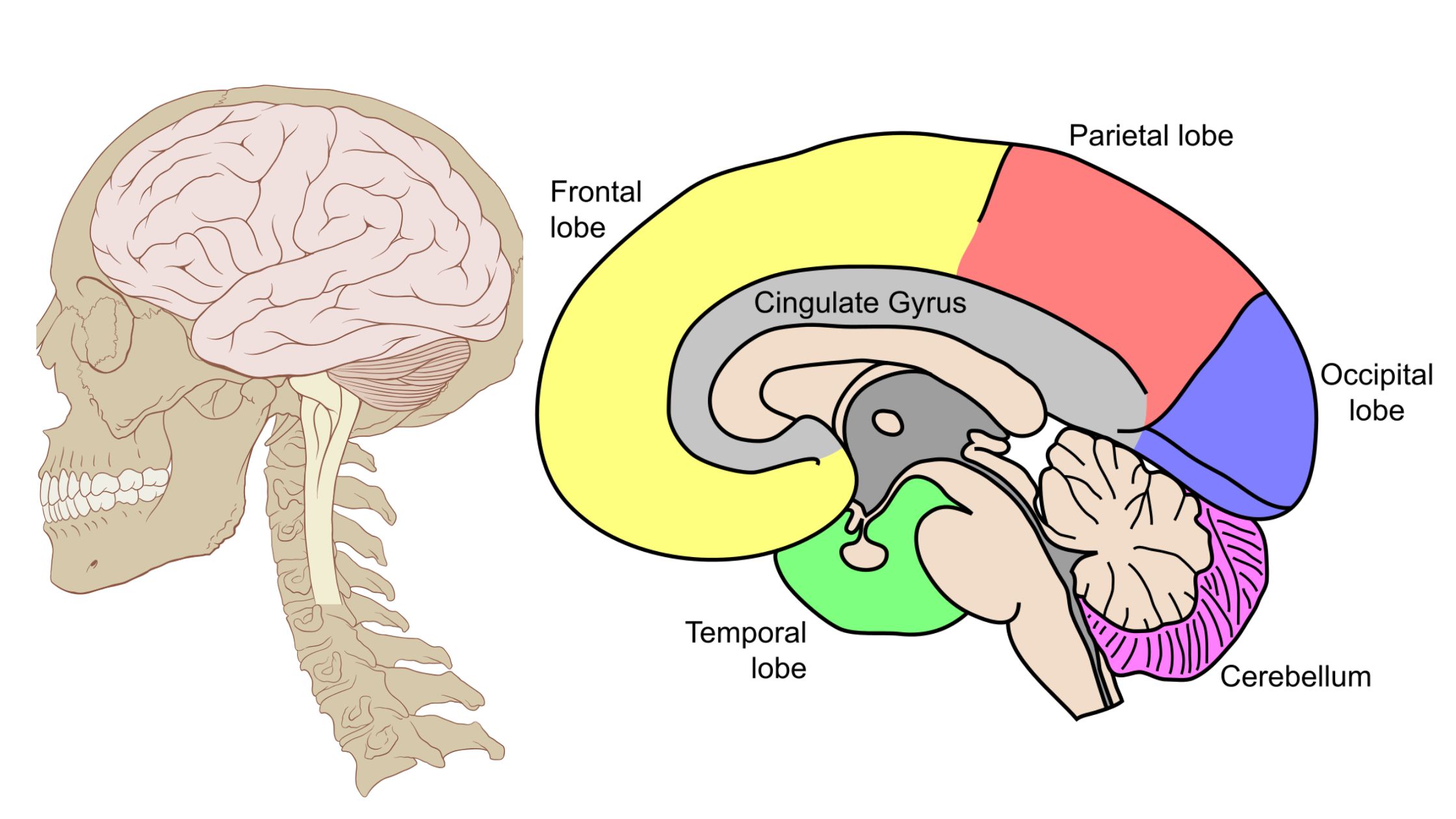
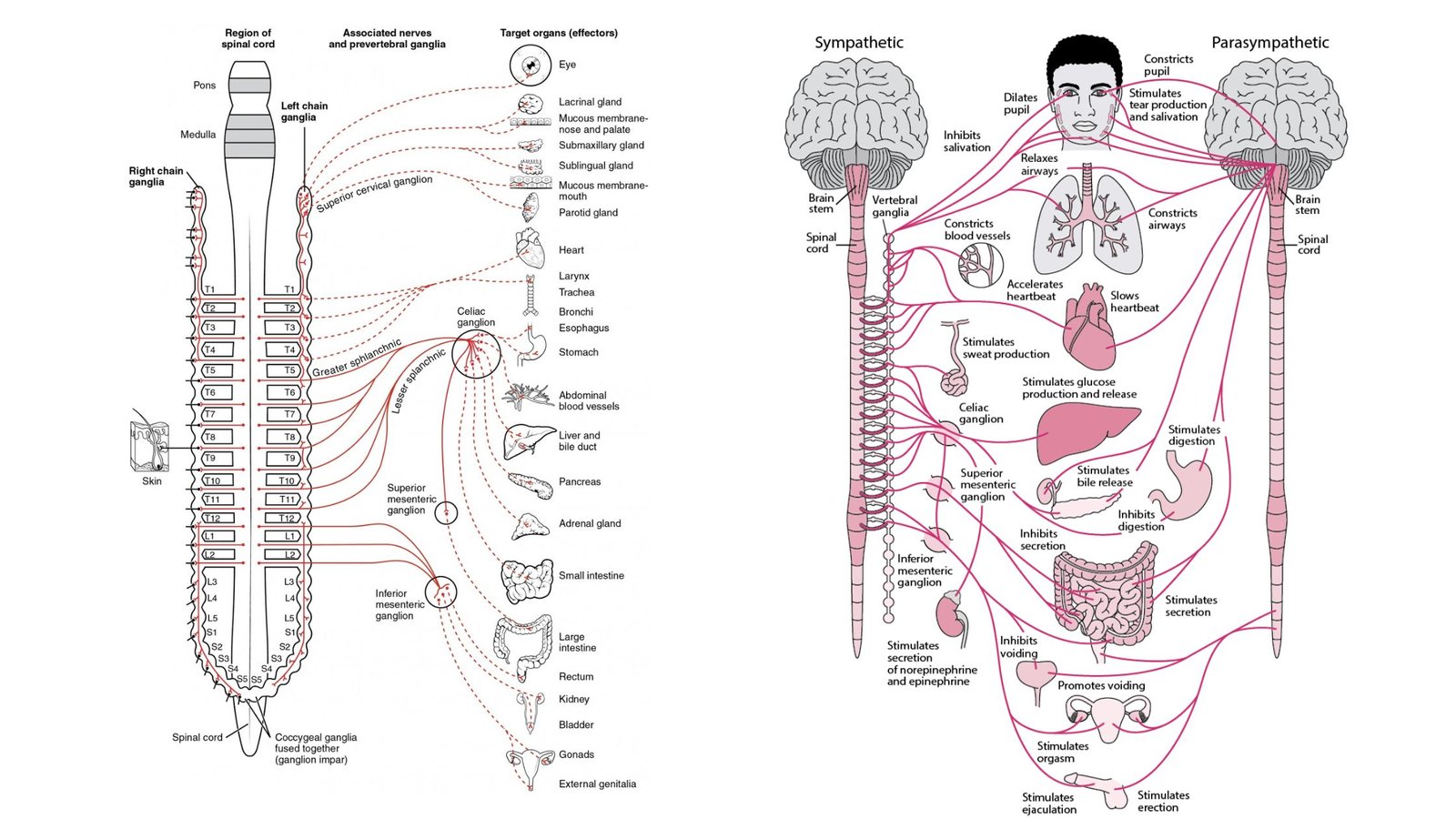
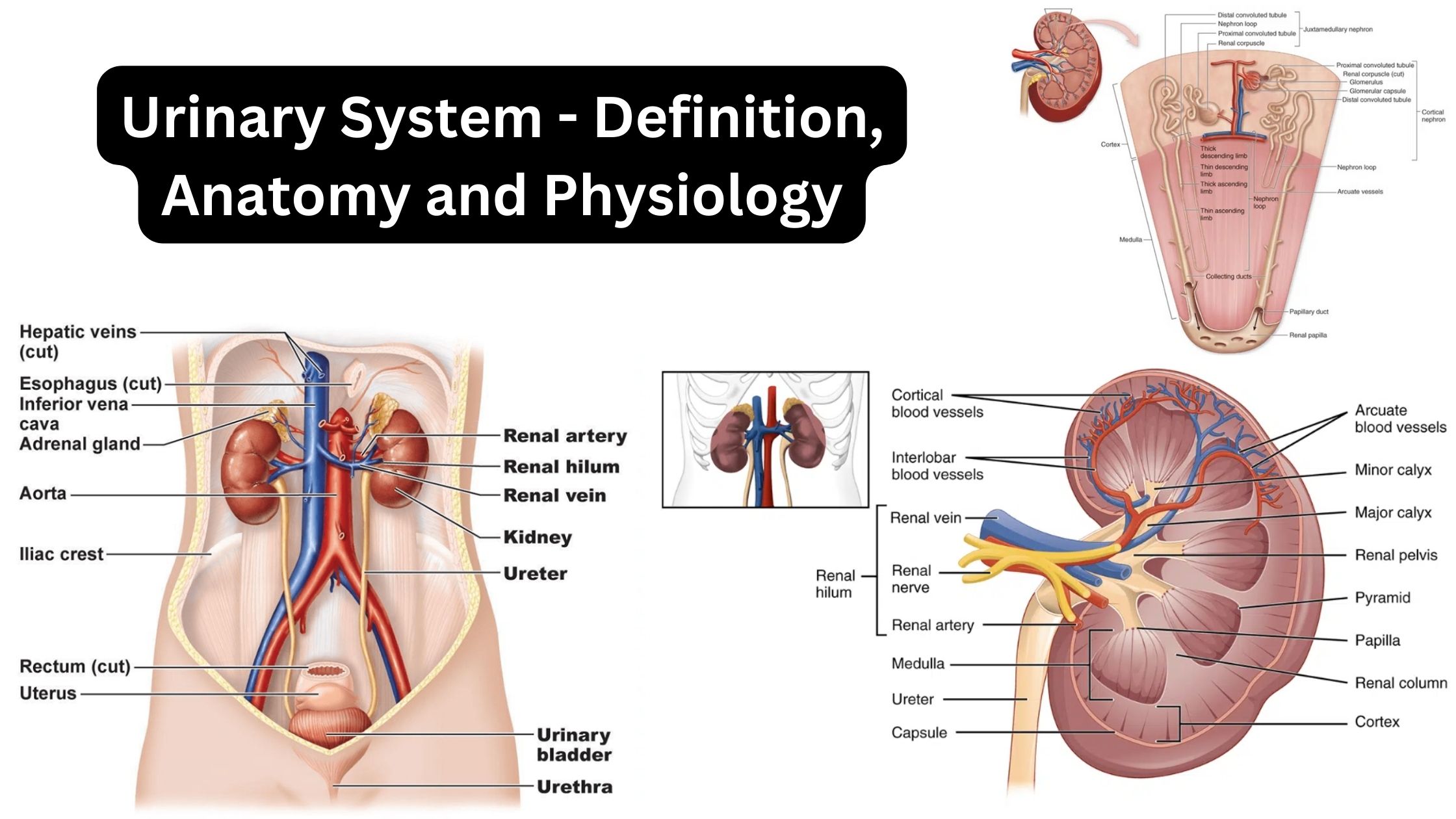
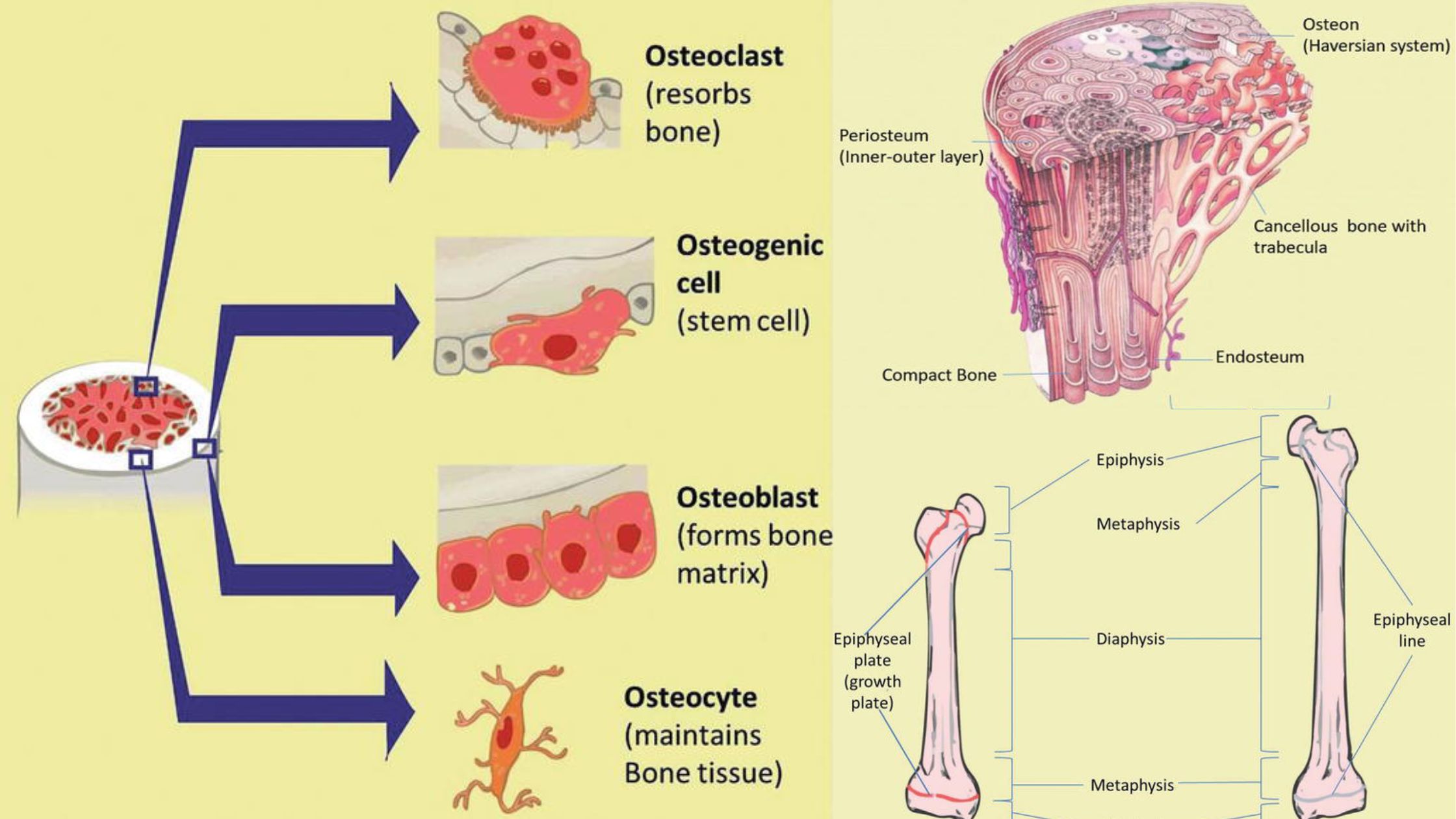
Nephron – Definition, Structure, Physiology, Functions
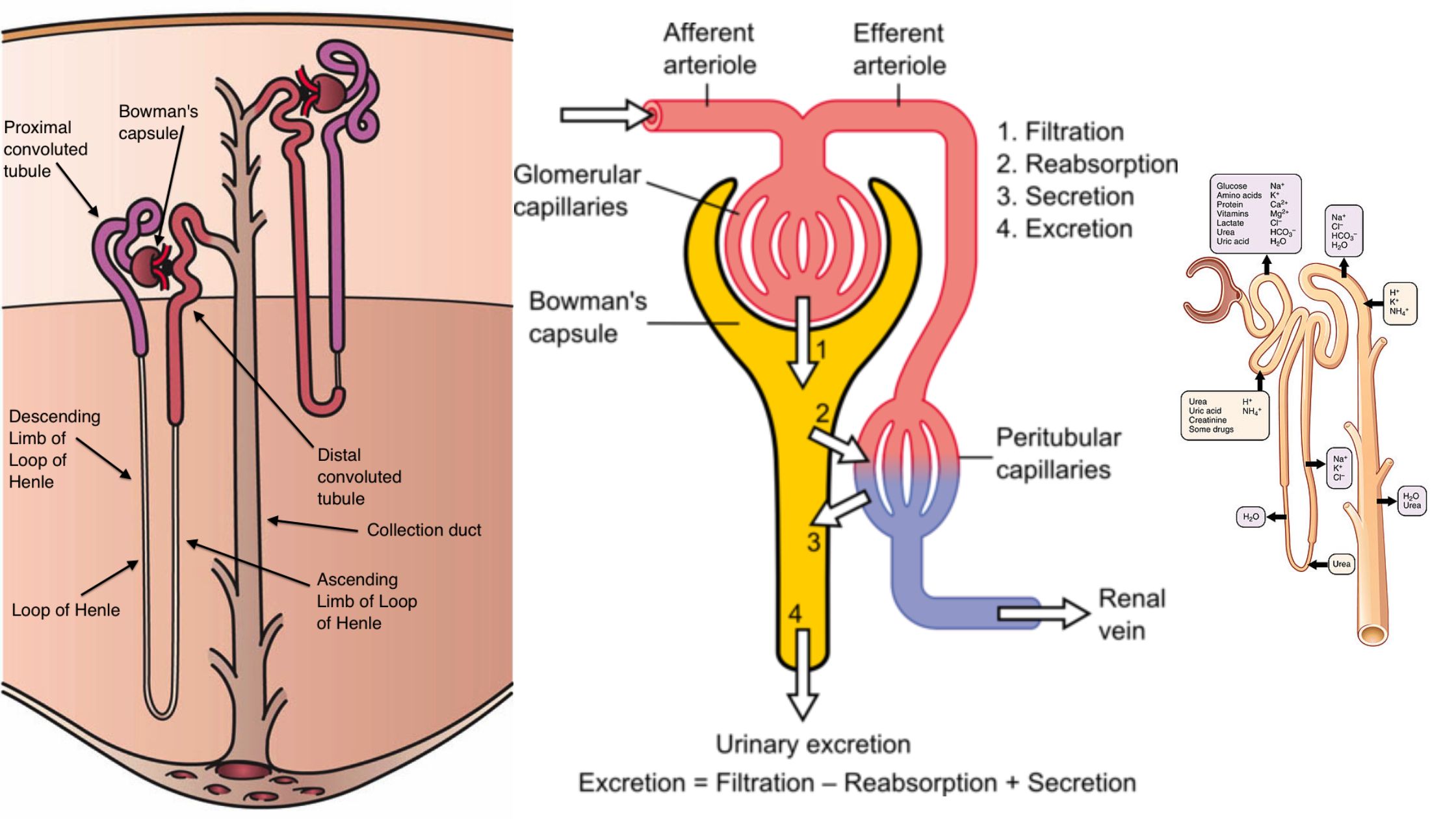
What is Nephron? Definition of Nephron A nephron is the basic functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. It consists of a glomerulus (a cluster of capillaries) and a tubule, which processes the filtrate by reabsorbing water and essential substances while excreting waste products. Types of Nephron Nephrons, the functional units … Read more