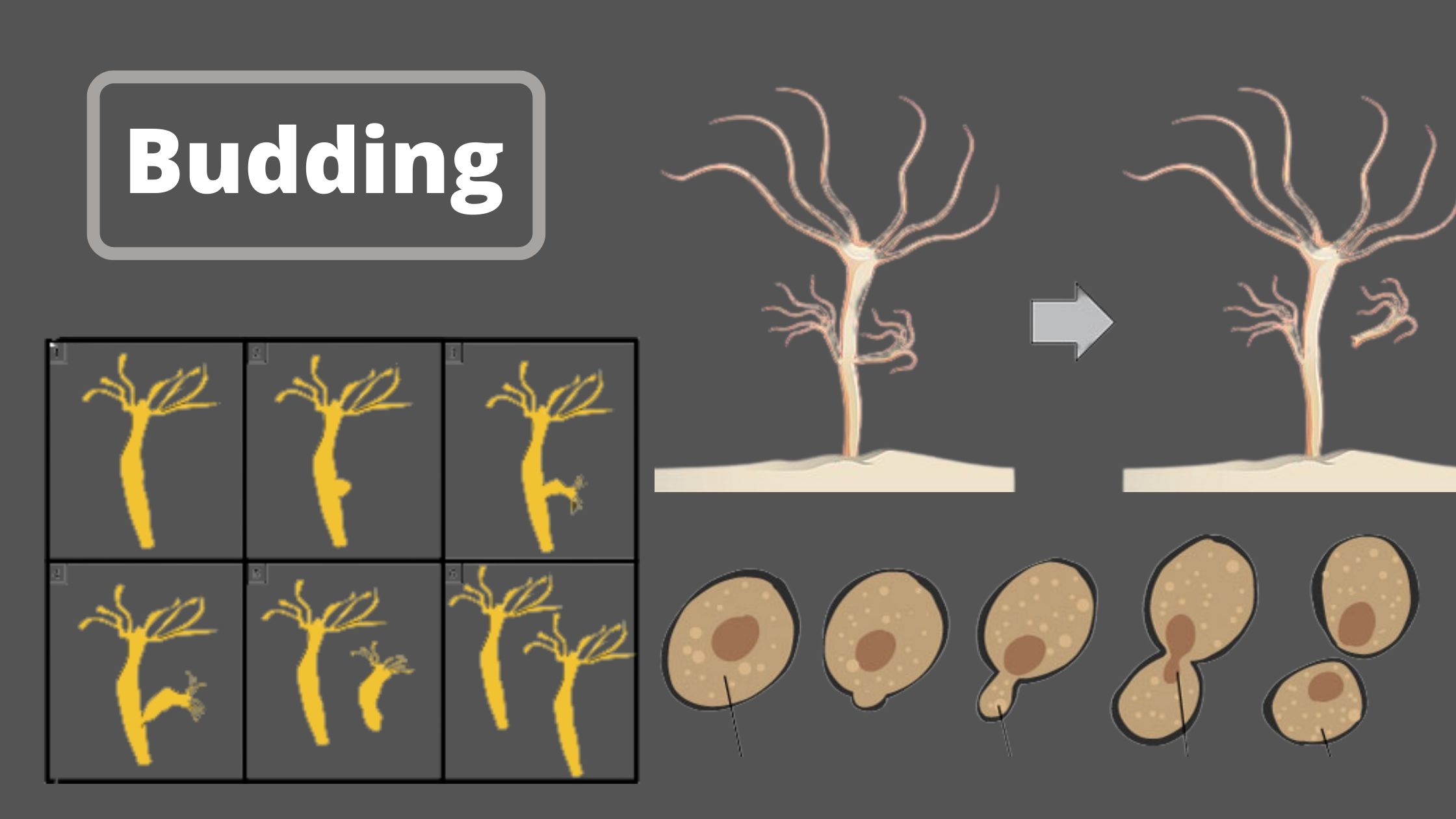
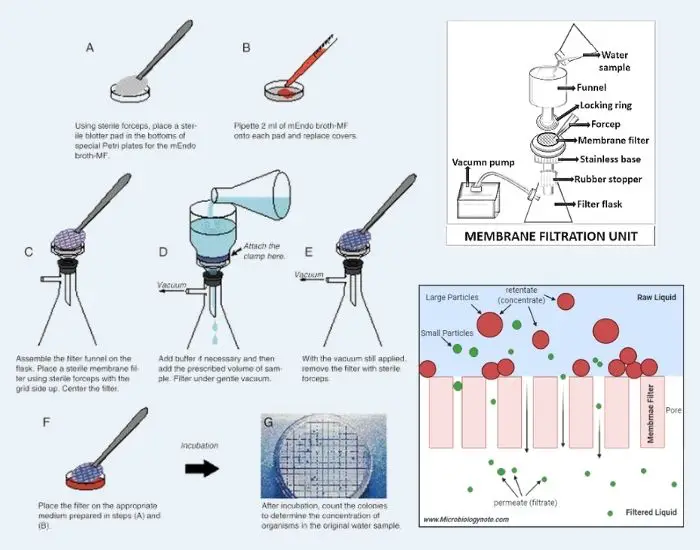
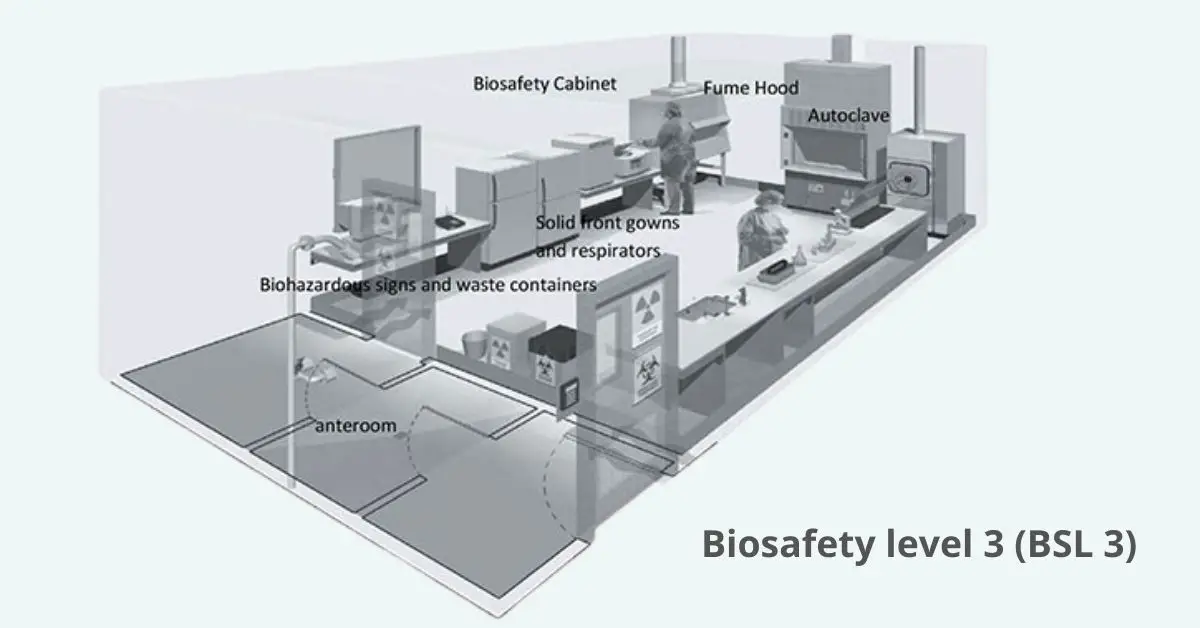
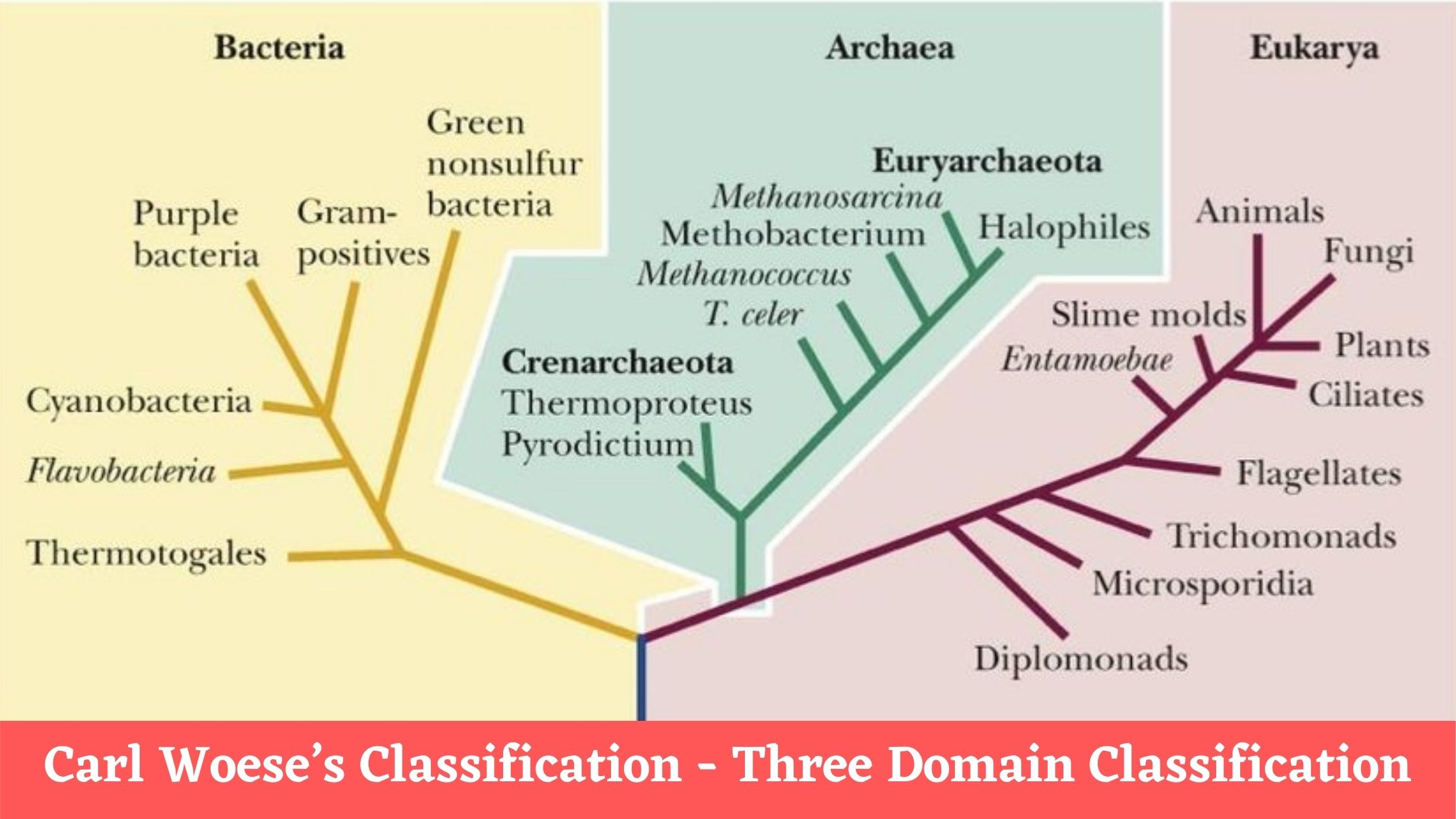
Career In Microbiology and Its Importance
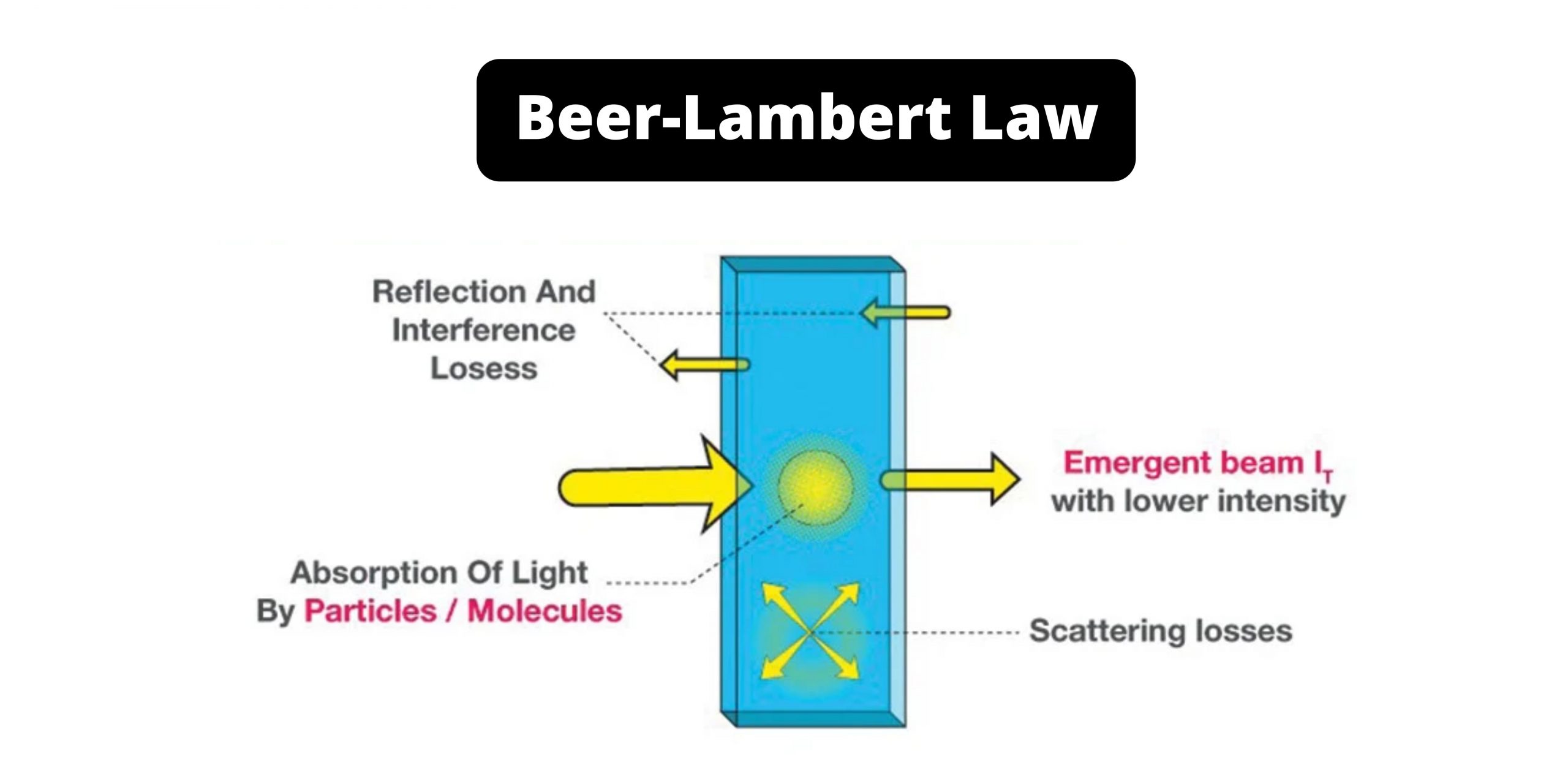
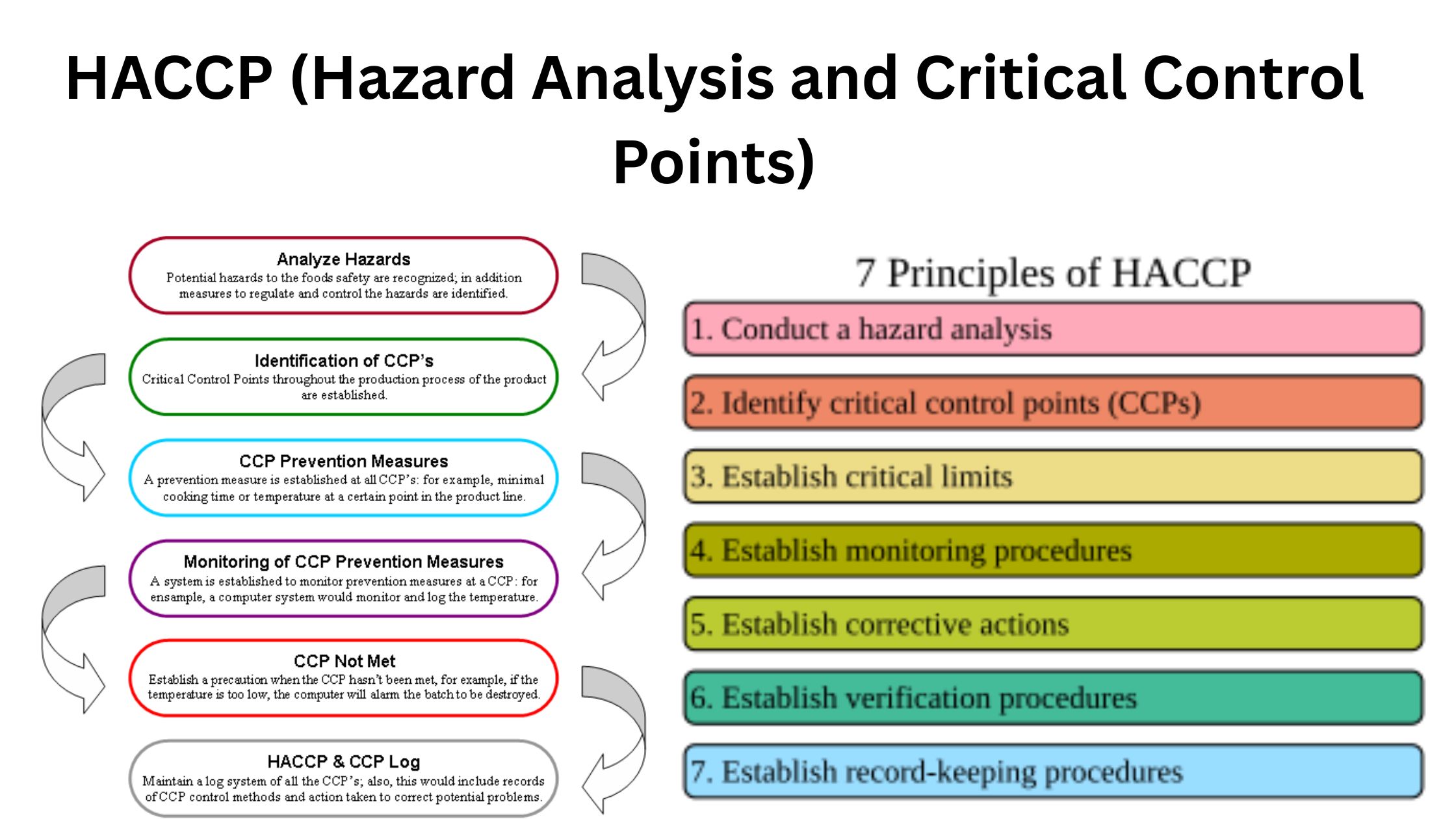
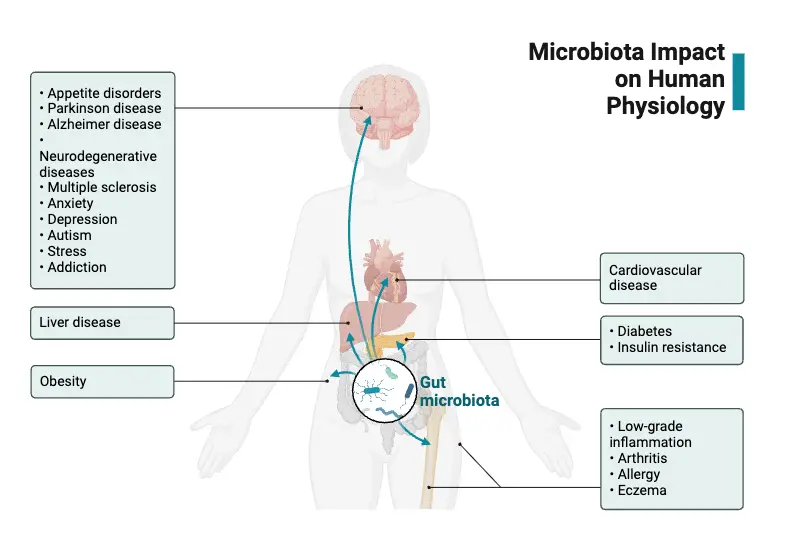
Microbiology is the study of microscopic organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi and some parasites, and it is the field that explains how these organisms is involved in different biological and environmental activities. A career in microbiology is followed when a person study these microbes and work with them in laboratories or research centers. It is … Read more