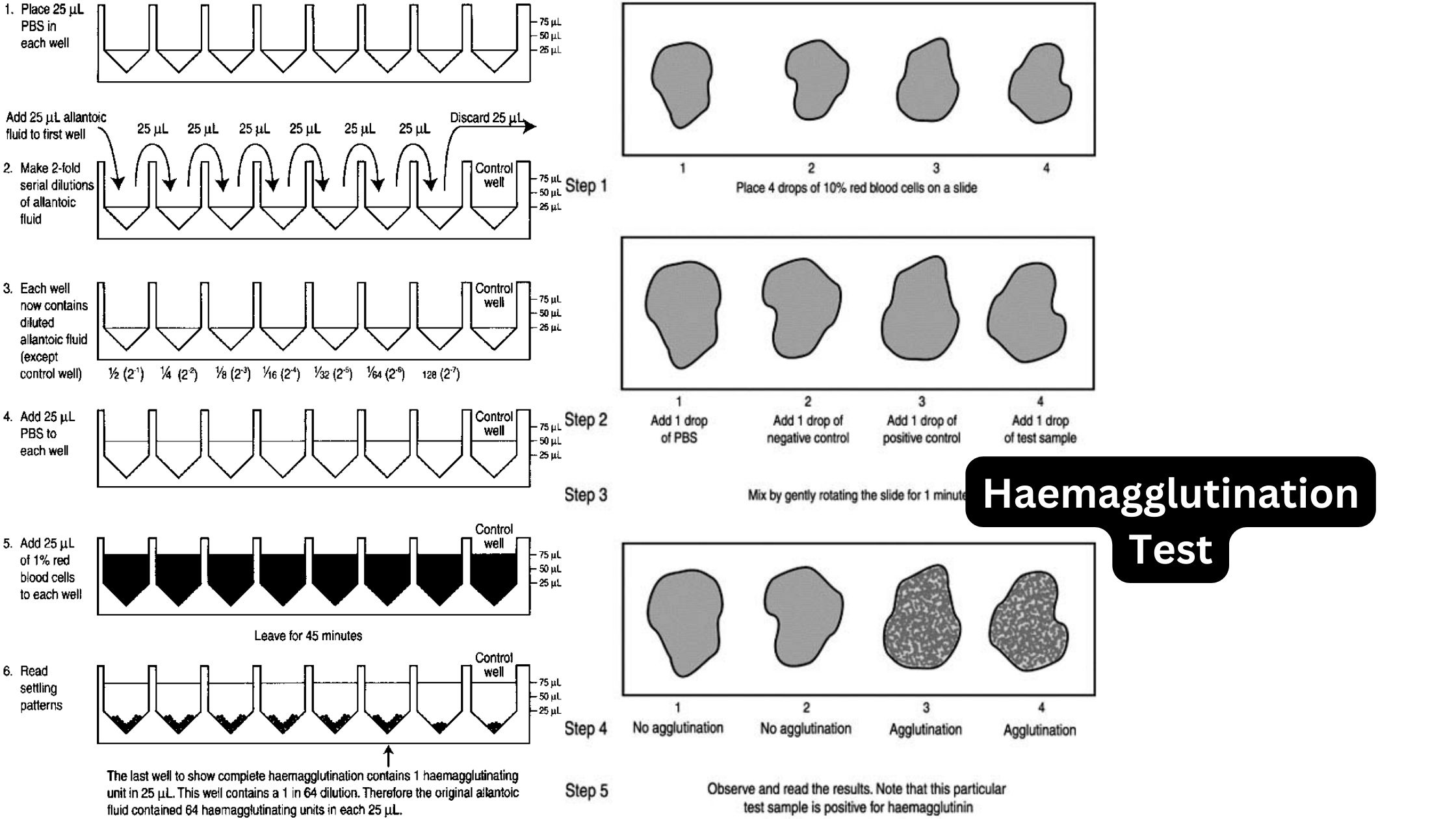
Hemagglutination Inhibition Test
The nucleic acids of many viruses encode surface proteins (such as hemagglutinin (HA) of influenza virus) that agglutinate red blood cells (RBC) of numerous species. Hemagglutination is the process by which viral hemagglutinins react with red blood cells to form a lattice of agglutinated cells that settle unevenly in a tube or microtiter well. Unagglutinated … Read more