Sterilization – Physical and Chemical methods
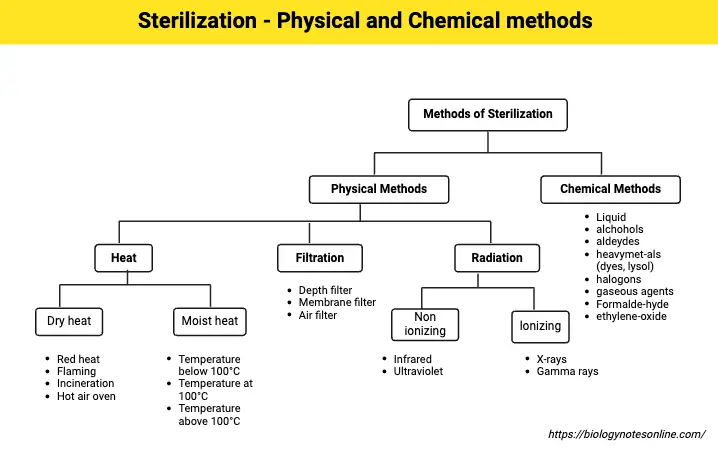
What is Sterilization? Important Definitions Methods of Sterilization A. Physical Methods of Sterilization Method Description Key Agents/Processes Applications Sunlight Utilizes ultraviolet rays for germicidal effects. Reduces microorganisms in natural bodies of water. Ultraviolet Rays Water sterilization Heat Involves dry heat and moist heat to kill microorganisms through protein denaturation and coagulation. Dry Heat, Moist Heat … Read more