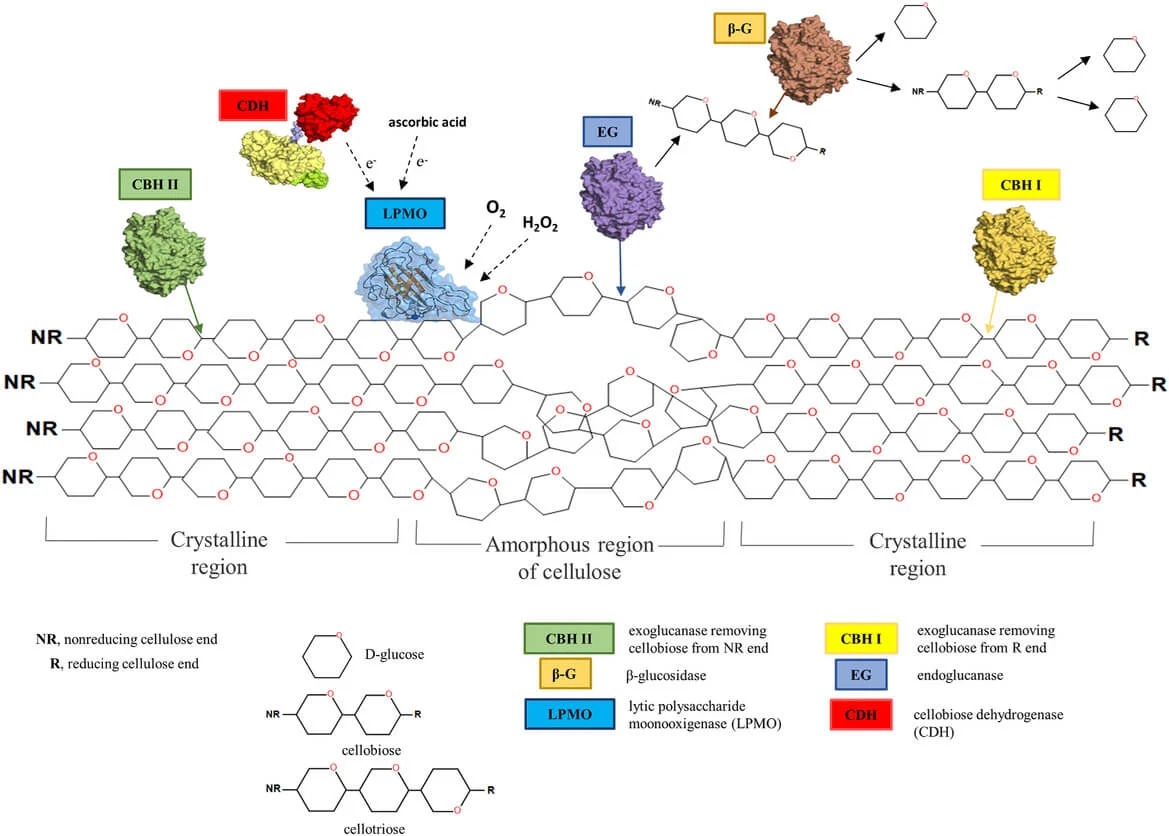
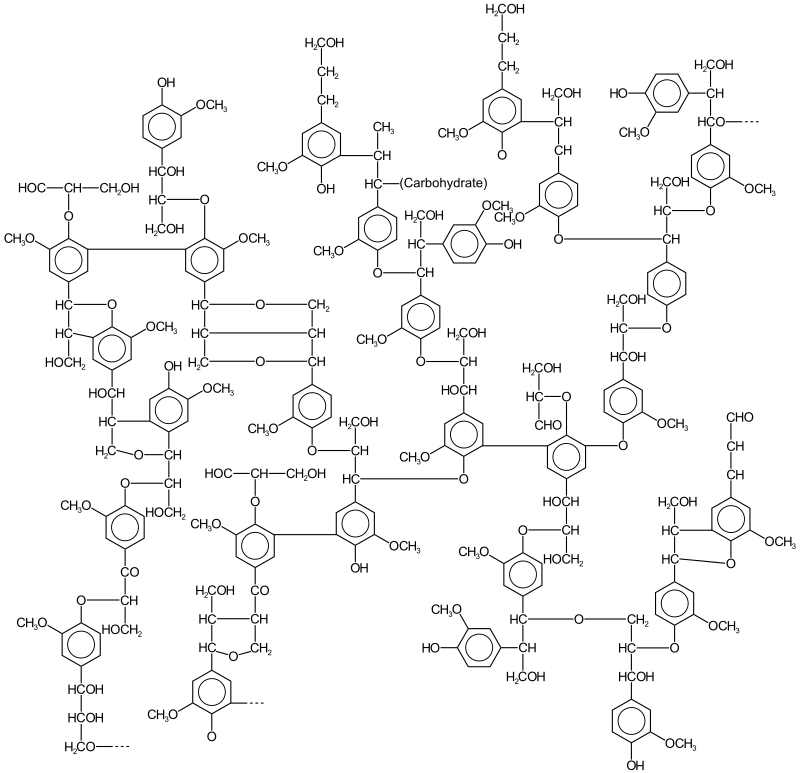
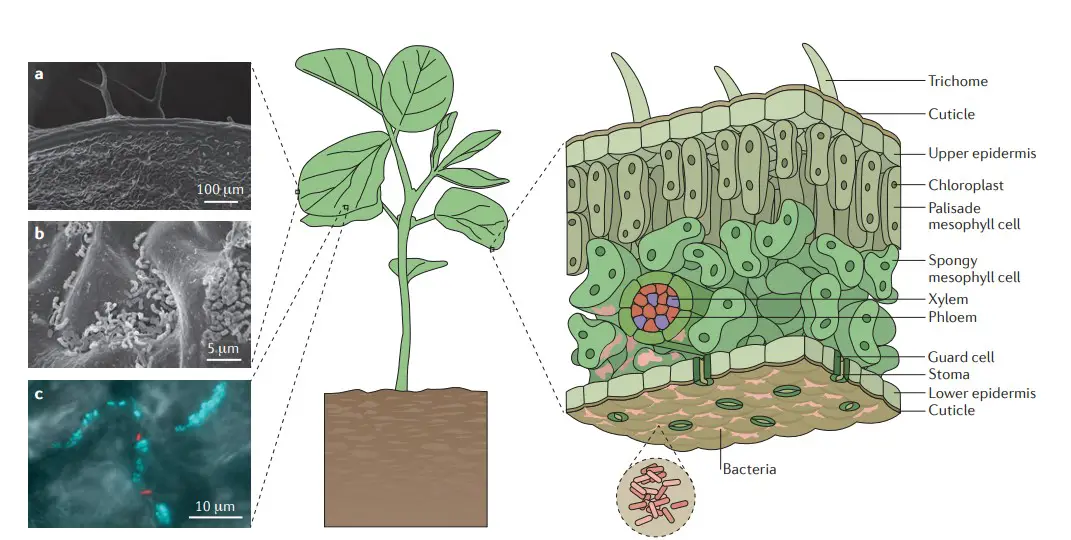
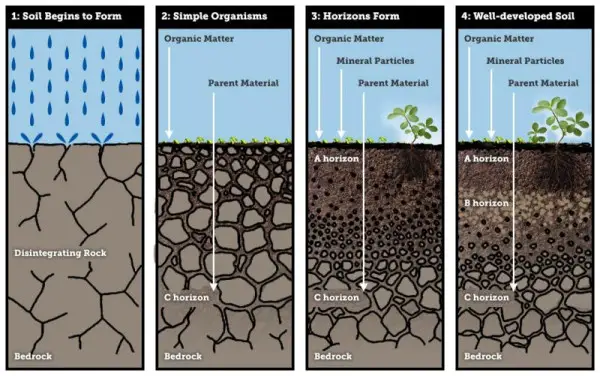
Microbial degradation of cellulose – Enzymes, Steps, Mechanisms
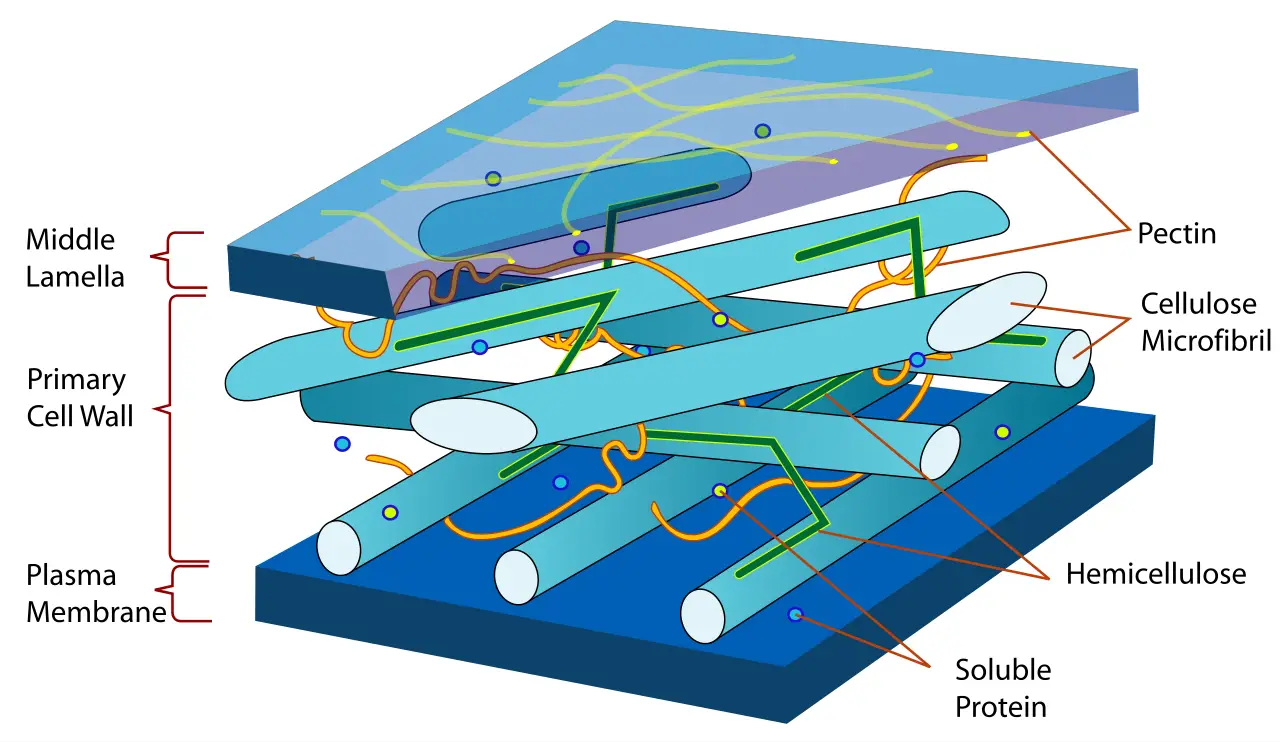
What is cellulose? (C6H10O5)n Cellulose Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass 162.1406 g/mol Density 1.5 g/cm³ Appears White powder Melting Point 260–270 °C Properties of cellulose Structure of cellulose What are cellulases? Cellulases are a group of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of cellulose, a complex polysaccharide present in plant cell walls. These enzymes are largely produced … Read more