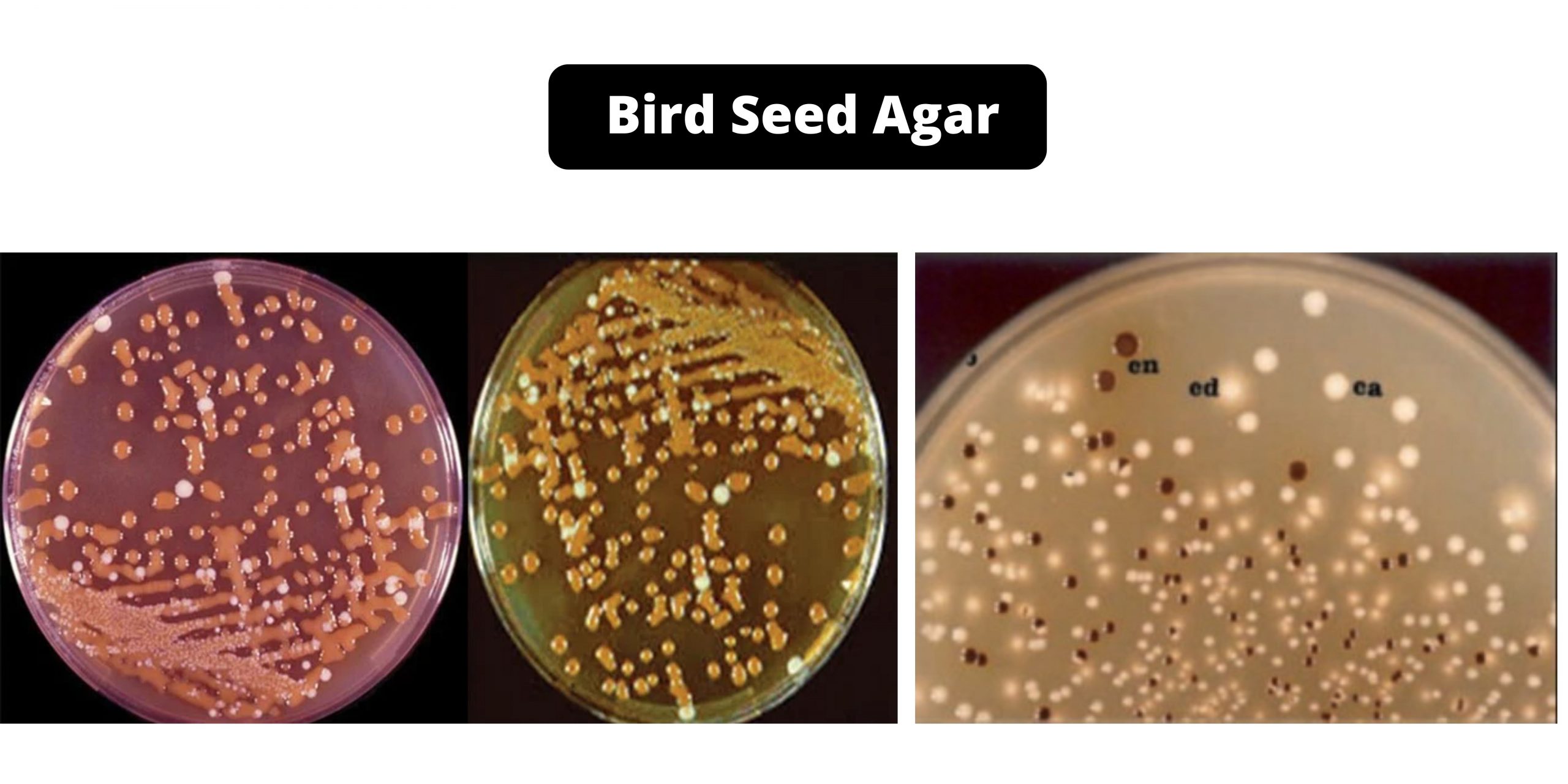
Bird Seed Agar (Staibs Medium) – Composition, Principle, Preparation
Bird Seed Agar Bird Seed Agar is an effective solid medium to isolate selectively and differentially of Cryptococcus Neoformans from clinical specimens. It is utilized for the specific isolation from Cryptococcus neoformans as well as C. Gattii. C. Neoformans typically grows as yeast (unicellular) and reproduces via budding. Cryptococcus Neoformans is an enclosed yeast, which makes the enzyme phenoloxidase an enzyme that is essential to melanin production.