A hot air oven is a laboratory device that sterilizes materials using dry heat. The main parts of a hot air oven are the outer cabinet, insulation, inner chamber, heating elements, thermostat, fan, and control panel. It works on the principle of heat conduction and convection.
What is Hot Air Oven?
- Hot Air Oven can define as a laboratory device used for dry heat sterilization by using hot air which circulated by fan inside the chamber.
- It mostly used for sterilizing glasswares, metal instruments, powders, oils, etc. which cannot be sterilized by moist heat (like autoclave).
- The instrument work by principle that dry heat cause oxidation of cell components and denaturation of proteins, leading to death of microorganisms.
- It generally operated at 160°C–180°C for 1–2 hours, depends upon material type and load inside the chamber.
- Inside of oven made by stainless steel and outside body are usually mild steel coated with enamel paint or powder coated for protection.
- The air inside is heated electrically and circulated uniformly by fan so temperature distribution can maintained properly (although sometimes uneven).
- Thermostat or digital temperature controller are provided for regulating the temperature and timing during sterilization process.
- Sterilization by hot air oven is preferred for sharp instruments and dry glass items because moisture may corrode or damage them.
- The door of oven must kept tightly closed during operation, otherwise heat may escape and sterilization efficiency reduced.
- After completion, the materials should not removed immediately because sudden cooling may cause cracking of glasswares or temperature shock.
- Thus, Hot Air Oven is very important apparatus in microbiology, pharmaceutical, and chemical laboratories, where sterilization by dry heat is required, etc.

Definition of Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven is an electrical apparatus that utilizes dry heat to sterilize heat-resistant materials, effectively eliminating microbial life, including bacterial spores, from the items placed within its chamber.
Working Principle of Hot air oven/Principle of Hot Air Oven
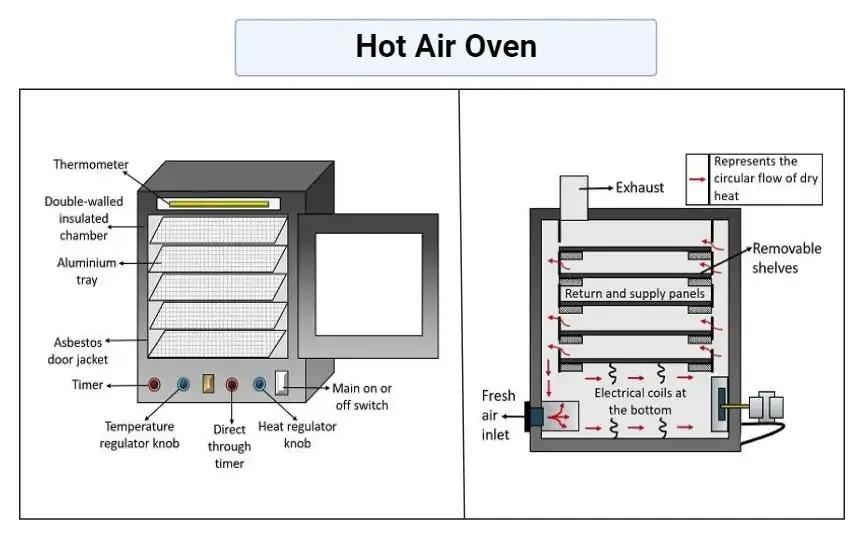
- The Hot Air Oven works on the principle of dry heat sterilization, where the sterilization occurs by oxidation of cell components and denaturation of proteins inside microorganisms.
- The hot air is circulated continuously inside the chamber so that uniform temperature can maintained throughout, and it help to kill all microbial life forms by prolonged exposure.
- Heat transfer mainly occurs by conduction, means first the outer surface of material gets heated then heat slowly pass to inner parts.
- As dry heat has low penetrating power, higher temperature and longer time are required as compared with moist heat method like autoclaving.
- The microbial death happens when their essential cell proteins, enzymes and other biomolecules are destroyed / oxidized due to exposure of high temperature (160°C–180°C).
- The destruction of microorganism is caused because moisture absence allow oxidation reactions to prevail instead of coagulation (which occur in moist heat).
- In this process, sterilization efficiency depends upon proper air circulation, accurate temperature control, and exposure duration.
- Thus, by oxidation and dehydration effect, all viable cells, spores and bacteria are killed, making materials completely sterilized.
- It’s mainly suitable for materials that can withstand dry heat and not affected by moisture or steam, e.g., glassware, oils, metal tools, etc.
- Therefore, the principle of hot air oven based on oxidative killing mechanism under controlled temperature for fixed time, ensuring total destruction of microbial contamination.
Parts of Hot air oven
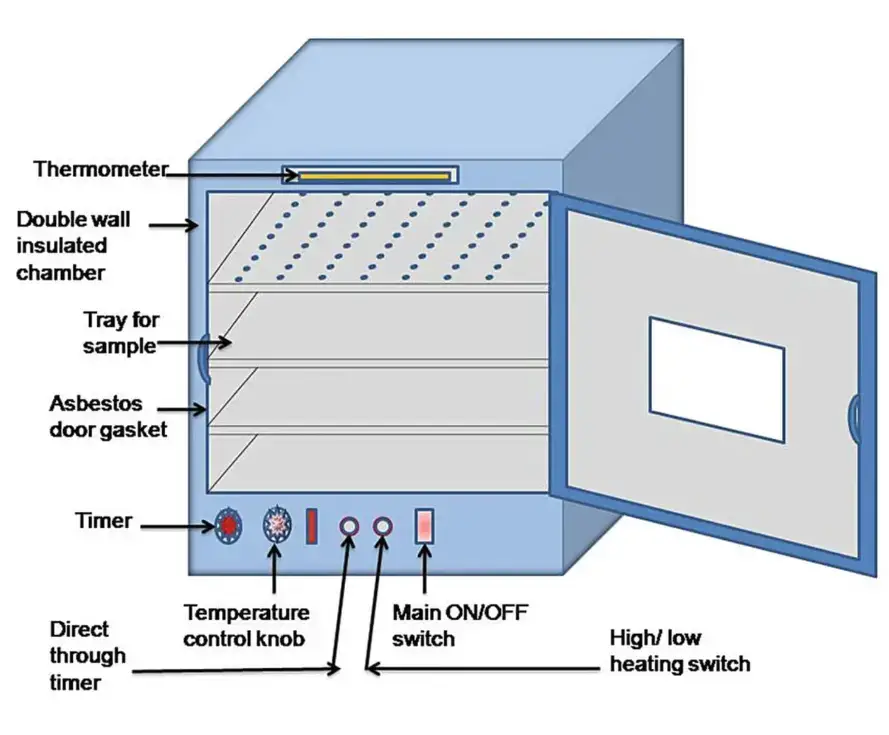
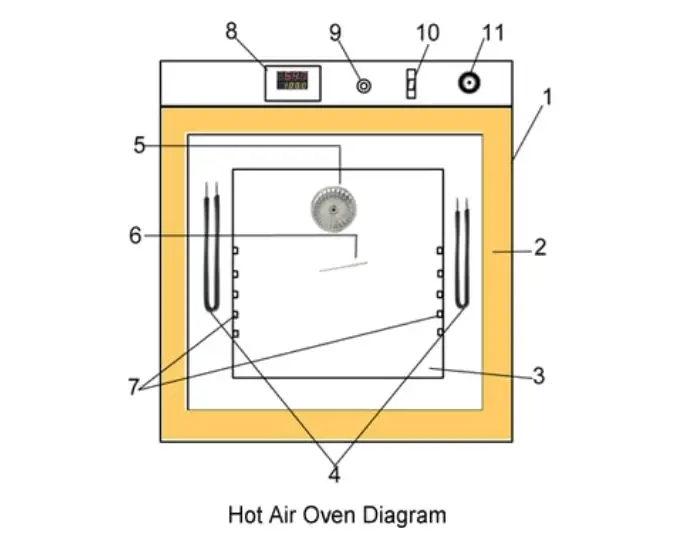
Each part work together to maintain constant dry heat environment (160°C–180°C) needed for sterilization of glasswares, metallic tools, oils, and powders etc.
1. Outer Body – It made of mild steel or stainless steel, coated with enamel or powder paint for protection from corrosion / heat damages. It gives strong and sturdy support to whole instrument.
2. Inner Chamber– The inside part constructed with stainless steel, it provide smooth surface which is easy for cleaning and resist rust formation. Shelves are fitted inside for placing materials to be sterilized.
3. Insulation Layer – Between inner and outer wall, a layer of glass wool / asbestos is kept for thermal insulation. It prevents the loss of heat by conduction and maintain uniform temperature inside chamber.
4. Heating Element – The heating coils or electric elements are located at bottom and sometimes around the chamber walls. They convert electrical energy into heat energy for raising temperature in oven.
5. Thermostat / Temperature Controller – It used to regulate and maintain the desired temperature automatically during sterilization period. When temperature reaches set point, the power supply is cut off and restored again when it falls down.
6. Fan / Air Circulation Unit – A small fan is installed to circulate hot air uniformly throughout the chamber, which ensures even distribution of heat and effective sterilization.
7. Thermometer or Digital Display – It helps to monitor the actual temperature inside the oven during operation (either manually or digitally).
8. Door with Locking System – The door fitted tightly with asbestos gasket to prevent the leakage of hot air. Proper locking arrangement provided to ensure safety and air-tight closure.
9. Control Panel – On the front side, there is panel having switches, indicators, and regulators for controlling power, temperature and timing.
10. Timer – It used for fixing sterilization duration, after completion it automatically turns off heating to avoid overheating or energy waste.
11. Shelves / Trays – Made of stainless steel and removable, used for holding glasswares, instruments, etc., in multiple layers inside chamber for efficient space use.
12. Ventilation Port – Small holes or vents are provided for release of moisture / hot air during operation and to maintain proper air flow.
13. Indicator Lamps – Red and green indicator lamps are used, one for showing power ON and another for heating ON condition, sometimes both blink alternately.
14. Fuse & Safety Cut – Fuse system is provided to prevail overload or short circuit, ensuring user and instrument protection.
Types of Hot Air Oven
Various types of Hot Air Ovens are used based on capacity, heating mode, and application requirement, each designed to achieve efficient sterilization under dry heat condition.
1. Static Air Hot Air Oven –
Also known as a Gravity Convection Oven or Natural Convection type, these ovens employ natural air movements for the distribution of hot air which are accompanied by the formation of cold air layers, thus the temperature of the air inside the chamber is not very uniform. The heating rate is slow as hot air goes up and cold air comes down, therefore sterilization takes longer time (usually 2 hrs or more).
2. Forced Air Hot Air Oven –
In this case, a fan or blower is installed inside the chamber for the circulation of the hot air all over the chamber, thus the temperature is the same everywhere. Because of this, heating is done in less time and sterilization is also achieved quickly. This is the mostly used type in laboratories and industries for better efficiency.
3. Mechanical Convection Oven –
Besides that, it operates very much alike with the forcibly ventilated oven, though it has more advanced features such as a motorized fan system and digital controls. The device also comes with automatic timers and a thermostat to minimize temperature changes and allow very precise control of the operation.
4. Mini / Portable Hot Air Oven –
Miniaturized oven designed specifically for labs, schools, and field works. It uses less power and can achieve a maximum temperature of 180°C but only for a very small load. Sterilization of a few small glasswares, metal parts like cutting tools, etc. is the most common purpose of this device.
5. Digital Hot Air Oven –
This kind of device is equipped with a digital temperature controller and a microprocessor system for very accurate temperature and time monitoring. It enables the user to save sterilization parameters on the pre-set and the display always shows the real temperature.
6. Industrial Hot Air Oven –
Such a system is used for performing large-scale operations in the likes of pharmaceutical or material testing industries. It is of a very high capacity (up to several cubic meters), powered by multiple fans and heavy-duty heaters for heat uniform distribution.
7. Hybrid / Programmable Hot Air Oven –
These are the latest generation ovens that are equipped with both dry and moist heat sterilization options along with programmable cycles for different sterilization needs. They save energy but are quite pricey and are mainly utilized in research or specialized labs.
Hot air oven procedure
- First of all, it is necessary to clean and dry all the glassware or materials that are going to be sterilized, since the presence of moisture may lower the disinfection efficiency.
- The materials are being wrapped with paper or aluminum foil or placed inside a container (depending on the type of the material).
- After that, they are laid out in the inner chamber of the oven in such a way that there is enough space between them for free air circulation.
- The door is being shut tightly so as to prevent the escape of heat, and the main switch of the oven is being turned ON.
- The required temperature (normally 160°C–180°C) and time (1–2 hrs) are being set by a thermostat or a digital controller depending on the type of the load.
- After the heating is started, the hot air is being circulated by a fan, thereby uniform temperature is maintained through the chamber.
- During sterilization, door should not be opened frequently, otherwise heat will be lost and the sterilization process will be extended.
- The indicator lamps point out whether the heating element is ON or OFF, and the user can check the temperature by means of a thermometer or a display screen.
- Once the allocated time is finished, the power supply is turned OFF automatically (in some models manually).
- The oven is allowed to cool gradually for about 30–45 min, sudden cooling must be avoided as it can cause the glasswares to crack.
- After the cooling, the sterilized materials are being taken out with the help of gloves or tongs so as not to be burned or contaminated.
- The oven is then completely turned OFF and the main plug is removed from the socket for safety purposes.
- After being used it needs to be regularly cleaned and checked for proper functioning of the thermostat, fan, and heating coils.
- So, if the correct steps are followed, the method of dry heat sterilization can be successfully utilized for the instruments, glassware, and other heat-resistant materials, which are usually found in the laboratory.
Calibration of Hot air Oven
- Calibration of Hot Air Oven is essentially a process to ascertain the uniformity and accuracy of the temperature displayed by the indicator across the chamber.
- So, it is a very significant step in instrument operation that sterilization should take place at the right temperature and within limits specified (usually ±2°C tolerance is accepted).
- Before starting with calibration, oven must be cleaned well and it should also be allowed to run empty for 30 min in order to get a stable condition.
- Various locations like corners, center, and near the door of the chamber are chosen for placing the temperature sensors / thermocouples in order to detect the temperature distribution.
- A standard thermometer or a digital temperature probe is used as a reference to compare the oven display readings.
- The temperature of the oven is set to certain values, such as 160°C, 170°C, and 180°C, and the readings at each set point after the stabilization time of 20–30 min are recorded.
- The temperature at all points is documented, and the mean temperature along with minimum and maximum values are determined.
- If the difference between the set and the measured temperatures is beyond the acceptable range, it is necessary to adjust or recalibrate the thermostat or the controller.
- Calibration report must have all the relevant details like instrument name, model no., location of sensors, date, the environment, and so on.
- After the work is done, the oven is left to cool down slowly, and the sensors are taken out with care so that they are not damaged.
- The results are put side by side with earlier records, and if any deviation is found, the corrective action should be taken without delay.
- Calibration should be done from time to time (usually every 6 months) or after a major repair, to be sure that the device is working reliably.
- Therefore, a suitable calibration procedure is a guarantee that the Hot Air Oven keeps proper and even temperature, thus, is capable of providing the required sterilization.
Sterilization Control of Hot air Oven
- Physical Control – It done by observing temperature and time maintained inside the oven (like 160°C for 2 hr or 170°C for 1 hr etc.).
- Thermometer Control – A thermometer usually placed inside the oven to monitor the accurate temperature, sometimes the reading slightly differ from dial one.
- Biological Control – Used to check if complete sterilization achieved or not by using spores of Bacillus subtilis (earlier called B. atrophaeus).
- Chemical Indicator Control – Chemical indicators strips / papers used which change color when specific temp. reached (for ex. color change from red to green).
- Mechanical Control – The thermostat and timer control heating cycle and maintain uniform heat circulation, sometimes fan also used for even distribution.
- Validation Control – The process validated by comparing actual sterilization result with expected result, it’s confirm efficiency of oven.
- Performance Control – Checked time to time by placing test materials at different positions, since uneven heating may occur in some parts.
Advantages of Hot Air Oven
- Sterilization by dry heat is considered more safe and reliable for metal / glass materials.
- It used for materials which can’t be sterilized by moisture like powders, oils and glasswares etc.
- The method is simple, and equipment need low maintenance or supervision.
- Corrosion or rusting of metallic instruments are prevented because moisture not used in process.
- After sterilization, articles can be stored directly without any cooling or drying period needed.
- The hot air oven can be operated easily, temperature usually maintained constant by thermostat.
- It’s economical because electricity consumption is lesser compared to autoclave (steam sterilizer).
- No pressure involved, so chance of accident or explosion is very less, which make it sturdy and hardy.
- Uniform heating achieved when fan is present, thus better sterilization of instruments occur.
- Long life of apparatus observed, since they are built of strong metal and less corrosion occur.
- The method is ideal for sterilization of laboratory items like Petri dish, flasks, pipettes, syringes, etc.
- Thus, Hot Air Oven considered efficient and durable apparatus for dry heat sterilization in laboratory practice.
Limitations of Hot air oven
- The hot air oven cannot used for materials which get damage by high temperature like plastics, rubber or surgical dressings etc.
- Sterilization by dry heat require more time, usually 2 hrs or more at 160°C, so the process is slower than moist heat.
- The penetration of heat is poor, because dry air is bad conductor of heat, so sterilization sometimes uneven.
- The energy consumption is more when large load placed, as heating elements must maintain high temp continuously.
- Instruments made of sharp edges (like surgical blades or needles) may get dull or brittle after repeated exposure.
- It’s not suitable for culture media, vaccines or biological fluids since proteins get coagulated by dry heat.
- The sterilization efficiency depend upon proper air circulation, so if fan not working then result become unreliable.
- Articles packed in paper or cotton wraps may char or burn when temperature slightly exceed required limit.
- Cooling of the oven after sterilization takes long time, so articles can’t be handled immediately.
- Thus, although Hot Air Oven is effective, its usage restricted only to heat resistant materials like glassware and metal apparatus etc.
Uses and Applications of hot air oven
- The Hot Air Oven mainly used for sterilization of glassware / metal instruments in laboratory.
- It applied for sterilizing Petri dishes, flasks, pipettes, test tubes and syringes etc.
- Dry powders like starch, zinc oxide and sulphur also sterilized safely by this method.
- It’s used to sterilize oils and greases which can’t be treated by moist heat.
- The hot air oven used widely in microbiology, pharmacy, and chemical laboratories for routine sterilization purpose.
- Sometimes it applied in hospitals for sterilization of metallic surgical instruments.
- It also used to dry or remove moisture from glass and metal equipment before further use.
- Materials which get corrode by steam (like carbon steel tools) are sterilized in hot air oven instead.
- It’s also useful for pre-heating or baking of certain lab materials at controlled temp. (like 160–180°C).
- Thus, the Hot Air Oven has wide applications wherever dry heat sterilization required or moisture must be avoided.
Precautions
- The Hot Air Oven must be preheated to required temperature before loading the materials inside.
- Articles should be arranged properly, leaving enough spaces for free air circulation inside the chamber.
- The oven door should not opened frequently during sterilization period, as heat loss may occur.
- Temperature and time must be maintained accurately (like 160°C for 2 hr or 170°C for 1 hr).
- Materials which get melted or burnt by high heat like plastic, rubber, or paper should not be placed inside.
- Thermometer / thermostat should be checked regularly to ensure proper functioning.
- Overloading of oven must be avoided, because it may cause uneven heating of articles.
- After sterilization, door should be kept closed until temperature falls below 60°C to prevent breakage of glasswares.
- Power supply must be disconnected before taking out sterilized materials for safety reason.
- The inner surface of oven should be cleaned regularly, since dust or residues may affect heat distribution.
- Control instruments and fan (if present) need periodic checking to maintain uniform heating.
Hot Air Oven Working Principle Video
Quiz
What is the primary mechanism of sterilization in a hot air oven?
a) Moist heat
b) Ultraviolet radiation
c) Dry heat
d) Chemical disinfection
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] c) Dry heat [/expand]
Which of the following is NOT suitable for sterilization in a hot air oven?
a) Glassware
b) Metal instruments
c) Rubber items
d) Zinc powder
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] c) Rubber items [/expand]
What is the recommended temperature range for sterilization in a hot air oven?
a) 100-120°C
b) 121-130°C
c) 160-180°C
d) 200-220°C
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] c) 160-180°C [/expand]
How does a hot air oven primarily kill microorganisms?
a) By denaturing proteins
b) By disrupting cell membranes
c) By oxidizing cell components
d) By inducing DNA mutations
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] a) By denaturing proteins [/expand]
Which of the following is a key advantage of using a hot air oven over an autoclave?
a) Faster sterilization
b) Sterilization of liquids
c) Non-corrosiveness for metals
d) Killing of all types of microorganisms
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] c) Non-corrosiveness for metals [/expand]
How often should a hot air oven be calibrated to ensure accurate temperature settings?
a) Once a week
b) Once a month
c) Once every six months
d) Once a year
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] d) Once a year [/expand]
Which biological indicator is commonly used for quality control testing of a hot air oven?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Clostridium tetani spores
c) Bacillus subtilis
d) Staphylococcus aureus
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] b) Clostridium tetani spores [/expand]
What is the primary disadvantage of dry heat sterilization compared to moist heat sterilization?
a) Higher temperature requirement
b) Longer exposure time
c) Less penetration power
d) All of the above
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] d) All of the above [/expand]
In a hot air oven, what ensures proper airflow inside the oven?
a) Keeping the door slightly open
b) Placing the oven near a window
c) Ensuring airflow around the blower motor is not restricted
d) Using a fan inside the oven
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] c) Ensuring airflow around the blower motor is not restricted [/expand]
Which of the following cannot be sterilized in a hot air oven due to its low melting point?
a) Surgical steel instruments
b) Glass pipettes
c) Plastic Petri dishes
d) Zinc powder
[expand title=”Show answer” swaptitle=”Hide answer”] c) Plastic Petri dishes [/expand]
FAQ
What is hot air oven?
A hot air oven is a laboratory instrument that uses dry heat to sterilize laboratory equipment and other materials.
What temperature of hot air oven used for sterilization?
The commonly-used temperatures and time that hot air ovens need to sterilize materials is 170 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, 160 degrees Celsius for 60 minutes, and 150 degrees Celsius for 150 minutes.
What is the principle of hot air oven?
Hot air ovens use extremely high temperatures over several hours to destroy microorganisms and bacterial spores. The ovens use conduction to sterilize items by heating the outside surfaces of the item, which then absorbs the heat and moves it towards the center of the item.
hot air oven act on which principle?
Sterilization by conduction of dry heat. Heat is absorbed by the material from outer layer towards center until finally the entire item reaches the temperature of sterilization.
What is the use of hot air oven?
Hot air sterilization is one method of effectively killing microbes of all kinds, especially bacteria, viruses and molds on heat-resistant materials. Contamination control during the incubation of cell cultures in a CO₂ incubator is of the greatest importance.
What is the temperature of hot air oven?
The standard settings for a hot air oven are: 1.5 to 2 hours at 160 °C (320 °F) 6 to 12 minutes at 190 °C (374 °F)
Which one cannot be sterilized by hot air oven?
Examples of items that aren’t sterilized in a hot air oven are surgical dressings, rubber items, or plastic material.
hot air oven is which type of sterilization?
A hot air oven is a type of dry heat sterilization.
What items can go into a hot air oven?
Items that are sterilized in a hot air oven include:
Glassware (like petri dishes, flasks, pipettes, and test tubes)
Powders (like starch, zinc oxide, and sulfadiazine)
Materials that contain oils
Metal equipment (like scalpels, scissors, and blades)
Who invented hot air oven?
Hot air ovens are electrical devices which use dry heat to sterilize. They were originally developed by Louis Pasteur. Generally, they use a thermostat to control the temperature.
What is pv and sv in hot air oven?
The oven begin to heat automatically with ‘PV’ showing present temperature in the chamber and ‘SV’ showing the target temperature the oven will reach to.
Which instrument is used for validation of hot air oven?
For the calibration of hot air oven use a standard thermometer ranging up to 300º C. 5.2 Start the calibration procedure after 1 hour of staring the oven. Set the oven at desired temperature. 5.4 Put the standard thermometer for 30 minutes on the upper shelf of the oven and close the door of the oven.
what is the difference between autoclave and hot air oven?
Autoclaving refers to a process of instrument sterilization that uses time, temperature and pressure to kill all forms of microbial life, whereas dry heat sterilization is basically sterilizing using an oven that uses time and heat to kill all forms of microbial life, including microbial spores and viruses.
how to check efficiency of hot air oven?
Due to the excessive temperatures used in dry heat, Bacillus atrophaeus spores are used to monitor the efficiency of the sterilization process.
What is the Temperature Range of Hot air oven?
A laboratory hot air oven has a normal temperature range of ambient+10°C to 150°C, but we can additionally reach 200°C and 250°C.
What are the uses of hot air oven in histopathology?
A hot air oven is a type of laboratory equipment used in histopathology to dry and fix biological samples, such as tissue samples, prior to staining and examination under a microscope. The samples are placed in the oven and exposed to high temperatures, which removes any water or other solvents and helps to preserve the samples for further analysis. The temperature and duration of heating can vary depending on the type of sample and the specific staining technique being used.
- Ananthanarayan, R., & Paniker, C. (1980). Textbook of microbiology (1st ed.). Orient Longman.
Manandhar, S., & Sharma, S. (2017). Practical Approach to Microbiology (3rd ed., pp. 8-9). National Book Centre. - Alkadhim, Saif Aldeen Saad, Hot Air Oven for Sterilization: Definition & Working Principle (December 14, 2018). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3340325 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3340325
- Types of Ovens, ProSciTech Pty Ltd, 2014-06-05, Available at https://laboratoryresource.com/?navaction=getitem&id=204
- Use of Hot air oven in laboratories, prestogroup, available at https://www.prestogroup.com/blog/use-of-hot-air-oven-in-laboratories/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hot_air_oven
- https://www.isotechpl.com/blog/post/use-hot-air-oven
- https://www.slideshare.net/TayyabTariq8/hot-air-oven-instrument