Community – Definition, Types, Characterisitcs, Importance
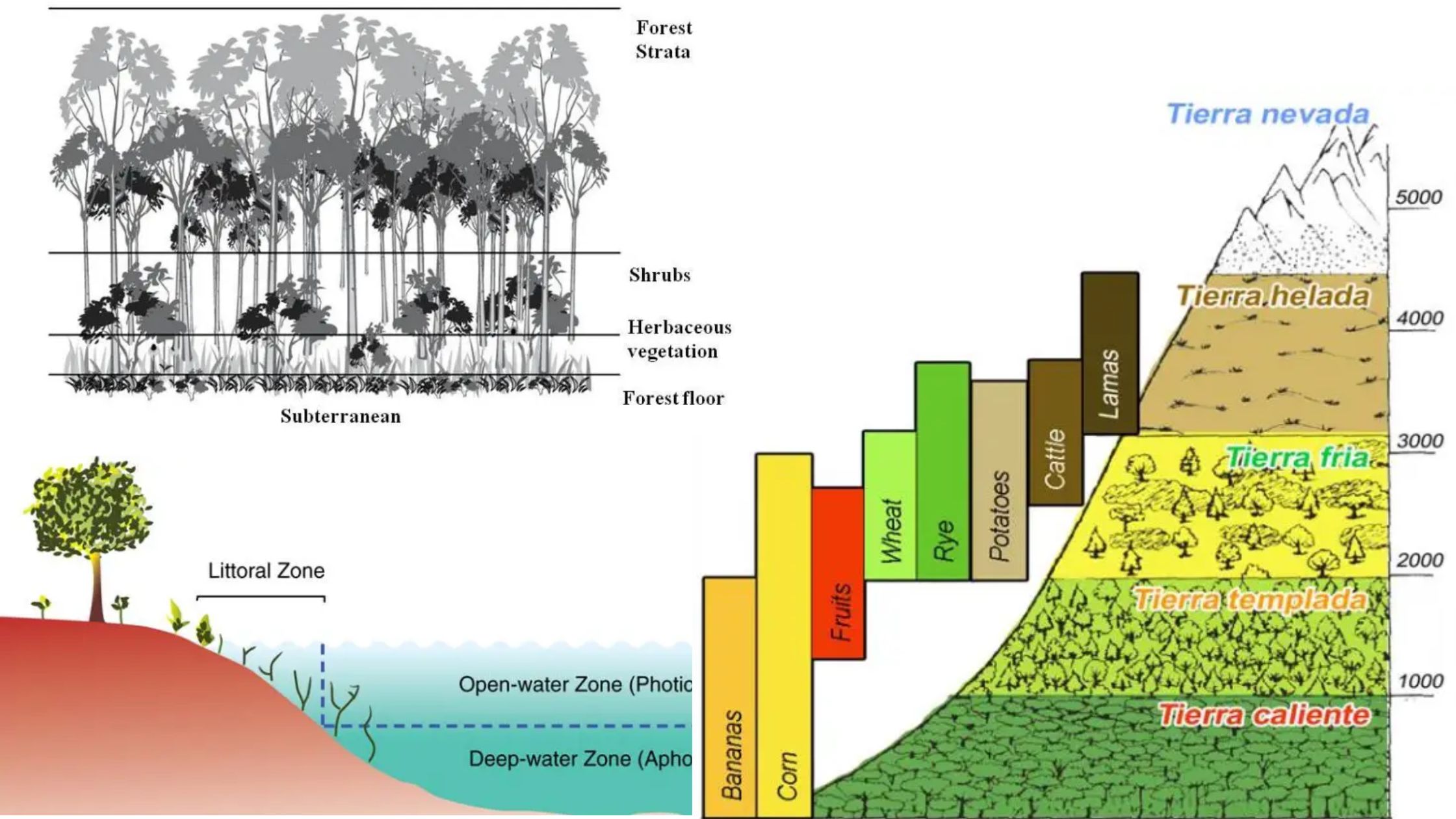
What is Community in Ecology? Types of Community Types of community can be classified based on their size and self-regulatory capabilities. Here are the main types of communities: Communities can also be classified based on their openness or closedness: Understanding the types of communities helps ecologists study the dynamics, interactions, and adaptations within different ecological … Read more