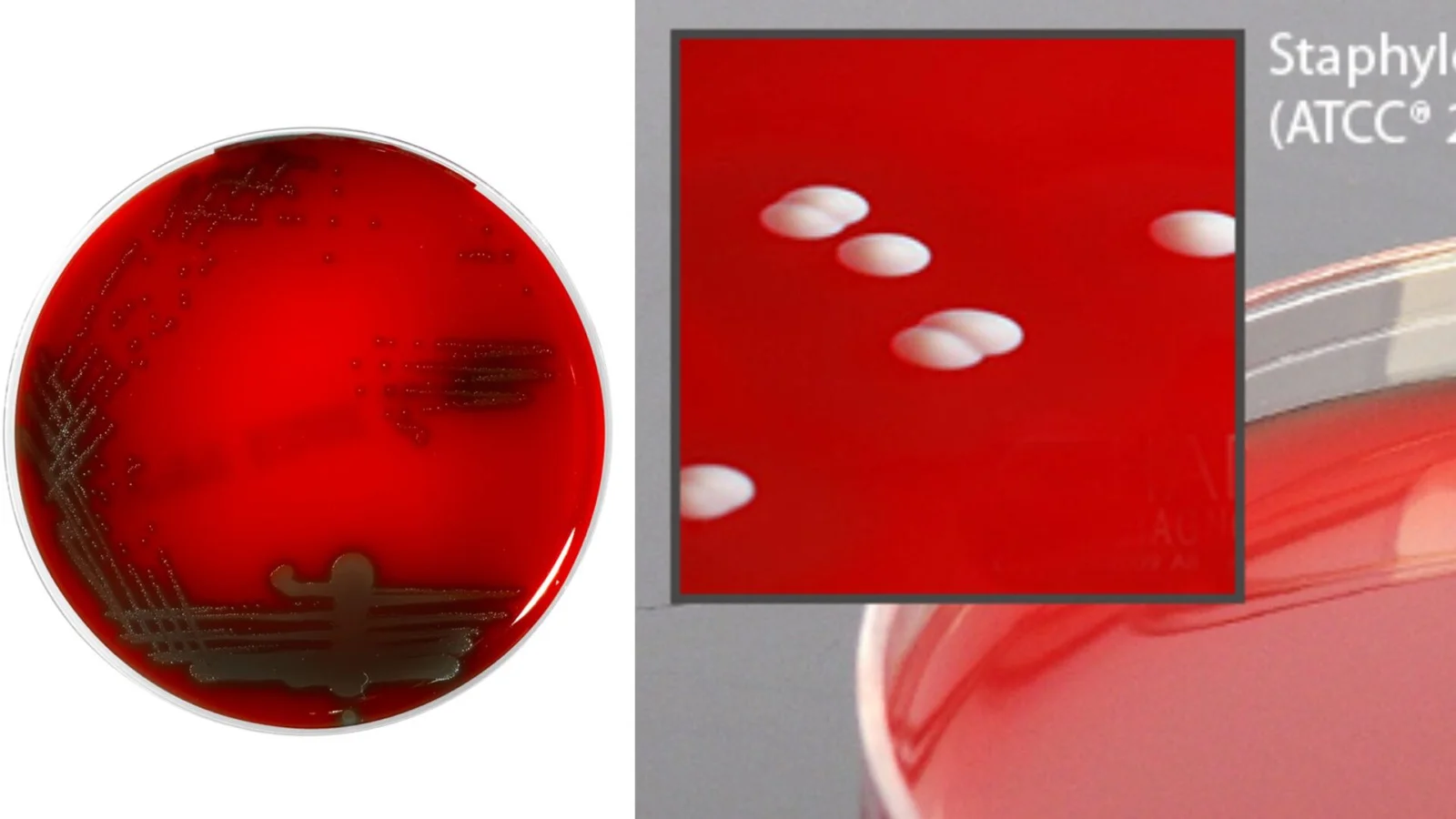
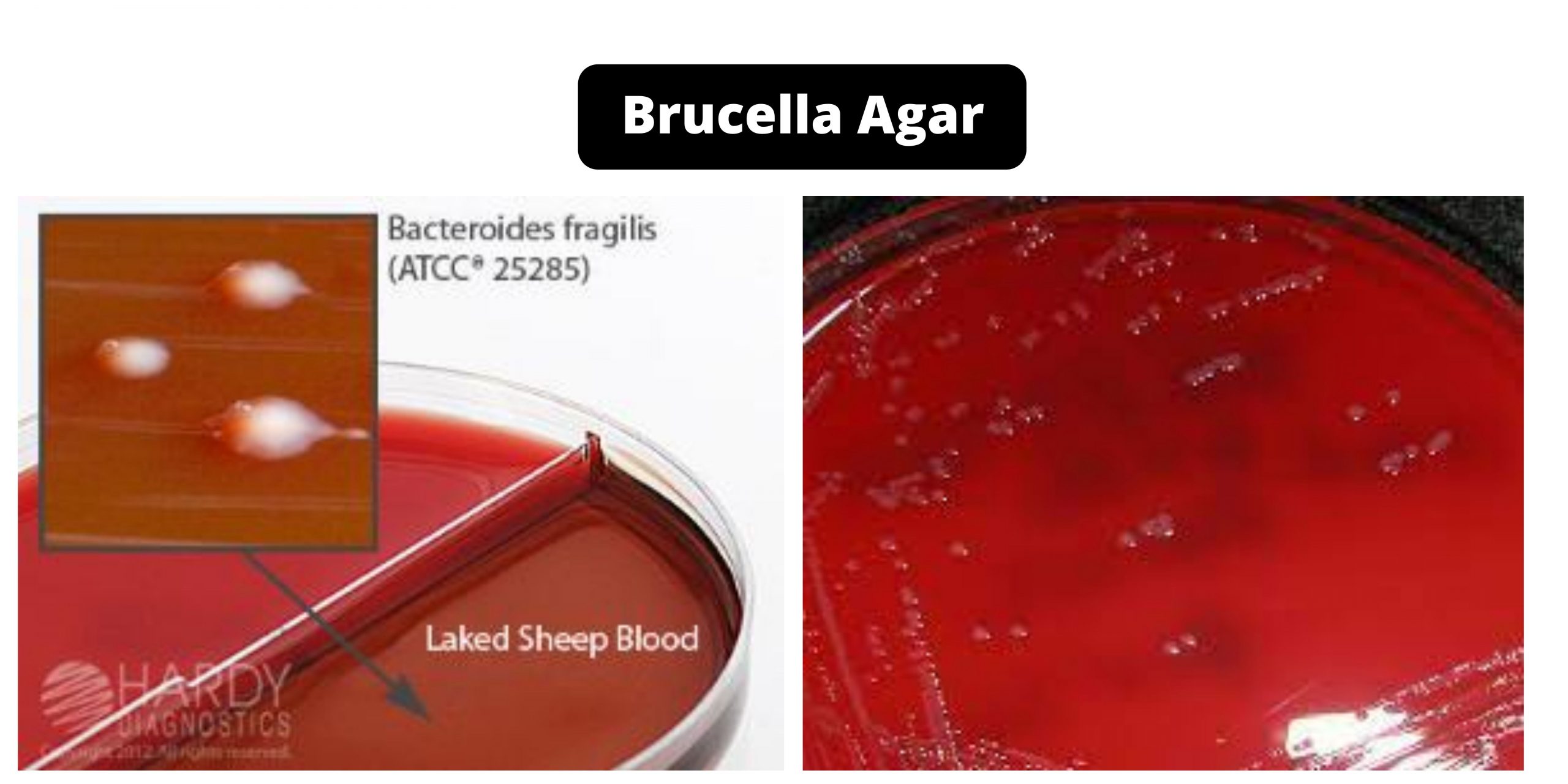
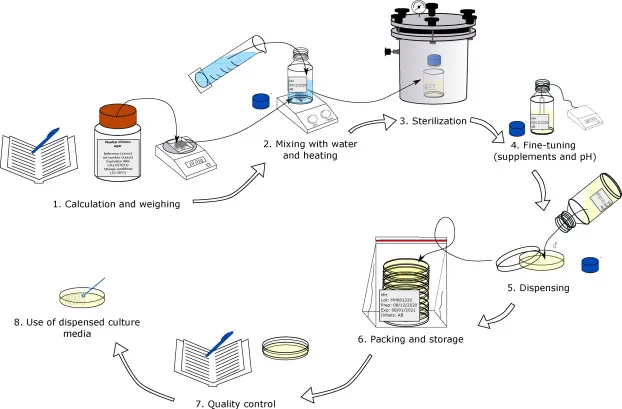
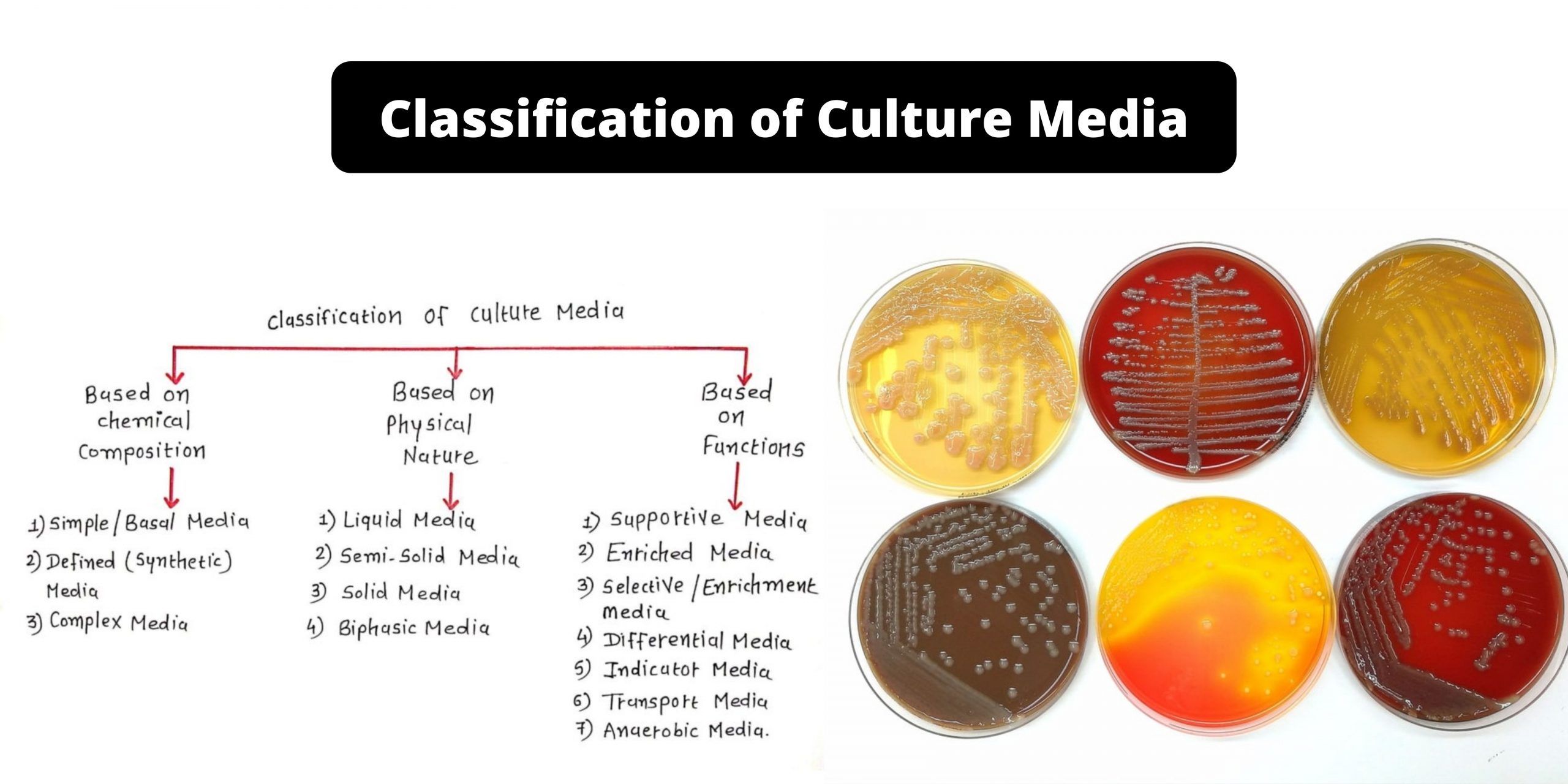
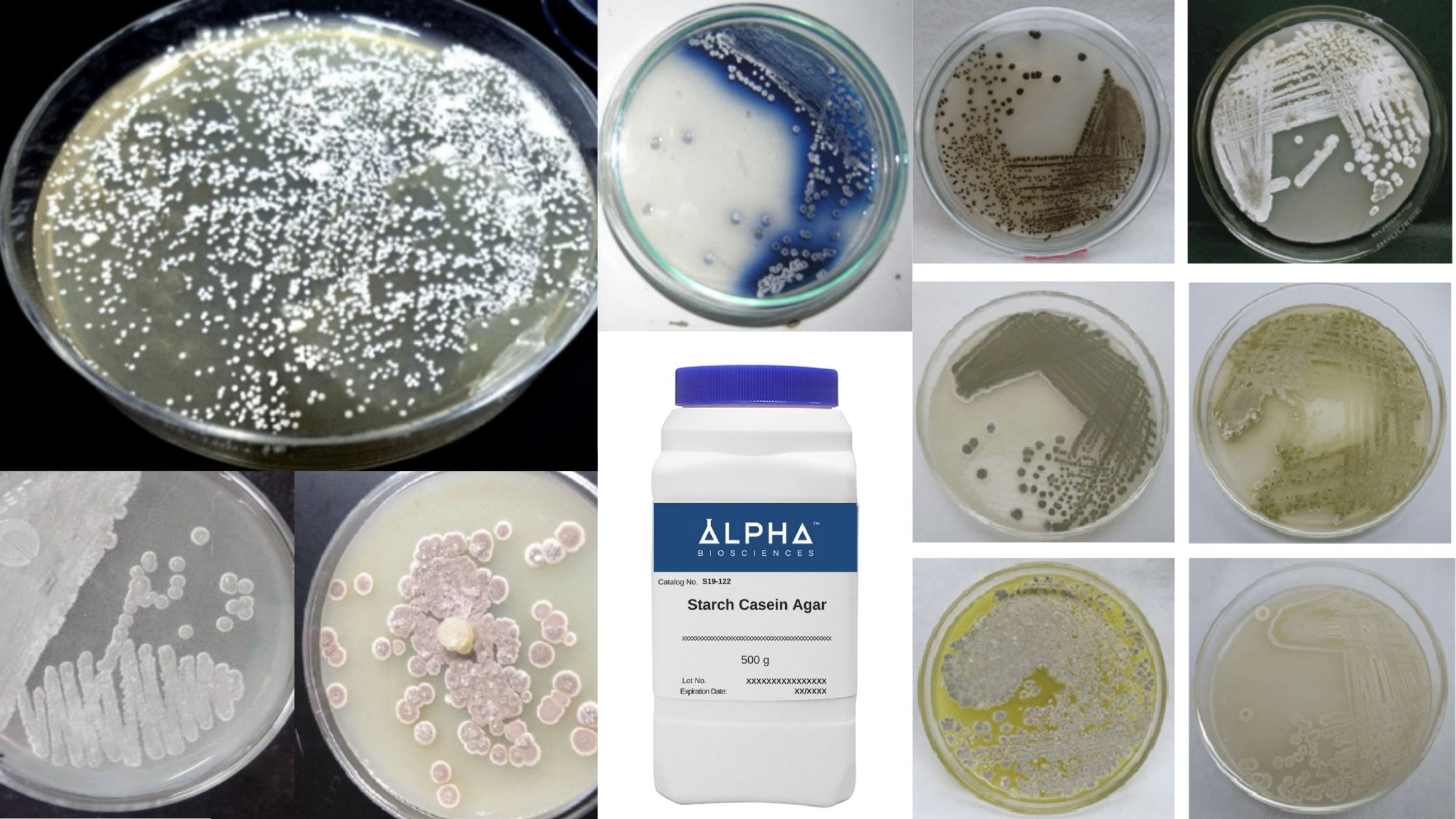
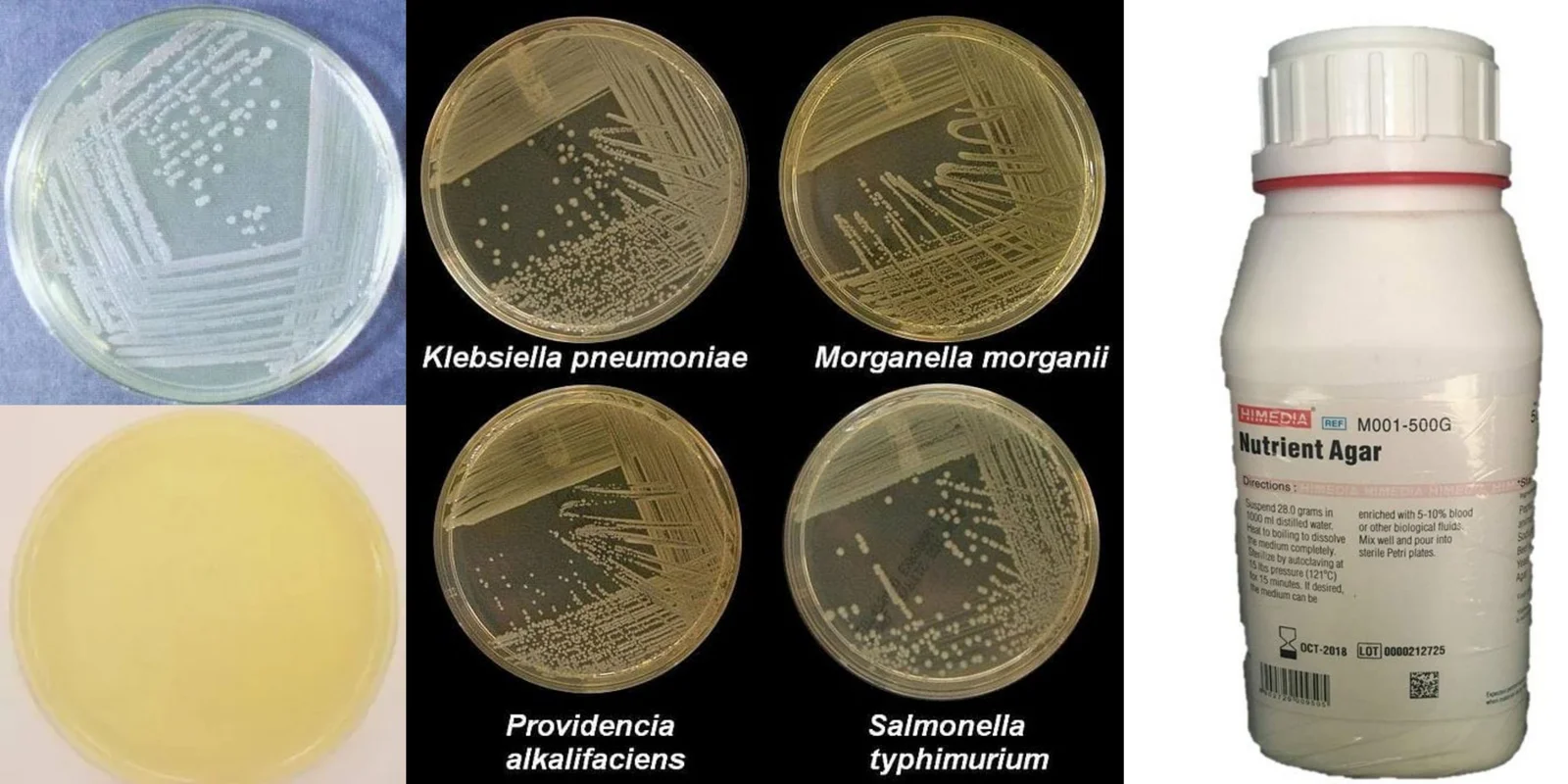
Brucella Agar – Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
Brucella is an intracellular parasite which causes epizootic abortions for animals, and septicemic febrile disease or localized infections of tissues, bones or organ systems of humans. Brucella species are very meticulous and require a rich nutrient environment to develop. Additionally, Brucella species are highly infectious, and therefore extreme caution should be exercised when handling.