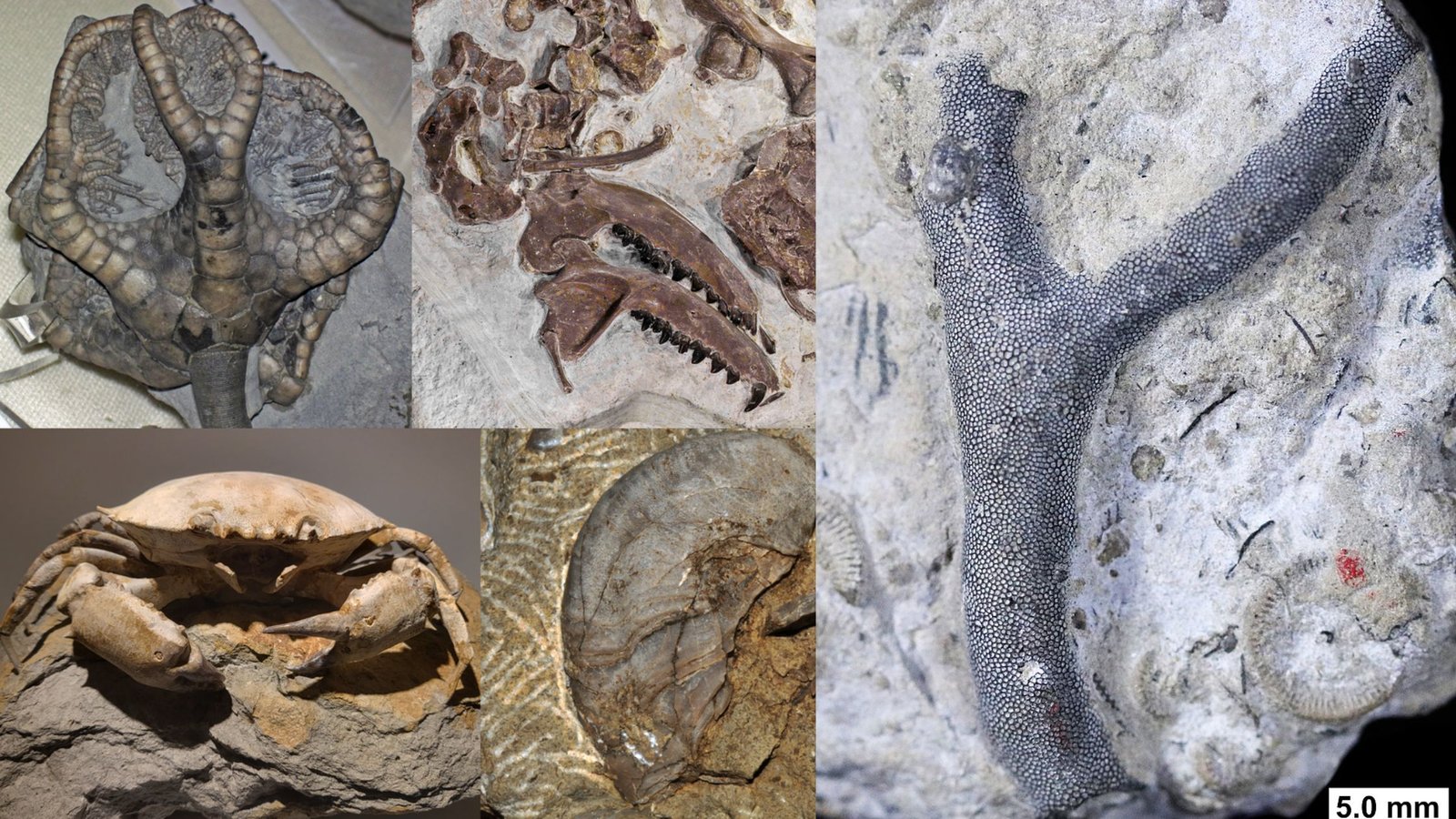
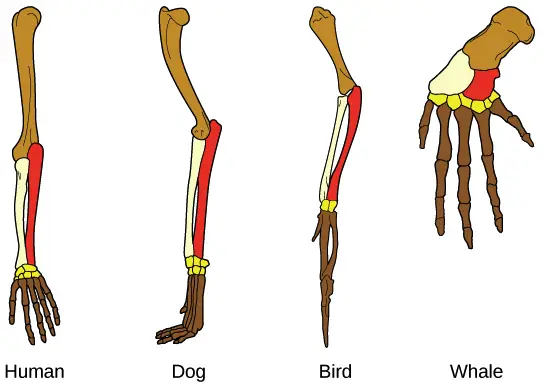
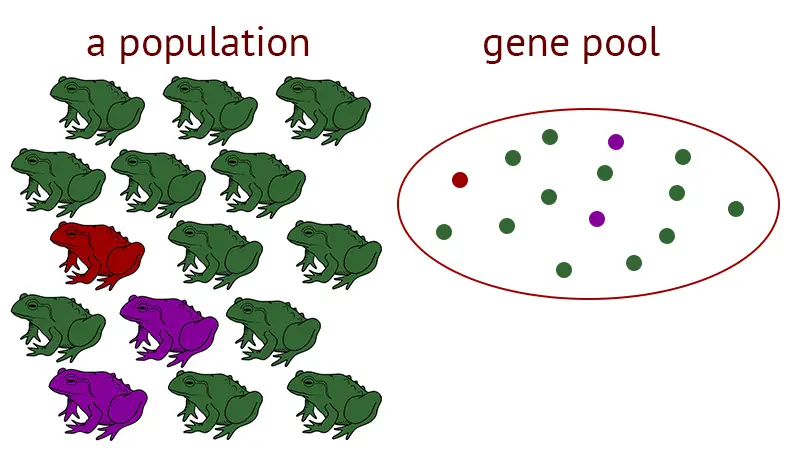
Orientation Patterns of Behaviour
What is Orientation? In animal behavior, orientation refers to the ability of an animal to determine and maintain a specific direction or position in relation to its environment. It involves the animal’s ability to perceive and respond to various stimuli, such as light, gravity, magnetic fields, landmarks, and chemical cues, in order to navigate and … Read more