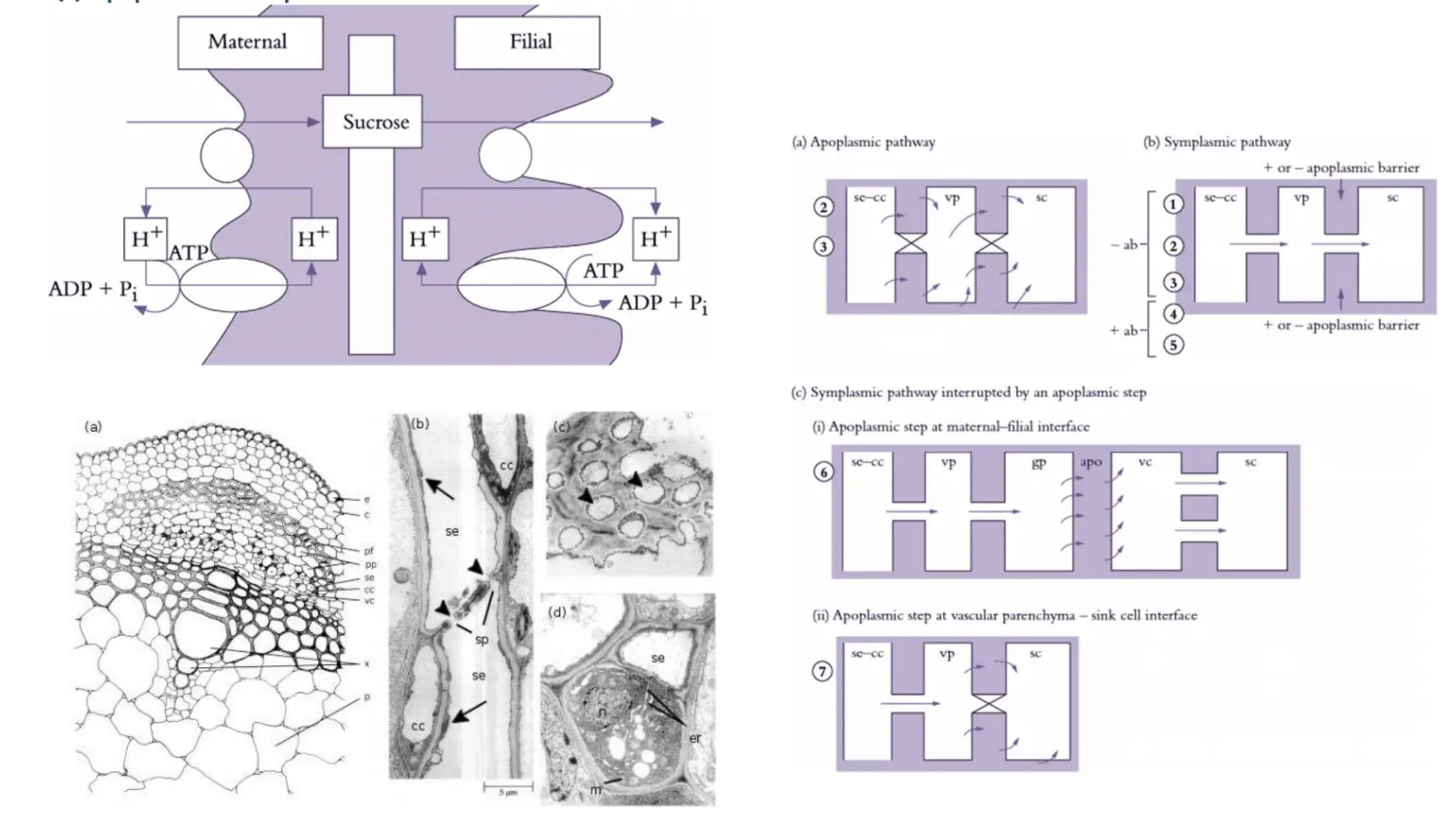
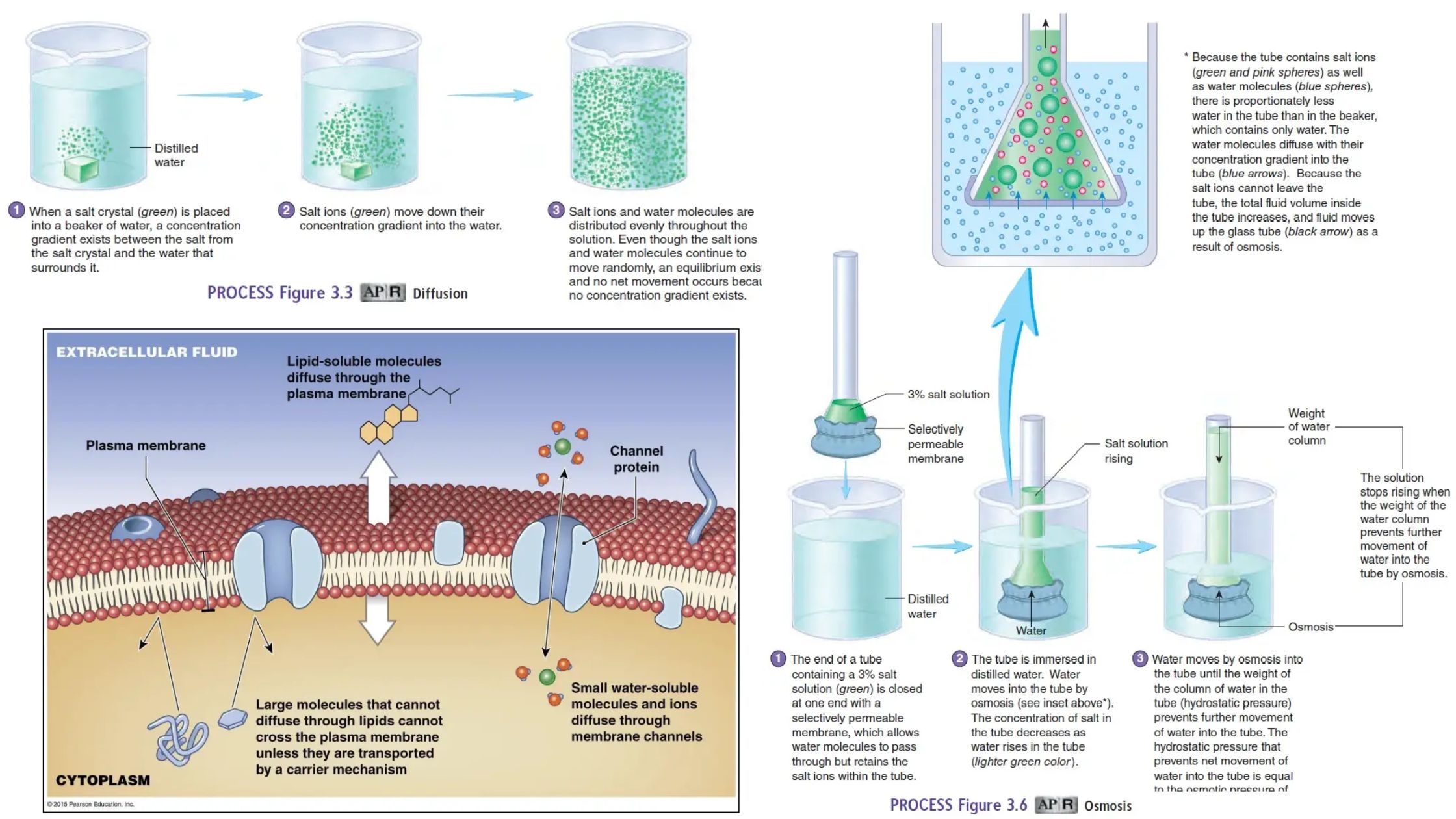
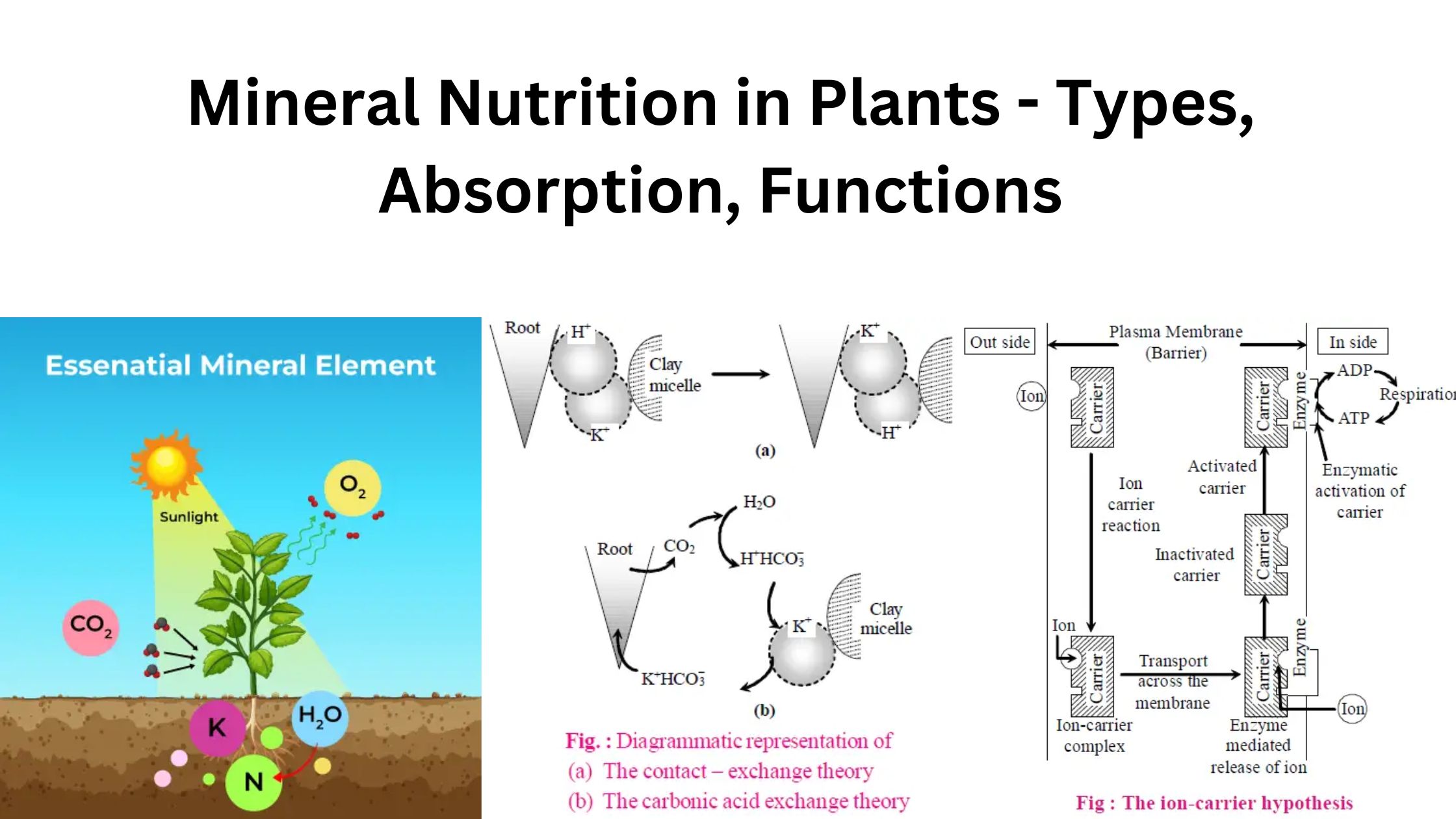
Photomorphogenesis – Definition, Types, Mechanism, Importance
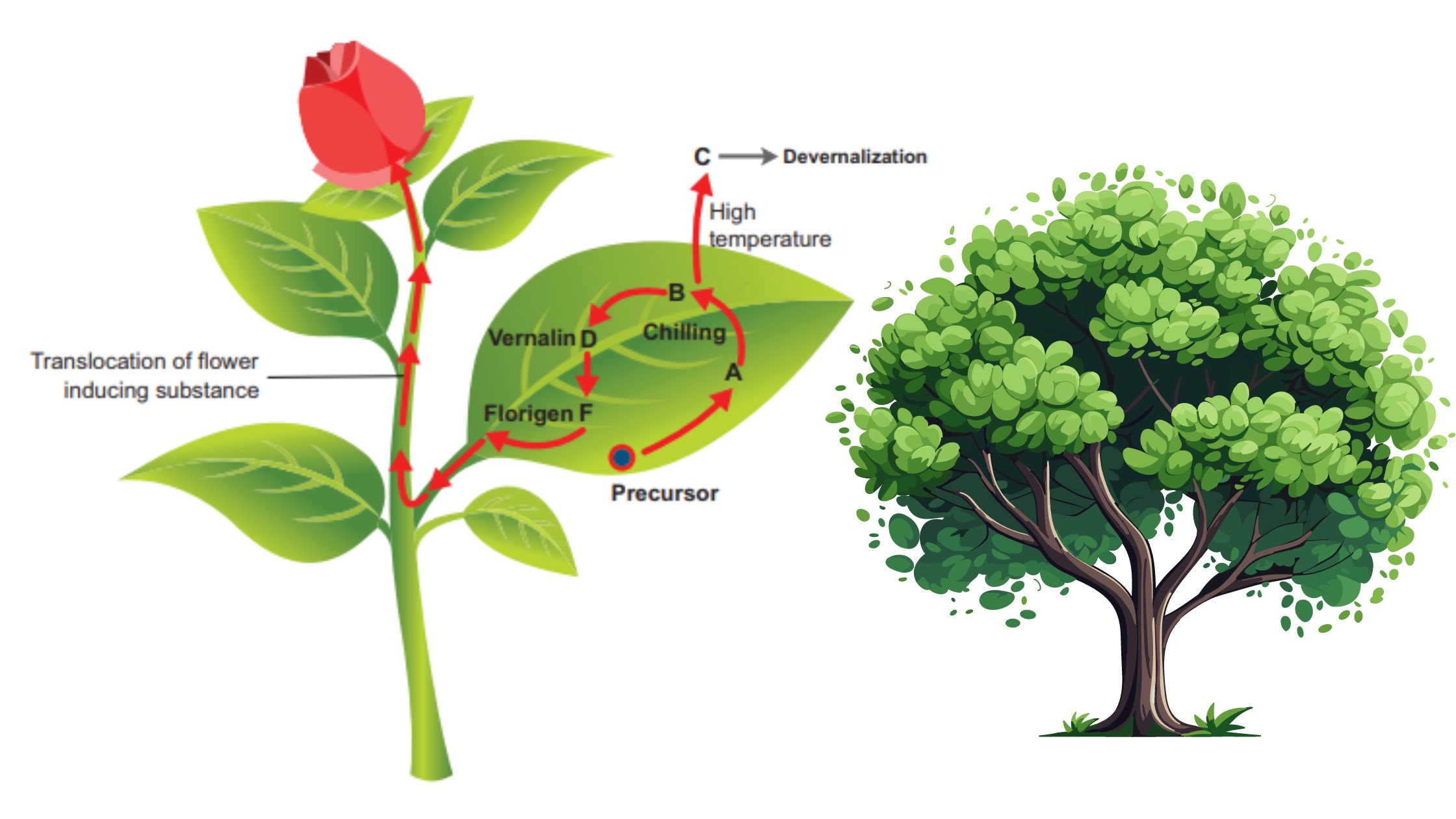
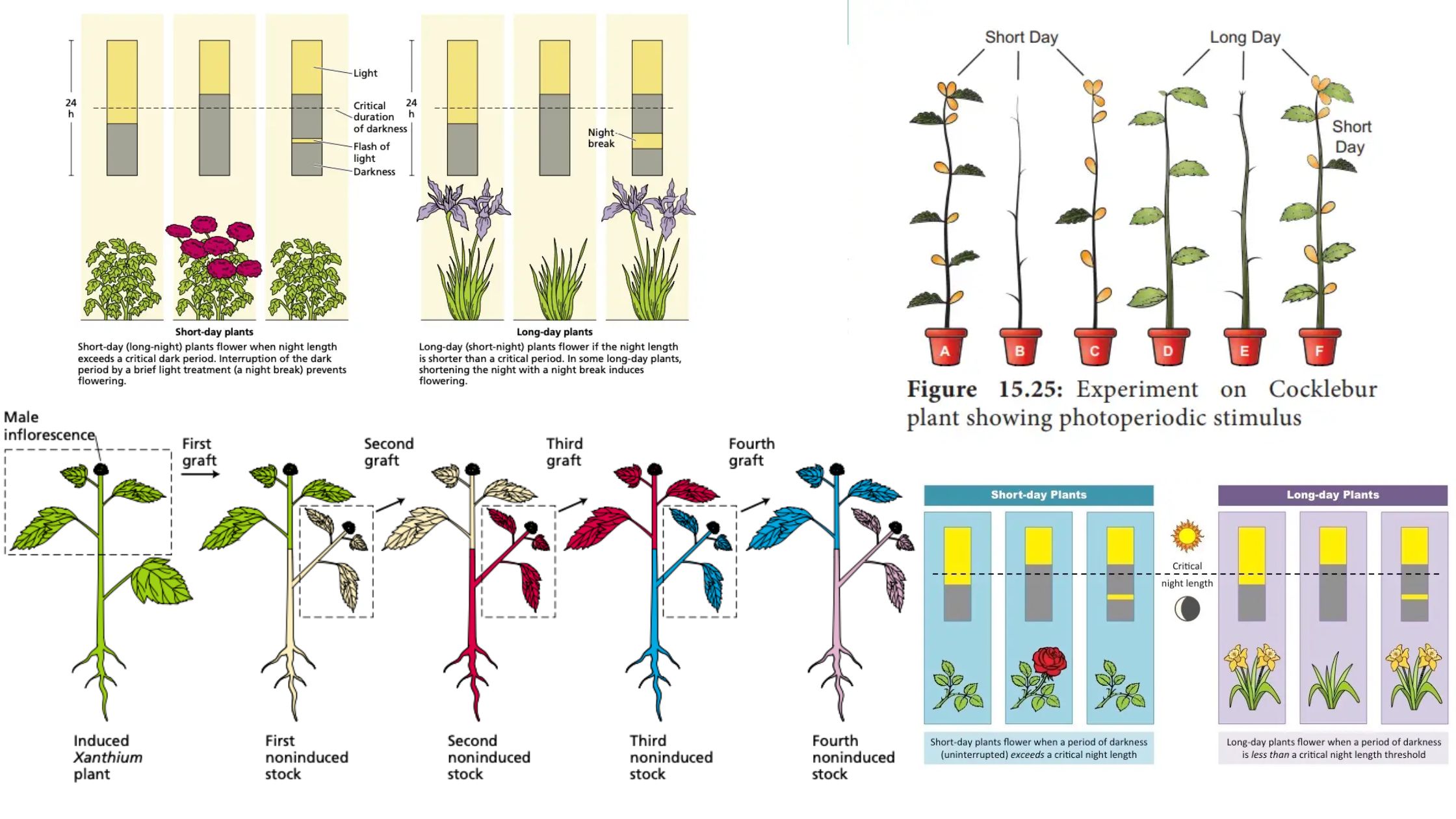
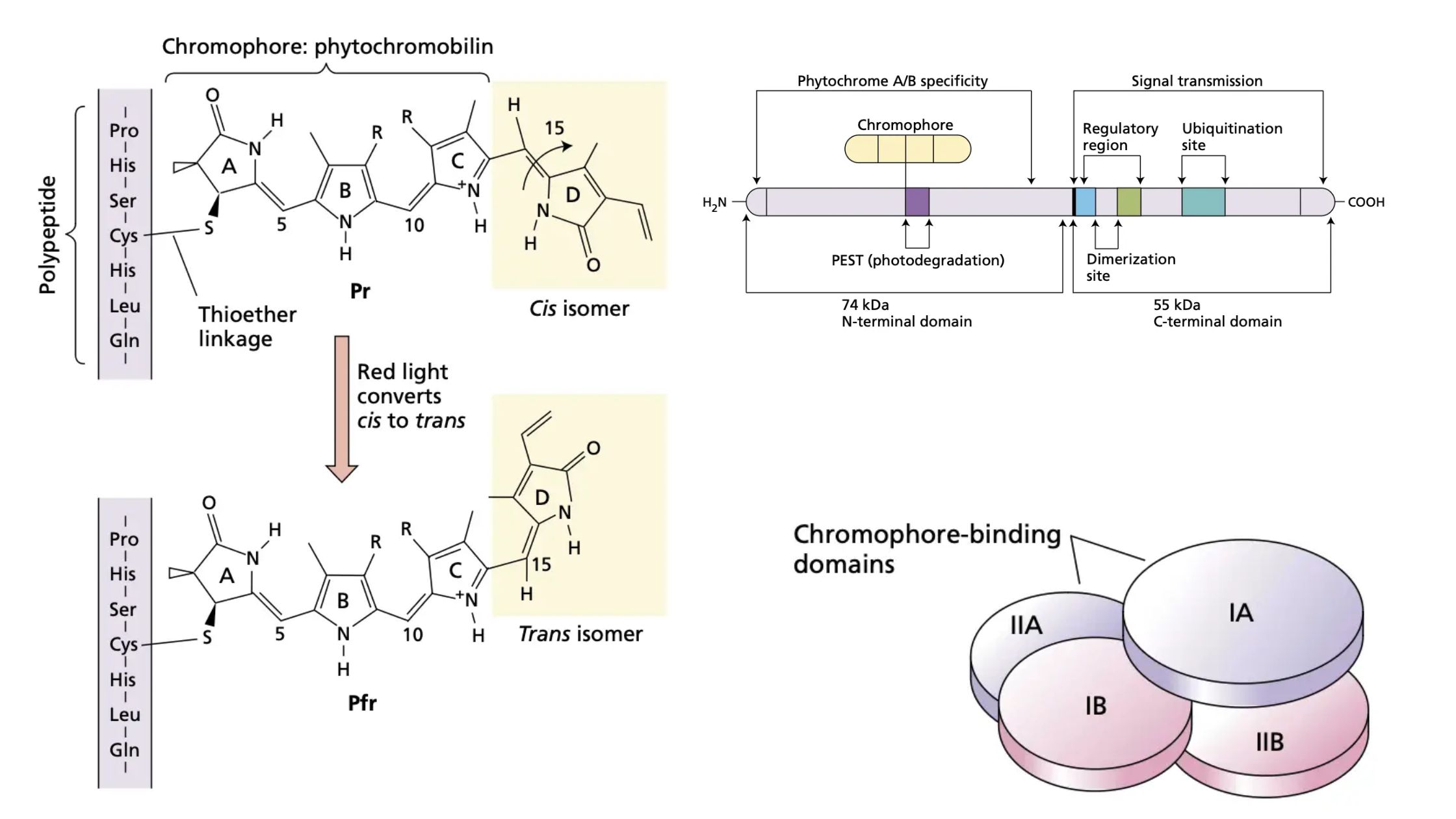
What is Photomorphogenesis? Definition of Photomorphogenesis Photomorphogenesis is the process by which plants use light as a signal to regulate growth and development, influencing stages such as seed germination, seedling growth, and flowering. Photoreceptors and Photomorphogenesis Photomorphogenesis in plants is regulated by specialized light-sensitive molecules known as photoreceptors. These photoreceptors are crucial for interpreting light signals … Read more