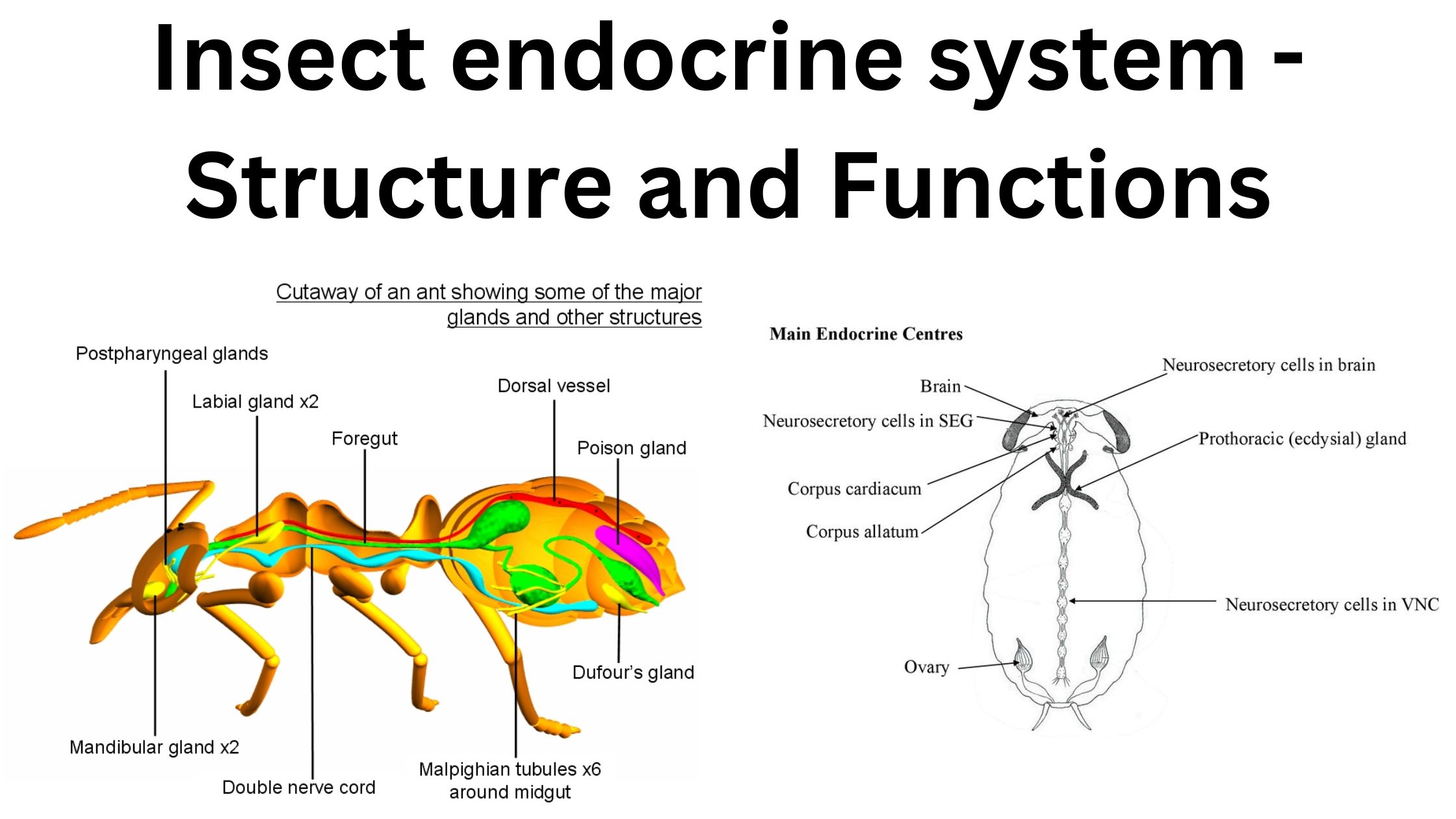
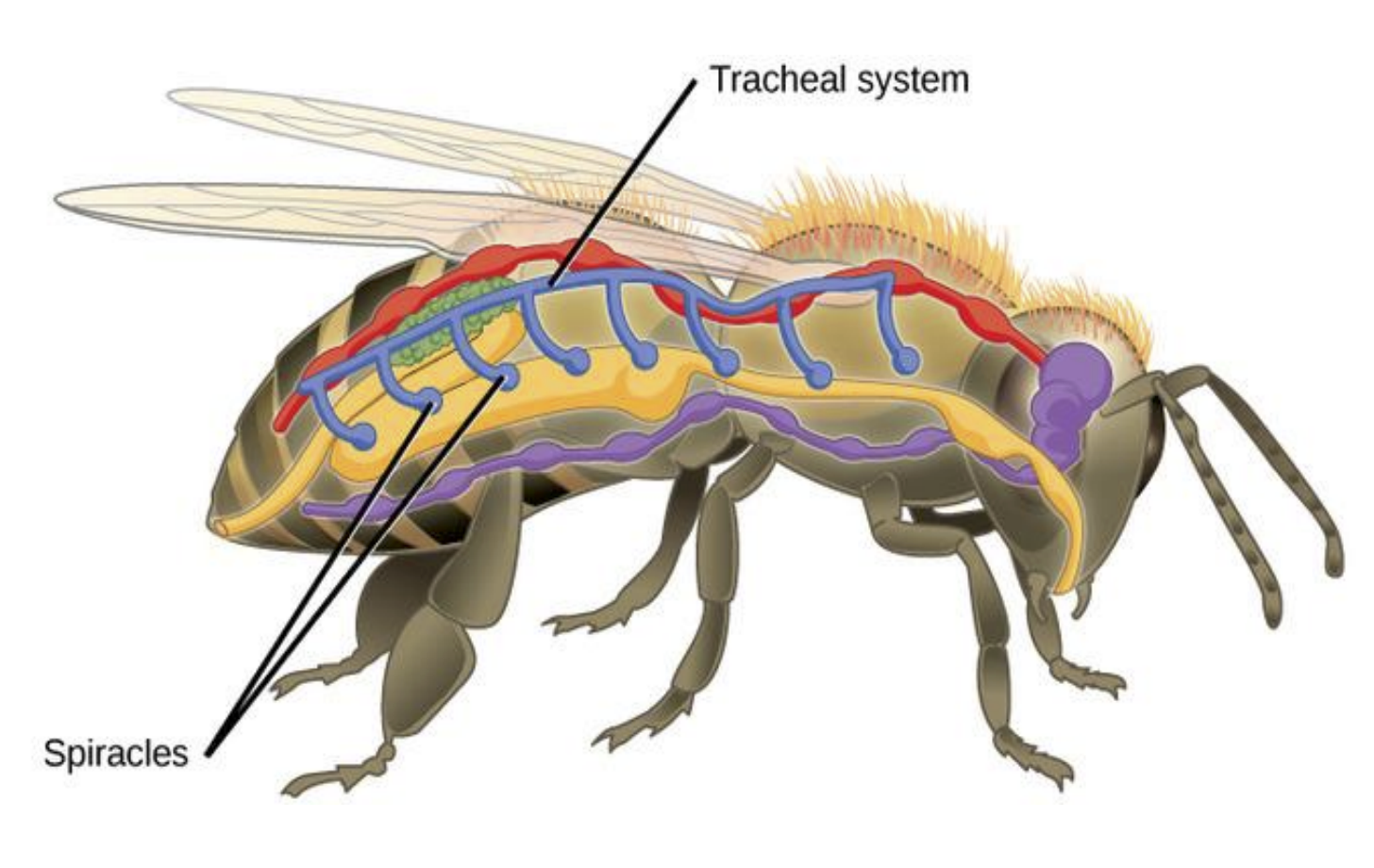
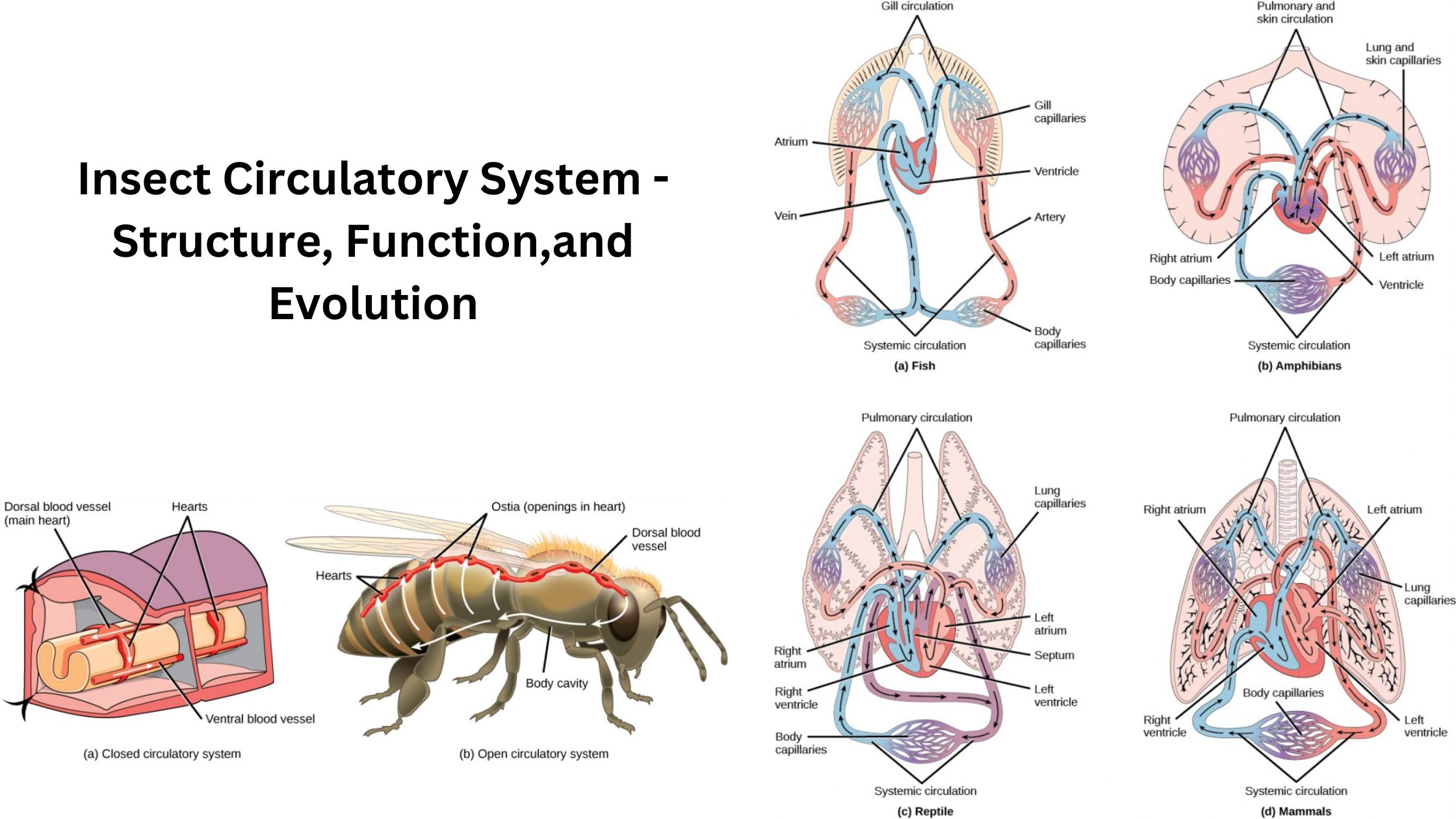
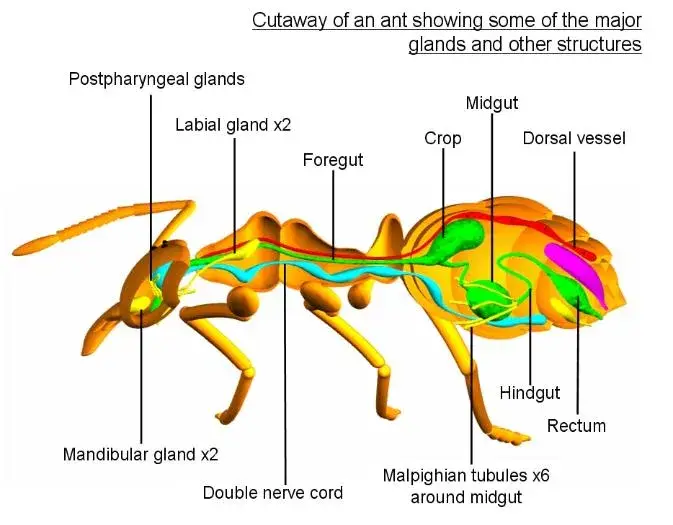
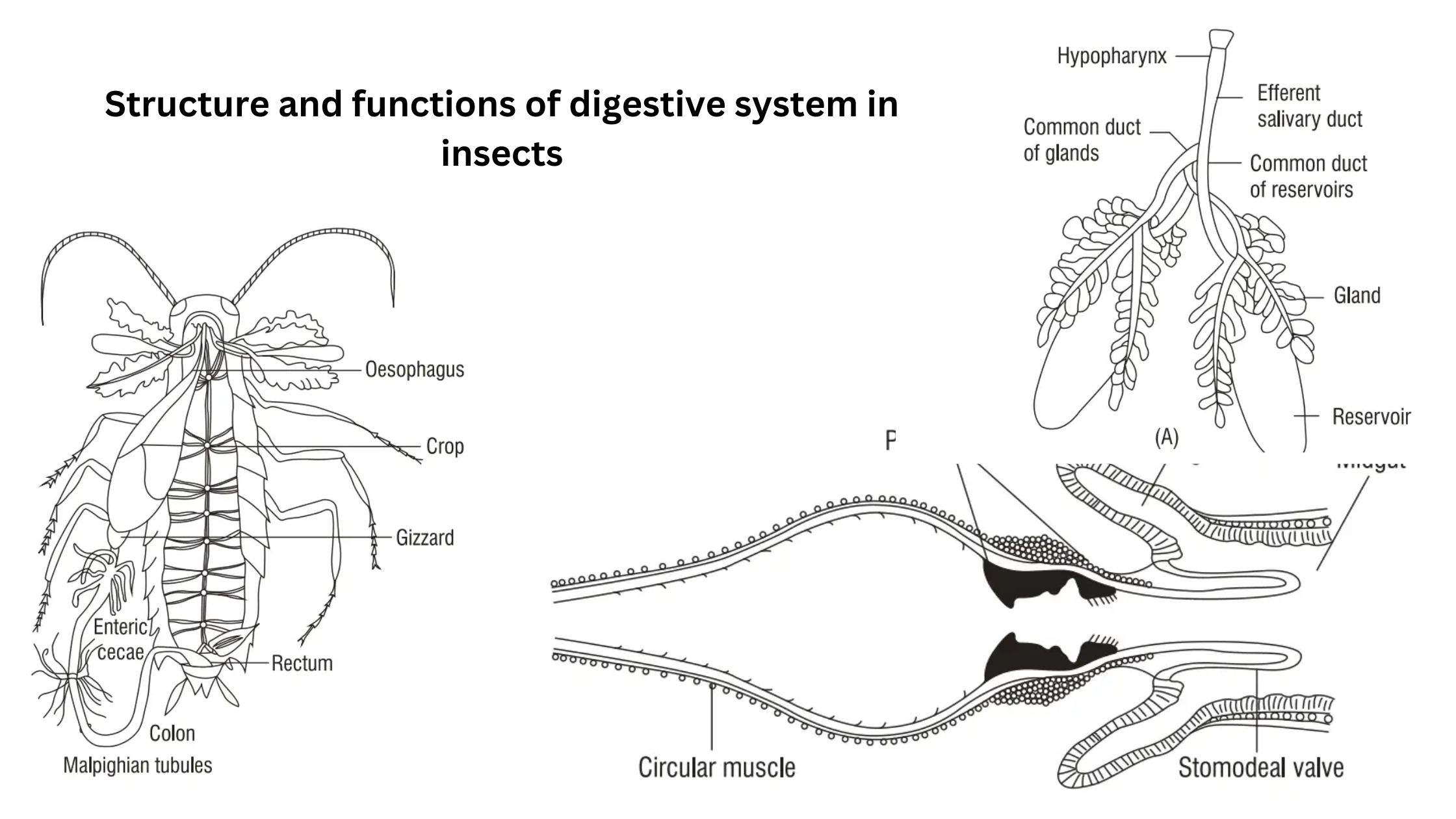
Insect Nervous System – Structure and functions
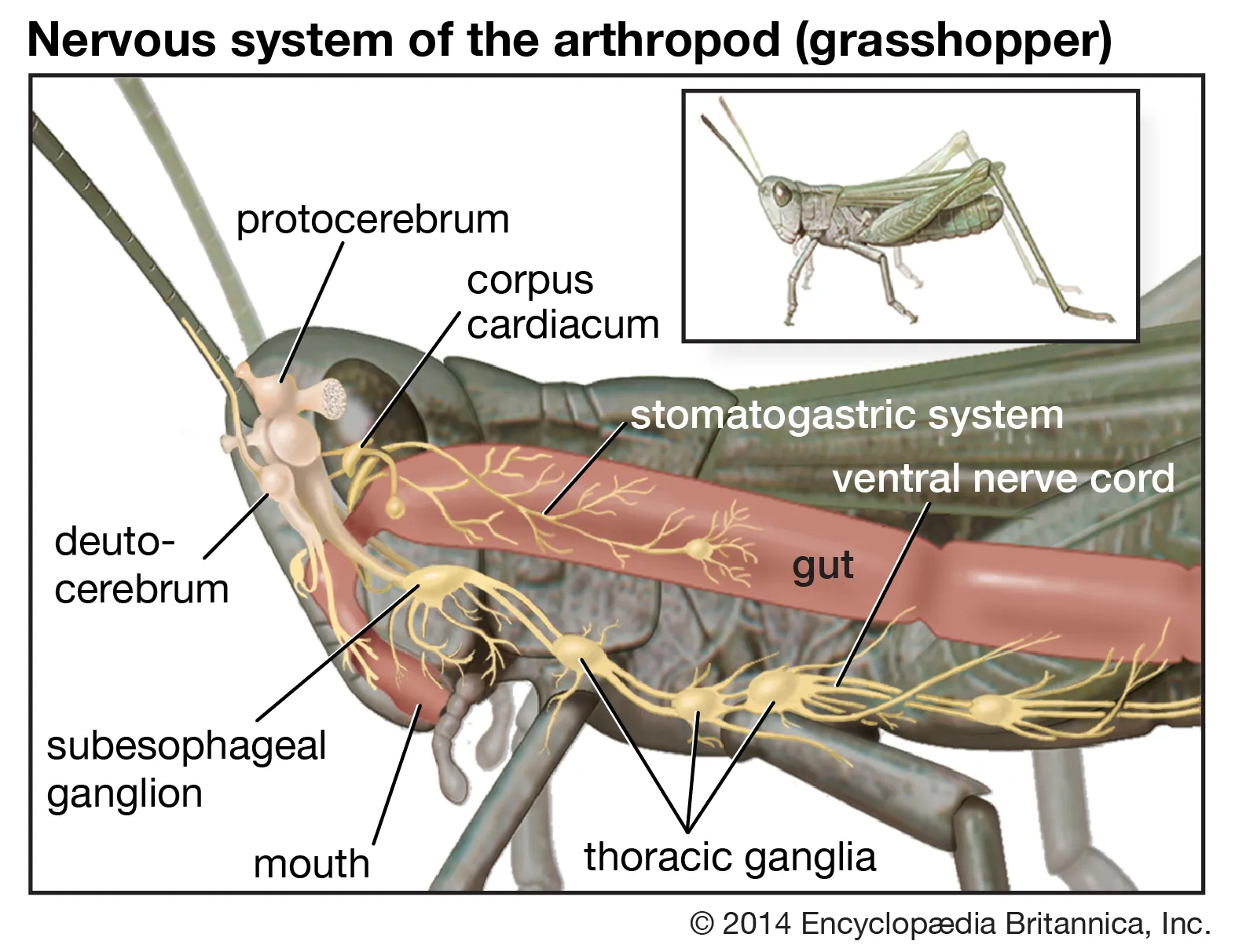
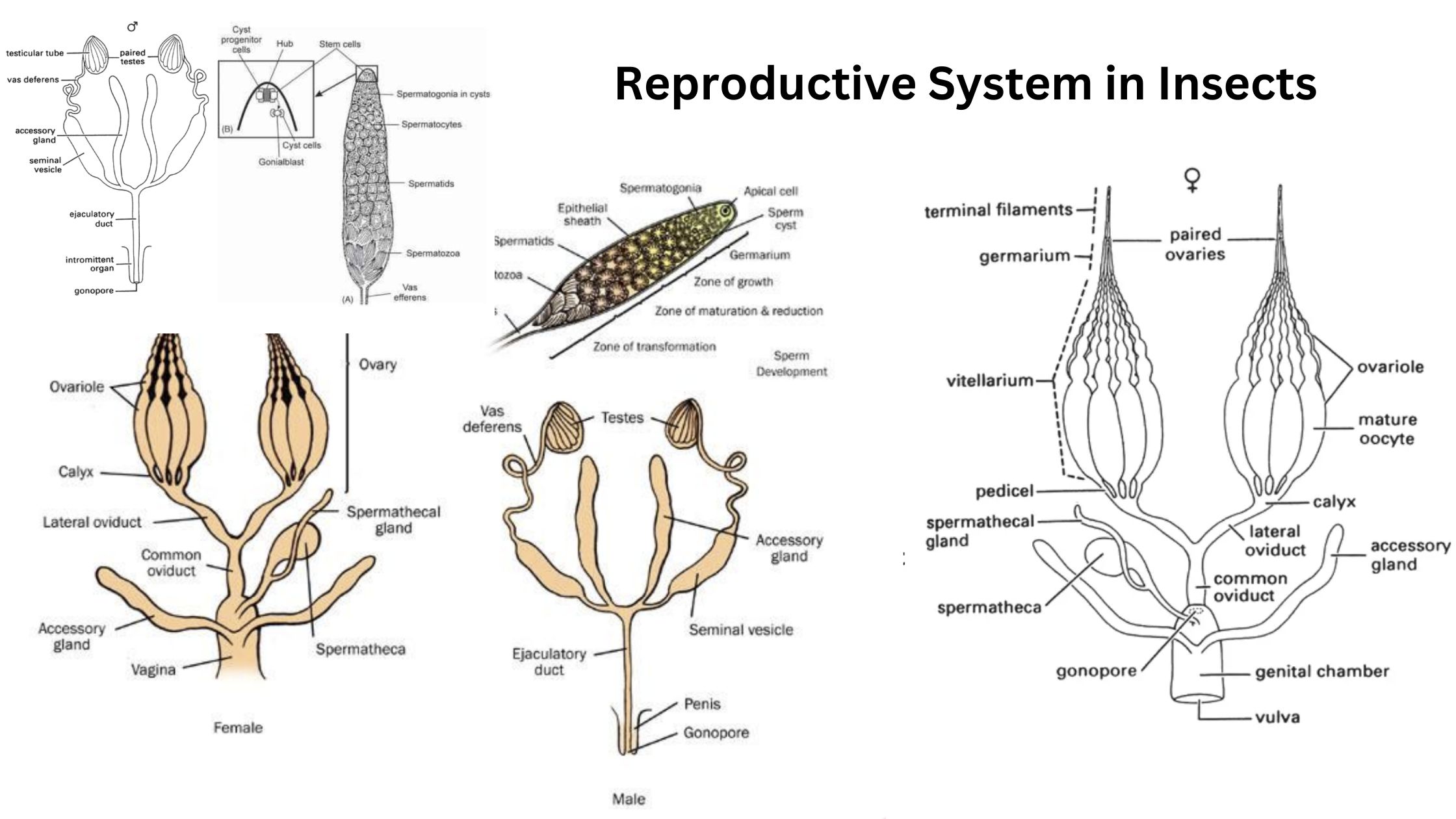
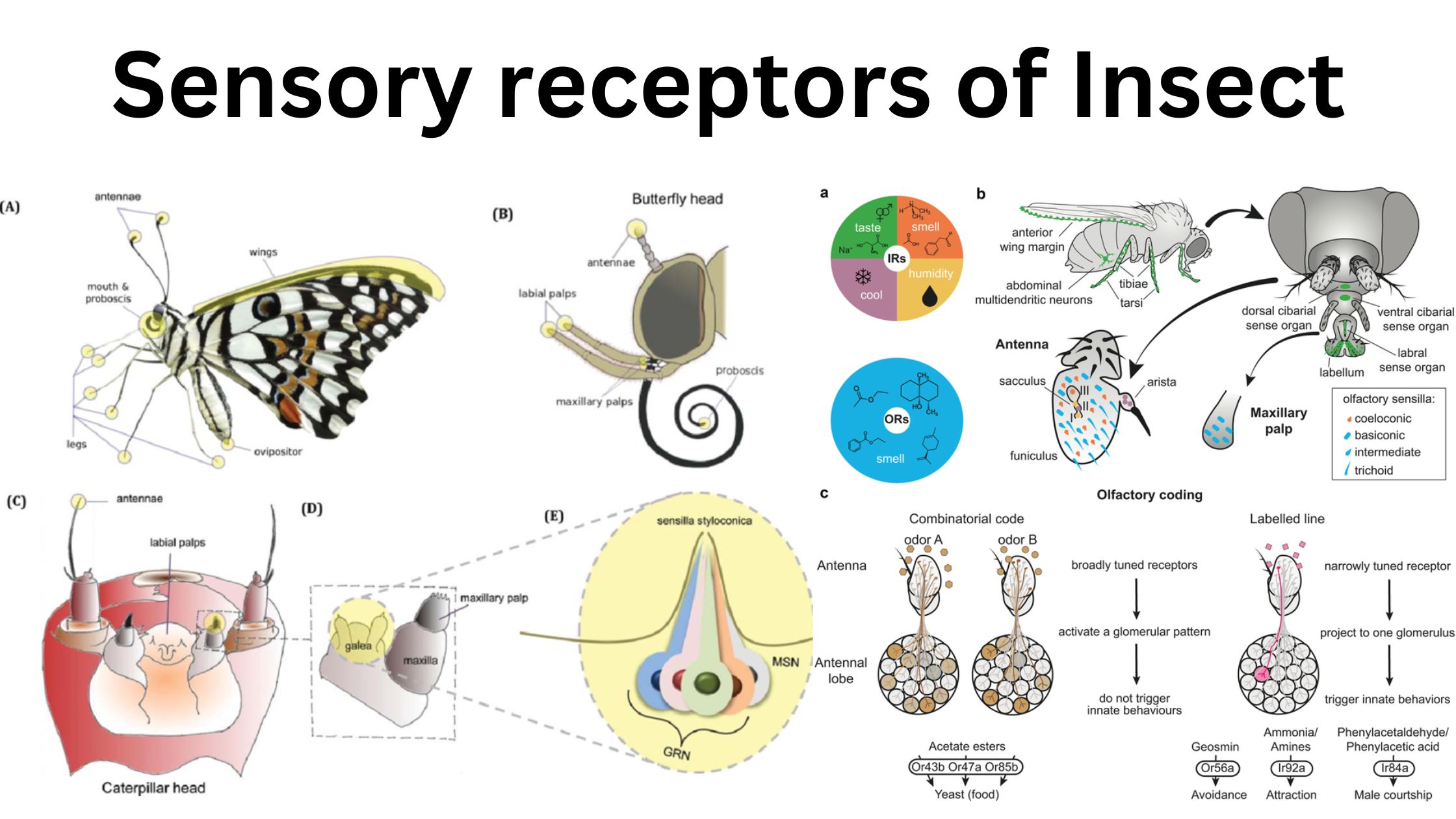
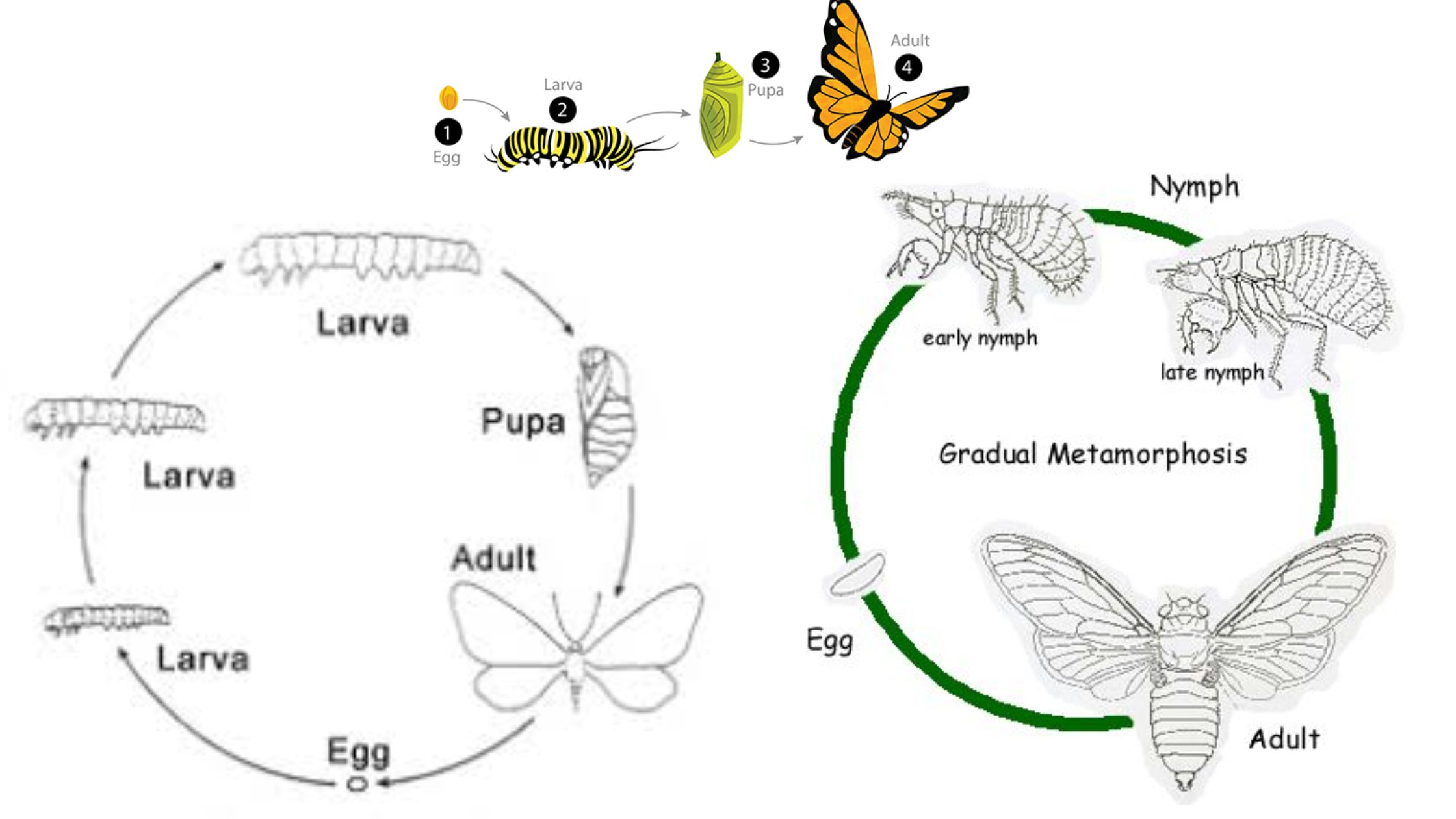
The insect nervous system is a complex and highly organized network that facilitates a wide array of functions crucial for the survival and adaptation of insects. It comprises two primary components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of a dorsal brain and a ventral chain of segmental … Read more