What is Prokaryotic Cell?
- Prokaryotic cells represent unicellular organisms characterised by the absence of a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, as delineated by traditional frameworks of cell biology.
- The designation “prokaryote” is derived from Greek terminology, specifically the words for before (“pro”) and kernel or nucleus (“karyon”). This nomenclature reflects the characteristic of these organisms, which possess genetic material that is not contained within a true nucleus.
- In prokaryotic cells, the genetic material is predominantly organised as a singular circular DNA molecule situated within a region referred to as the nucleoid. Additionally, a significant number of these cells harbour supplementary small circular DNA entities, termed plasmids, which may provide advantages in terms of environmental adaptability.
- The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells is characterised by the presence of ribosomes, which facilitate protein synthesis. However, it is notable that these cells do not possess membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, or Golgi apparatus.
- Prokaryotic cells feature a plasma membrane made up of phospholipids, which plays a crucial role in regulating the exchange of substances. Additionally, many of these cells possess a cell wall, frequently composed of peptidoglycan in bacteria, which offers structural support and protection.
- Prokaryotic surface structures encompass pili or fimbriae, which facilitate attachment and genetic exchange, flagella that provide motility in various species, and occasionally a capsule that contributes to protection against environmental stressors or host immune responses.
- Prokaryotic cells typically exhibit a smaller size range, often measuring between 1 and 10 μm, compared to eukaryotic cells. This size advantage contributes to a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, which is beneficial for efficient nutrient absorption and growth across various environmental conditions.
- Prokaryotes are represented by the domains Bacteria and Archaea, which demonstrate significant metabolic and ecological diversity. These groups inhabit a wide range of environments on Earth, from human microbiomes to extreme conditions such as hydrothermal vents.
- Prokaryotes exhibit asexual reproduction through the process of binary fission and participate in horizontal gene transfer mechanisms, including transformation, transduction, and conjugation. These processes significantly contribute to their rapid adaptation and genetic diversity.
- Prokaryotic cells play a crucial role in biogeochemical cycles, such as nitrogen fixation and carbon cycling. They can function as symbionts or pathogens within multicellular hosts and are instrumental in driving ecosystems through primary production across various contexts.
- Édouard Chatton introduced the terms “prokaryote” and “eukaryote” in the 1920s, identifying fundamental cellular differences, albeit without comprehensive conceptual elaboration.
- In the early 1960s, Roger Yates Stanier and C. B. van Niel contributed significantly to the classification, highlighting the lack of internal membranes, the process of nuclear division through fission, and the characteristics of the cell wall as essential distinguishing features.
- Carl Woese’s research in 1977, utilising 16S rRNA sequencing, demonstrated that prokaryotes are composed of two fundamentally distinct domains: Bacteria and Archaea. This finding challenged the prevailing view of prokaryotes as a single monophyletic group and significantly altered the landscape of taxonomy.
- The distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes highlights significant tiers of cellular organisation. However, contemporary phylogenetic studies emphasise the relationships among different domains, rather than suggesting a linear evolution from prokaryotic to eukaryotic forms.
- Investigating prokaryotic cell structure and evolution yields valuable insights into essential biological processes, the emergence of cellular complexity, and potential applications in fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and environmental science.
- Potential areas for further investigation encompass an in-depth analysis of prokaryotic cell ultrastructure, such as microcompartments, the exploration of regulatory mechanisms, comparative genomic studies of Bacteria and Archaea, as well as their contributions to global ecosystems and implications for human health.
What is Eukaryotic Cell?
- Eukaryotic cells are characterised by the presence of a membrane-bound nucleus that contains linear chromosomes, which sets them apart from prokaryotic cells that do not possess a nucleus.
- The cells in question are characterised by the presence of various membrane-bound organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and, in the case of photosynthetic lineages, chloroplasts. Each of these organelles plays a specialised role that is crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating metabolic processes.
- The term eukaryote originates from the Greek words “eu” meaning true and “karyon” meaning nucleus. It was first introduced by Édouard Chatton in 1925 to differentiate these cells from prokaryotes. The concept gained prominence in the 1960s through the work of Roger Stanleyner and C.B. van Niel.
- Eukaryotic cells possess a dynamic cytoskeleton, which is comprised of actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. This structure plays a crucial role in determining cell shape, enabling intracellular transport, and facilitating essential processes such as mitosis and motility.
- The nucleus contains genetic material that is organised into chromatin structures. Nuclear pores play a crucial role in regulating the transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Additionally, the processes of mitosis and meiosis are essential for the precise segregation of chromosomes during cell division and sexual reproduction.
- Mitochondria, found in nearly all eukaryotic organisms or their derivatives, are responsible for ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation. They also play crucial roles in various signalling pathways, apoptosis, and metabolic integration, which underscores their evolutionary origin linked to bacterial endosymbiosis.
- In photosynthetic eukaryotes, chloroplasts are responsible for the process of photosynthesis, wherein light energy is transformed into chemical energy. The origin of chloroplasts can be traced back to cyanobacterial endosymbionts, which serves as a significant example of serial endosymbiotic events that have occurred throughout eukaryotic evolution.
- The endoplasmic reticulum, comprising both rough and smooth variants, is responsible for the synthesis of proteins and lipids. The Golgi apparatus plays a critical role in modifying and sorting macromolecules for subsequent transport. Additionally, lysosomes or vacuoles are involved in the degradation of macromolecules. This compartmentalisation within the cell enhances both efficiency and regulatory mechanisms.
- The plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells is characterised by the presence of sterols, such as cholesterol in animal cells, which play a crucial role in regulating fluidity. Additionally, it houses receptor proteins that facilitate signalling processes and transporters that are essential for nutrient uptake and waste export. These components collectively contribute to the intricate interactions between the cell and its environment.
- Eukaryotic cells frequently participate in intricate cell–cell communication through mechanisms such as extracellular vesicles and receptor-mediated signalling pathways, including kinase cascades and G-protein coupled receptors. These processes facilitate multicellularity and the specialisation of tissues in various organisms, including animals, plants, and fungi.
- Reproduction encompasses mitotic cell division, which is essential for growth and asexual propagation. Additionally, in numerous lineages, meiosis plays a critical role in sexual reproduction, facilitating the generation of genetic diversity through the processes of recombination and the segregation of homologous chromosomes.
- Eukaryotic cells exhibit a significant range in both size and complexity. Their dimensions can span from a few micrometres to several centimetres in multicellular organisms. Furthermore, they encompass a diverse array of forms, ranging from unicellular protists to specialised cells that contribute to the formation of organs and tissues in various kingdoms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
- The origin of eukaryotes can be elucidated through the concept of symbiogenesis, wherein an archaeal host assimilated bacterial endosymbionts that subsequently evolved into mitochondria. In certain lineages, further events facilitated the acquisition of plastids, signifying a significant evolutionary transition that occurred approximately 1.6 to 2.7 billion years ago.
- Eukaryotic cells serve essential functions within ecosystems, acting as primary producers such as algae and plants, as well as decomposers represented by fungi. In multicellular organisms, they function as fundamental structural and functional units. Furthermore, their significance extends to biotechnology and medicine, particularly in elucidating disease mechanisms, and they are frequently utilised as model systems in scientific research.
- The comparison between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells reveals a greater complexity in the genome of eukaryotes, characterised by multiple linear chromosomes, the presence of introns, and various regulatory elements. Additionally, eukaryotic cells exhibit extensive intracellular compartmentalisation and intricate regulatory networks. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that eukaryotes also preserve certain features typical of prokaryotes, including conserved metabolic pathways and ribosomes resembling those found in bacteria, particularly within organelles.
- The investigation of eukaryotic cell biology significantly enhances our comprehension of various domains, including developmental processes, disease mechanisms such as cancer and neurodegeneration, evolutionary biology, and applications in synthetic biology. Contemporary research methodologies incorporate genomics, proteomics, imaging techniques, and computational modelling to clarify intricate cellular processes.
- Additional areas for investigation encompass the characteristics of the last eukaryotic common ancestor (LECA), the diversity of organelle functions among various lineages, the processes involved in intracellular trafficking, the modulation of gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms, and the evolutionary origins of multicellularity across distinct kingdoms.
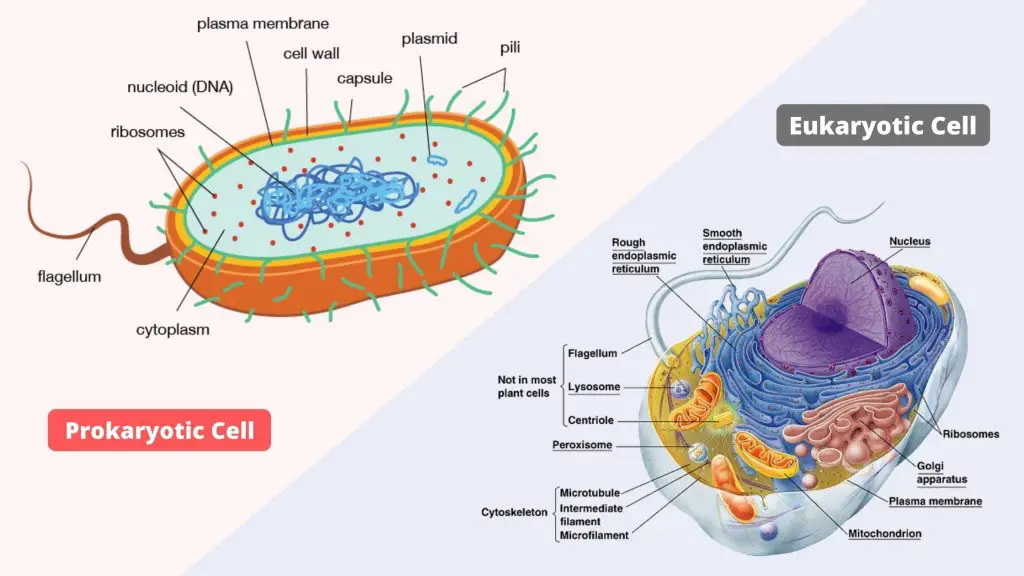
Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
| Feature | Prokaryotic | Eukaryotic |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent; genetic material located in a nucleoid region. | Present; genetic material enclosed within a nuclear envelope. |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Generally absent (e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus). | Present (e.g., mitochondria, chloroplasts in photosynthetic cells, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles). |
| DNA structure | Typically a single, circular chromosome located in the nucleoid. | Multiple, linear chromosomes located in the nucleus. |
| Ribosomes | 70S type (composed of 30S and 50S subunits). | 80S type in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum (composed of 40S and 60S subunits); 70S type in mitochondria and chloroplasts. |
| Cell size | Generally smaller, typically 0.1-5 micrometers (µm). | Generally larger, typically 10-100 micrometers (µm). |
| Cell wall | Usually present, often containing peptidoglycan (in bacteria). | Present in plants (cellulose) and fungi (chitin); absent in animal cells. |
| Reproduction | Primarily asexual reproduction via binary fission. | Asexual reproduction via mitosis; sexual reproduction via meiosis and fertilization. |
| Genetic exchange | Horizontal gene transfer (conjugation, transduction, transformation). | Sexual reproduction (meiosis and fertilization) leading to genetic recombination. |
| Cytoskeleton | Simple or rudimentary (e.g., FtsZ, MreB, CreS proteins). | Complex and extensive (e.g., microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments). |
| Chromosomes | Single, circular chromosome; plasmids often present. | Multiple, linear chromosomes; plasmids rare (except in some fungi like yeast). |
| Transcription and translation | Coupled; occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm. | Separated; transcription occurs in the nucleus, translation in the cytoplasm. |
| Cell division | Binary fission. | Mitosis (for growth and asexual reproduction) and meiosis (for sexual reproduction). |
| Motility | Simple flagella composed of flagellin, rotate. | Complex flagella and cilia composed of tubulin, wave or beat. |
| Plasma membrane | Lacks sterols (except Mycoplasma). | Contains sterols (e.g., cholesterol) to maintain fluidity. |
| Respiration | Occurs in the cytoplasm and on the plasma membrane. | Occurs primarily in mitochondria. |
| Photosynthesis | Occurs in the cytoplasm and on internal membrane systems (e.g., thylakoids in cyanobacteria). | Occurs in chloroplasts. |
| Endomembrane system | Absent. | Present (includes endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, nuclear envelope). |
| Cell type | Primarily unicellular organisms. | Unicellular and multicellular organisms. |
| RNA processing | Absent or minimal. | Extensive (e.g., splicing of introns, capping, polyadenylation). |
| Gene structure | Genes often organized into operons; introns are rare. | Genes typically not in operons; introns are common in protein-coding genes. |
| Histones | Absent; DNA associated with histone-like proteins. | Present; DNA wrapped around histone proteins to form chromatin. |
| Plasmids | Often present; small, circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules. | Rarely present (e.g., in some yeasts); generally not a common feature. |
| Glycocalyx | Often present as a capsule or slime layer. | Present in some forms (e.g., cell wall in plants/fungi, extracellular matrix in animals). |
| Pili/Fimbriae | Often present for attachment or genetic exchange (conjugation). | Absent. |

Reference
- https://www.livescience.com/65922-prokaryotic-vs-eukaryotic-cells.html
- https://www.technologynetworks.com/cell-science/articles/prokaryotes-vs-eukaryotes-what-are-the-key-differences-336095
- https://biodifferences.com/difference-between-prokaryotic-cells-and-eukaryotic-cells.html?
- https://www.diffen.com/difference/Eukaryotic_Cell_vs_Prokaryotic_Cell