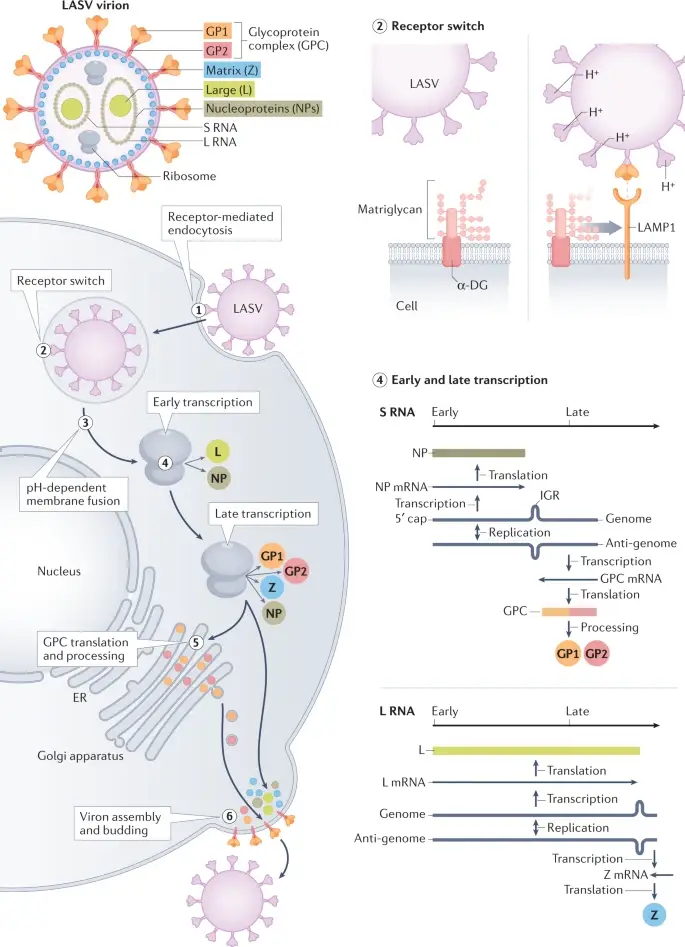
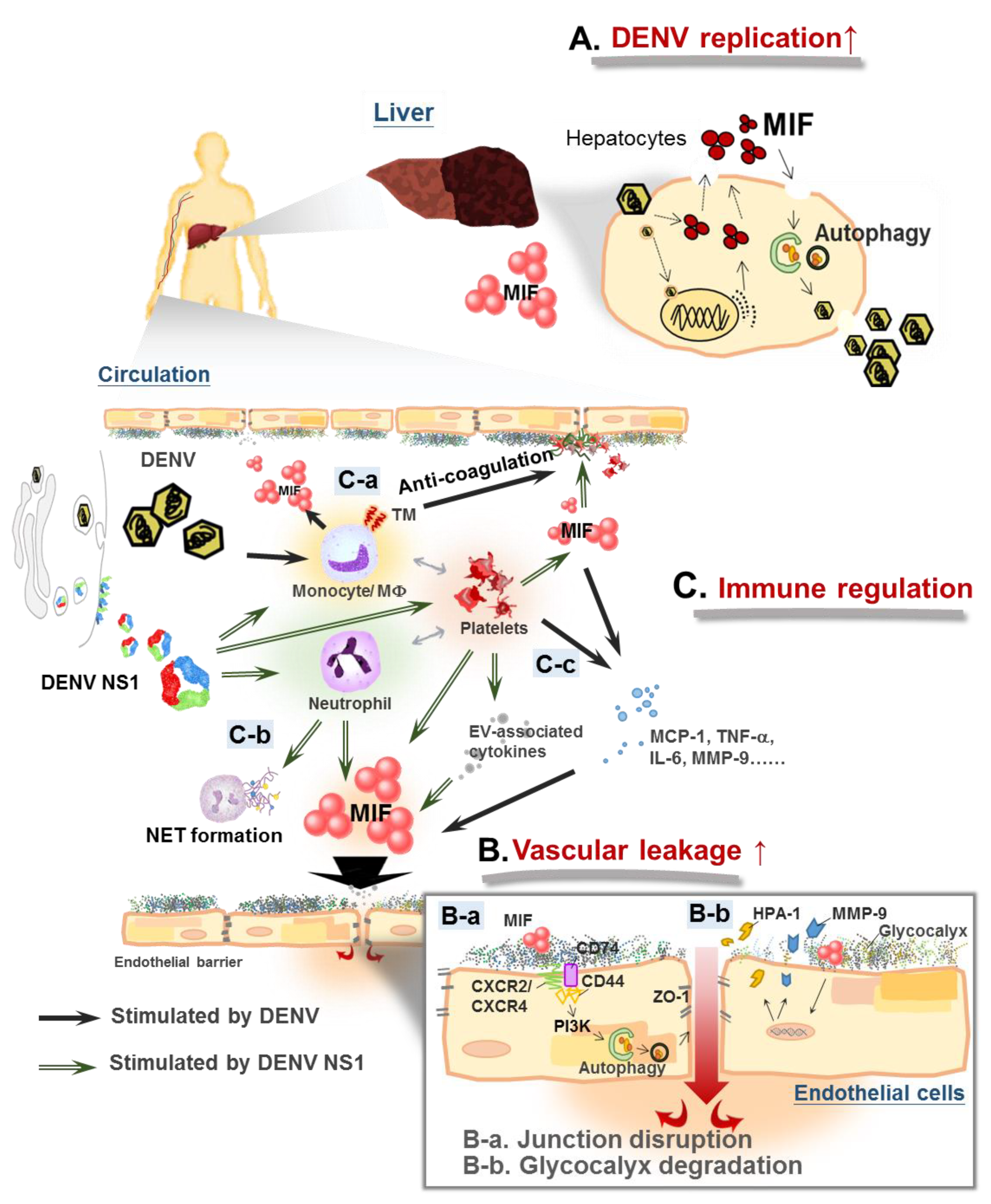
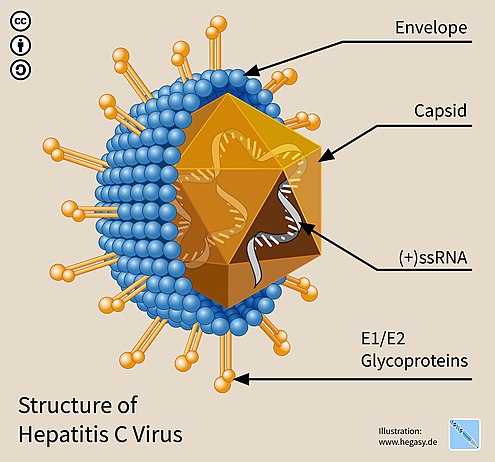
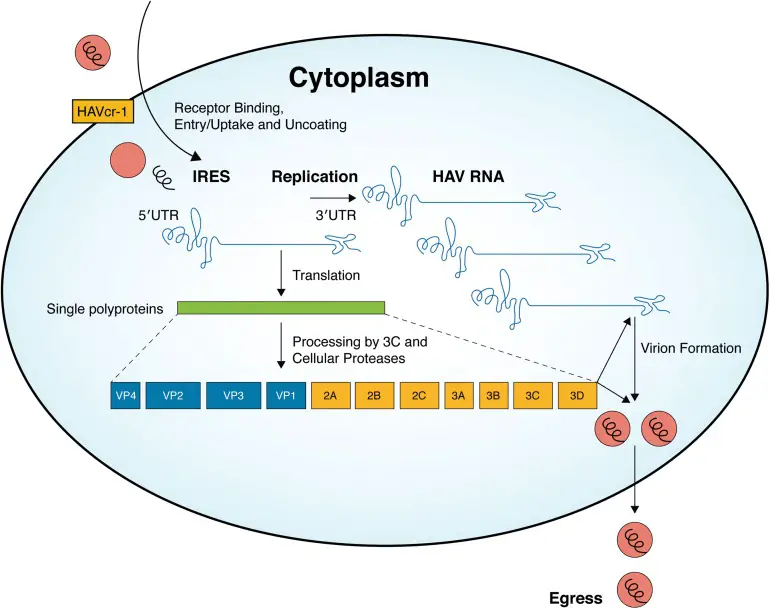
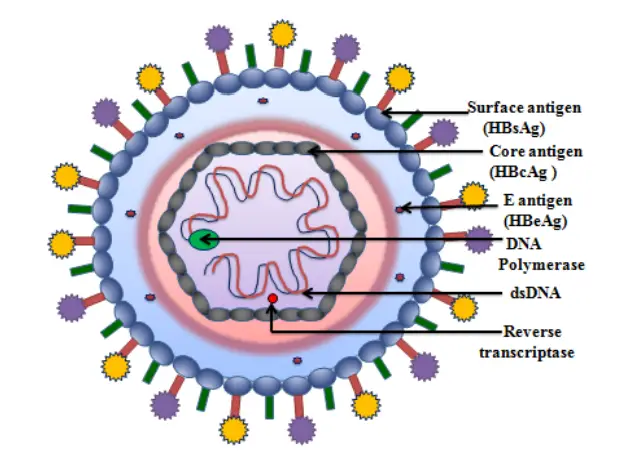
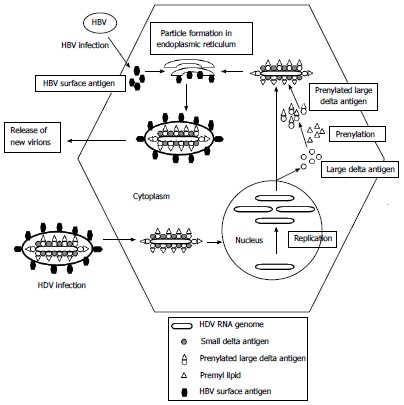
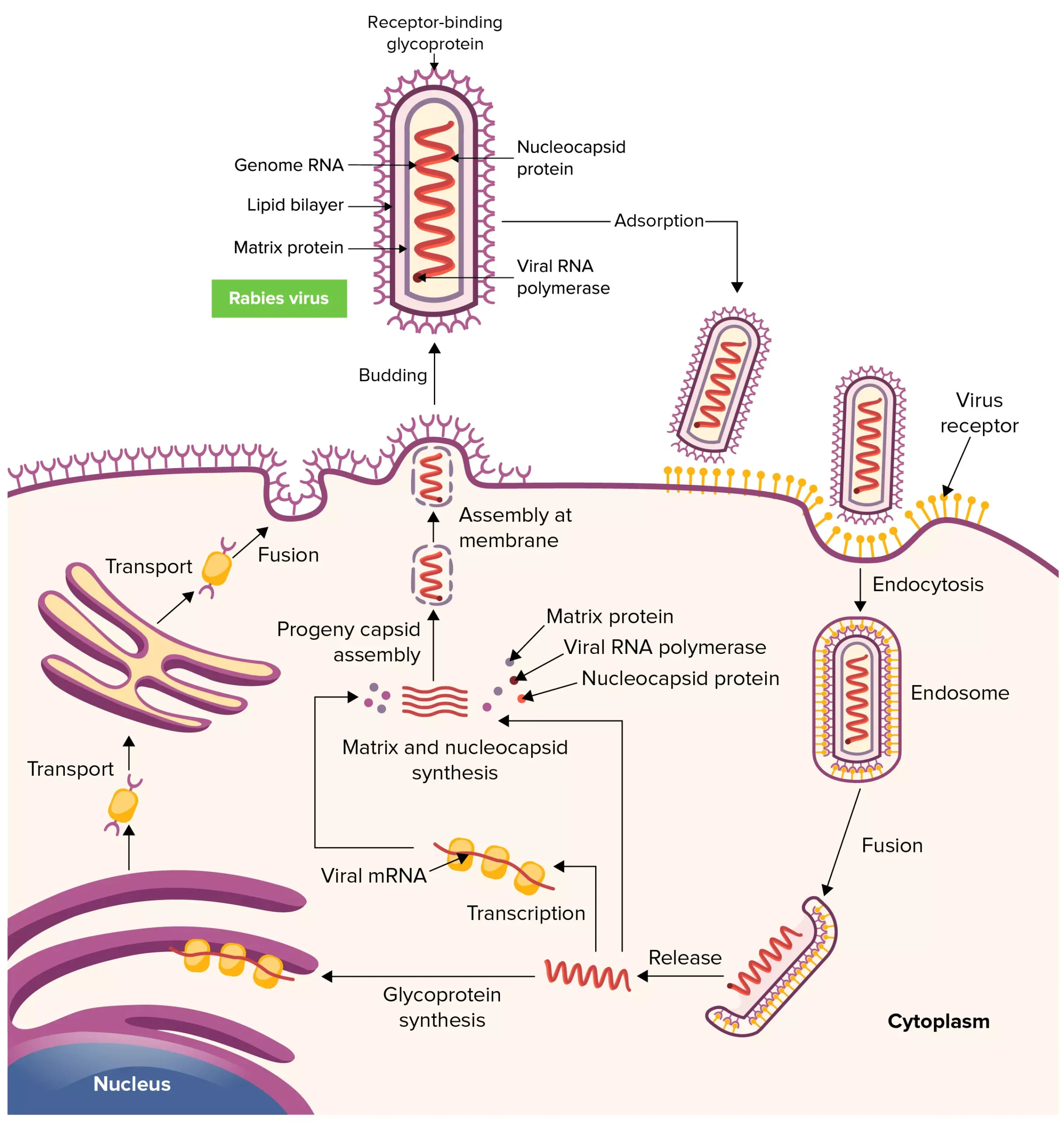
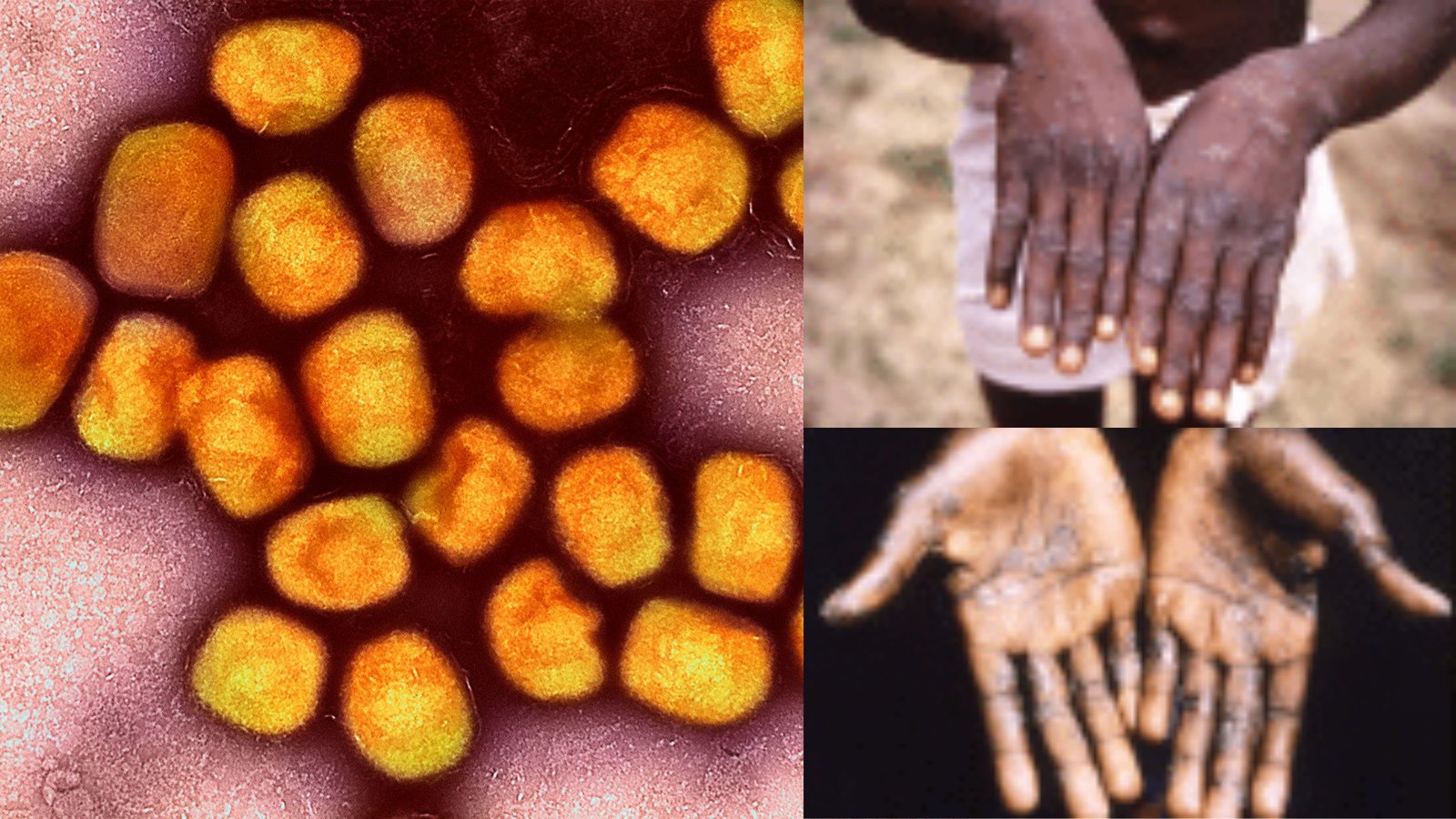
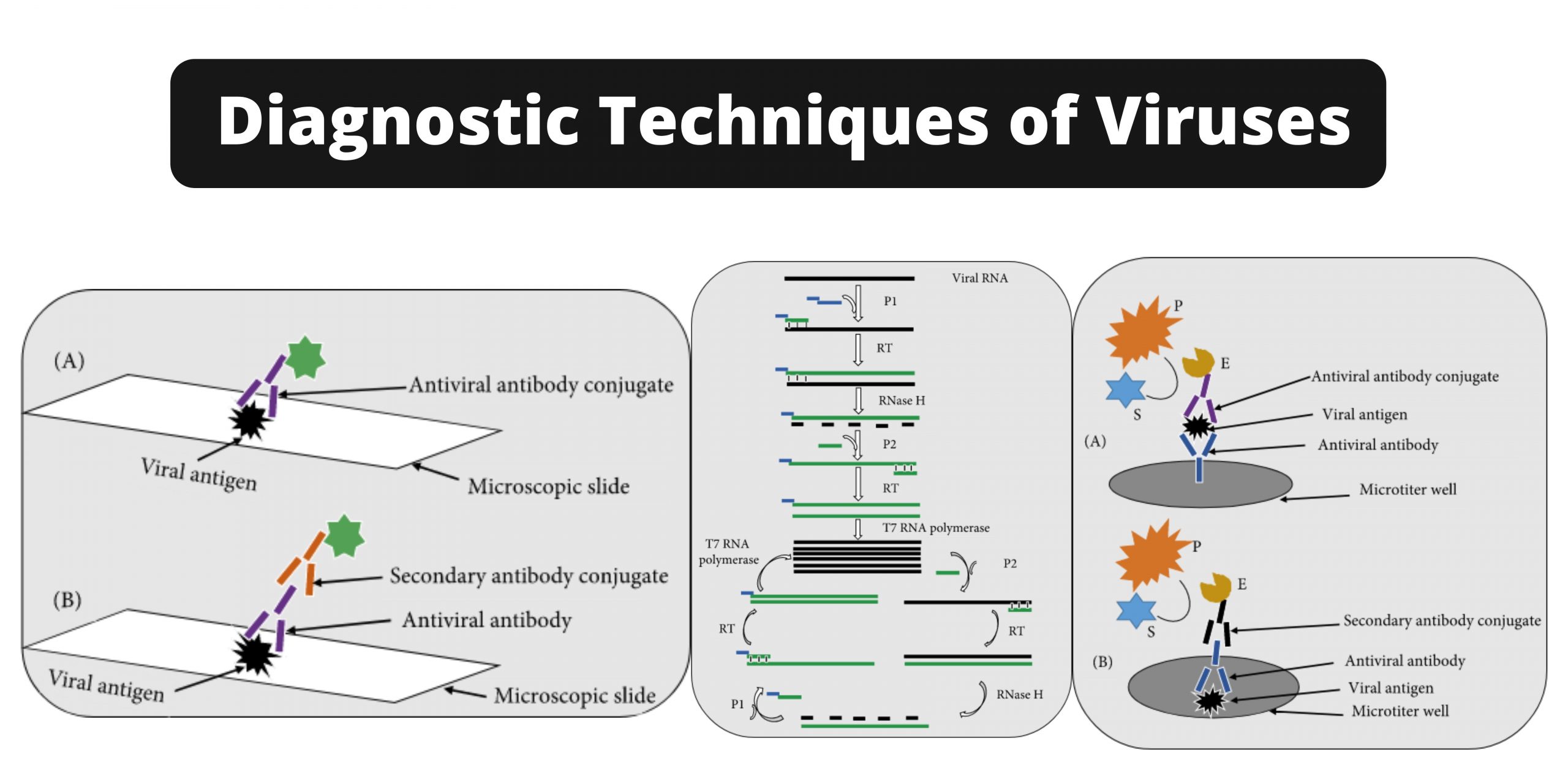
Lassa Virus – An Overview
Lassa virus is an RNA virus that is spread to humans through contact with the urine or feces of an infected Mastomys rat. It is a type of virus known as an arenavirus, and it is endemic in West Africa. The virus is named after the town of Lassa, in Borno State, Nigeria, where it … Read more