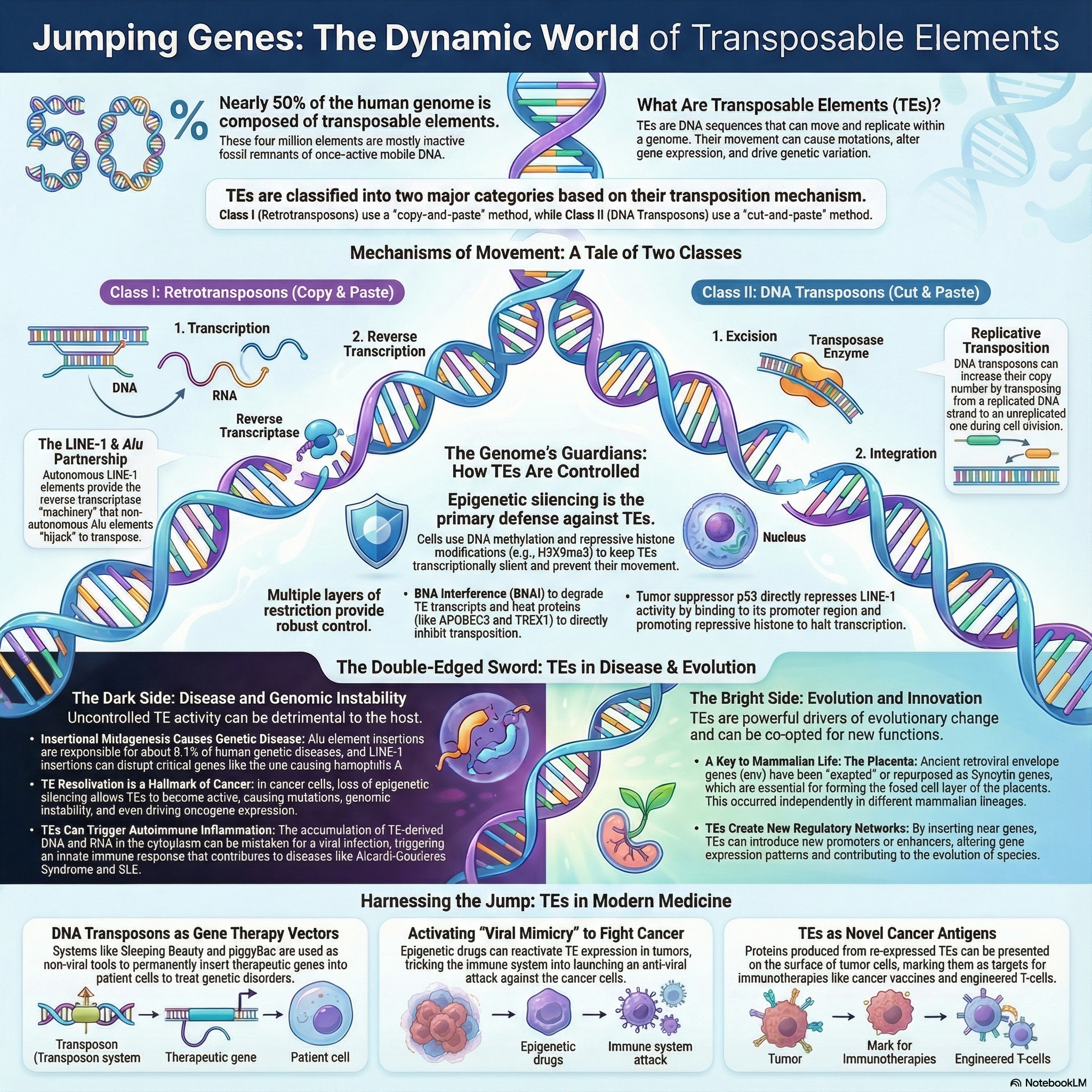
Casein Hydrolysis Test – Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
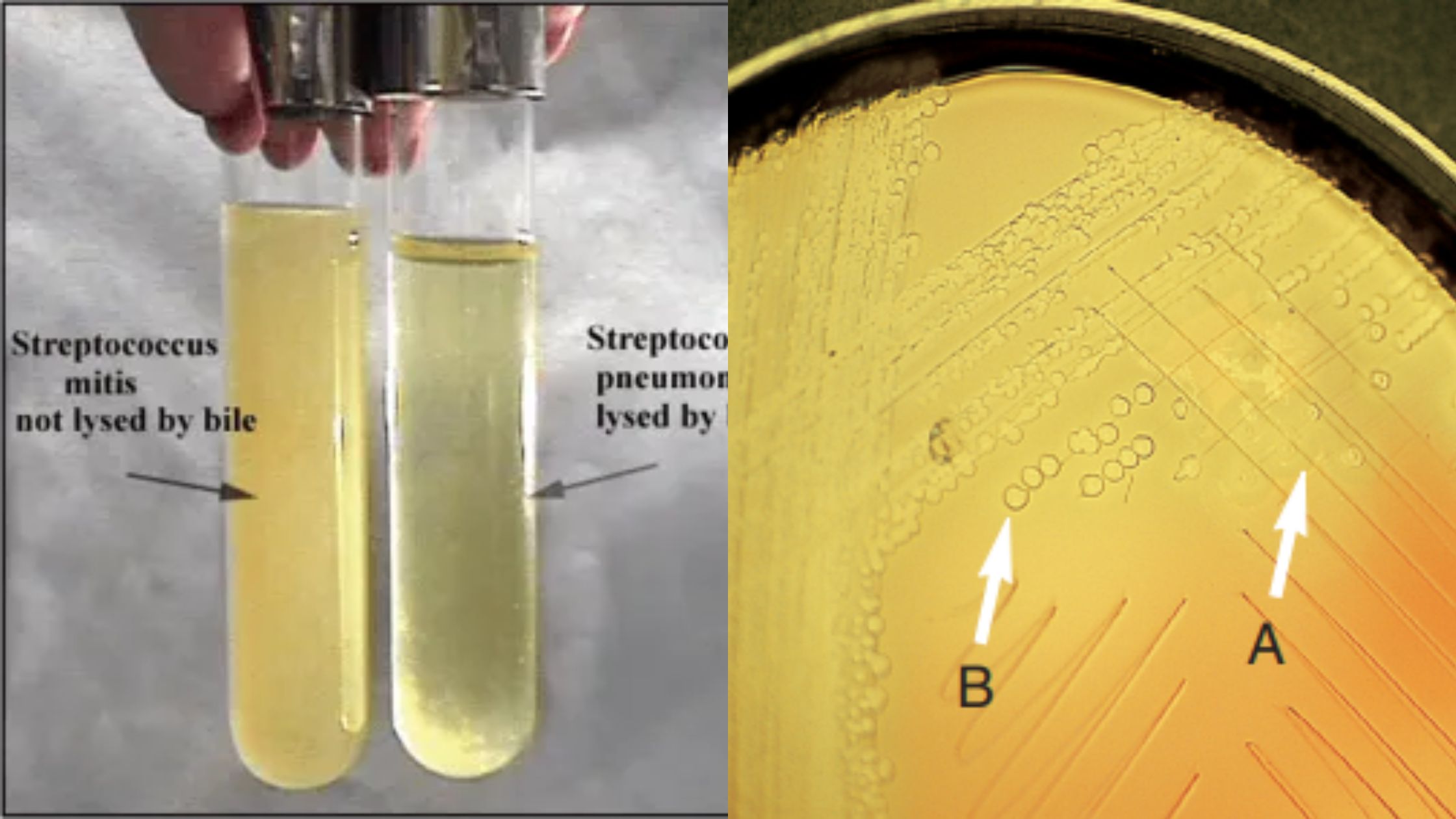
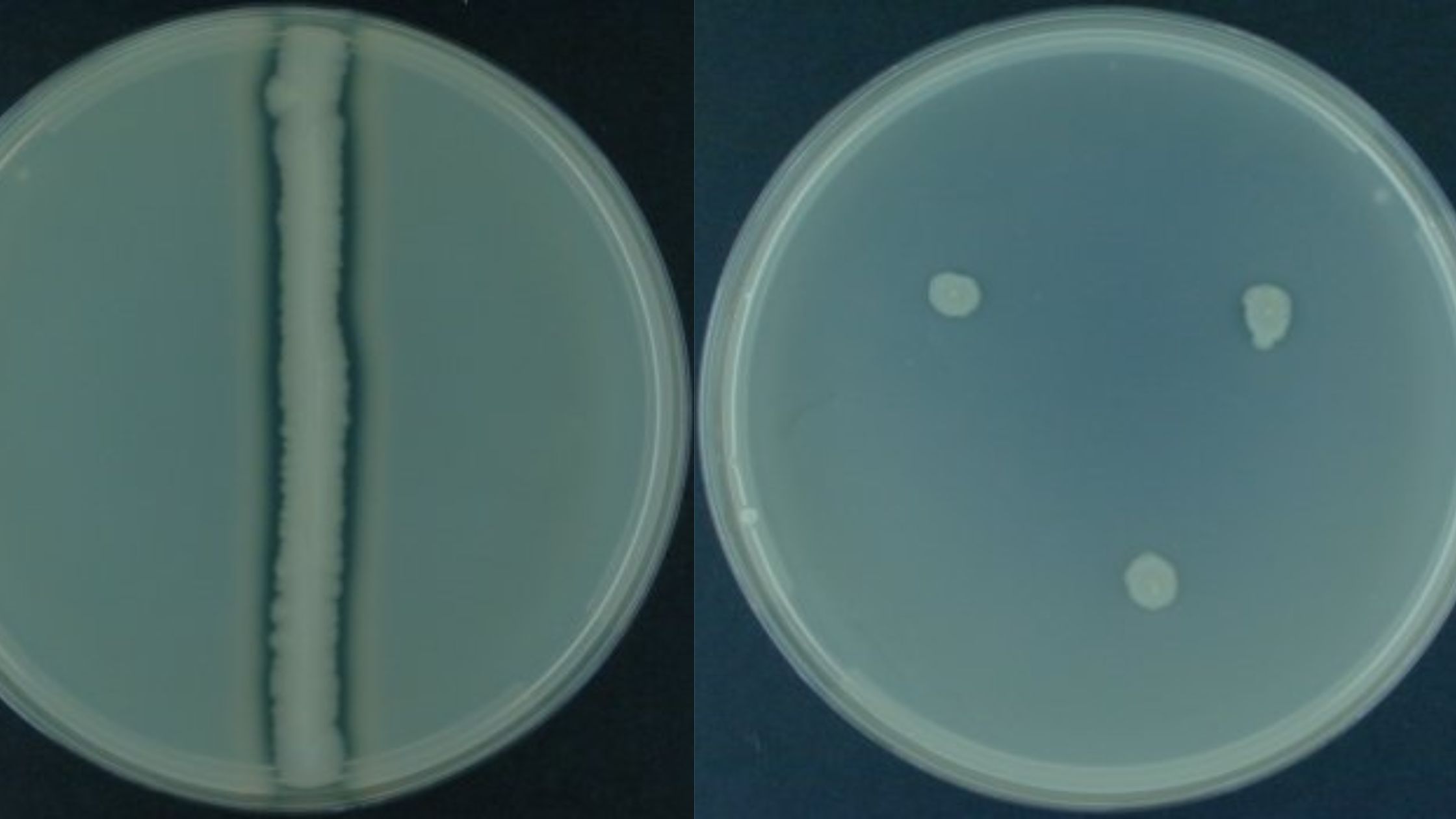
The Casein Hydrolysis Test is a biochemical test that is used to determine the ability of microorganism to produce and secrete extracellular proteolytic enzyme known as caseinase. It is the process in which casein protein of milk is broken down into smaller soluble products. Casein is the main protein present in milk and it is … Read more