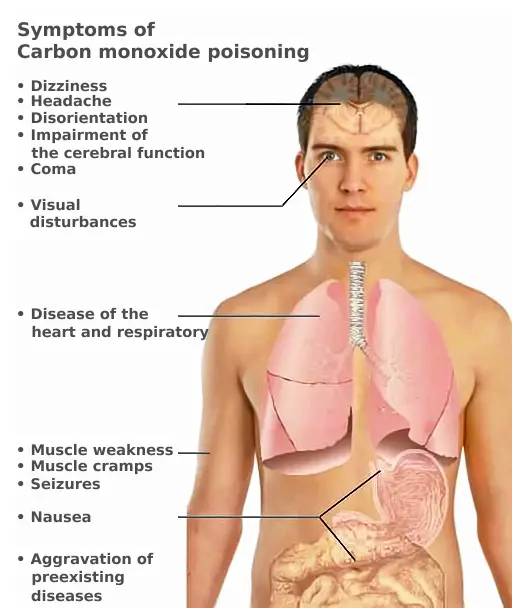
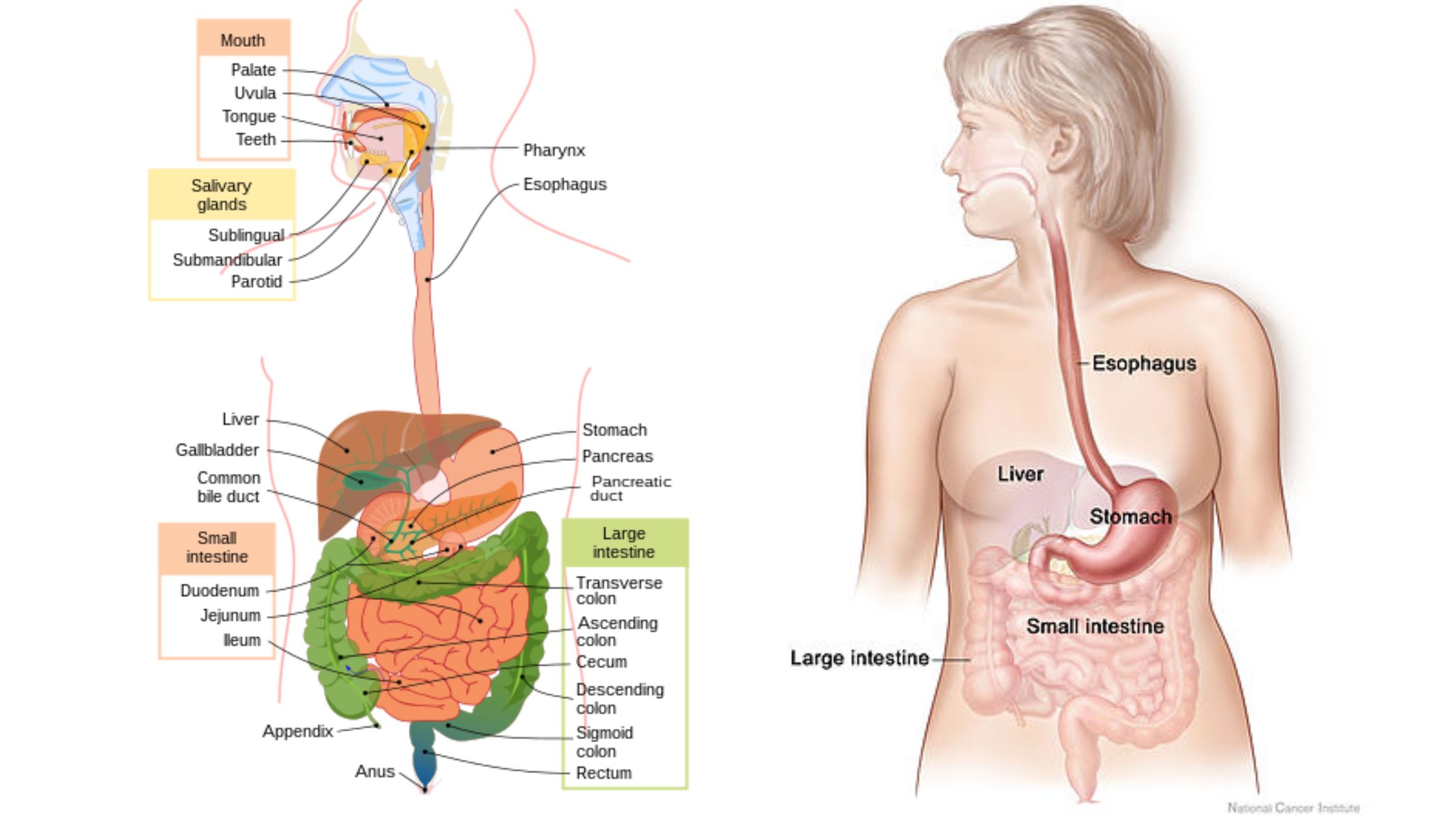
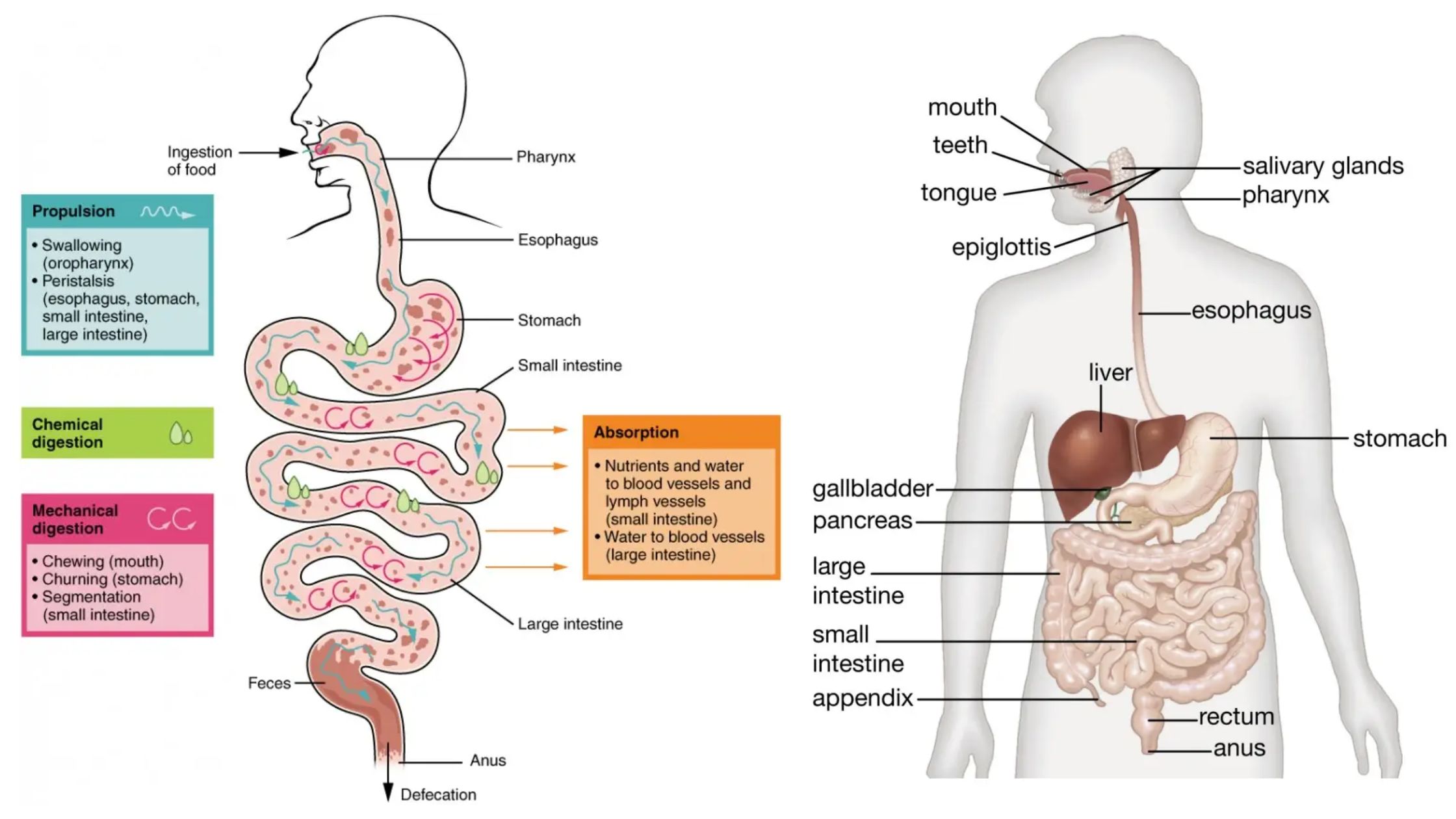
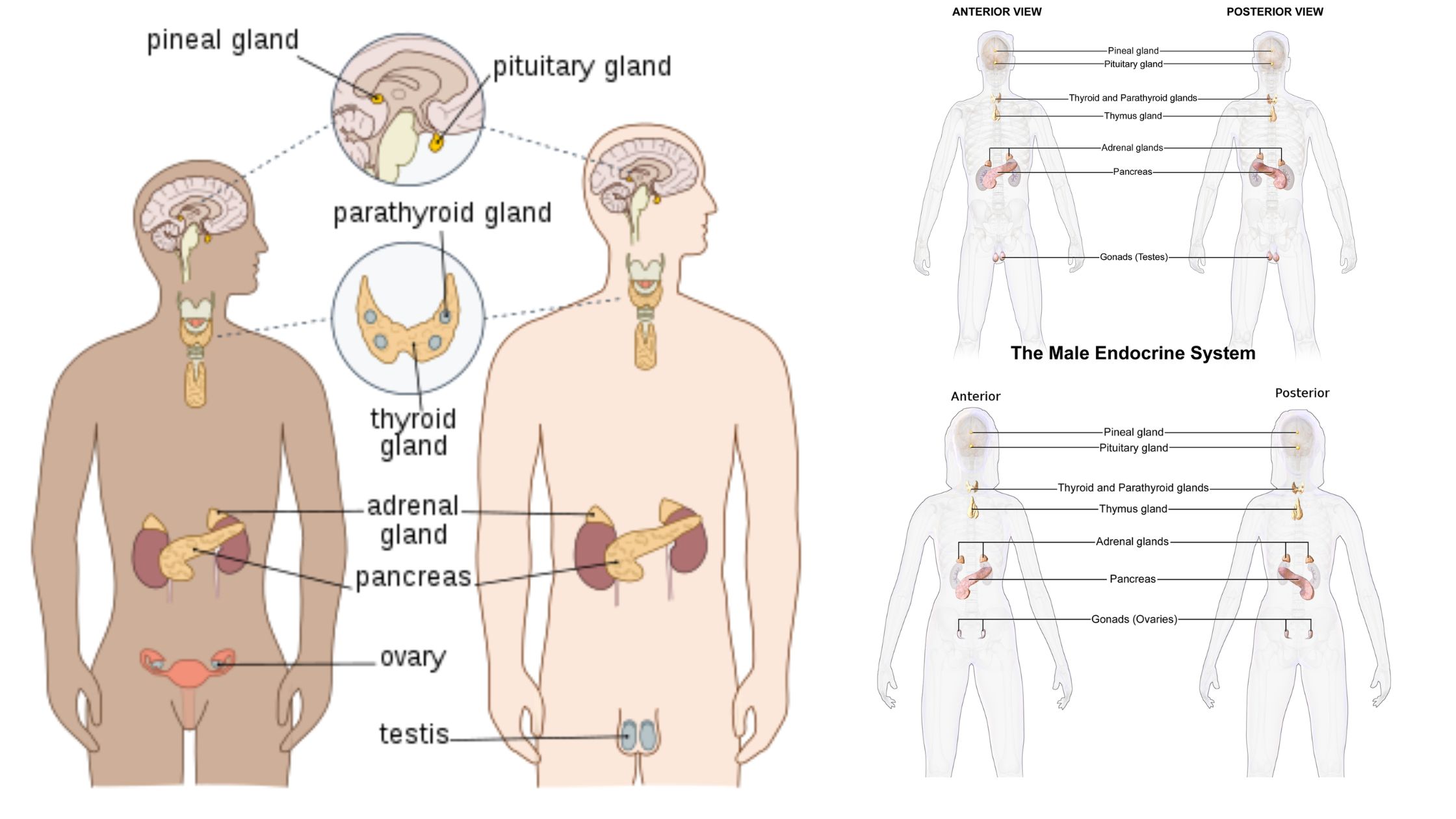
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning – Pathophysiology, Toxicokinetics, Diagnosis, Prevention, Symptoms
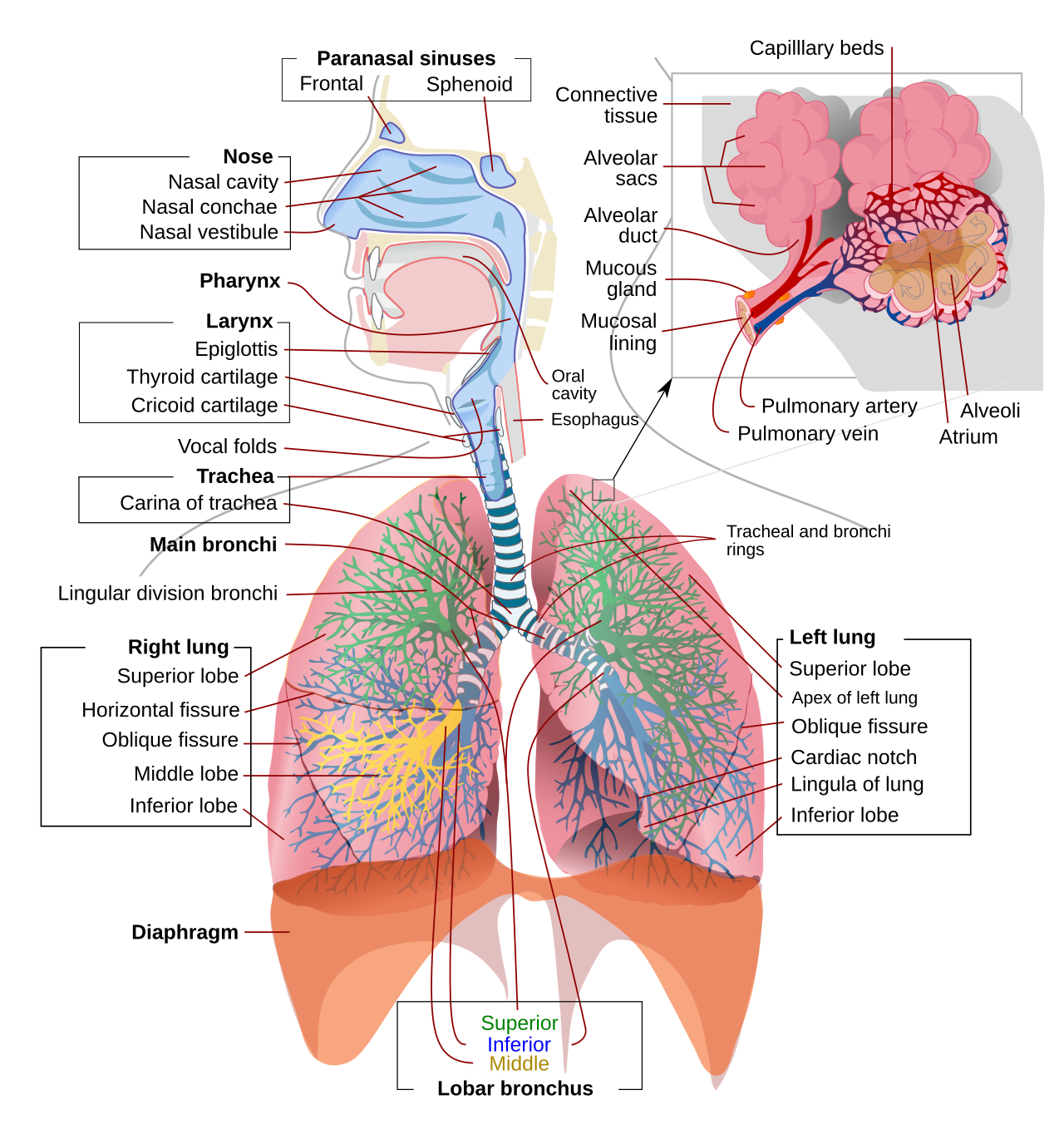
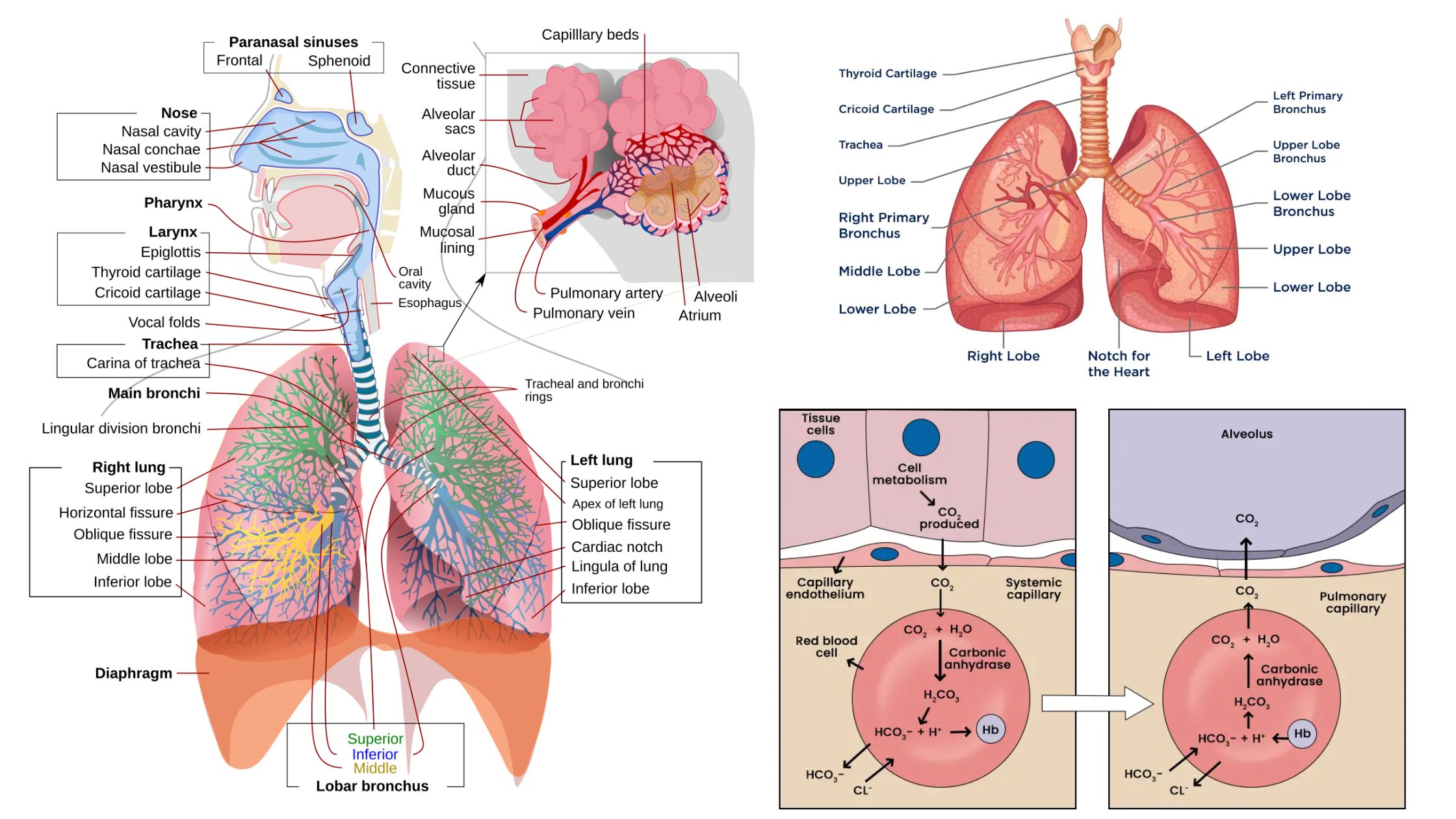
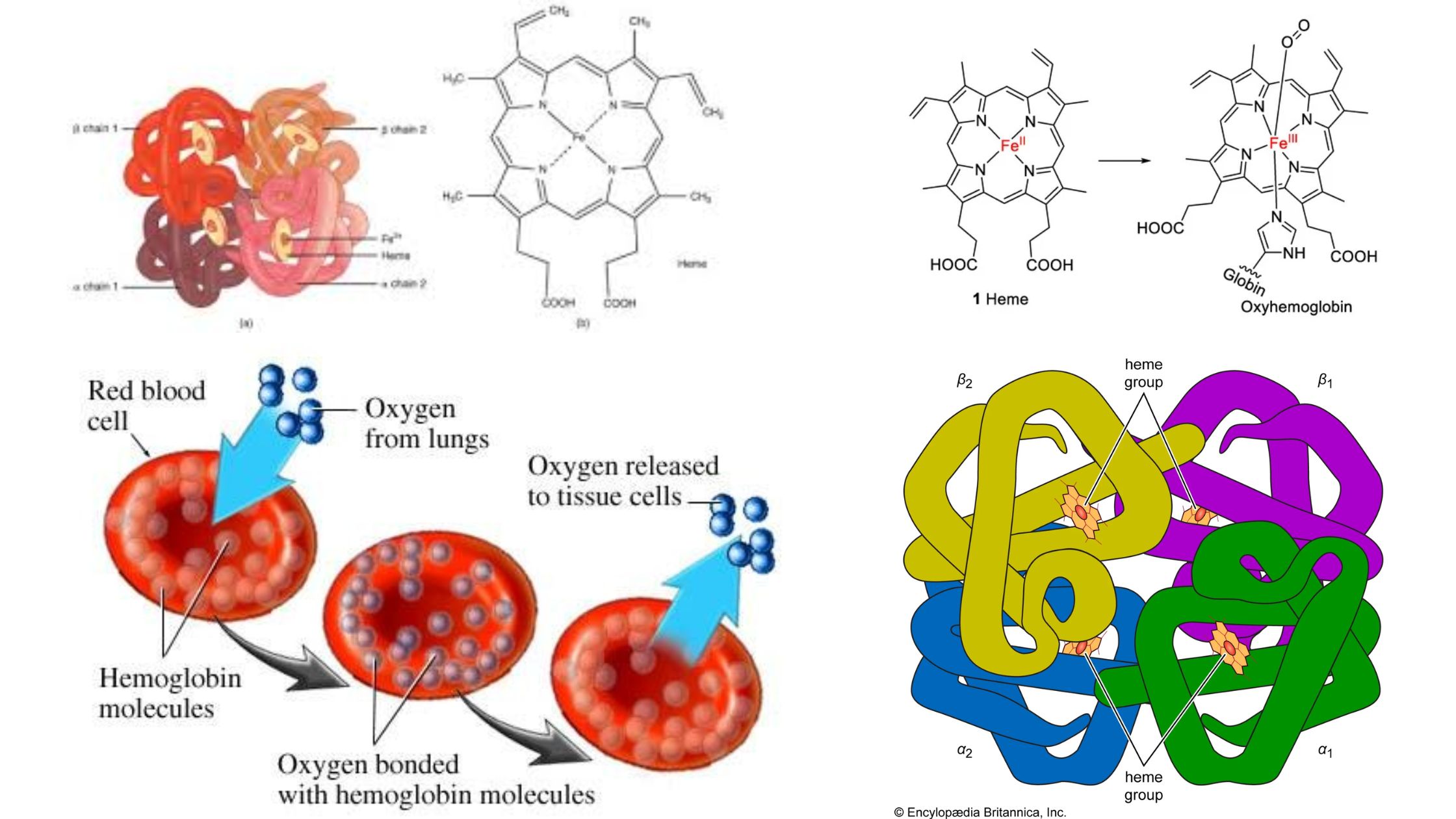
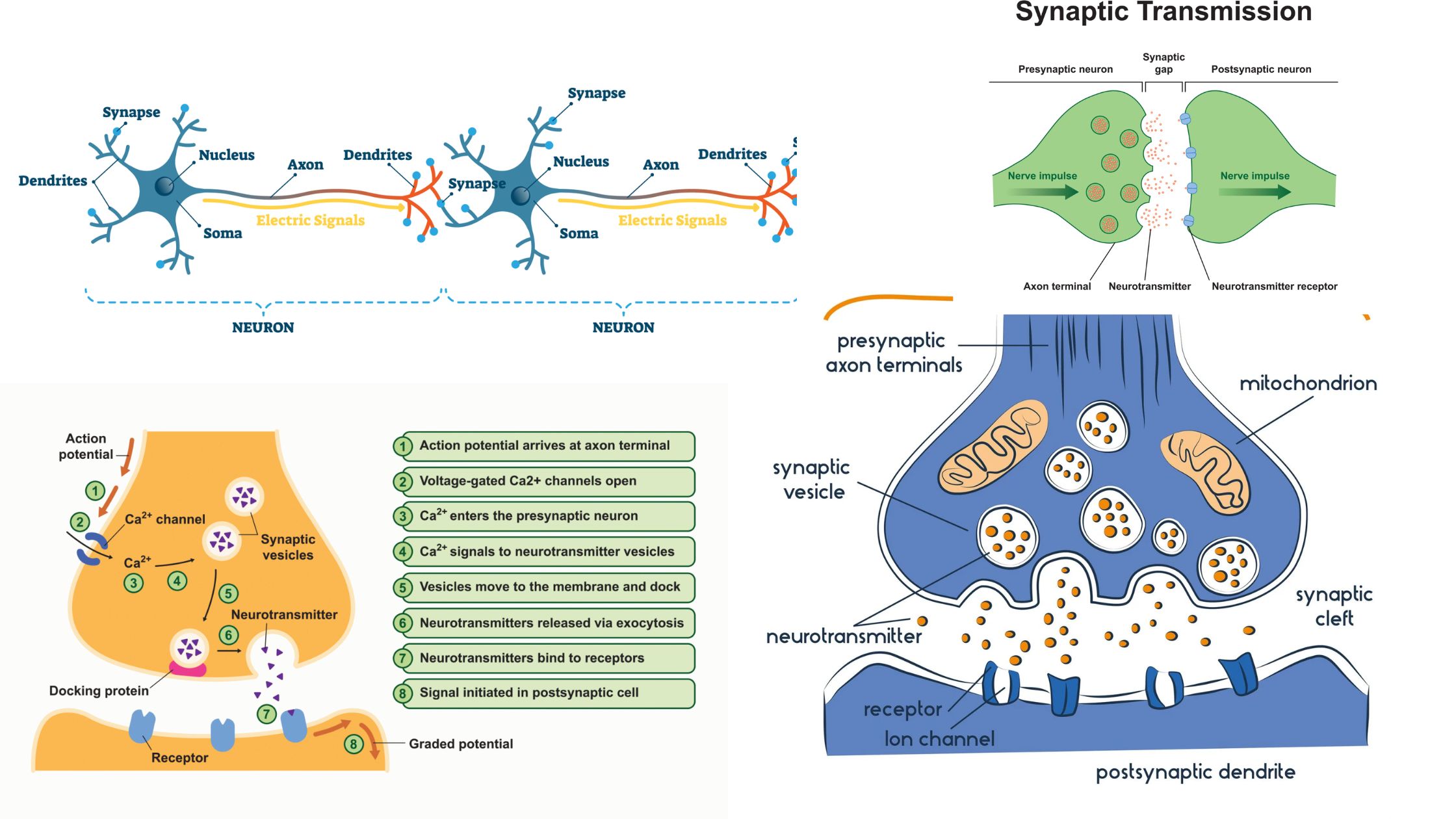
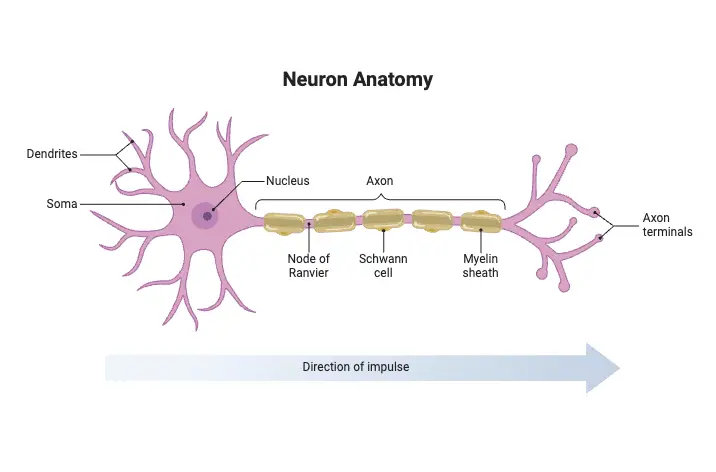
What is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning? Pathophysiology of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning The pathophysiology of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning involves complex interactions within the body that result in severe physiological disturbances. The following points summarize the key aspects of how carbon monoxide affects human health: Toxicokinetics of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning The toxicokinetics of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning … Read more