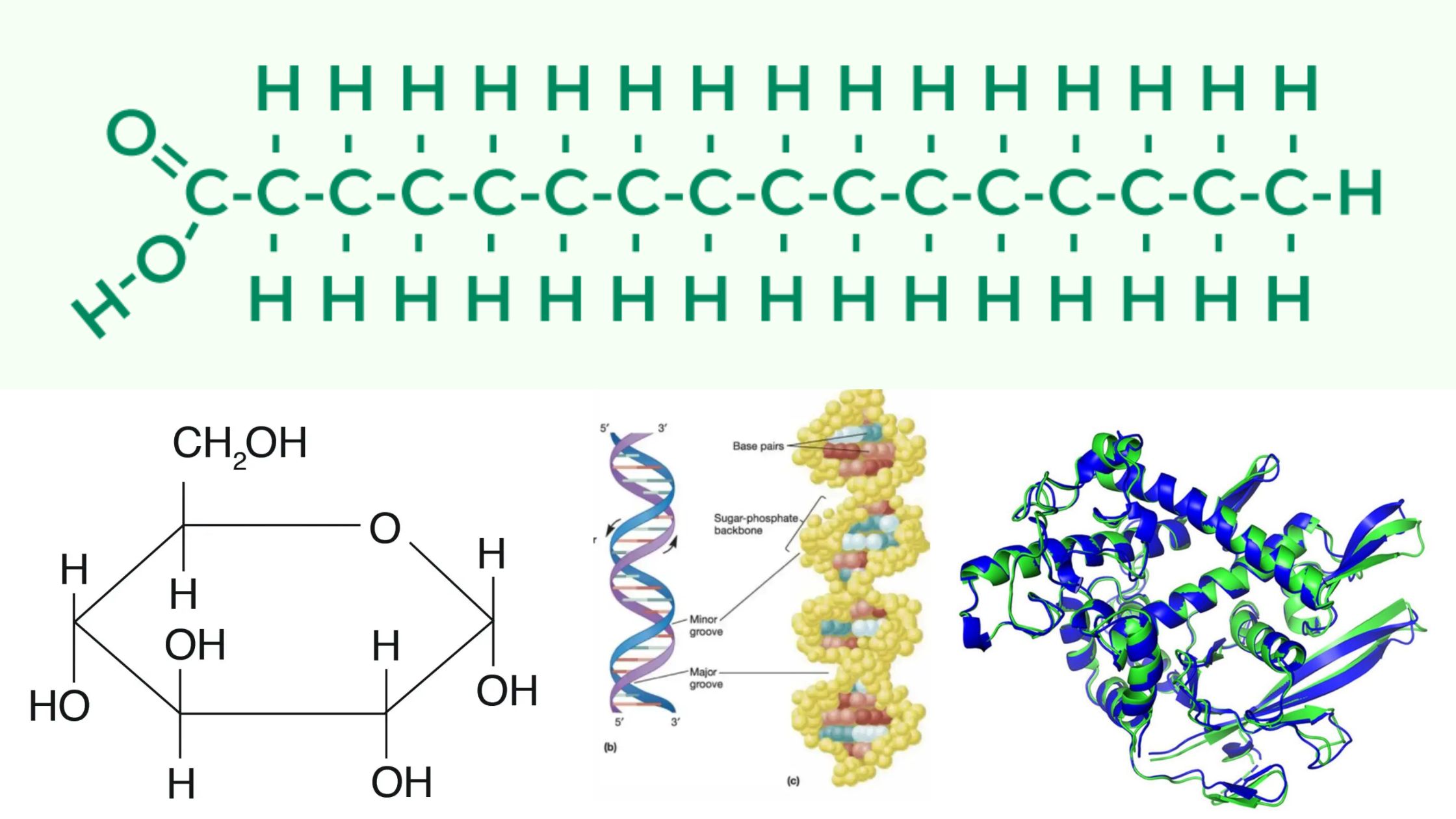
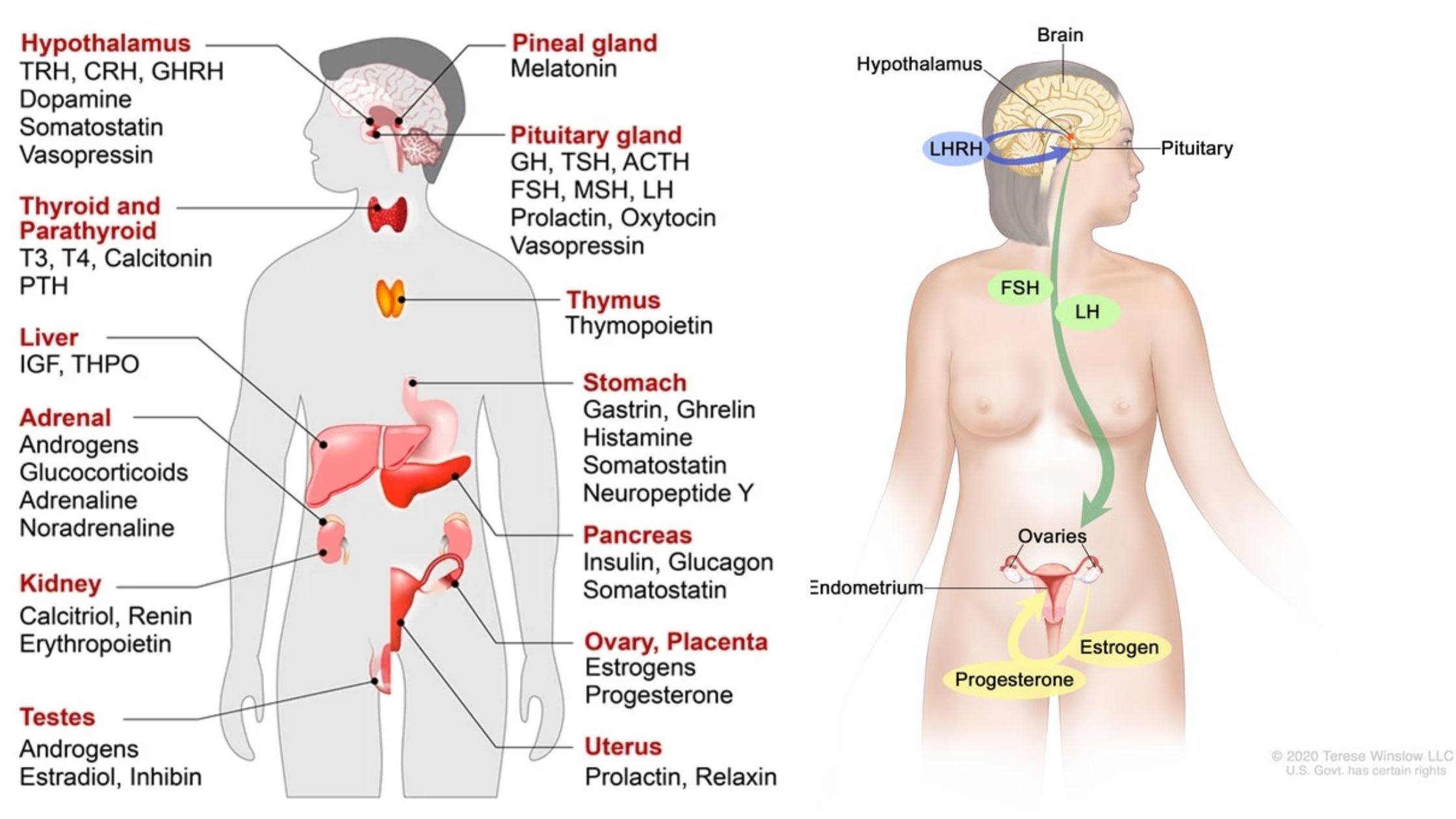
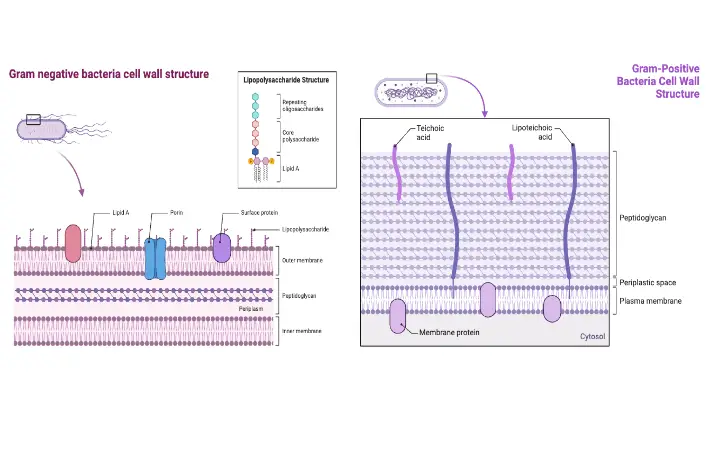
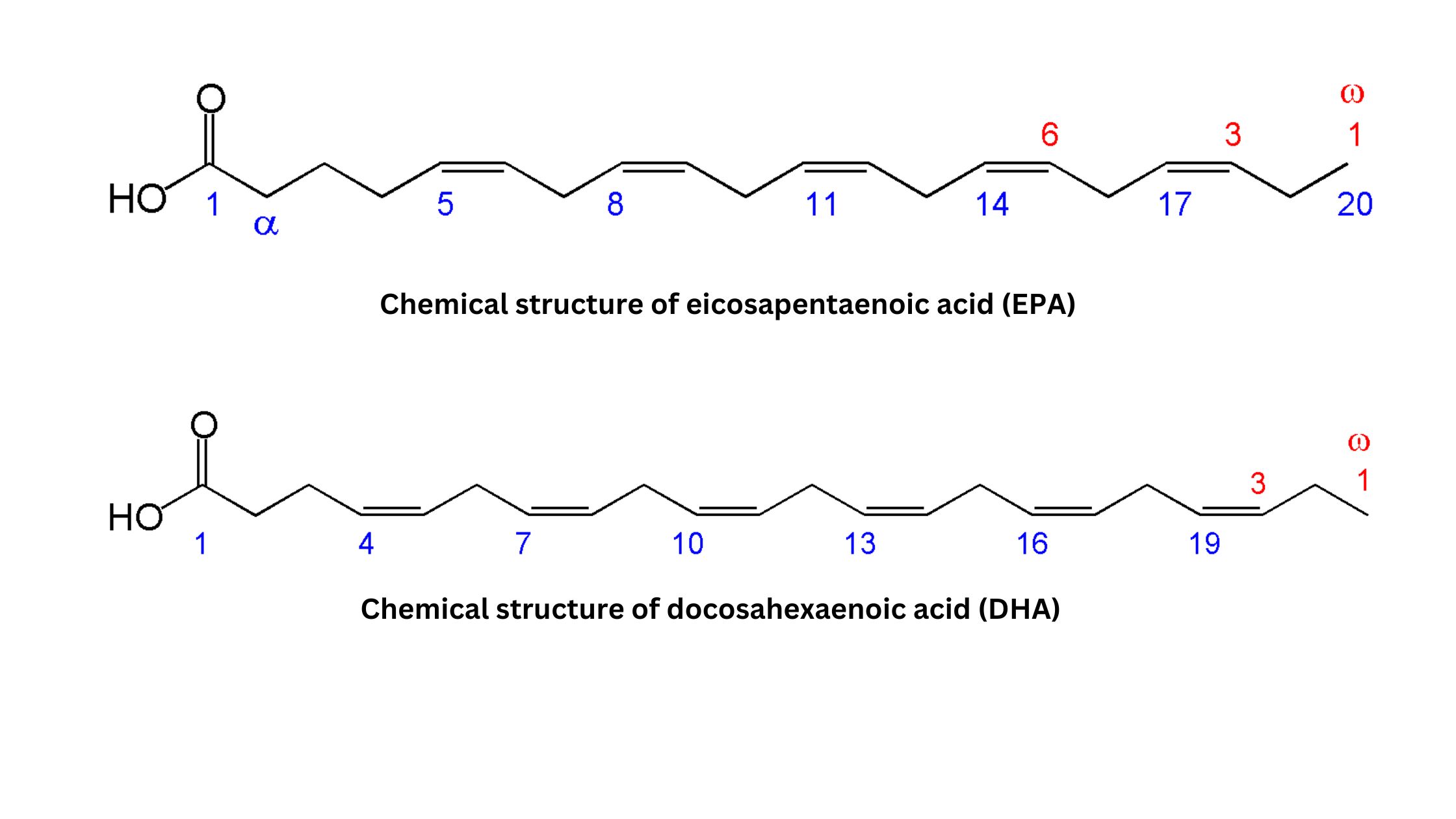
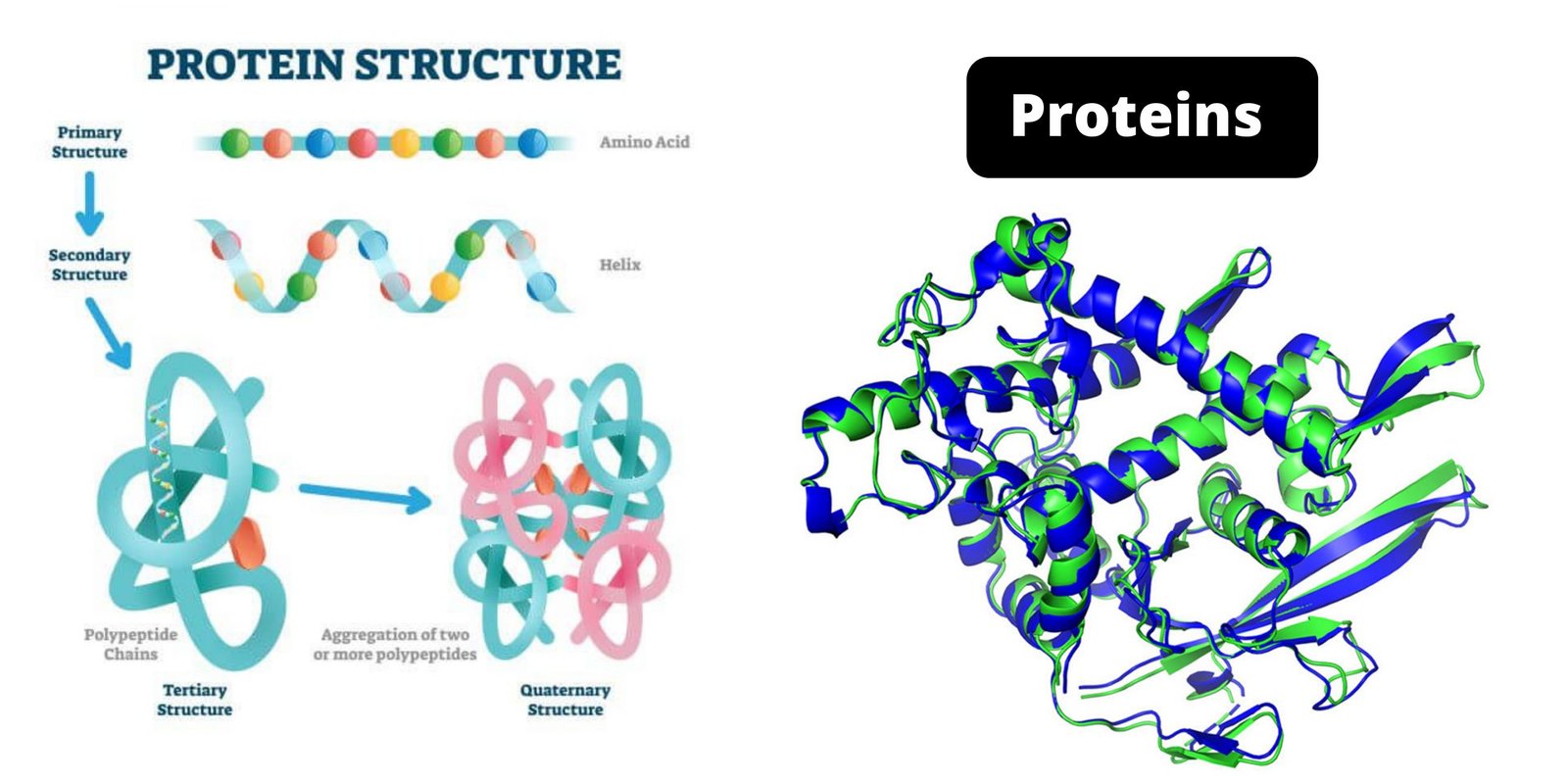
What are Biological Macromolecules? Definition of Biological Macromolecules Biological macromolecules are large, complex molecules essential for life, typically classified into four main categories: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. They are composed of smaller units called monomers, which are linked together to form polymers. These macromolecules play crucial roles in biological processes, including energy storage, … Read more