What is Yersinia Selective Agar?
- Yersinia Selective Agar is a specialized medium designed for the isolation and identification of Yersinia enterocolitica, a bacterium responsible for gastroenteritis. It was developed by Schiemann as an alternative to other commonly used media like MacConkey Agar. Yersinia enterocolitica is a significant food and waterborne pathogen that can cause various symptoms in animals, including diarrhea, lymphadenopathy, pneumonia, and spontaneous abortions.
- Yersinia Selective Agar is both selective and differential, providing optimal conditions for the growth of Yersinia enterocolitica and some other Yersinia species. The medium is particularly useful for the isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from clinical and non-clinical samples, such as food or feces.
- The formulation of Yersinia Selective Agar is based on the CIN (Cefsulodin-Irgasan-Novobiocin) Agar developed by Schiemann. This modified medium replaces bile salts with sodium deoxycholate. The agar differentiates between bacteria that ferment mannitol and those that do not. Mannitol-fermenting bacteria produce acid that lowers the pH of the medium around the colonies, resulting in a localized drop in pH. In the presence of neutral red dye, these colonies appear red. On the other hand, mannitol-negative organisms form colorless and translucent colonies.
- The selective properties of Yersinia Selective Agar are due to the inclusion of sodium deoxycholate and crystal violet, which inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and many Gram-negative bacteria. To enhance selectivity for Yersinia, an antibiotic supplement is added to the medium.
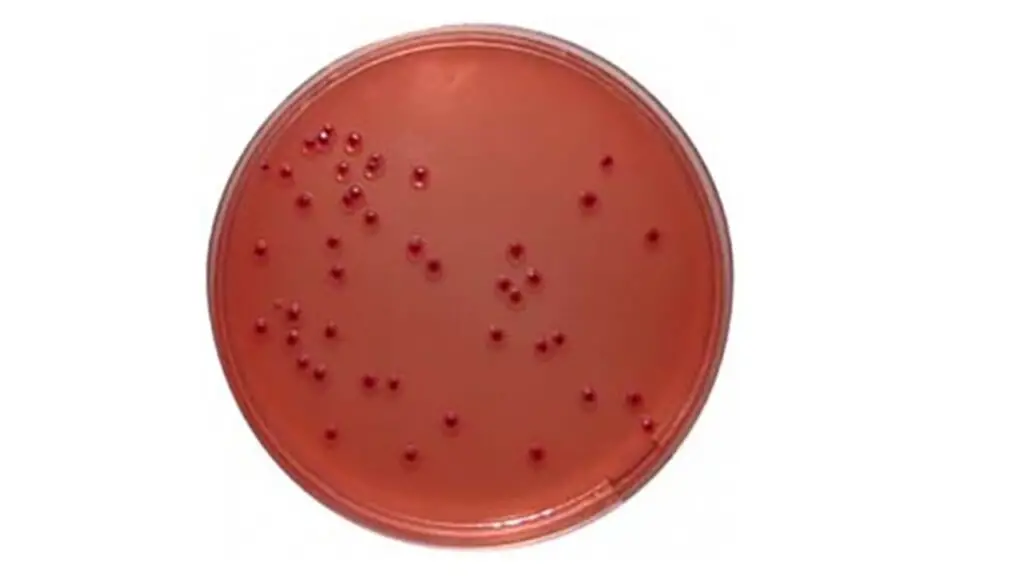
- Typical colonies of Yersinia enterocolitica on Yersinia Selective Agar appear as dark red colonies with a bull’s-eye-like appearance, surrounded by a transparent border. It’s important to note that colony characteristics, such as size, smoothness, and the ratio of the border to center diameter, may vary among different serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica.
- To isolate Yersinia enterocolitica using Yersinia Selective Agar, the specimen can be directly plated onto the medium or suspended in sterile Phosphate Buffer Saline and incubated for up to 21 days at 4°C. Incubation at a temperature range of 22-32°C for 24-48 hours is also suitable. Periodic subculturing onto Yersinia Agar Plates and incubation under the specified conditions allows for the continued growth and isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica.
- In summary, Yersinia Selective Agar is a specialized medium that supports the growth of Yersinia enterocolitica and some Yersinia species. It provides selective and differential properties to facilitate the isolation and identification of Yersinia enterocolitica from various samples, including clinical and non-clinical specimens.
Principle of Yersinia Selective Agar
The principle of Yersinia Selective Agar is based on several key factors:
- Differentiation of Mannitol Fermenters: The medium is designed to differentiate between bacteria that can ferment mannitol and those that cannot. Microorganisms capable of fermenting mannitol produce acid as a byproduct, which leads to the acidification of the medium and a localized drop in pH around the colonies.
- Neutral Red Indicator: In the presence of neutral red, mannitol-fermenting colonies appear red due to the acid production and subsequent pH decrease. Additionally, the localized pH decrease may result in the precipitation of bile, which can be observed as a zone surrounding the colonies.
- Colorless Translucent Colonies: Non-fermenting organisms that do not metabolize mannitol will not cause acidification of the medium. As a result, these mannitol-negative organisms form colorless and translucent colonies.
- Selective Properties: Yersinia Selective Agar exhibits selectivity due to the presence of sodium deoxycholate and crystal violet. These components inhibit the growth of gram-positive bacteria as well as a number of gram-negative bacteria, creating a favorable environment for Yersinia species.
- Antibiotic Supplement: The addition of an antibiotic supplement enhances the selectivity of the medium specifically for Yersinia. This supplement further inhibits the growth of competing bacteria, allowing for the isolation and identification of Yersinia enterocolitica.
- Colony Characteristics: Typical colonies of Yersinia enterocolitica on Yersinia Selective Agar appear as dark red colonies resembling a bull’s-eye pattern, often surrounded by a transparent border. However, it’s important to note that colony size, smoothness, and the ratio of the border to center diameter can vary among different serotypes of Yersinia enterocolitica.
In addition to these specific components, other ingredients in the medium play supporting roles. Sodium chloride helps maintain the osmotic balance of the medium, while sodium pyruvate and magnesium sulfate serve as growth stimulants for the organisms. Agar is used as a solidifying agent, providing a solid surface for colony formation and observation.
Overall, the principle of Yersinia Selective Agar lies in its ability to differentiate mannitol fermenters from non-fermenters, selectively inhibit the growth of unwanted bacteria, and provide specific colony characteristics that aid in the identification of Yersinia enterocolitica.
Composition of Yersinia Selective Agar
| Ingredients | Gms/liter |
| Peptone, special | 20.000 |
| Yeast extract | 2.000 |
| Mannitol | 20.000 |
| Sodium pyruvate | 2.000 |
| Sodium chloride | 1.000 |
| Magnesium sulfate | 0.010 |
| Sodium deoxycholate | 0.500 |
| Neutral red | 0.030 |
| Crystal violet | 0.001 |
| Agar | 12.500 |
Final pH (at 25°C): 7.4±0.2
Note: Yersinia Selective Agar is used with cefsulodin and novobiocin for the isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica in a laboratory setting.
Preparation of Yersinia Selective Agar
To prepare Yersinia Selective Agar, follow these steps:
- Weigh out 29.02 grams of Yersinia Selective Agar powder.
- Add the powder to 500 ml of distilled water, ensuring that it is completely suspended.
- Heat the mixture to boiling to dissolve the agar medium thoroughly.
- Autoclave the medium at 15 pounds of pressure (121°C) for 15 minutes to sterilize it.
- Allow the medium to cool down to approximately 45-50°C.
- Aseptically add the reconstituted contents of 1 vial of Yersinia Selective Supplement (FD034) to the cooled medium.
- Mix the medium and supplement well to ensure proper distribution.
- Pour the prepared agar medium into sterile Petri plates.
- Allow the agar to solidify.
Now, the Yersinia Selective Agar plates are ready to be used for culturing and isolating Yersinia enterocolitica. The prepared plates can be stored at a suitable temperature until needed.
Method of Use of Yersinia Selective Agar
To use Yersinia Selective Agar for culturing and isolating Yersinia enterocolitica, follow these steps:
- Inoculate the specimen as soon as possible after receiving it in the laboratory to ensure optimal viability of the bacterium.
- If the material is in the form of a swab, roll the swab over a small area of the surface of the Yersinia Selective Agar plate. Then, using a streaking technique, spread the inoculum over the agar surface to promote the isolation of individual colonies.
- Incubate the inoculated plates aerobically at a temperature of 25°C for 24-48 hours. This temperature range provides suitable conditions for the growth of Yersinia enterocolitica.
- If a cold enrichment method is preferred, transfer the specimen into Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) or an appropriate alternative. Maintain the PBS specimen at a temperature of 4°C for up to 21 days. Periodically, subculture the PBS onto fresh Yersinia Selective Agar plates according to the laboratory’s established guidelines.
- Incubate the subcultured plates aerobically at 25°C for 24-48 hours to allow for colony development.
- Examine the plates for the presence of typical colonies of Yersinia enterocolitica. These colonies will exhibit a characteristic appearance with a dark red “bull’s-eye” center and a translucent border. It’s important to note that further biochemical and/or serological testing may be required to definitively identify Yersinia enterocolitica. Consult appropriate references and follow specific instructions for further testing procedures.
If using a pour tube of Yersinia Selective Agar, follow these additional steps:
- Melt the Yersinia Selective Agar pour tube in a boiling water bath until it liquefies. Allow it to cool to a temperature of 45-50°C.
- Add the rehydrated CN Selective Supplement to the melted agar medium. Ensure thorough mixing of the supplement with the agar.
- Dispense the agar medium into sterile Petri dishes and proceed with the instructions mentioned above for inoculation, incubation, and colony examination.
By following these steps, Yersinia Selective Agar can be effectively used for the isolation and identification of Yersinia enterocolitica from specimens, facilitating further analysis and characterization of the bacterium.
Result Interpretation on Yersinia Selective Agar
The interpretation of results on Yersinia Selective Agar can be done based on the appearance of colonies. Here is the result interpretation:
- Yersinia enterocolitica:
- Appearance: Translucent colonies with a dark pink center.
- Colony Edge: Entire or irregular.
- After 48 hours of incubation: Colonies appear dark pink with a translucent border. They may be surrounded by a zone of precipitated bile.
- Note: Yersinia enterocolitica colonies exhibit a characteristic “bull’s-eye” appearance.
- Yersinia pseudotuberculosis:
- Appearance: Growth with a dark pink center.
- After 48 hours of incubation: Colonies show a dark pink center with bile precipitate. There is no transparent zone observed around the colonies.
It’s important to note that Yersinia Selective Agar is designed to selectively inhibit the growth of non-Yersinia organisms. Therefore, the growth of non-Yersinia organisms is marked to completely inhibited on this agar.
When using Yersinia Selective Agar, the colonies of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis can be distinguished based on their colony appearance and the presence or absence of a translucent border or a transparent zone around the colonies.
Further confirmatory tests, such as biochemical and/or serological testing, may be required to definitively identify the specific Yersinia species present. Consulting appropriate references and following established laboratory guidelines are essential for accurate result interpretation and identification.
| Organisms | Growth |
| Yersinia enterocolitica | Translucent with dark pink center & bile precipitate (bulls-eye colonies) |
| Yersinia pseudotuberculosis | Growth with dark pink center & bile precipitate. No transparent zone around the colonies. |
Quality Control of Yersinia Selective Agar
The quality control of Yersinia Selective Agar involves several parameters to ensure its performance and reliability. Here is the information regarding the quality control of Yersinia Selective Agar:
- Appearance: The Yersinia Selective Agar is a light yellow to pink homogeneous free-flowing powder.
- Gelling: The agar medium should form a firm gel comparable to a 1.25% Agar gel.
- Colour and Clarity of Prepared Medium: After preparation, the medium in Petri plates should have an orange-red color and appear clear to slightly opalescent.
- Reaction: The pH of a 5.8% w/v aqueous solution of Yersinia Selective Agar at 25°C should be 7.4±0.2.
- pH Range: The acceptable pH range for the medium is 7.20-7.60.
- Cultural Response: When Yersinia Selective Supplement (FD034) is added to the medium and incubated at 22-32°C for 24-48 hours, the expected cultural response is as follows:
- Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212: Growth should be inhibited.
- Proteus mirabilis ATCC 25933: Growth should be inhibited.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853: Growth should be inhibited.
- Yersinia enterocolitica ATCC 27729: Good to luxuriant growth with colonies being translucent with a dark pink center and bile precipitate.
- Yersinia enterocolitica ATCC 23715: Good to luxuriant growth with colonies being translucent with a dark pink center and bile precipitate.
- Yersinia enterocolitica ATCC 9610: Good to luxuriant growth with colonies being translucent with a dark pink center and bile precipitate.
- Escherichia coli ATCC 25922: Growth should be inhibited.
- Escherichia coli ATCC 8739: Growth should be inhibited.
- Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus ATCC 25923: Growth should be inhibited.
- Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus ATCC 6538: Growth should be inhibited.
It is important to note that the performance of the medium is expected when used according to the directions on the label and within the expiration period while stored at the recommended temperature.
The limitations of Yersinia Selective Agar include the possibility of other bacteria, such as Serratia liquefaciens, Citrobacter freundii, and Enterobacter agglomerans, resembling Yersinia enterocolitica. Biochemical tests are necessary to differentiate these organisms.
Proper handling of specimens, adherence to safety guidelines, and following good microbiological laboratory practices are essential while working with Yersinia Selective Agar.
Overall, the quality control measures ensure the reliability and effectiveness of Yersinia Selective Agar in its intended use for the isolation and identification of Yersinia species.
Uses of Yersinia Selective Agar
Yersinia Selective Agar has several uses in microbiology, primarily focused on the selective isolation and enumeration of Yersinia enterocolitica and other Yersinia species. Here are the main applications of Yersinia Selective Agar:
- Selective Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica: Yersinia Selective Agar is recommended for the selective isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from clinical specimens. It provides the necessary selective and differential properties to suppress the growth of unwanted bacteria and facilitate the growth of Yersinia enterocolitica. This agar allows for the isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica colonies, which can then be further analyzed and identified using biochemical and serological tests.
- Enumeration of Yersinia enterocolitica: Yersinia Selective Agar can also be used for the enumeration of Yersinia enterocolitica in clinical specimens. By plating dilutions of the specimen on Yersinia Selective Agar, the number of Yersinia enterocolitica present can be estimated by counting the resulting colonies.
- Isolation of Other Yersinia Species: In addition to Yersinia enterocolitica, Yersinia Selective Agar can be utilized for the isolation of other Yersinia species, such as Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. While it is primarily recommended for Yersinia enterocolitica, the medium’s selective and differential properties can support the growth of various Yersinia species, aiding in their isolation and identification.
The use of Yersinia Selective Agar provides a specific and controlled environment for the growth and isolation of Yersinia species, enabling researchers and clinicians to detect, enumerate, and identify these pathogenic bacteria in clinical specimens and food samples. It plays a crucial role in the diagnosis, surveillance, and epidemiological studies related to Yersinia infections.
Limitations of Yersinia Selective Agar
Yersinia Selective Agar, while a valuable tool in the isolation and identification of Yersinia species, has certain limitations. These limitations include:
- Resemblance of Other Bacterial Species: Some bacterial species, such as Serratia liquefaciens, Citrobacter freundii, and Enterobacter agglomerans, may resemble Yersinia enterocolitica colonies on Yersinia Selective Agar. Additional biochemical tests are necessary to differentiate these species from Yersinia enterocolitica.
- Detection of Other Pathogens: Yersinia Selective Agar is primarily designed for the selective isolation of Yersinia species. However, for the detection of other pathogens involved in the infection, it is recommended to inoculate a less selective medium like MacConkey Agar alongside Yersinia Selective Agar. Incubation at a temperature of 35 +/- 2°C may be required for the growth of certain pathogens.
- Need for Cold Enrichment: In some cases, a “cold enrichment” procedure may be necessary to isolate Yersinia enterocolitica from stool specimens and food samples. This involves incubating the samples at a lower temperature (4°C) for an extended period to enhance the growth of Yersinia species.
- Biochemical and Serological Confirmation: While Yersinia Selective Agar provides selective growth conditions, biochemical and serological tests are still required for the complete identification and confirmation of suspicious isolates.
- Intended Use Limitation: Yersinia Selective Agar is not intended for the diagnosis of diseases or conditions in humans. It is primarily used for the isolation and enumeration of Yersinia species in clinical and food samples.
- Nutritional Variation: Some Yersinia strains may exhibit poor or no growth on Yersinia Selective Agar due to nutritional variations. In such cases, further tests and alternative media may be necessary for the confirmation of Yersinia species.
- Differentiation of Yersinia Species: Yersinia Selective Agar does not inhibit the growth of certain Yersinia species, including Yersinia frederiksenii, Y. kristensenii, Y. pseudotuberculosis, and Y. intermedia. Differentiation of colonies of these organisms from Yersinia enterocolitica requires additional characteristics and tests.
These limitations highlight the importance of additional tests and careful interpretation of results when using Yersinia Selective Agar for the identification and characterization of Yersinia species.
FAQ
What is Yersinia Selective Agar?
Yersinia Selective Agar is a specialized medium used for the selective isolation and identification of Yersinia enterocolitica and other Yersinia species.
What is the purpose of Yersinia Selective Agar?
The primary purpose of Yersinia Selective Agar is to suppress the growth of unwanted bacteria and provide selective conditions that promote the growth of Yersinia species, allowing for their isolation and identification.
How does Yersinia Selective Agar select for Yersinia species?
Yersinia Selective Agar contains components such as sodium deoxycholate and crystal violet, which inhibit the growth of gram-positive bacteria and many gram-negative bacteria, providing selectivity for Yersinia species.
What are the distinguishing characteristics of Yersinia enterocolitica colonies on Yersinia Selective Agar?
Typical colonies of Yersinia enterocolitica on Yersinia Selective Agar appear as translucent colonies with a dark pink center. They may also exhibit a “bull’s-eye” appearance surrounded by a zone of precipitated bile.
Can Yersinia Selective Agar be used to isolate species other than Yersinia enterocolitica?
Yes, Yersinia Selective Agar can be used for the isolation of other Yersinia species, such as Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, in addition to Yersinia enterocolitica.
Are there any limitations to using Yersinia Selective Agar?
Some bacterial species, such as Serratia liquefaciens, Citrobacter freundii, and Enterobacter agglomerans, may resemble Yersinia enterocolitica on Yersinia Selective Agar. Biochemical tests are necessary to differentiate these species.
Is Yersinia Selective Agar suitable for the diagnosis of diseases in humans?
No, Yersinia Selective Agar is not intended for use in the diagnosis of diseases or other conditions in humans. It is primarily used for research and laboratory purposes.
How should Yersinia Selective Agar be stored?
Yersinia Selective Agar should be stored according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Typically, it should be stored in a dry place at room temperature.
What is the shelf life of Yersinia Selective Agar?
The shelf life of Yersinia Selective Agar depends on the manufacturer and storage conditions. It is important to check the expiration date on the label before use.
Can Yersinia Selective Agar be used for environmental or food testing?
Yes, Yersinia Selective Agar can be used for the isolation and enumeration of Yersinia species from environmental samples and food samples, helping in surveillance and identification of these bacteria in those contexts.
References
- https://exodocientifica.com.br/_technical-data/M843.pdf
- https://assets.fishersci.com/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/IFU1998.pdf
- https://www.dalynn.com/dyn/ck_assets/files/tech/PY47.pdf
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/IN/en/product/sial/95760
- https://alphabiosciences.com/yersinia-selective-agar-y25-100/