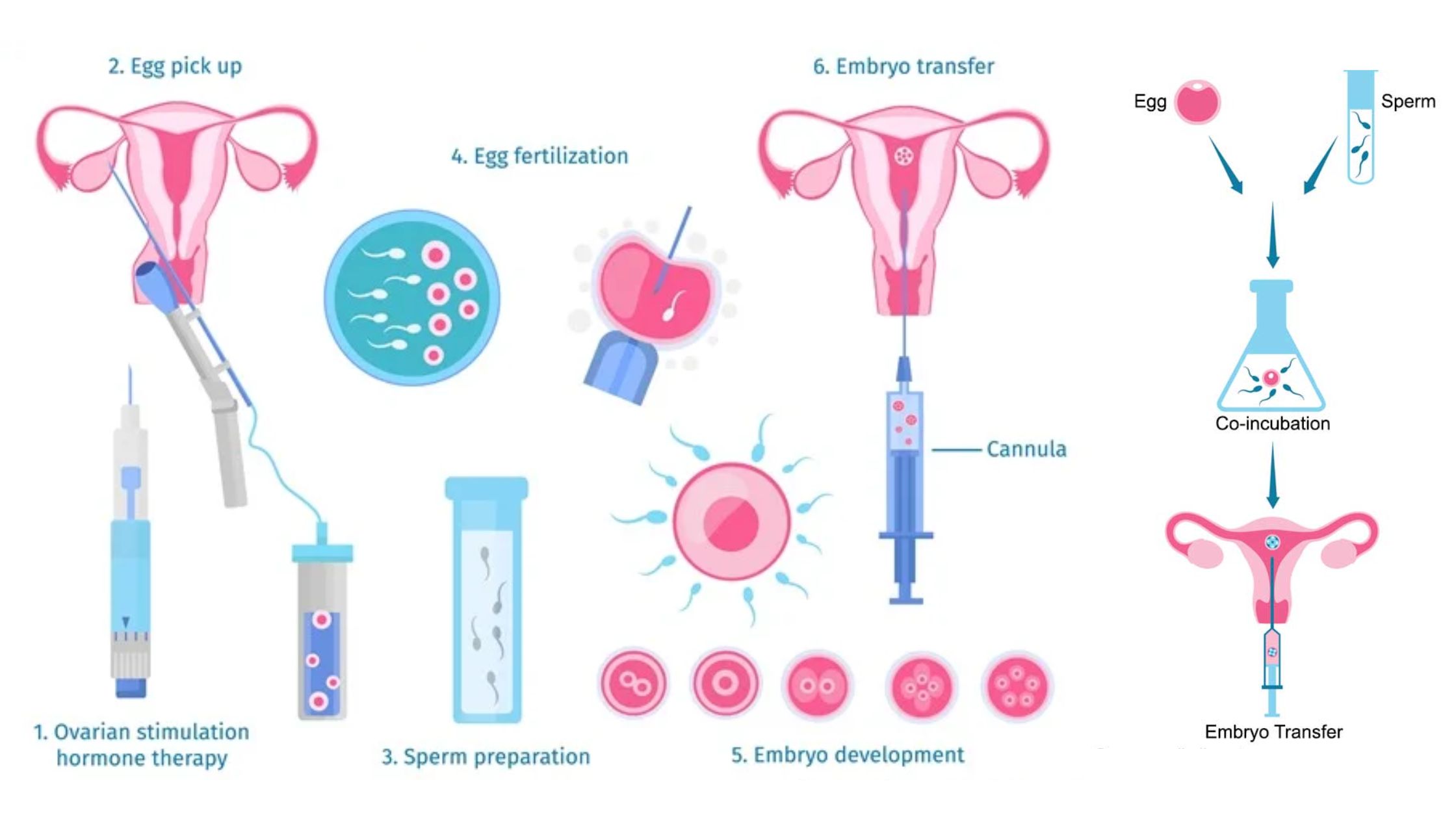
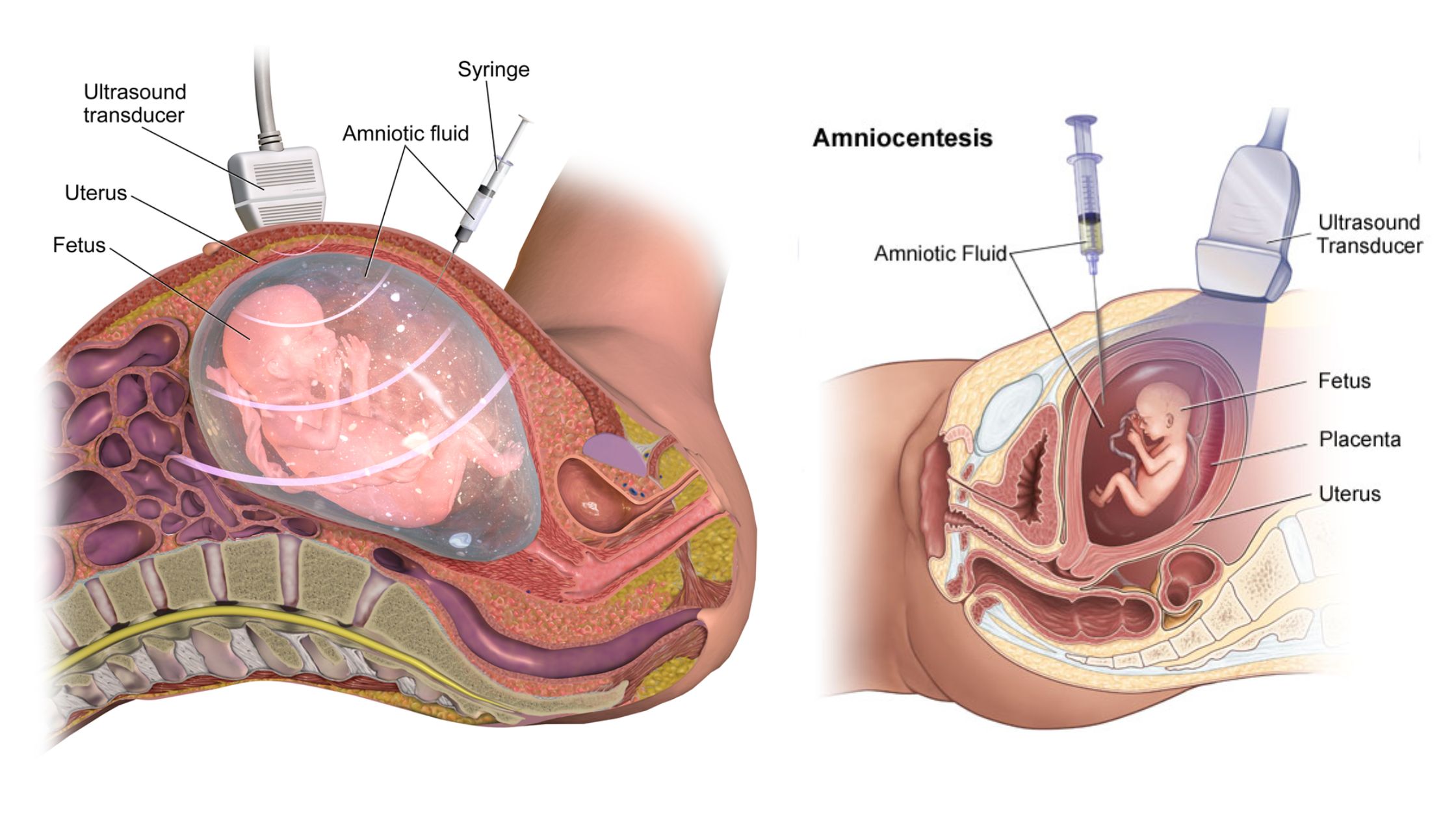
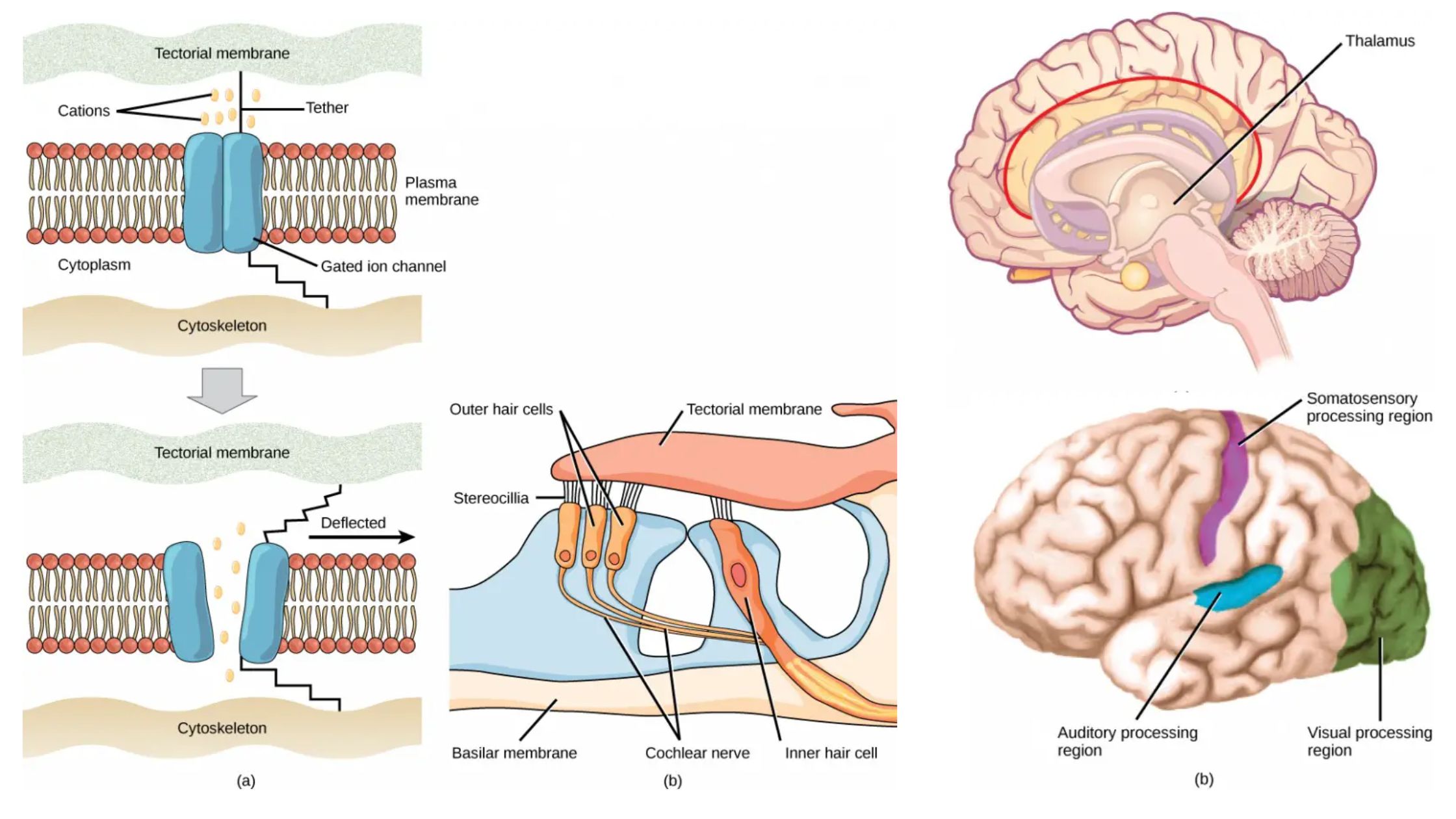
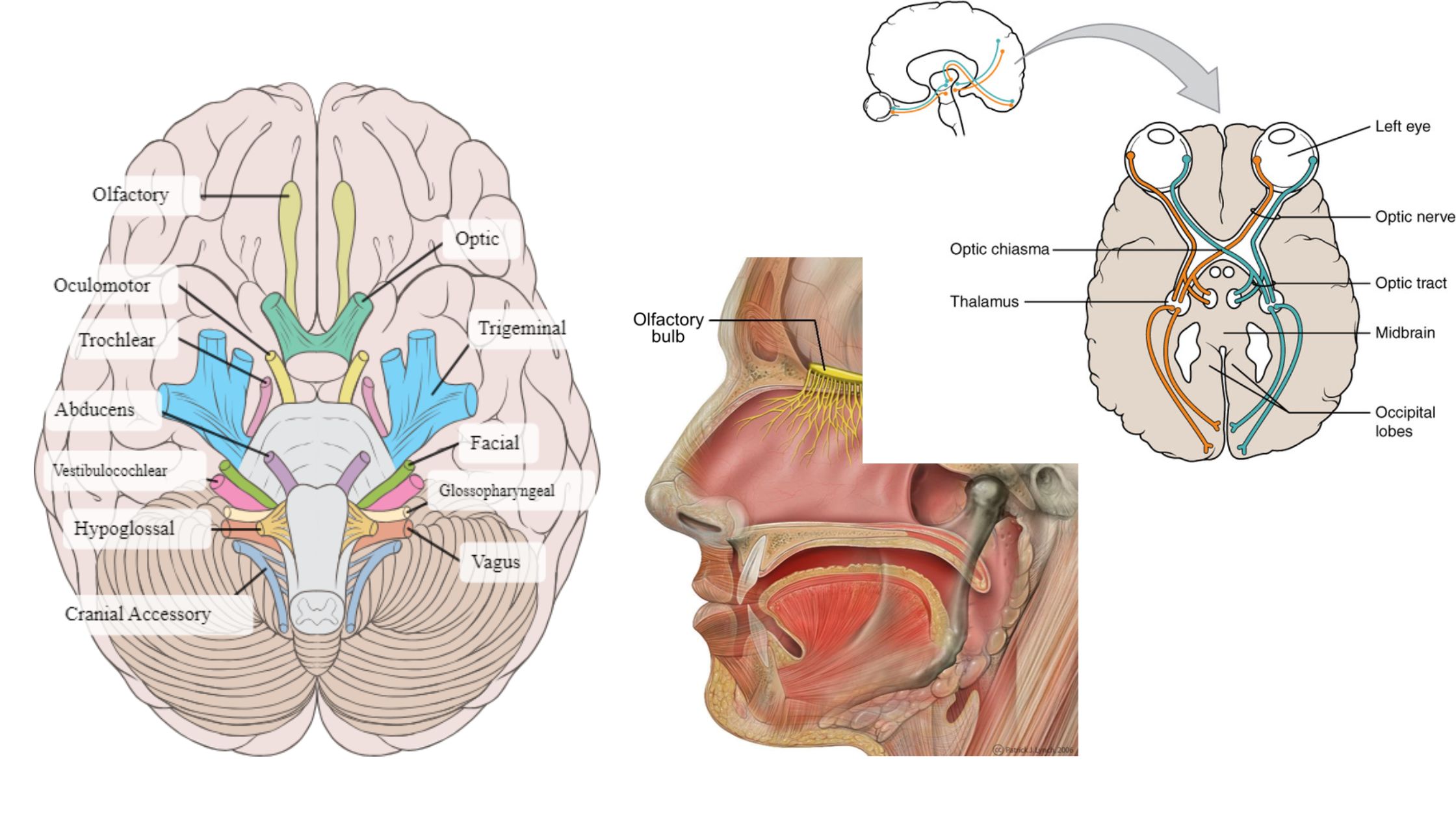
Sampling of Bacteria From Air
The process of collecting bacteria from the air for analysis involves several techniques, one of the simplest being the utilization of open Petri dishes filled with a growth medium. These dishes are exposed to the air, allowing airborne bacteria to settle and subsequently grow on the medium, which can then be examined to identify the … Read more