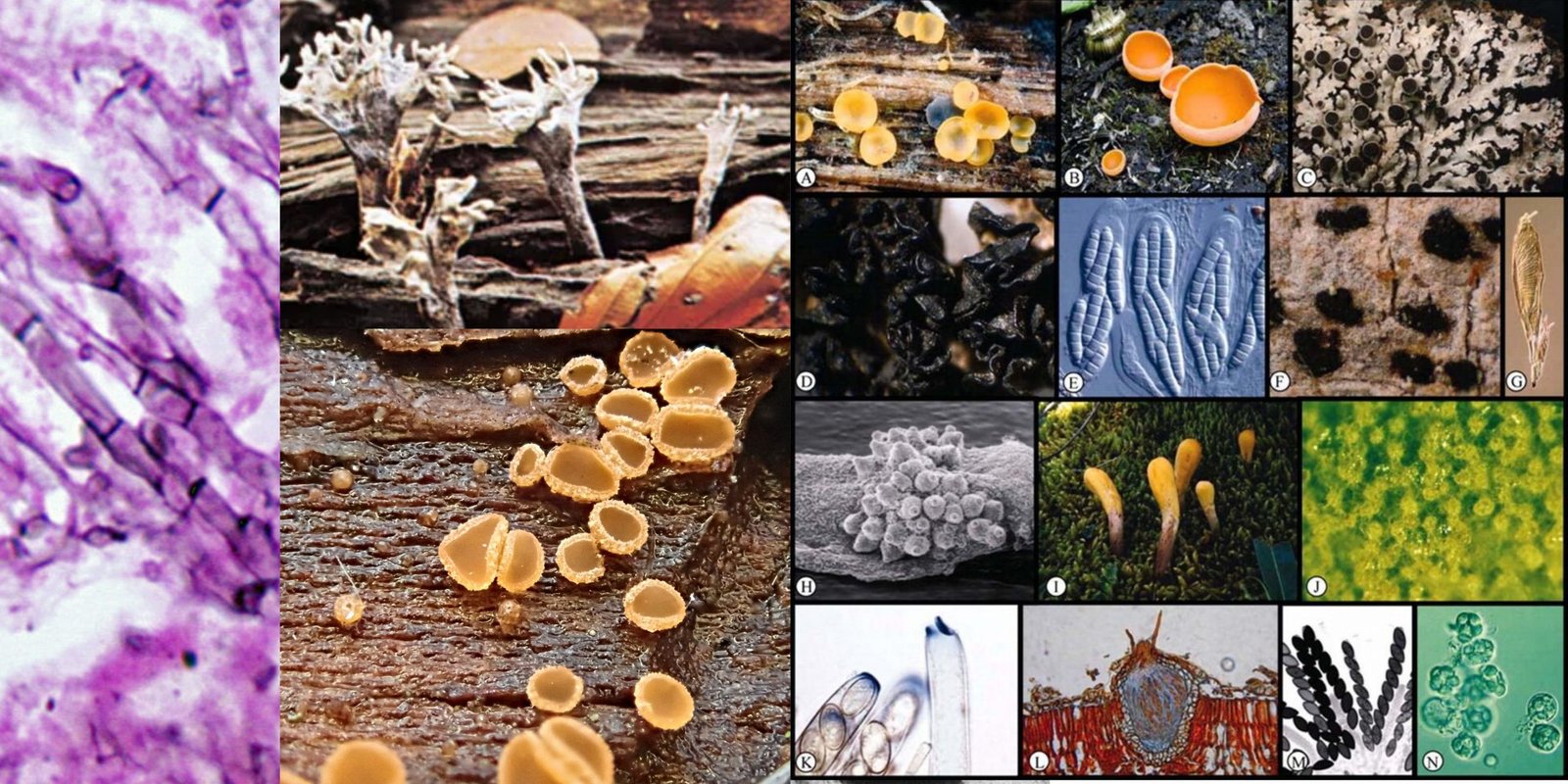
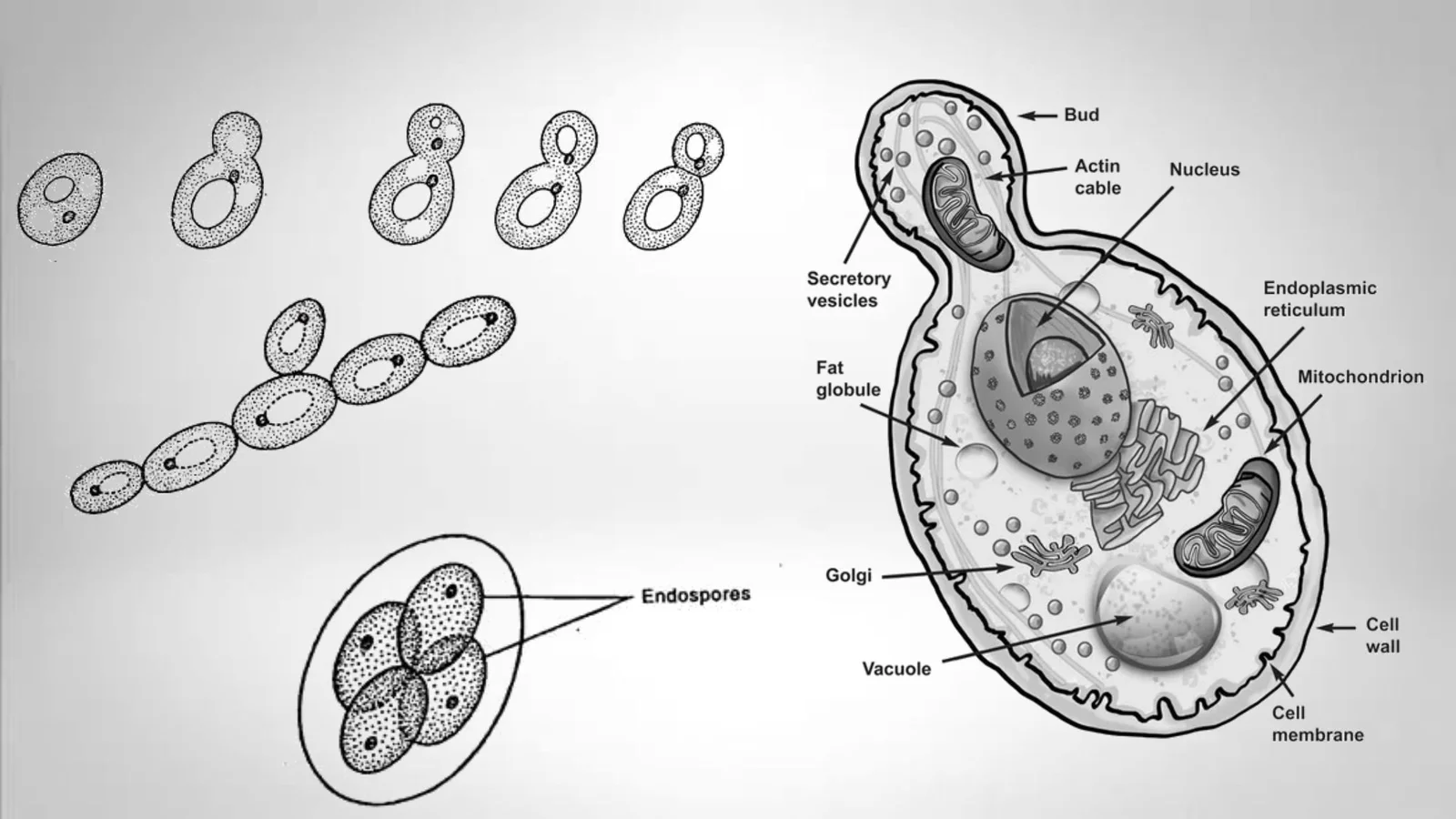
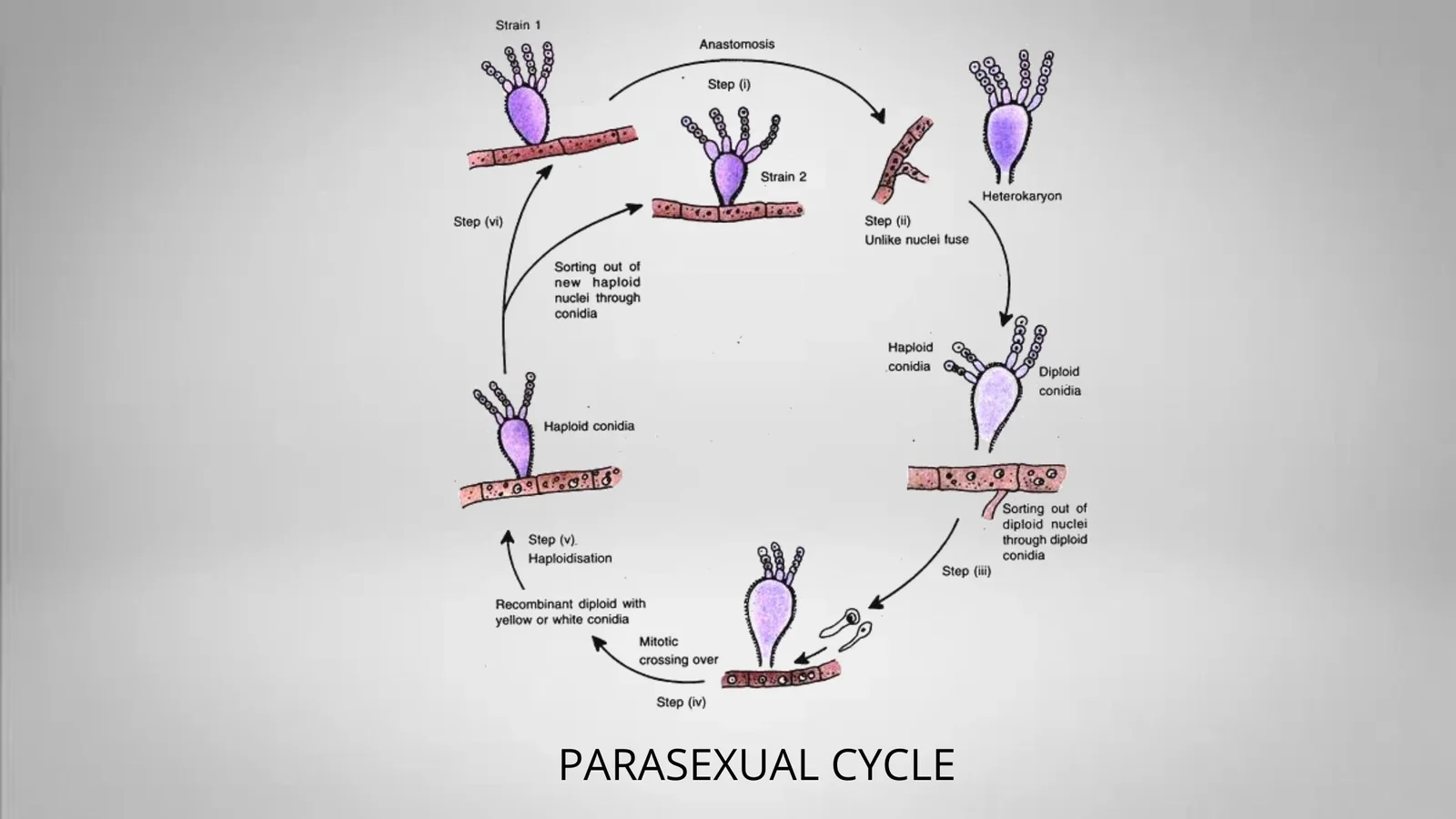
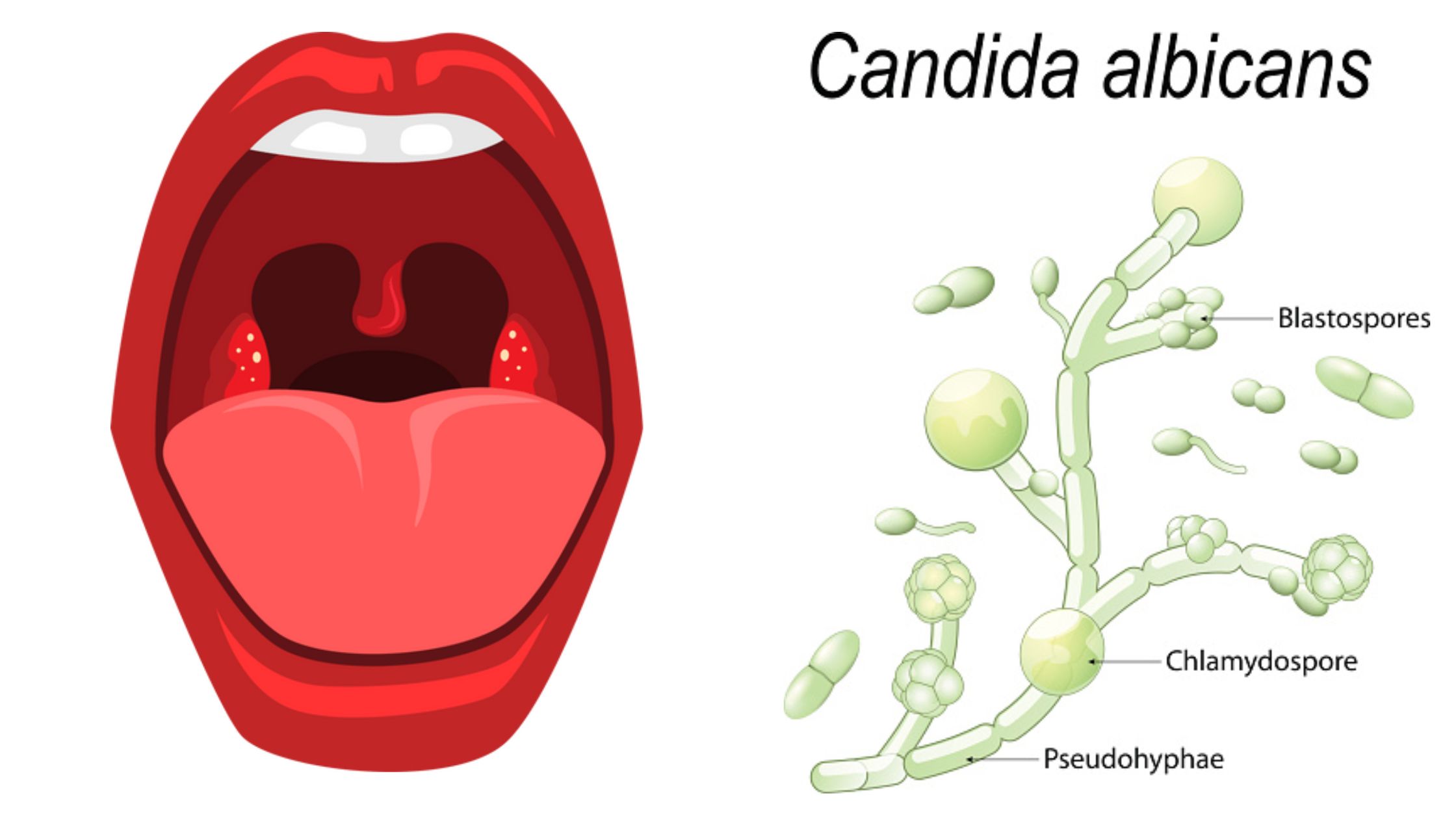
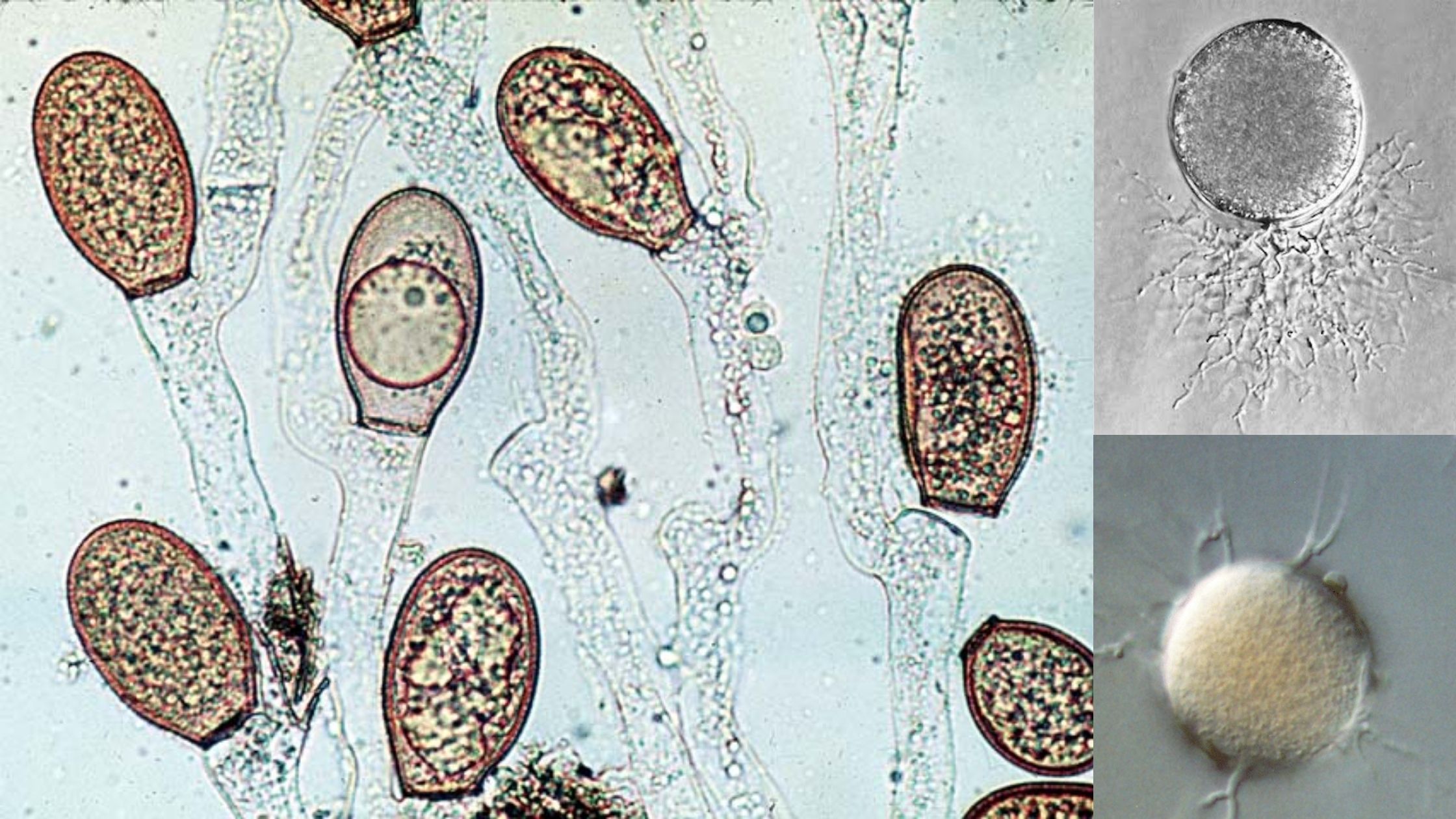
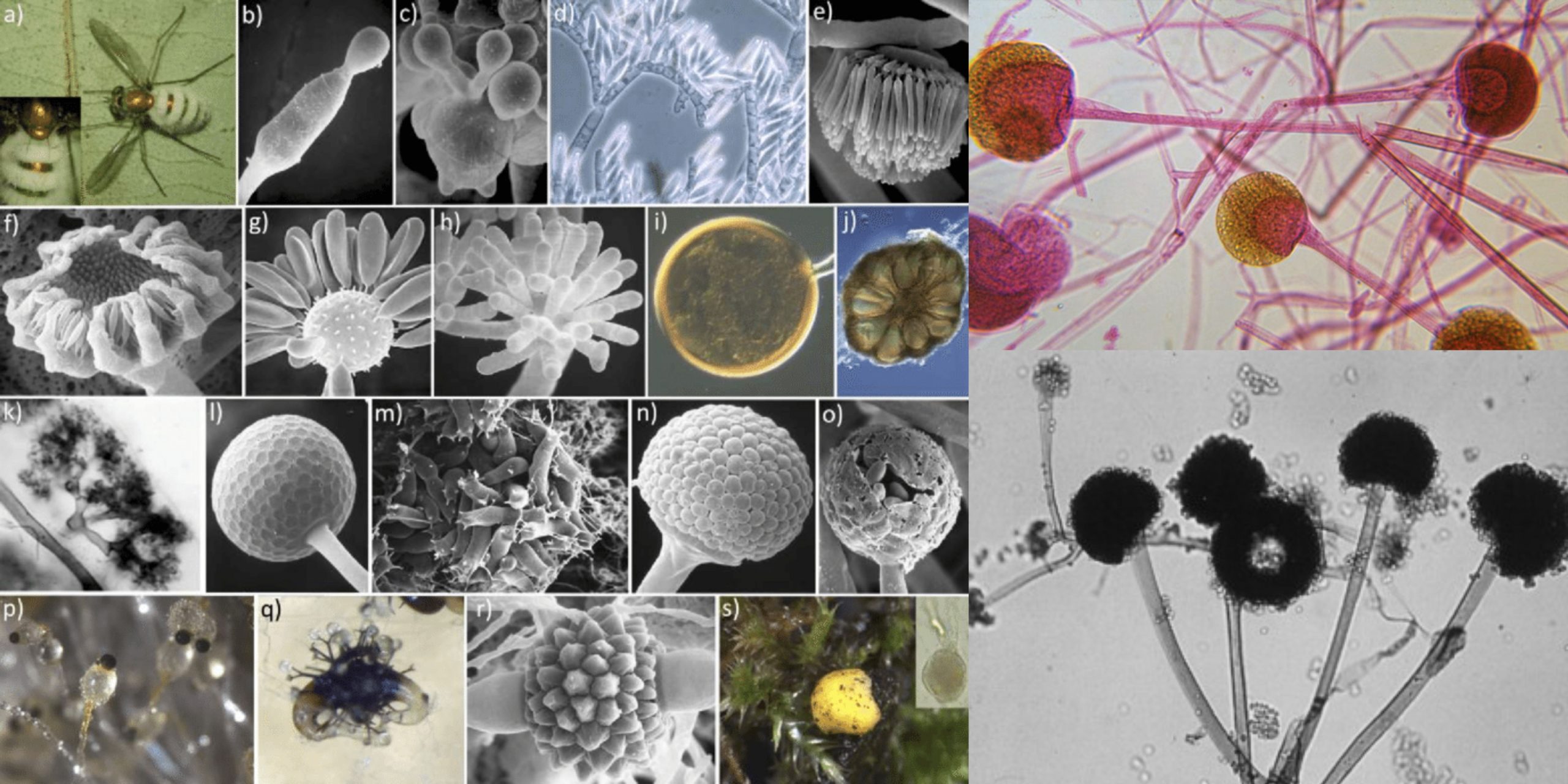
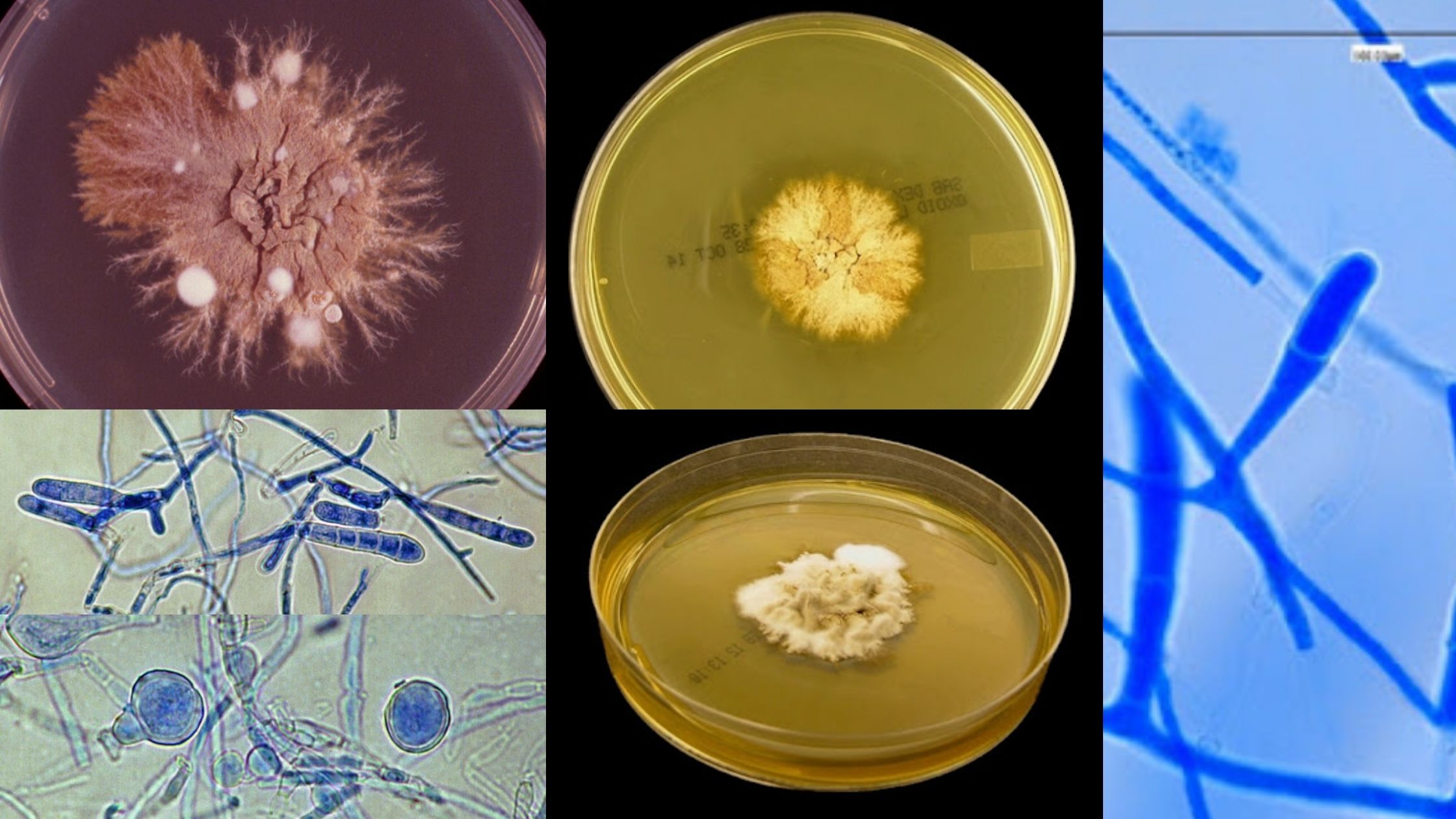
The Ascomycota sac fungi is monophyletic and comprises about 75% of the described fungi. It comprises the majority of fungi that mix together with algae to create lichens as well as the vast majority of fungi do not have morphological evidence for sexual reproduction. Among the Ascomycota are some famous fungi: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the yeast of commerce and foundation of the baking and brewing industries (not to mention molecular developmental biology), Penicillium chrysogenum, producer of penicillin, Morchella esculentum, the edible morel, and Neurospora crassa, the “one-gene-one-enzyme” organism.