Glucose, a key sugar molecule, plays a vital role in the human body as the primary carbohydrate found in the bloodstream. Its importance lies in its function as the main source of energy for various body tissues, notably the brain. When glucose is metabolized, it undergoes a sequence of chemical processes that result in the production of energy essential for bodily functions.
The monitoring of blood glucose levels is critical in the healthcare field, particularly in diagnosing and managing conditions related to carbohydrate metabolism. Diseases such as diabetes are directly linked to the levels of glucose in the blood. An accurate measurement of these levels assists healthcare professionals in determining whether a patient is experiencing hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), both of which have significant implications for health and require appropriate management strategies. Understanding glucose and its impact on the body is fundamental in comprehending broader concepts in human physiology and health care.
Different Methods for Estimation Of Blood Glucose
The estimation of blood glucose is a crucial aspect of medical diagnostics and is achieved through various methods, each based on distinct properties of glucose. These methods can be broadly categorized into several types:
- Reduction Methods: These methods involve the reduction of glucose by different agents. The Ferric reduction methods, such as the Hagedorn-Jensen and Hoffman’s methods, use ferric ions. In Cupric reduction methods, including the Somogyi-Nelsen, Neocuproine, Shaffer-Hartmann, Folin-Wu, and Benedict’s methods, cupric ions are used for the reduction process.
- Aromatic Amine Condensation Methods: This category includes the O-toluidine method, which involves the condensation of glucose with an aromatic amine.
- Enzymatic Methods: These methods are based on the reaction of glucose with specific enzymes. The Glucose-oxidase Peroxidase (GOD POD) method, also known as the Trinder method, uses glucose oxidase and peroxidase enzymes. The Hexokinase method involves the enzyme hexokinase, while the Glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) method utilizes glucose dehydrogenase. Additionally, there are Kinetic and Polarographic methods that rely on the enzymatic reaction kinetics and electrochemical properties, respectively.
- Electrochemical Methods: This modern and commonly used method includes devices like glucometers, which measure glucose levels through electrochemical reactions on test strips.
Each of these methods has its own merits and limitations. The choice of method depends on various factors including accuracy, convenience, cost, and the specific requirements of the medical condition being managed or diagnosed. Understanding these methods provides insight into the complexity and precision involved in monitoring and managing blood glucose levels.
What is GOD-POD Method for Glucose Estimation?
- The GOD-POD method, standing for Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase method, is a widely used enzymatic technique for estimating glucose levels. This method is favored in modern clinical settings due to its specificity, ease of use, and high accuracy.
- In the GOD-POD method, the enzyme glucose oxidase catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide. Subsequently, the hydrogen peroxide reacts with a chromogen in the presence of the enzyme peroxidase to produce a colored compound. The intensity of the color produced is directly proportional to the concentration of glucose in the sample.
- This method’s accuracy and specificity for glucose make it a reliable choice for routine blood glucose monitoring. Its ease of use has also enabled its widespread adoption in various healthcare settings and even for personal use in the form of home glucose testing kits. Understanding the GOD-POD method is essential for those looking to grasp the principles behind modern glucose estimation techniques.
Principle of GOD-POD Method
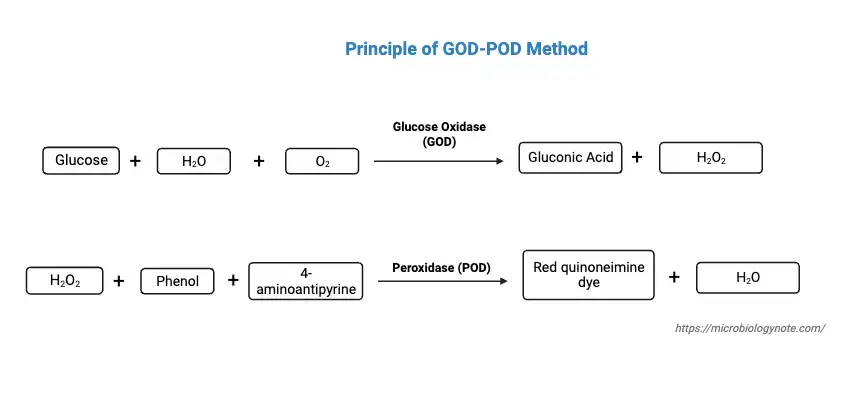
The principle of the Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase (GOD-POD) method for glucose estimation is grounded in a biochemical reaction involving the oxidation of glucose. This method operates on the fundamental reaction where glucose present in a specimen reacts with atmospheric oxygen under the catalytic action of the enzyme glucose oxidase (GOD). This reaction results in the formation of gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Following this, the hydrogen peroxide thus formed engages in a subsequent reaction. In the presence of the enzyme peroxidase (POD), it couples oxidatively with 4-aminoantipyrine and phenol. This chemical reaction leads to the creation of a red-colored quinoneimine dye. The measurement of this dye is conducted colorimetrically at a specific wavelength of 540nm. Crucially, the intensity or depth of the color produced in this reaction is directly proportional to the glucose concentration in the specimen.
This method’s reliance on a colorimetric analysis allows for a precise quantification of glucose levels, making it a valuable tool in clinical diagnostics. The GOD-POD method’s principle illustrates the intricate interplay of enzymatic reactions and chemical analysis in modern biochemical methodologies.
Requirements
To effectively carry out the GOD-POD method for glucose estimation, certain specific requirements need to be met in terms of specimen, reagents, and instruments.
Specimen Requirements:
- The specimen typically used is serum or plasma that is free from hemolysis, as hemolysis can interfere with the accuracy of the test.
- Sodium fluoride is the preferred anticoagulant for collecting plasma. Its use is crucial because it inhibits glycolysis, thus preventing the breakdown of glucose in the blood sample, which could lead to inaccurately low glucose readings.
Reagent Requirements:
- A glucose standard, typically at a concentration of 100 mg/dl, is required for calibration and comparison purposes.
- The GOD-POD reagent is a critical component. This enzyme reagent mixture contains glucose oxidase (GOD), peroxidase (POD), 4-aminoantipyrine, phenol, and a phosphate buffer with an approximate pH of 7.0. Additionally, the mixture includes some stabilizers and activators to maintain reagent stability and enhance reaction efficiency.
Instrumentation Requirements:
- Test tubes are needed for the preparation and mixing of samples and reagents.
- Pipettes, along with disposable tips and a rack, are essential for accurate measurement and transfer of liquids.
- A water bath is required to maintain the reaction mixture at a constant temperature, which is crucial for the consistency and accuracy of the reaction.
- A colorimeter is used to measure the intensity of the colored product formed. This instrument allows for the quantification of glucose concentration based on the color intensity.
Procedure
- Preparation of Test Tubes:
- Begin by labeling three clean, dry test tubes as Blank (B), Standard (S), and Test (T). This labeling is crucial for accurate identification and comparison during the testing process.
- Pipetting into Test Tubes:
- Add 1 ml of GOD-POD Reagent to each of the three test tubes.
- Into the Blank test tube (B), add 10 µl of Distilled water.
- Into the Standard test tube (S), add 10 µl of Glucose standard solution.
- Into the Test test tube (T), add 10 µl of the sample that is being tested for glucose.
- Mixing and Incubation:
- After adding the respective solutions, mix the contents of each test tube well.
- Incubate the test tubes either at 37°C for 10 minutes or at room temperature, approximately 25°C, for 30 minutes. This incubation step is essential for the reaction to occur.
- Measurement of Absorbance:
- Following incubation, measure the absorbance of the solutions in the Standard (S) and Test (T) tubes at a wavelength of 540nm using a green filter. This measurement is to be made against the Blank (B) as a reference.
- It is important to perform this measurement within 60 minutes of incubation to ensure accuracy.
Calculation for GOD-POD Method
In laboratory practices, especially when measuring blood glucose levels, the concentration of glucose in a specimen can be determined through the use of a mathematical calculation. This calculation involves comparing the absorbance of light by the test sample to that of a known standard.
The formula to calculate the concentration of glucose in the specimen is as follows:
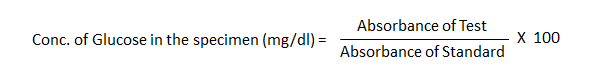
Here’s a breakdown of the calculation:
- Absorbance of Test: This is the measure of how much light the test sample absorbs at a particular wavelength. In glucose testing, this would be the absorbance measured at 540nm, which corresponds to the red-colored quinoneimine dye formed during the GOD-POD reaction.
- Absorbance of Standard: This is the absorbance value obtained from a glucose solution of known concentration. It serves as a reference point for interpreting the test results.
- Multiplying by 100: Since the standard glucose solution is typically 100 mg/dl, multiplying by 100 adjusts the ratio to the concentration of the test specimen.
To obtain the glucose concentration in the specimen, you would measure the absorbance of both the test sample and the standard under identical conditions using a spectrophotometer or a similar device. Then, apply the absorbance values to the formula to calculate the glucose concentration.
This calculated concentration provides a quantitative measure of glucose in the specimen, which is essential for diagnostic and monitoring purposes in various medical conditions, such as diabetes. It’s crucial for healthcare professionals and laboratory technicians to understand and apply this calculation accurately to ensure reliable patient care.
References
- Shaker G, Swift CJ. Peroxidase-Coupled Glucose Method. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK594277/
- Ambade VN, Sharma YV, Somani BL. METHODS FOR ESTIMATION OF BLOOD GLUCOSE : A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION. Med J Armed Forces India. 1998 Apr;54(2):131-133. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(17)30502-6. Epub 2017 Jun 26. PMID: 28775446; PMCID: PMC5531325.
- https://www.zmchdahod.org/pdf/college/07_ESTIMATION_OF_GLUCOSE_BY_GOD-POD-18-12-2018.pdf
- https://gmcsurat.edu.in/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=biochemistry:method_of_glucose_analysis_2018.pdf