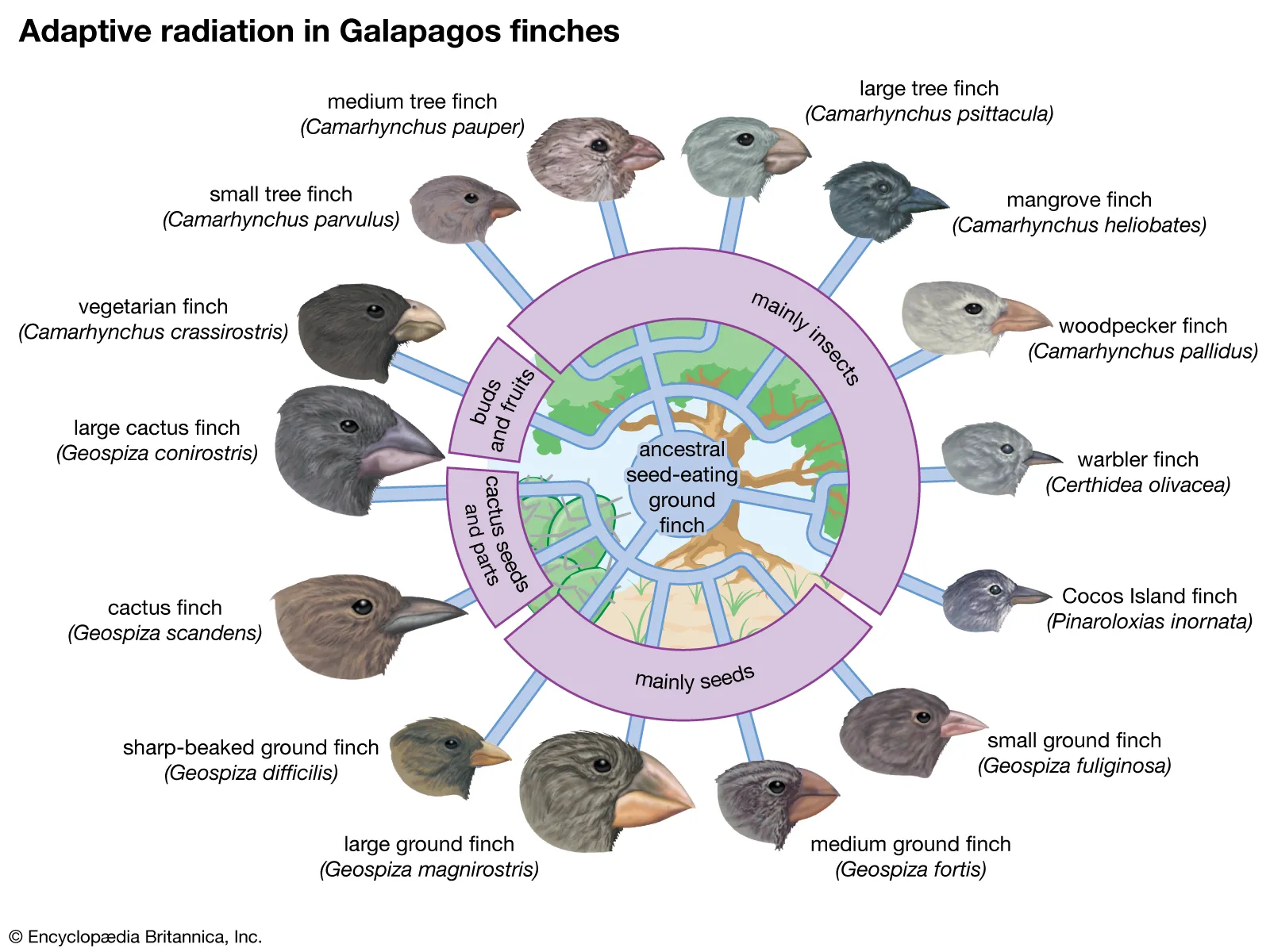
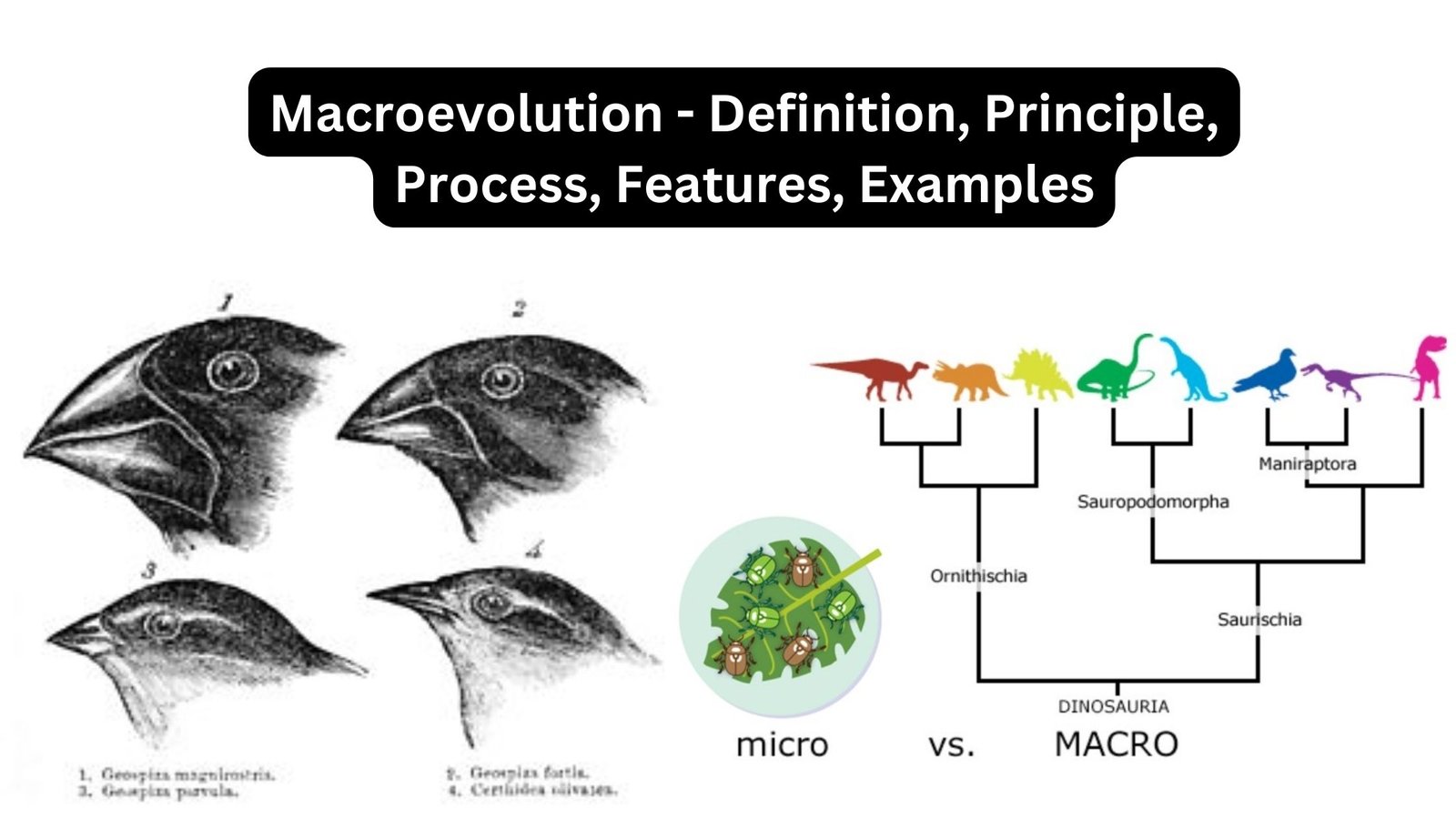
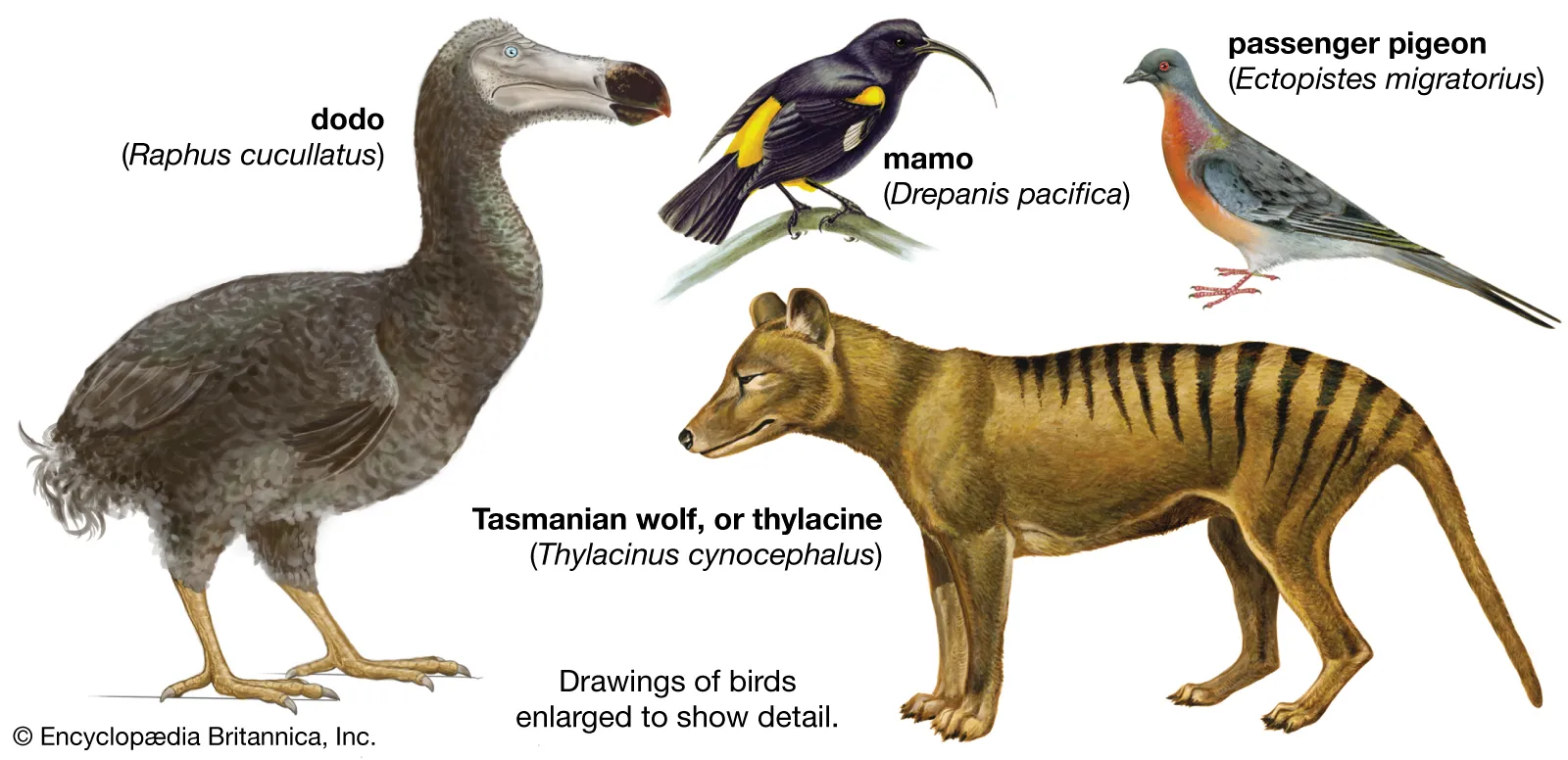
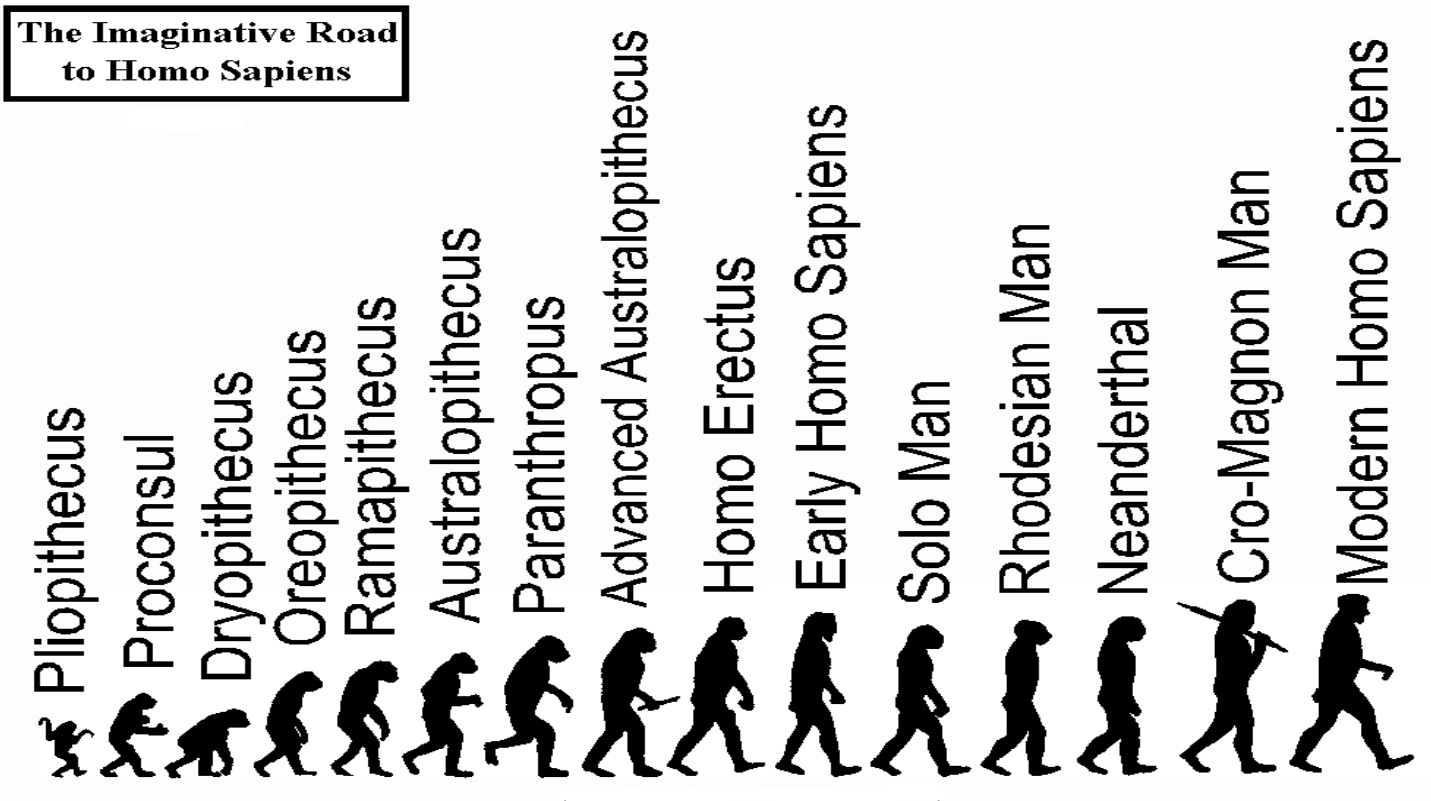
Concept of Species – Definition, Types, Importance, Modes of speciation
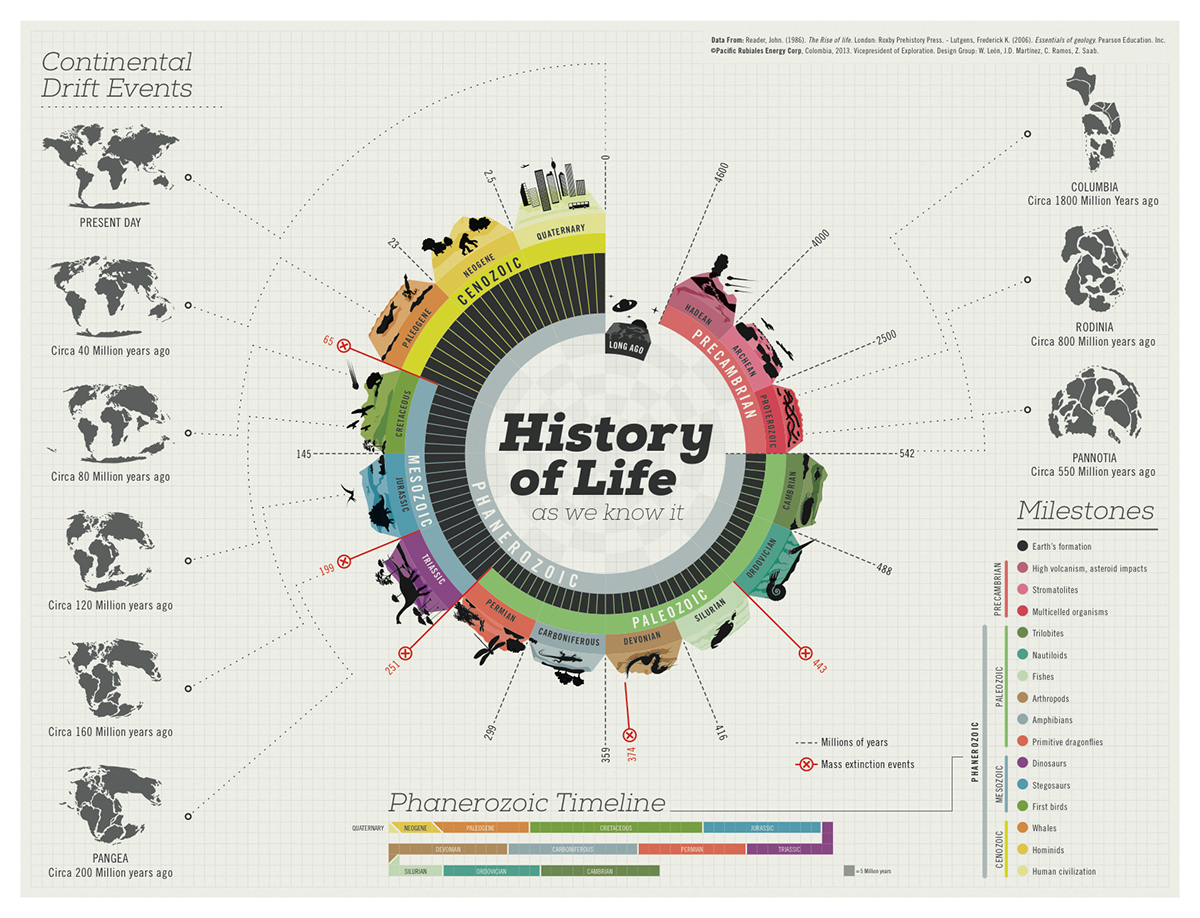
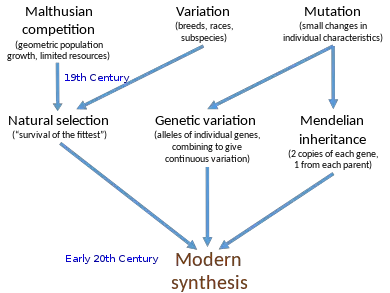
The concept of species has been a subject of ongoing debate and controversy among taxonomists and biologists. The task of defining and recognizing species is crucial for understanding the diversity and organization of life on Earth. Over time, various species concepts have been proposed to tackle this challenge, each with its own merits and limitations. … Read more