It is a rapid and simple test used for the determination of microbiological quality of milk. It is commonly employed in dairy laboratories to estimate the bacterial load present in milk samples. The test is based on the principle that actively growing bacteria utilize dissolved oxygen during their metabolic activities. Due to this oxygen consumption the oxidation–reduction potential of milk decreases which results in colour change of the indicator.
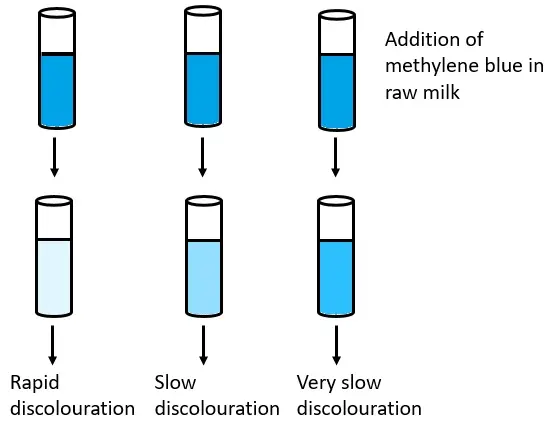
In this test a definite quantity of methylene blue dye is added to milk and the mixture is incubated at 37°C. Methylene blue acts as a redox indicator which is blue in oxidized form and becomes colourless when reduced. As bacteria multiply oxygen is depleted and the dye is reduced to leuco form. The time taken for disappearance of blue colour is referred to as reduction time and it is inversely proportional to number of bacteria present. Milk showing rapid decolourization is considered to be of poor quality whereas milk with longer reduction time indicates good microbiological quality.
Objectives of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
- To assess the microbiological quality of milk samples.
- To estimate the bacterial load present in raw and pasteurized milk.
- To determine the sanitary condition of milk at collection and processing centers.
- To carry out rapid screening of milk for acceptance or rejection.
- To grade milk samples on the basis of reduction time of methylene blue.
- To measure the metabolic activity of microorganisms present in milk.
- To indicate the spoilage potential of milk due to active bacterial growth.
- To provide a simple and cost-effective method for routine quality control.
- To support quality based payment systems in dairy industries.
- To evaluate the viability and activity of starter cultures used in dairy fermentation.
Principle of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
The principle of Methylene Blue Reduction Test is based on the utilization of dissolved oxygen in milk by microorganisms during their metabolic activity. It is the process in which actively growing bacteria consume oxygen present in milk for aerobic respiration and in this process the oxidation–reduction potential of the medium is lowered. Methylene blue is used as an oxidation–reduction indicator which remains blue in presence of sufficient oxygen but gets reduced to a colourless form known as leuco methylene blue when oxygen level decreases.
As the bacterial population increases in milk the rate of oxygen consumption also increases and reducing substances or enzymes like reductases are produced. Once the dissolved oxygen is exhausted the dye starts accepting hydrogen ions and gets reduced resulting in loss of blue colour. Thus faster the decolourization of methylene blue higher is the bacterial load present in milk. Milk containing fewer bacteria takes longer time for colour disappearance due to slow oxygen utilization whereas milk with heavy microbial contamination shows rapid reduction indicating poor bacteriological quality.
Requirements for Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
- Sterile test tubes of 10 ml or 15 ml capacity.
- Sterile rubber stoppers or screw caps to prevent entry of atmospheric oxygen.
- Sterile graduated pipettes of 1 ml and 10 ml capacity.
- Water bath maintained at 37°C for incubation.
- Test tube rack for holding tubes in water bath.
- Stopwatch or clock for recording reduction time.
- Standard methylene blue solution (approximately 0.005%).
- Methylene blue tablets for preparation of standard solution.
- Sterile distilled water for dissolving dye.
- Fresh milk sample (raw or pasteurized).
- Aseptic conditions during handling of samples.
- Dim light or dark place to avoid photo reduction of dye.
- Uniform concentration of dye for all tests.
Procedure of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
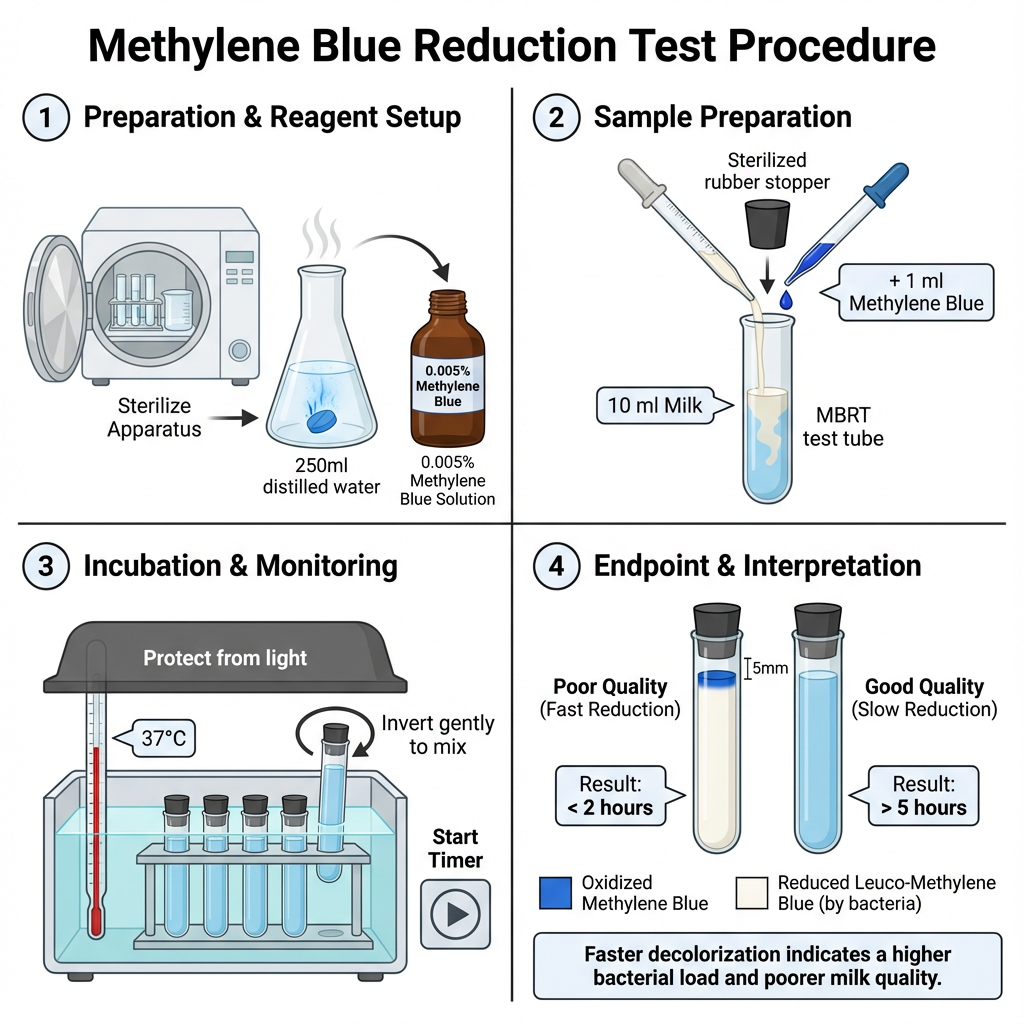
- Prepare standard methylene blue solution by dissolving one methylene blue tablet in 200 ml of sterile distilled water.
- Sterilize all test tubes rubber stoppers and pipettes before use.
- Mix the milk sample properly by inverting the container several times to ensure uniform distribution of fat and microorganisms.
- Transfer 10 ml of milk sample into a sterile test tube using a sterile pipette.
- Add 1 ml of methylene blue solution to the milk sample.
- Close the test tube with sterile rubber stopper and gently mix by inverting the tube 4–5 times.
- Place the test tubes in a water bath maintained at 37°C.
- Incubate the tubes without disturbance or invert periodically in modified method to avoid cream layer formation.
- Observe the tubes at regular intervals for disappearance of blue colour.
- Decolourization is considered complete when about four-fifth of milk column becomes colourless.
- Record the time taken for decolourization which is noted as reduction time.
Interpretation and Result of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBR test)
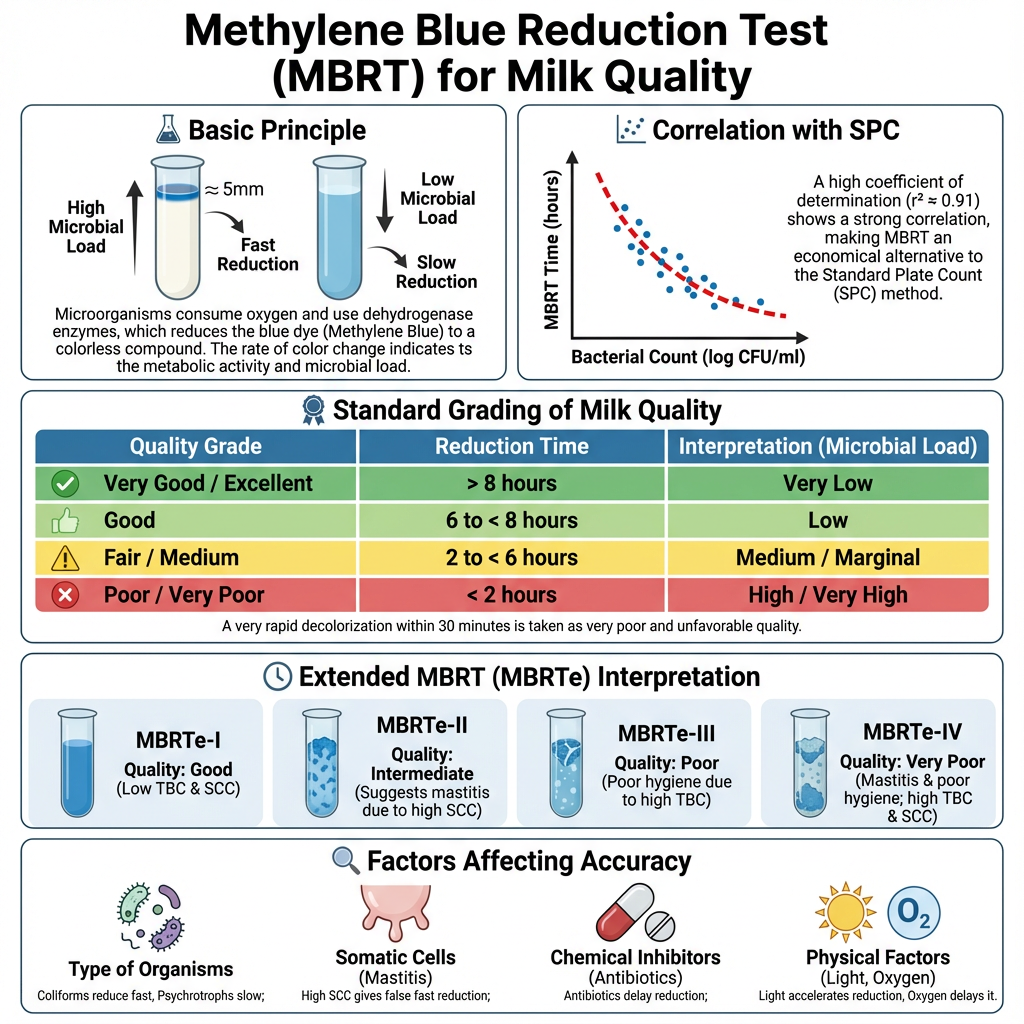
The result of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT) is expressed in terms of reduction time. It is the total time taken from the start of incubation till the disappearance of blue colour. The reduction is considered complete when about four-fifths (80%) of the milk column becomes white. Shorter reduction time indicates higher bacterial activity.
Interpretation of Result (BIS Standard)
Based on reduction time the milk sample is graded as follows–
- Very Good – No decolorization for 5 hours or more. It indicates low bacterial load (around 5 × 10⁵ bacteria per ml or less).
- Good – Blue colour disappears within 3 to 4 hours. The milk is acceptable for pasteurization and domestic use.
- Fair – Decolorization occurs between 1 to 2 hours. The milk is of marginal quality and should be processed immediately.
- Poor – Reduction occurs within 30 minutes. It shows heavy microbial contamination and milk is rejected.
High-Mark Industry Standard (Extended Scale)
Some industries follow a stricter scale based on longer reduction time–
- Excellent – No reduction for 8 hours or more.
- Good – Decolorization between 6 to 8 hours.
- Fair – Decolorization between 2 to 6 hours.
- Poor – Reduction in less than 2 hours.
General Result Expression
- Positive Result – Decolorization within 30 minutes. The milk is unsatisfactory and of poor bacteriological quality.
- Negative Result – Blue colour persists beyond 30 minutes. The milk sample is considered of good quality.
Correlation with Bacterial Load
The reduction time is inversely related to number of bacteria present. Milk containing more than 2 × 10⁷ bacteria per ml usually reduces methylene blue in less than 30 minutes. Longer reduction time indicates fewer actively respiring bacteria.
Thus the result of MBRT provides a rapid indirect assessment of microbial quality of milk.
Organisms Giving Positive MBR test Result
- Coliform bacteria such as Escherichia coli.
- Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis.
- Fecal streptococci.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Micrococci.
- Mesophilic lactic acid bacteria.
- Yeast and fungi present as contaminants.
- Somatic cells (leukocytes) present in large number in mastitic milk.
Organisms Giving Negative MBR test Result
- Psychrotrophic organisms such as Pseudomonas species.
- Thermoduric bacteria surviving pasteurization but showing low activity at 37°C.
Grading of milk in MBR test
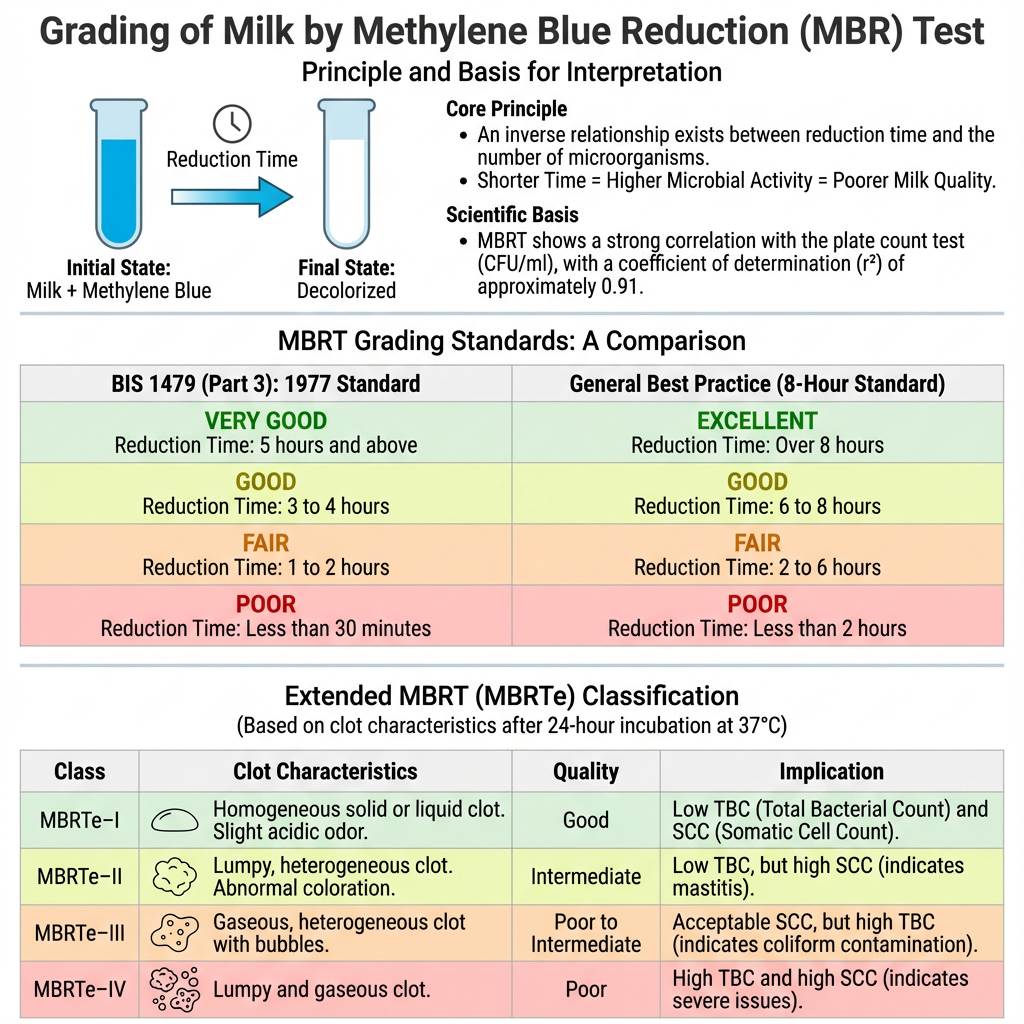
1. Principle of Grading
- The grading is based on the inverse relation between the reduction time and the microbial quality of milk.
- When the dye becomes colorless very fast, it shows high metabolic activity of microorganisms and the milk becomes poor in quality.
- The reduction time is taken as the main basis for acceptance or rejection at dairy collection points.
2. Grading Based on BIS 1479 (Part 3): 1977
- Very Good
Reduction time: 5 hours and above. - Good
Reduction time: 3 to 4 hours. - Fair
Reduction time: 1 to 2 hours. - Poor
Reduction time: less than ½ hour.
Milk decolorizing within 30 minutes is considered very poor and unfavorable.
3. General / Best Practice Grading (8-Hour Standard)
- Excellent
Reduction time: over 8 hours.
Basis: very low contamination risk. - Good (High Quality)
Reduction time: 6 to 8 hours (or 6½–7½ hours). - Fair (Medium Quality)
Reduction time: 2 to 6 hours (or 2½–6 hours).
Basis: moderate risk; common in properly collected raw milk. - Poor
Reduction time: less than 2 hours.
Basis: high microbial load and should be heated before use.
4. Basis for Interpretation
- The grading is supported by strong correlation between MBRT reduction time and microbial load counted as CFU/ml.
- A coefficient of determination (r² around 0.91) is reported, which shows MBRT can act as an economical substitute to plate count test.
5. Extended MBRT (MBRTe) Classification
This method uses 24-hour incubation at 37°C and the grading depends on clot characteristics.
- MBRTe–I
Clot: homogeneous solid or liquid; slight acidic odor.
Quality: good.
Implication: about 95% show first-quality TBC and SCC. - MBRTe–II
Clot: lumpy heterogeneous, abnormal coloration.
Quality: intermediate to good.
Implication: TBC in first-quality range but SCC exceeds limit, showing mastitis tendencies. - MBRTe–III
Clot: gaseous heterogeneous with bubbles and grooves.
Quality: poor to intermediate.
Implication: SCC acceptable but TBC high, often due to coliform contamination. - MBRTe–IV
Clot: lumpy plus gaseous characteristics.
Quality: poor.
Implication: both TBC and SCC exceed limits, indicating severe mastitis and management problems.
Factors Affecting on MBR test
1. Dissolved Oxygen Level– It is an important factor affecting MBR test. The reduction of methylene blue occurs only after the dissolved oxygen is completely utilized. Cold milk contains more dissolved oxygen than warm milk. Pouring milk from one container to another or excessive shaking increases oxygen content and hence reduction time is increased.
2. Type of Microorganisms Present– The rate of reduction depends on type of microorganisms present in milk. Coliform bacteria reduce the dye rapidly due to high metabolic activity. Lactic acid bacteria, fecal streptococci and micrococci reduce at moderate rate. Psychrotrophic and thermoduric organisms reduce dye very slowly.
3. Incubation Temperature -The metabolic activity of bacteria is temperature dependent. Increase in incubation temperature increases bacterial activity and shortens reduction time. Standard temperature of 37±1°C must be maintained for accurate result.
4. Presence of Somatic Cells– Milk from mastitic cows contains high number of leukocytes. These cells possess dehydrogenase enzymes which can reduce methylene blue independently of bacteria. This leads to faster decolorization and poor grading of good quality milk.
5. Exposure to Light– Methylene blue is photosensitive in nature. Exposure to light accelerates reduction of dye even in absence of microbial activity. Therefore the test should be carried out in dark or covered condition.
6. Concentration of Dye – The concentration of methylene blue should be uniform. Higher concentration of dye increases reduction time as more dye molecules are to be reduced. Standard concentration is usually 0.005%.
7. Presence of Inhibitory Substances– Antibiotics and chemical preservatives present in milk inhibit bacterial growth and respiration. Due to this reduction time is prolonged and milk may show false good quality.
8. Creaming Effect -Fat globules rise to surface carrying bacteria with them. Due to this uneven distribution occurs where upper layer reduces faster than lower layer. Wilson’s modification (periodic inversion of tube) is used to overcome this defect.
9. Age of Milk Sample -In old milk, natural reducing substances increase even without bacterial multiplication. This results in quicker reduction of dye and reduction time becomes shorter.
Precautions
- All glassware such as test tubes pipettes and stoppers should be properly cleaned and sterilized before use.
- Milk sample should be mixed thoroughly by gentle inversion so that fat and bacteria are evenly distributed.
- The test should be carried out away from direct light as methylene blue is light sensitive.
- Incubation temperature should be maintained at 37°C throughout the test period.
- Test tubes should be inverted at regular intervals during incubation to prevent creaming of milk.
- Standard concentration of methylene blue solution should always be used.
- Dye should be added carefully without shaking to avoid incorporation of excess oxygen.
- Decolorization should be noted only when four-fifths of the milk column becomes white.
- Presence of antibiotics or preservatives in milk should be considered as it may delay reduction.
- Fresh methylene blue solution should be used for accurate result.
- Excessive agitation of milk before the test should be avoided.
- Mouth pipetting should not be done and hands should be washed after handling reagents.
Uses of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
- It is used to assess the bacterial load and sanitary quality of raw milk.
- It is used at milk collection centers for acceptance or rejection of milk sample.
- It is used for grading of milk into very good good fair or poor based on reduction time.
- It is used by dairy cooperatives for quality based payment and incentive calculation.
- It is used to check the activity of starter cultures used in curd cheese and fermented milk products.
- It is used to determine freshness and keeping quality of milk.
- It is used to estimate metabolically active viable microorganisms in milk.
- It is used to evaluate cleanliness of milking practices and animal hygiene.
- It is used to detect improper storage or old milk supply.
- It is used as a laboratory test for teaching purpose to demonstrate effect of temperature on microbial activity.
Advantages of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
- It is a simple and economical test requiring very less chemicals and apparatus.
- It does not require complex laboratory equipment or highly trained personnel.
- It gives rapid result as compared to standard plate count method.
- It helps in quick decision making for acceptance or rejection of milk.
- It measures metabolic activity of bacteria rather than only counting colonies.
- It gives better indication of spoilage potential of milk.
- It is not affected by bacterial clumping as each cell participates in reduction.
- It uses milk itself as medium which reflects actual condition of sample.
- It is suitable as a routine screening test at milk collection centers.
- The color change is easily visible and interpretation of result is simple.
Limitations of Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)
- It is not a specific test and does not differentiate between harmful and non harmful bacteria.
- Different bacteria reduce methylene blue at different rate which affects accuracy of result.
- Psychrotrophic bacteria reduce dye very slowly and may not be detected properly.
- It is not suitable for testing pasteurized or heat treated milk.
- Presence of somatic cells in mastitic milk may reduce dye and give false poor result.
- Antibiotics and chemical preservatives interfere with bacterial activity and give false good result.
- It is not sensitive for very good quality milk having low bacterial count.
- Creaming effect causes uneven distribution of bacteria and affects reduction time.
- End point of color change is subjective and varies from person to person.
- Methylene blue is light sensitive and exposure to light alters test result.
- The test requires continuous observation and is time consuming.
FAQ on MBR test
Q1. What is the Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)?
A. The Methylene Blue Reduction Test is a simple dye reduction test used to assess the microbial quality of milk. It is based on the ability of microorganisms present in milk to reduce methylene blue dye.
Q2. What is the principle of the Methylene Blue Reduction Test?
A. The principle of MBRT is based on reduction of methylene blue dye by actively respiring microorganisms. The dye remains blue in presence of oxygen and becomes colorless when oxygen is depleted due to microbial activity.
Q3. What is the purpose of the Methylene Blue Reduction Test?
A. The purpose of MBRT is to estimate the bacterial load and general sanitary quality of raw milk. It is used as a rapid screening test in dairy industry.
Q4. How is the Methylene Blue Reduction Test performed?
A. In this test a measured quantity of methylene blue solution is added to a milk sample. The tube is mixed gently and incubated at 37°C. The time taken for disappearance of blue color is recorded.
Q5. How do you interpret the results of the MBRT test?
A. The result is interpreted based on the time required for decolorization of methylene blue. Shorter reduction time indicates poor quality milk whereas longer reduction time indicates good quality milk.
Q6. What does a shorter reduction time indicate in MBRT?
A. A shorter reduction time indicates high bacterial load and poor microbiological quality of milk.
Q7. What does a longer reduction time indicate in MBRT?
A. A longer reduction time indicates low bacterial activity and better sanitary quality of milk.
Q8. What are the different grades of milk quality based on MBRT?
A. Based on reduction time milk is graded as very good good fair or poor.
Q9. What factors can influence the Methylene Blue Reduction Test results?
A. Factors such as type of microorganisms incubation temperature dissolved oxygen creaming effect presence of somatic cells light exposure and chemical inhibitors influence the test result.
Q10. What are the limitations of the MBRT test?
A. The test is not specific does not differentiate bacterial types is affected by somatic cells antibiotics light exposure and is not suitable for pasteurized milk.
Q11. Why is methylene blue used in the MBRT test?
A. Methylene blue is used because it is an oxidation reduction indicator which changes color based on availability of oxygen.
Q12. What is the significance of oxygen depletion in the MBRT test?
A. Oxygen depletion indicates active microbial respiration. The faster the oxygen is used up the faster the dye is reduced.
Q13. What types of microorganisms are detected by the MBRT test?
A. The test mainly detects actively respiring bacteria such as coliforms lactic acid bacteria and other aerobic microorganisms.
Q14. Is the MBRT test suitable for raw milk or pasteurized milk?
A. The MBRT test is suitable for raw milk and is not suitable for pasteurized or heat treated milk.
Q15. How does bacterial metabolism relate to methylene blue reduction?
A. During metabolism bacteria consume oxygen and release reducing substances. This reduction process converts methylene blue from blue to colorless state.
- Agriculture Institute. (2023, December 29). Using dye reduction methods to measure bacterial activity.
- Ahlawat, S. (n.d.). MBRT | PDF | Milk | Food and drink. Scribd.
- Alhussien, M. N., & Dang, A. K. (2018). Milk somatic cells, factors influencing their release, future prospects, and practical utility in dairy animals: An overview. Veterinary World, 11(5), 562–577.
- Amrita Virtual Lab. (2013). Methylene blue reductase test (Theory). Microbiology Virtual Lab I.
- Anwer, S. S., Zaki, S. M., Rasul, S. A., Hassan, R. J., Ahmad, I. J., & Qader, A. J. (2018). Detection of kids milk quality using methylene blue reduction test. International Journal of Environment, Agriculture and Biotechnology, 3(4).
- AOAC International. (2023). Scientific standards & methods.
- Barkworth, H., Irwin, J. O., & Mattick, A. T. R. (1941). The plate count and methylene-blue reduction test applied to milk. Journal of Dairy Research, 12(3), 265–314.
- Bhullar, G. K., Sharma, N., Sharma, G., & Chaudhary, M. (2023). A review paper based upon the methylene blue reduction test for the analysis of quality of milk and various microorganisms present in the different sources of milk. TIJER – International Journal for Engineering Research, 10(6).
- Bindulekha, D. S. (2019). Determination of microbiological quality of milk from different breeds of cattle using methylene blue reduction test. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research, 6(5).
- Borneman, D. L., & Ingham, S. (2014). Correlation between standard plate count and somatic cell count milk quality results for Wisconsin dairy producers. Journal of Dairy Science, 97(5), 2646–2652.
- Comprehensive Technical Analysis. (n.d.). Comprehensive technical analysis of the methylene blue reduction test in dairy quality microbiology [Technical Report].
- Dairy Knowledge Portal. (n.d.). Methylene blue dye reduction test for assessing the raw milk quality.
- Dhanya, K. C. (n.d.). Microbiological analysis of milk part II [SlideShare].
- Dr. Oracle. (2025, August 31). What is the mechanism of action of methylene blue?
- Fadillah, A., van den Borne, B. H. P., Poetri, O. N., Hogeveen, H., Slijper, T., Pisestyani, H., & Schukken, Y. H. (2023). Evaluation of factors associated with bulk milk somatic cell count and total plate count in Indonesian smallholder dairy farms. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 10.
- Fox Valley Quality Control Lab. (n.d.). Standard plate count or plate loop count (SPC or PLC) is the measure of the total number of aerobic bacteria in the milk.
- Gupta, C. (2016, February 24). Determination of methylene blue reduction time for pasteurized milk (MBRT Test). AgriMoon.
- Jain, N. (n.d.). Dye reduction test.pptx [SlideShare].
- Kansas State University. (n.d.). Blue’s the clue [Food Safety Module 3].
- Matuszewski, T., & Supińska, J. (1940). Studies on the methylene-blue reduction test II. Comparison between the old and the modified methods. Journal of Dairy Research, 11(1), 43–50.
- Mirek, E., & O’Donnell, S. (2007). A comparison of Pyronin Y-methyl green stain and methylene blue stain for somatic cell count in sheep milk [Honors Project]. University of Rhode Island.
- MIT ESP. (n.d.). The methylene blue story.
- Polzin, L. (n.d.). Policies and regulations governing milk and dairy testing: A Wisconsin overview. Extension University of Wisconsin-Madison.
- Purdue Extension. (n.d.). Section 7. Standards for Grade “A” milk and/or milk products.
- Rovai, M., & Costa, L. B. C. (n.d.). Summer matters – Factors affecting somatic cell count on milk. Ohio State University Extension.
- Roy, L., Banerjee, A., Pan, N., Ghosh, R., Mondal, S., Das, M., Hasan, M. N., Singh, S., Chattopadhyay, A., Bhattacharyya, K., Mondal, S., & Pal, S. K. (2024). A spectroscopy-based proof-of-concept (POC) for developing loading of pathogen analyzer (LOPA) for dairy products. Heliyon, 10(19).
- Safe Milk Labs. (2022). Milk quality.
- Schubert, W. F., & Nagle, P. M. (1951). The value of the resazurin test for the determination of milk quality. Division of Dairying, Dairy Research Branch.
- Shirodkar, S. T. (n.d.). Grading of milk by dye reduction test: MBRT and Resazurin test [Module MIG 102].
- Sui Generis Brewing. (2022, October 12). The methylene blue test.
- The Science Company. (n.d.). Methylene blue milk test.
- Unacademy. (2023). Quality analysis of milk- SPC, MBRT.
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Methylene blue.
- Ying, C., Yang, C.-B., & Hsu, J.-T. (2004). Relationship of somatic cell count, physical, chemical and enzymatic properties to the bacterial standard plate count in different breeds of dairy goats. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 17(4), 554–559.
wow you writing well. keep going
thank you very much
Best and helpfull Post,Hi Sir,I am your regular website viewer and user,just as your other articles attracts us, your articles help us a lot.Thanks for publishing this article.
Thank you very much