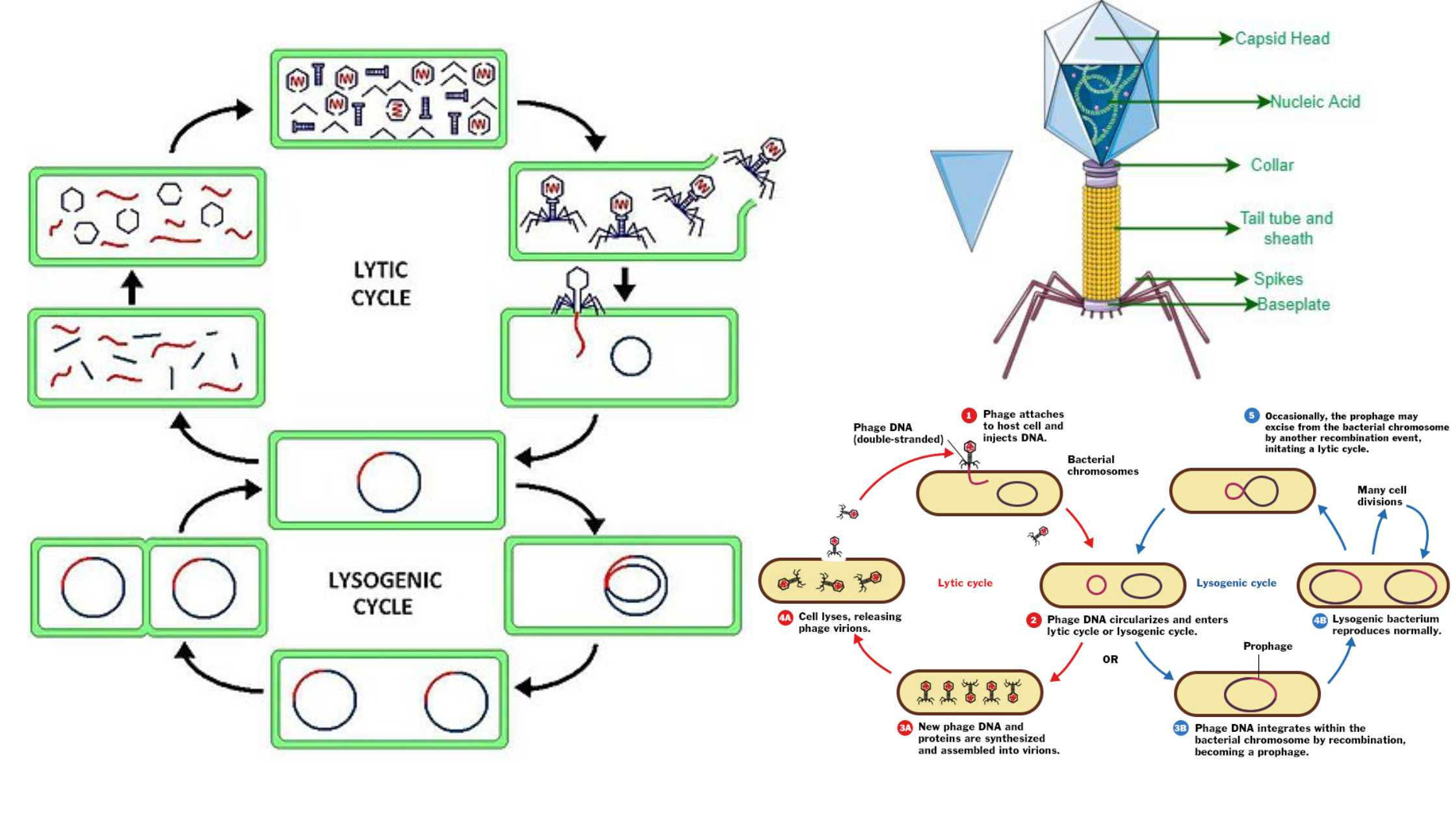
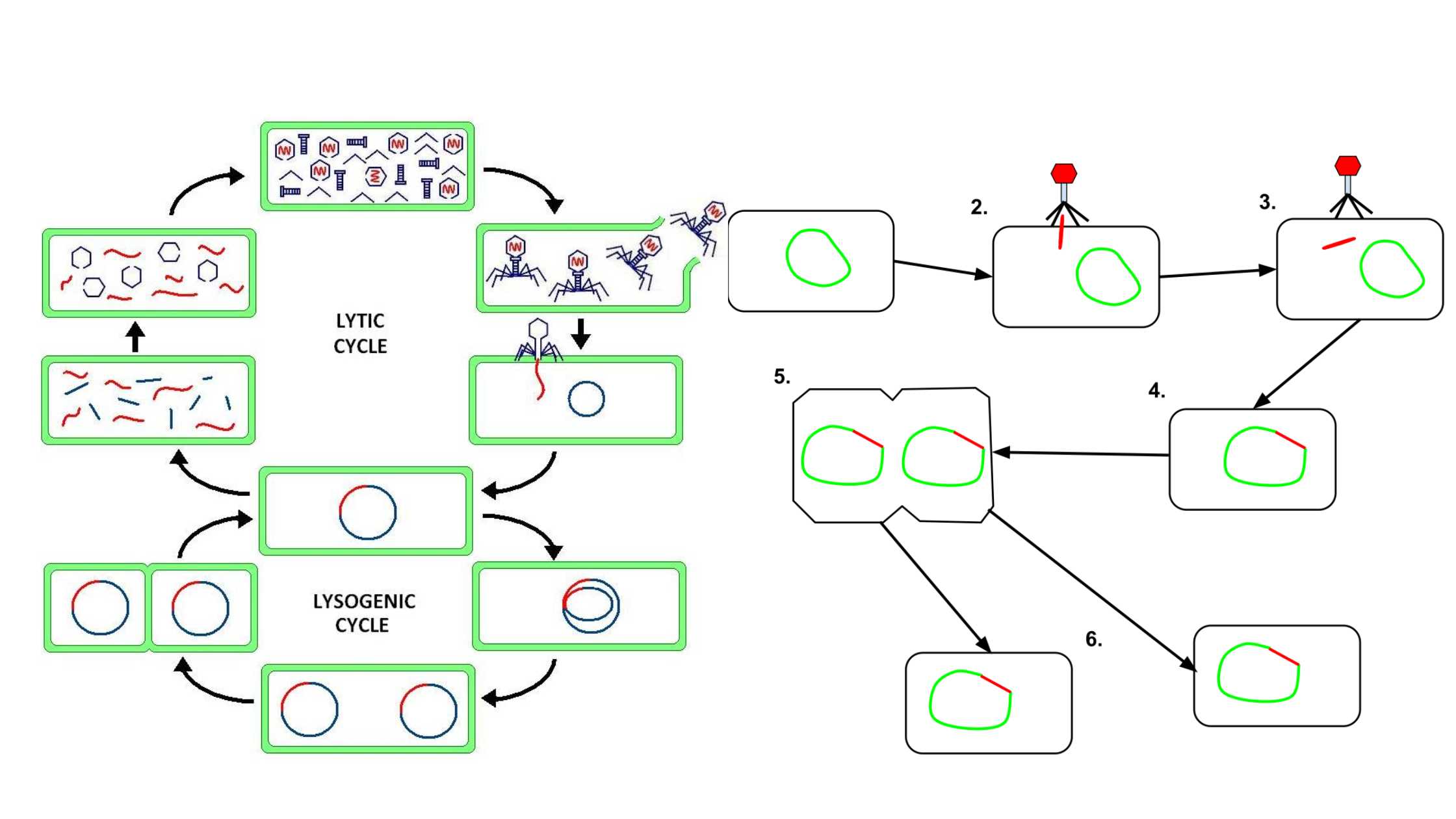
Lytic Cycle – Definition, Steps, Importance, Examples
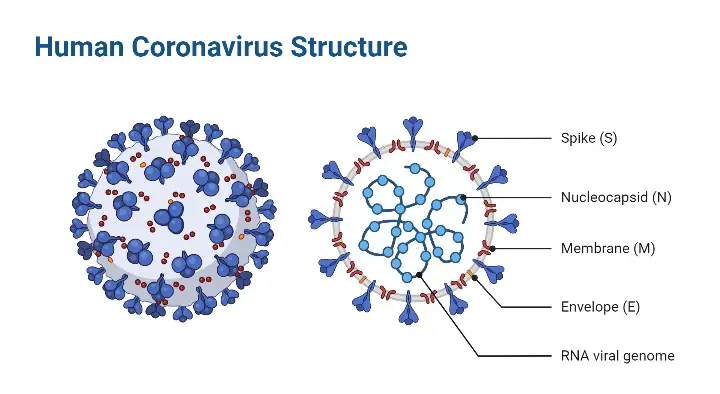
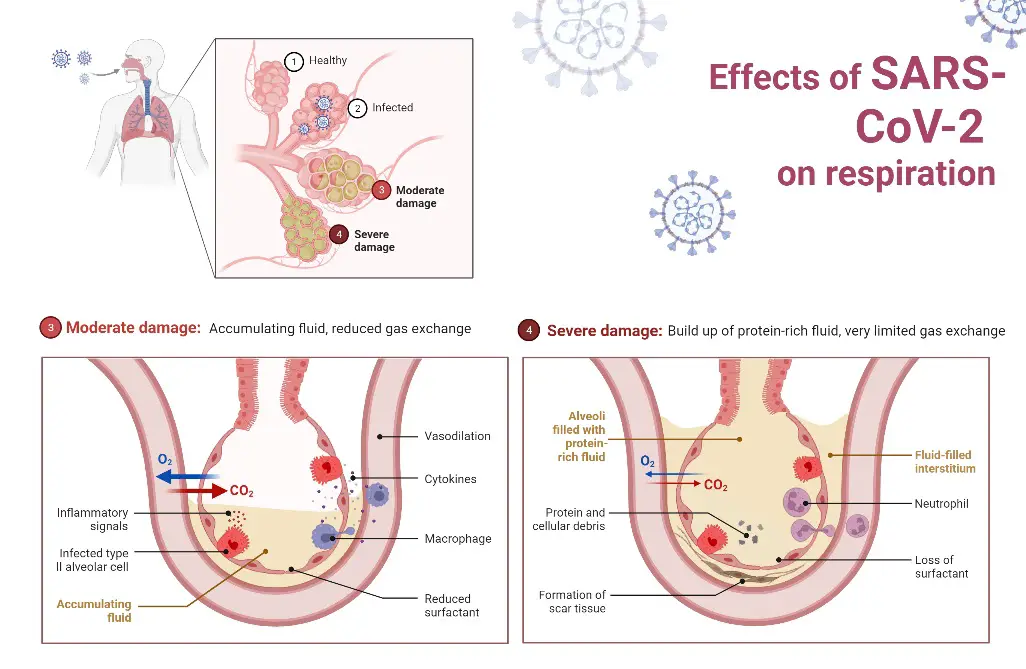
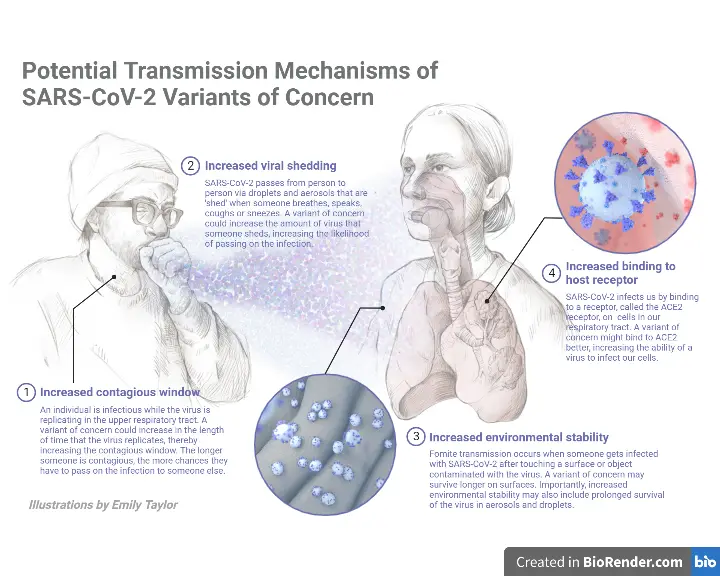
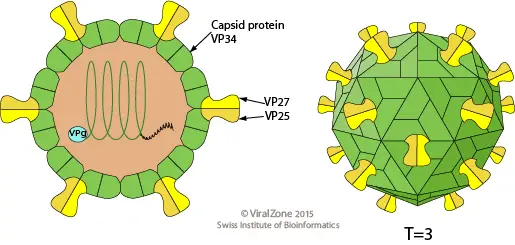
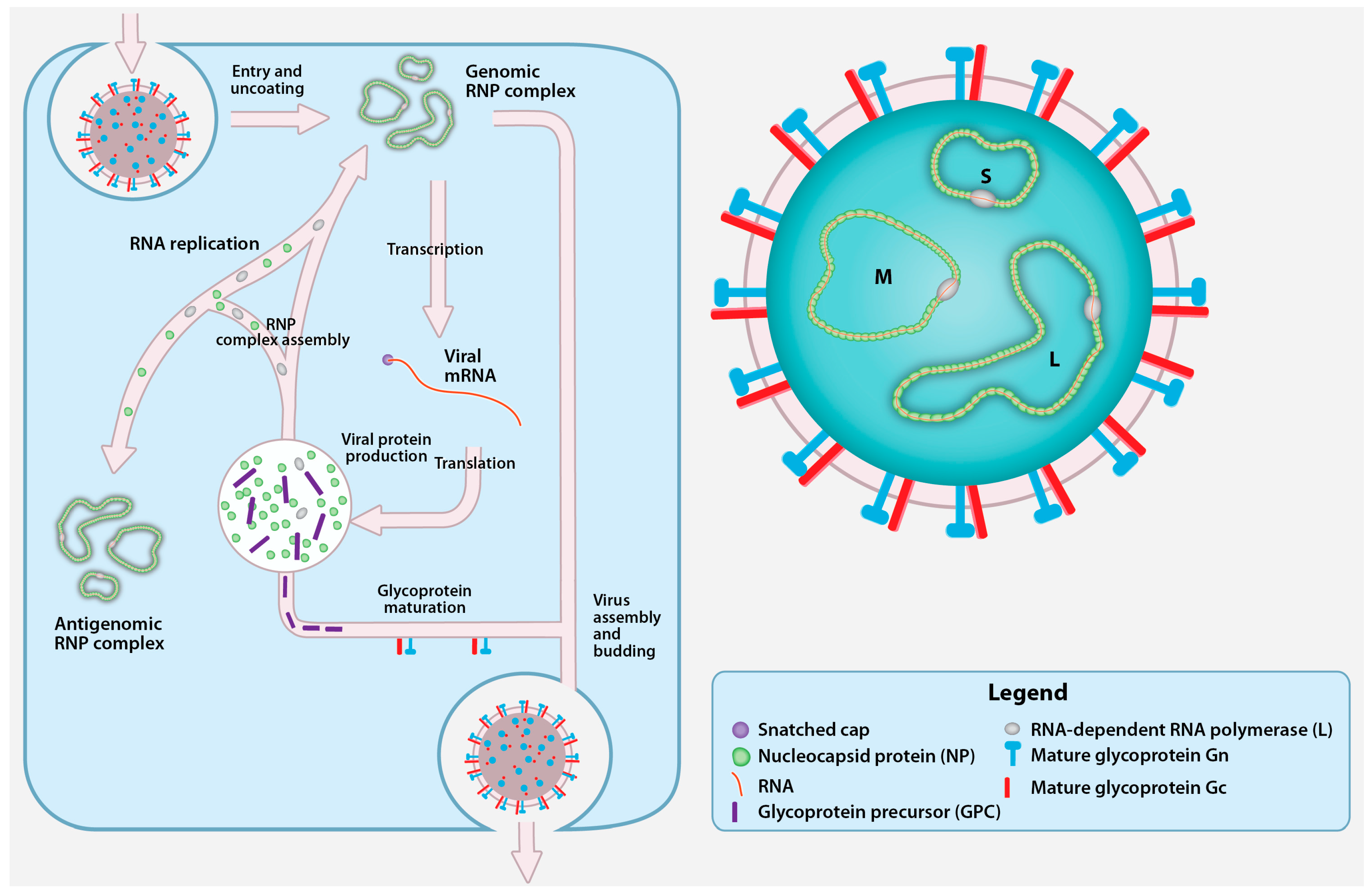
What is Lytic Cycle? Definition of Lytic Cycle The lytic cycle is a phase of viral reproduction wherein a virus infects a host cell, utilizes the cell’s machinery to replicate, and subsequently causes the cell to burst (lyse), releasing new virions to infect other cells. Bacteriophage(virus) Life cycle of bacteriophage Steps of the Lytic Cycle … Read more