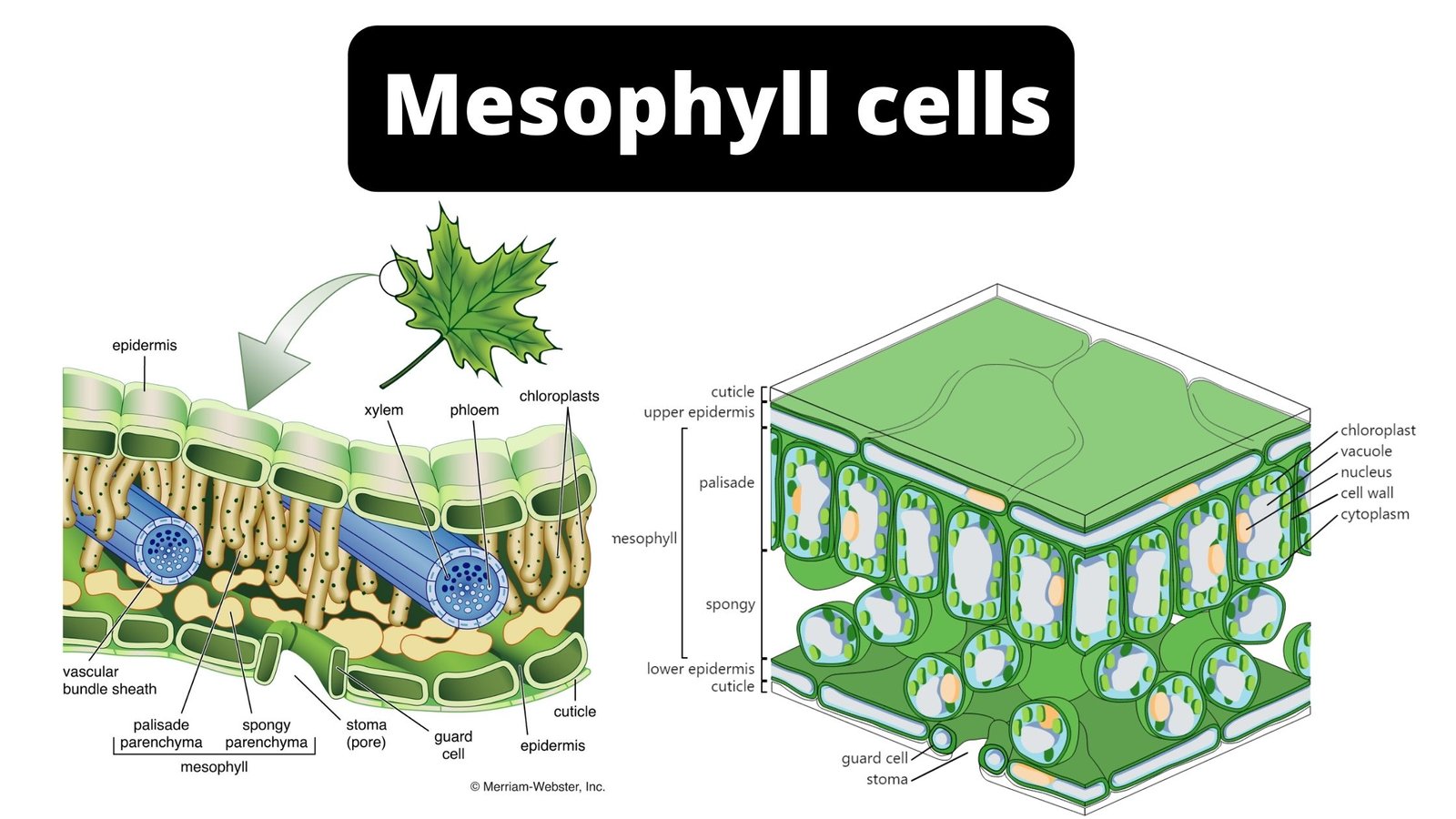
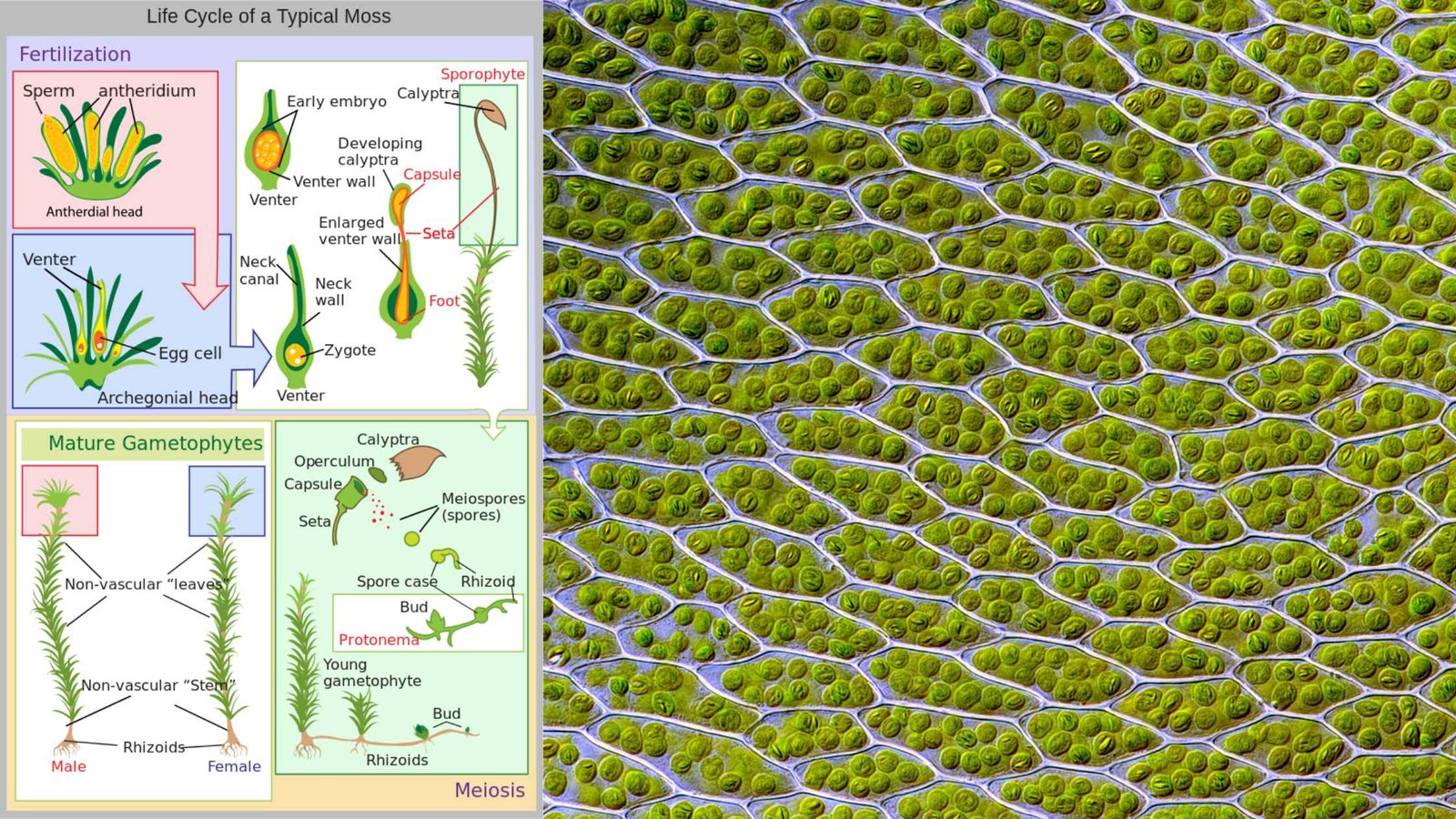
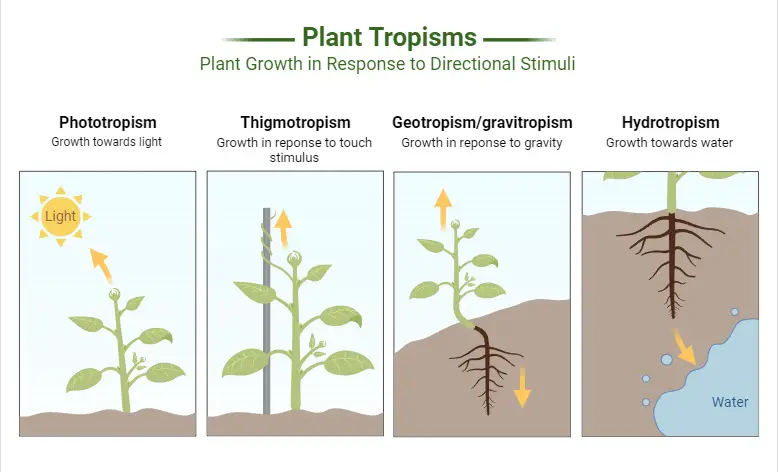
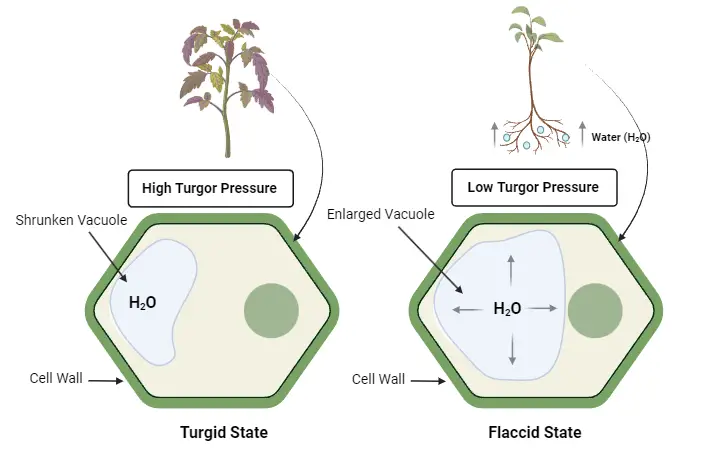
Plant communities – Characters, Ecotone and edge effect, Succession, Processes and types
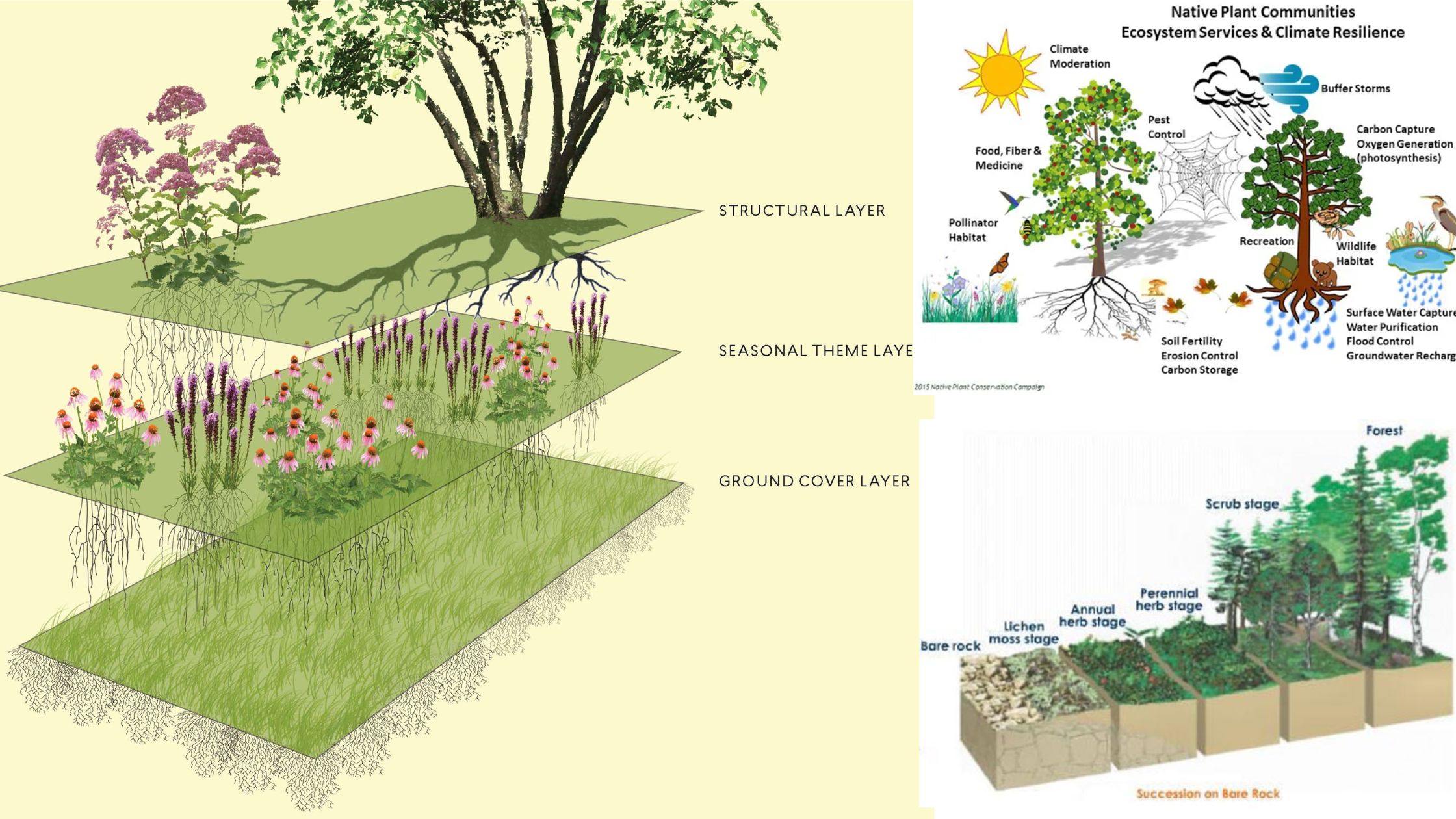
What are Plant communities? Definition of Plant community A plant community is a group of plant species that coexist and interact within a specific geographical area, forming a distinct and relatively uniform vegetation patch. Examples of Plant community Characteristics of Plant Communities Plant communities exhibit various characteristics that can be broadly categorized into analytic and … Read more