Mitochondrial transporter
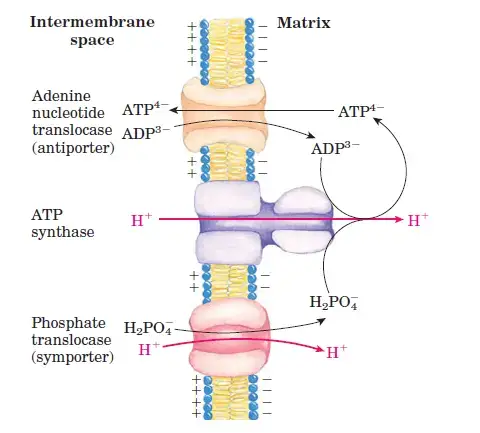
The mitochondria contain different types of transporter proteins within the intermembrane. These transporters transfers ADP, Pi, and H atom(Substrate) from Inter membrane space to matrix and ATP (Product) from matrix to inner membrane space.
There are presently three transporter protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane such as;
Adenine Nucleotide Translocase
It is an antiporter that transports ADP3- from intermembrane space to matrix and at the same time, it also transports ATP4- from the matrix to intermembrane space.
Phosphate translocase
The phosphate translocase transfers Phosphate in form of H2PO4 from the inner membrane space to the matrix. It is a symporter. It also transfers protons from inner membrane space to matrix.
ATP Synthase
This transporter only transfers protons or hydrogens from the intermembrane to the matrix, thus it is a uniporter because it transfers the substrate or molecules in only one direction.
Mitochondrial Shuttle System
The Mitochondrial Shuttles transfer NADH indirectly from intermembrane space to the matrix, thus NADH can transfer electrons to the Electron Transport Chain.
There are two types of NADH shuttle in Mitochondria such as;
Malate-aspartate shuttle
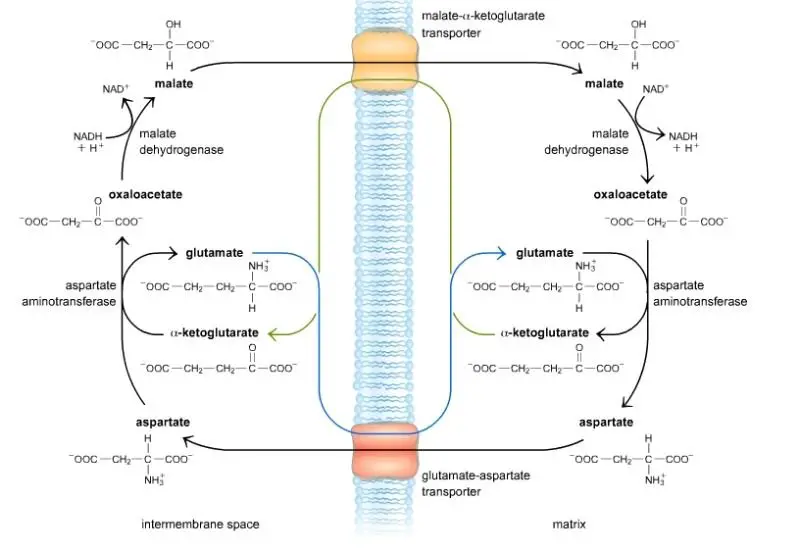
- The malate-aspartate shuttle functions in the liver, kidney, and heart mitochondria. This shuttle transports reducing equivalents from cytosolic NADH into the mitochondrial matrix.
- The Malate-aspartate shuttle contains two transporter called Malate α-ketoglutarate transporter and Glutamate-aspartate transporter.
- In cytosol or intermembrane space, the NADH transfers two reducing equivalents to oxaloacetate and forms malate with the help of an enzyme called cytosolic malate dehydrogenase.
- Malate is transferred to the matrix from the intermembrane space with the help of the Malate α-ketoglutarate transporter. In the matrix, it converted into Oxaloacetate by passing two reducing equivalents to the NAD, and as a result, it forms NADH. This reaction is catalyzed by the Mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase.
- Within in matrix, the Oxaloacetate is converted into aspartate in presence of glutamate and enzyme mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase. In this reaction, glutamate is converted into α-ketoglutarate.
- Now the α-ketoglutarate is transported into intermembrane space or cytosol from the matrix through the Malate α-ketoglutarate transporter.
- Aspartate is transported into intermembrane space or cytosol from the matrix through the Glutamate aspartate transporter.
- Inside the cytosol or intermembrane space, the aspartate is again converted into oxaloacetate with the help of cytosolic aspartate aminotransferase enzyme. In this reaction, the α-ketoglutarate is converted into Glutamate. This glutamate is now transported into the matrix with the help of a Glutamate aspartate transporter.
- The oxaloacetate again converted into malate and completes the cycle.
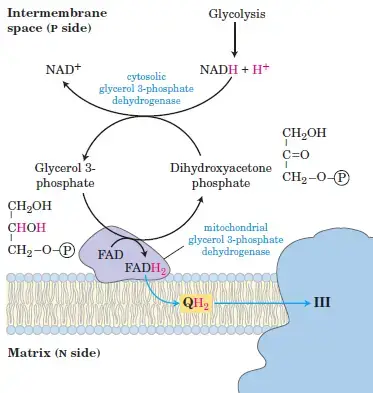
Glycerol 3 Phosphate Shuttle
This types of NADH shuttle mainly found in Skeletal muscle and the brain. In this type the reducing equivalents transferred from NADH to ubiquinone and thus into Complex III, not Complex I.