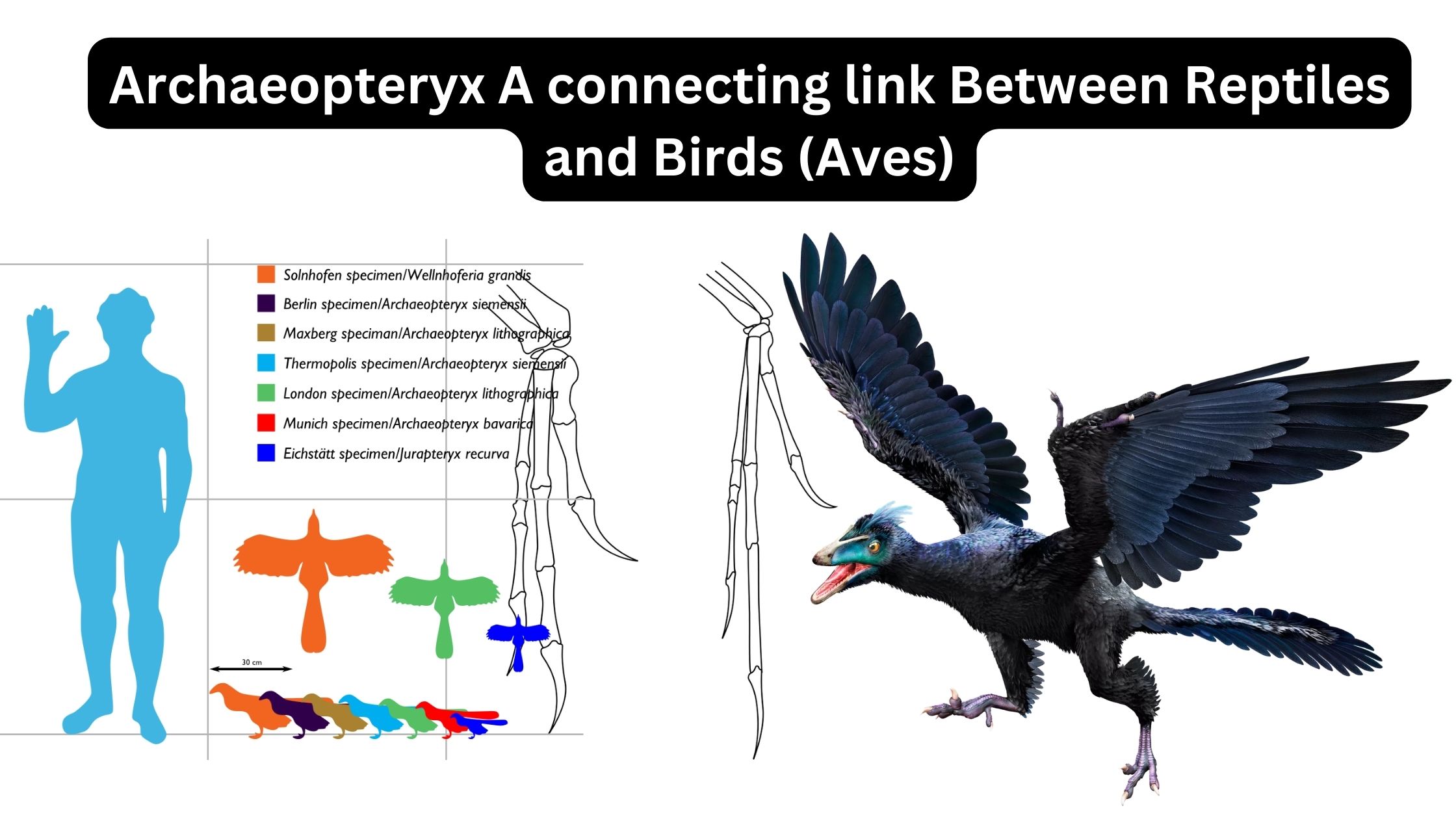
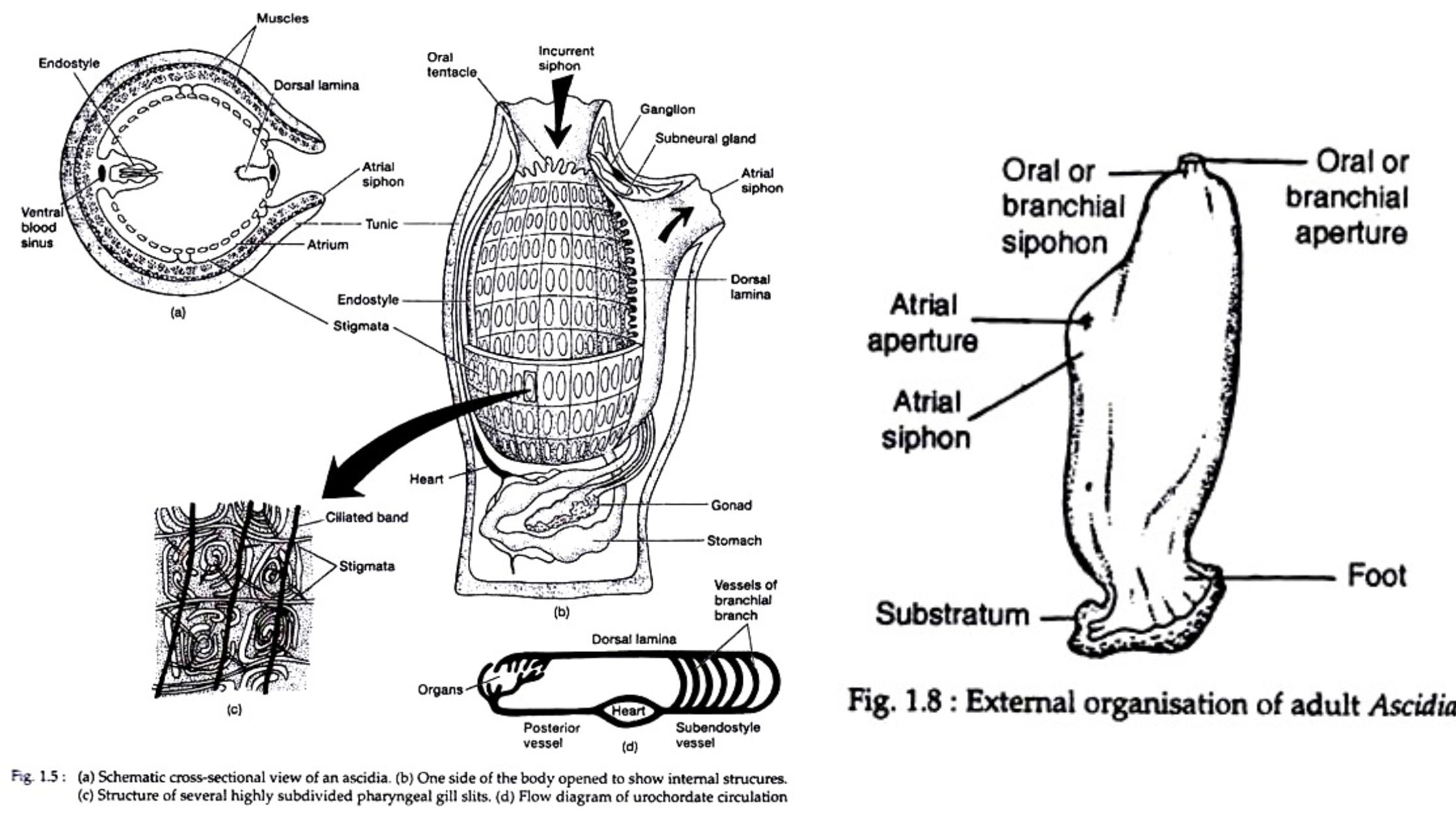
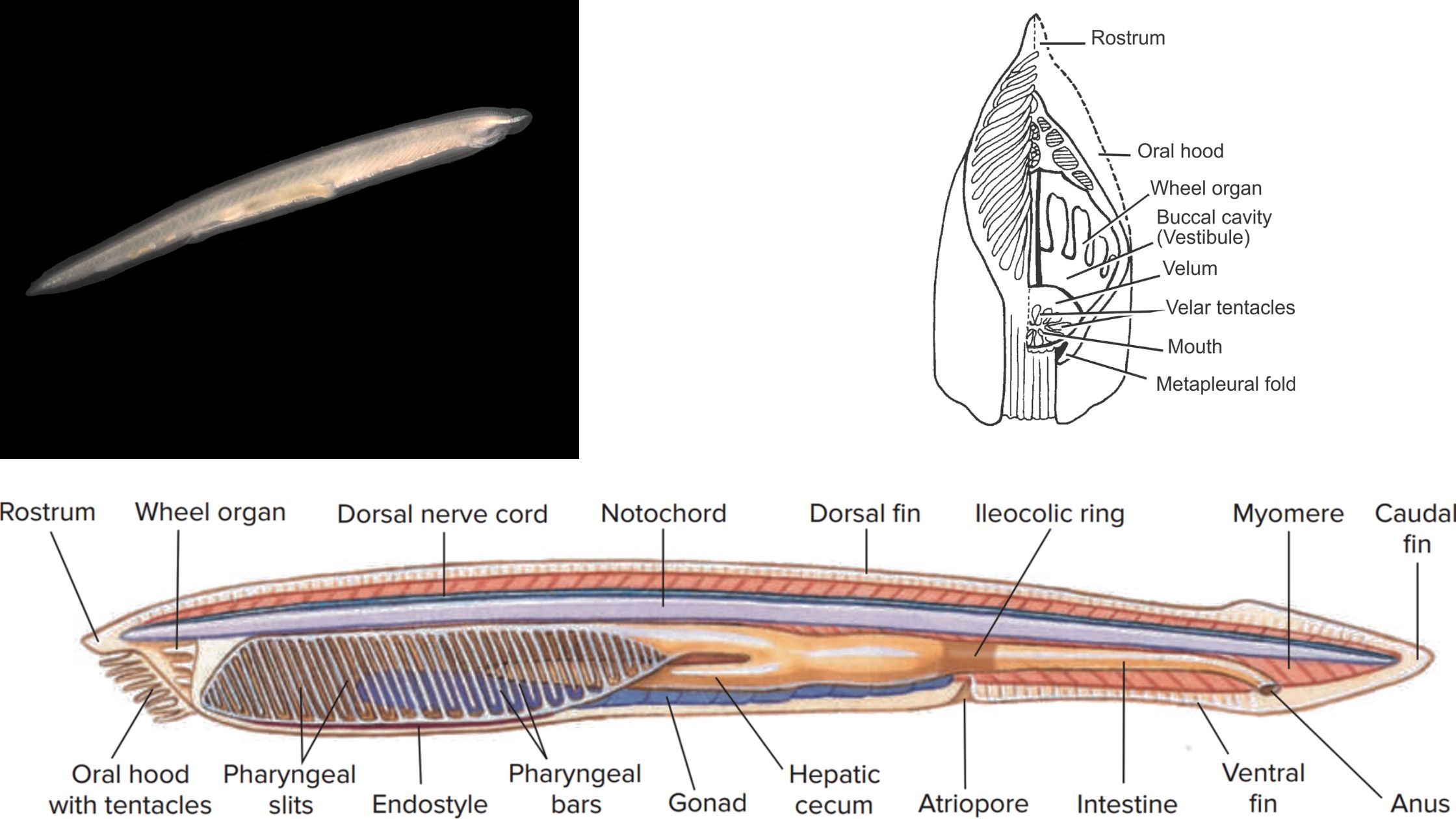
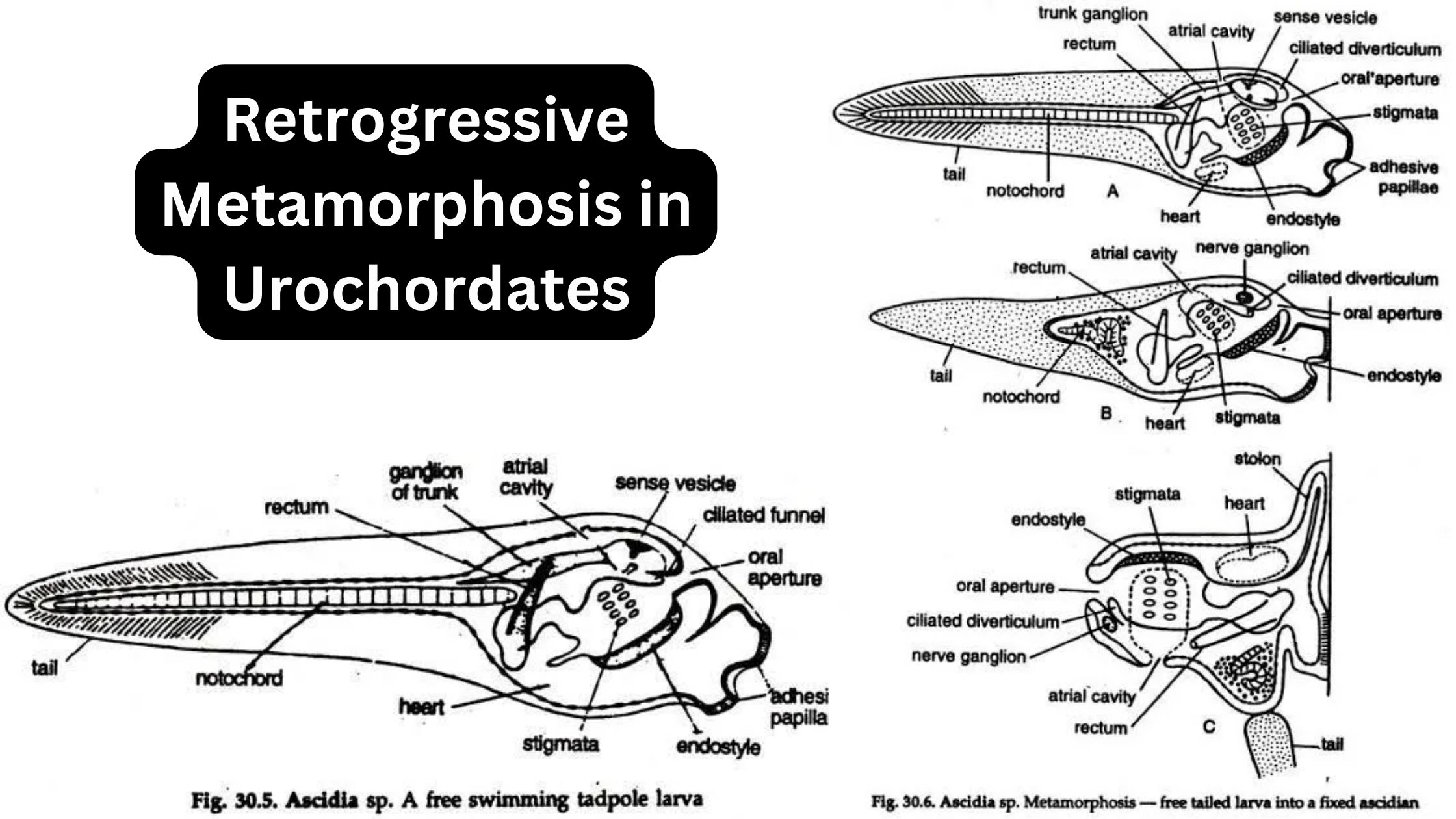
Archaeopteryx A connecting link Between Reptiles and Birds (Aves)
What is Archaeopteryx? Discovery of Archaeopteryx Authenticity: Description of Archaeopteryx How Archaeopteryx is a connecting link Between Reptiles and Birds (Aves)? Archaeopteryx is considered a connecting link between reptiles and birds (Aves) due to its combination of characteristics from both groups. Here’s a description of how Archaeopteryx exhibits features that bridge the gap between reptiles … Read more