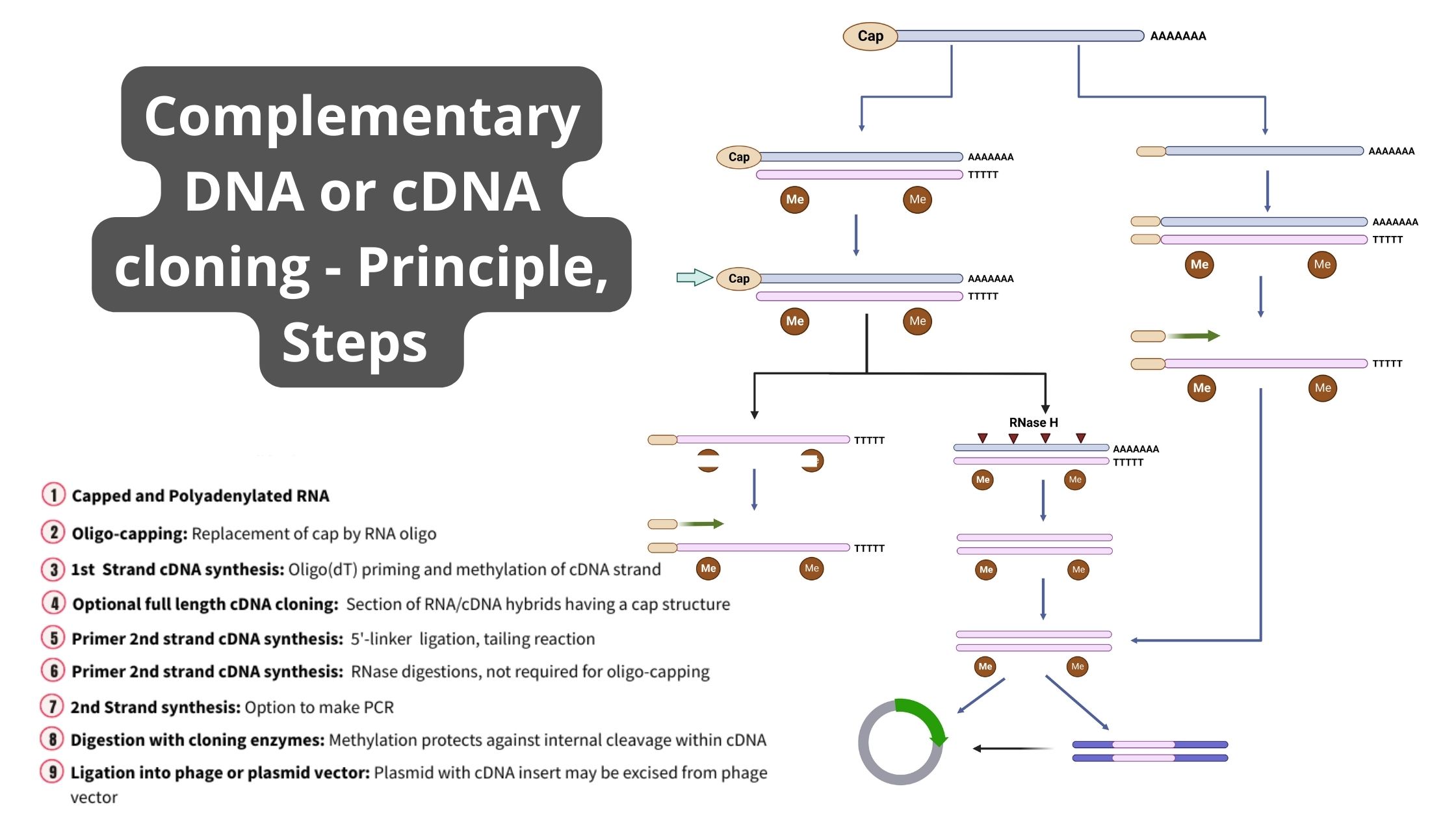
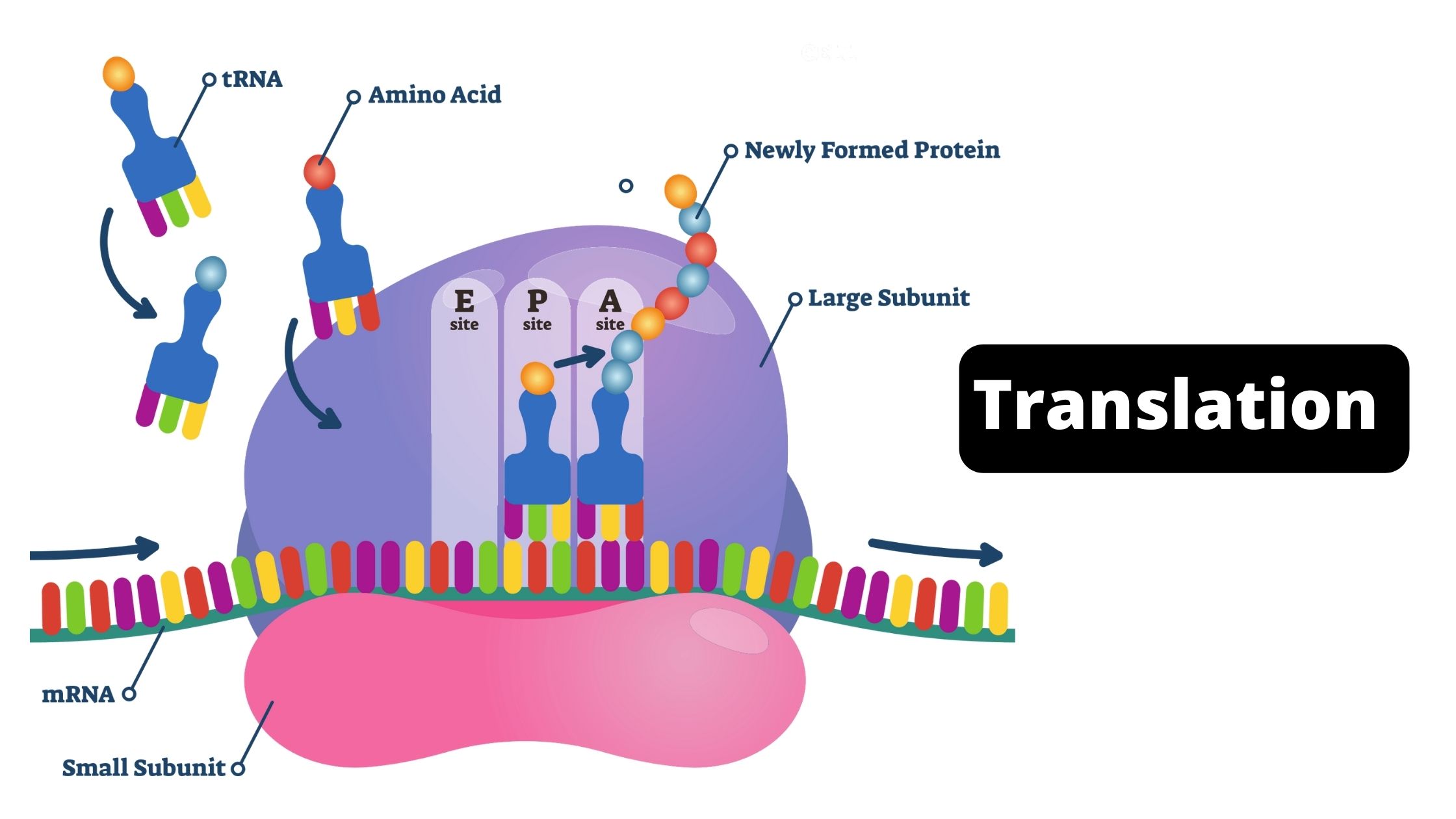
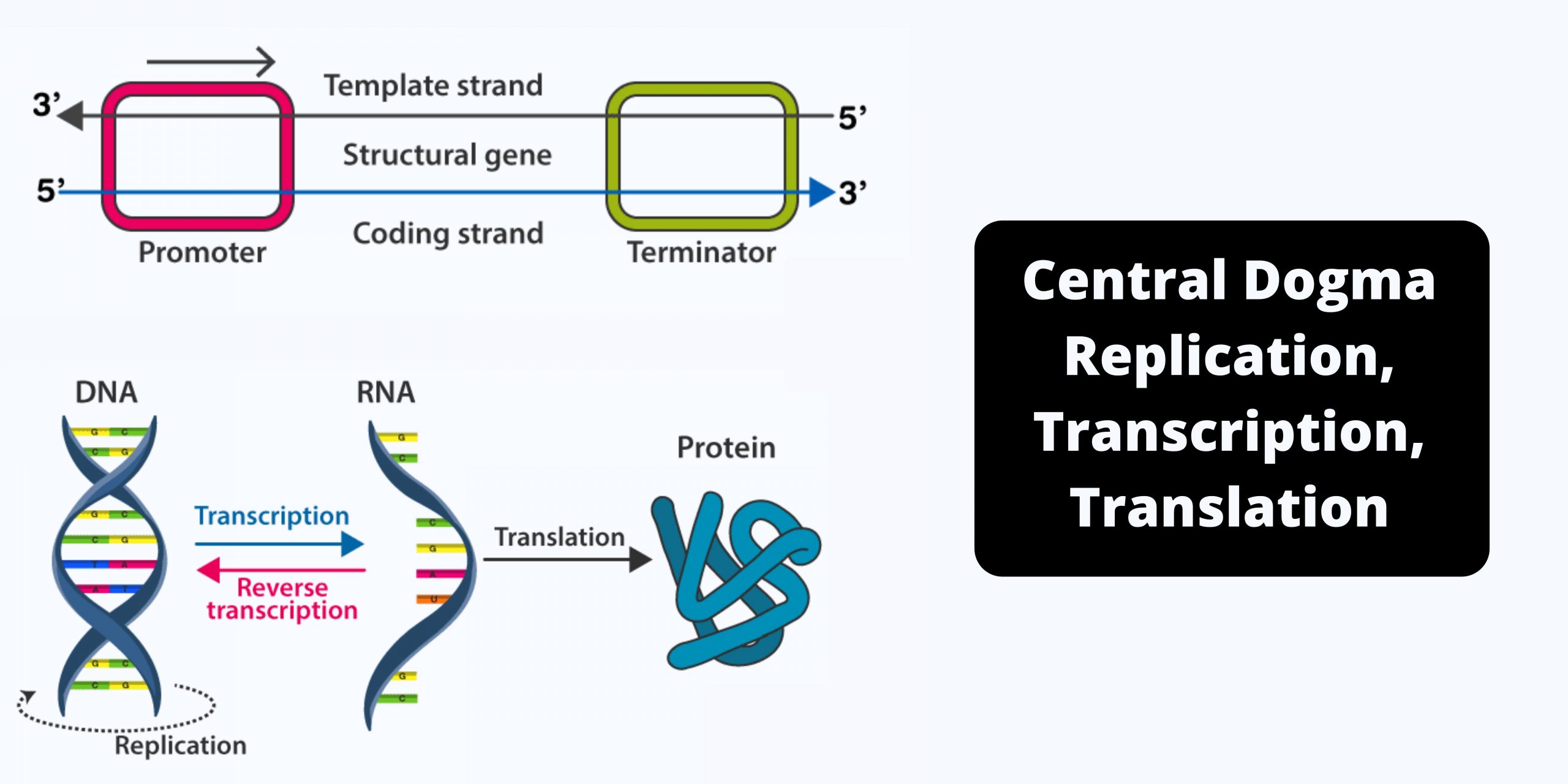
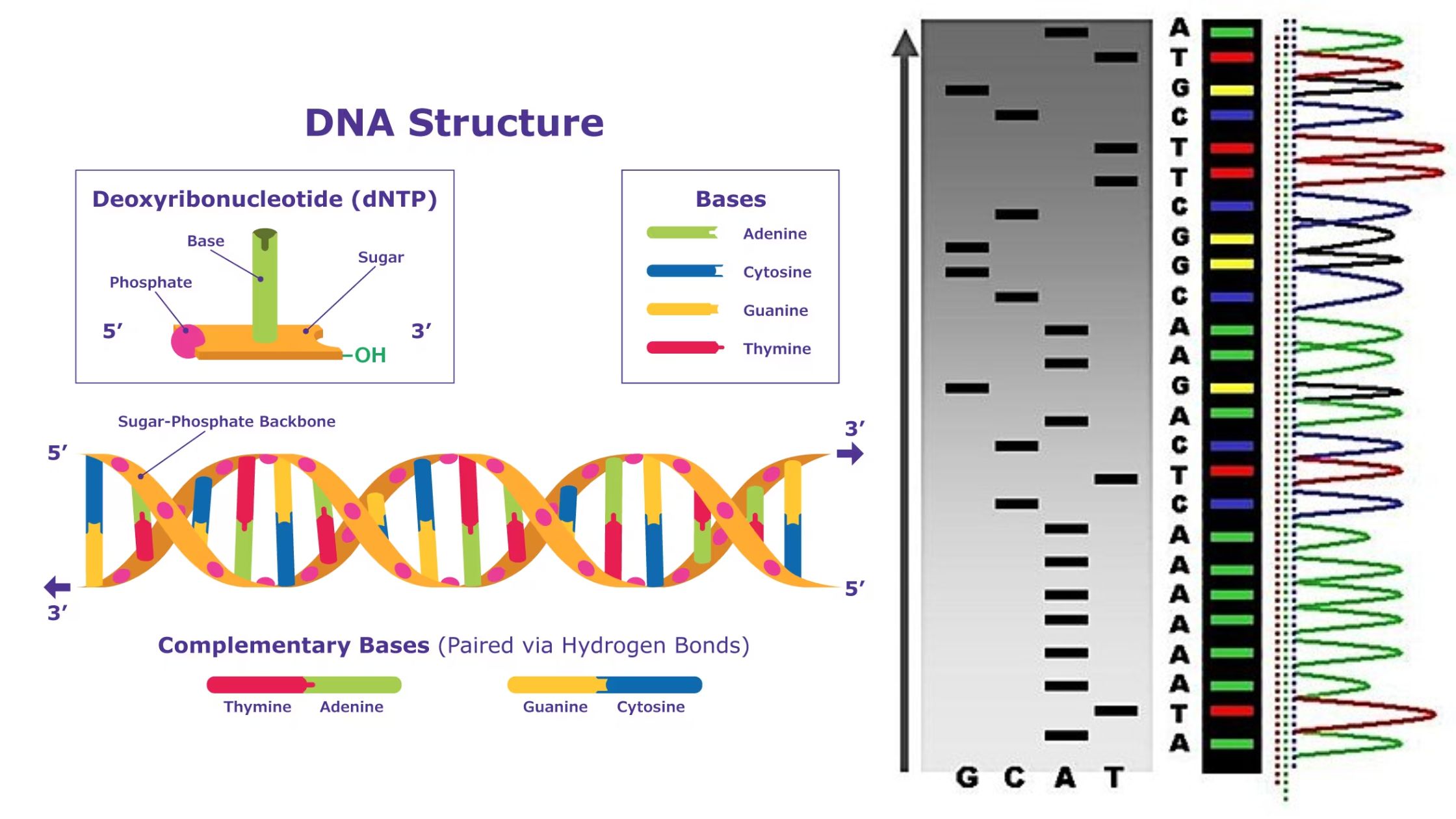
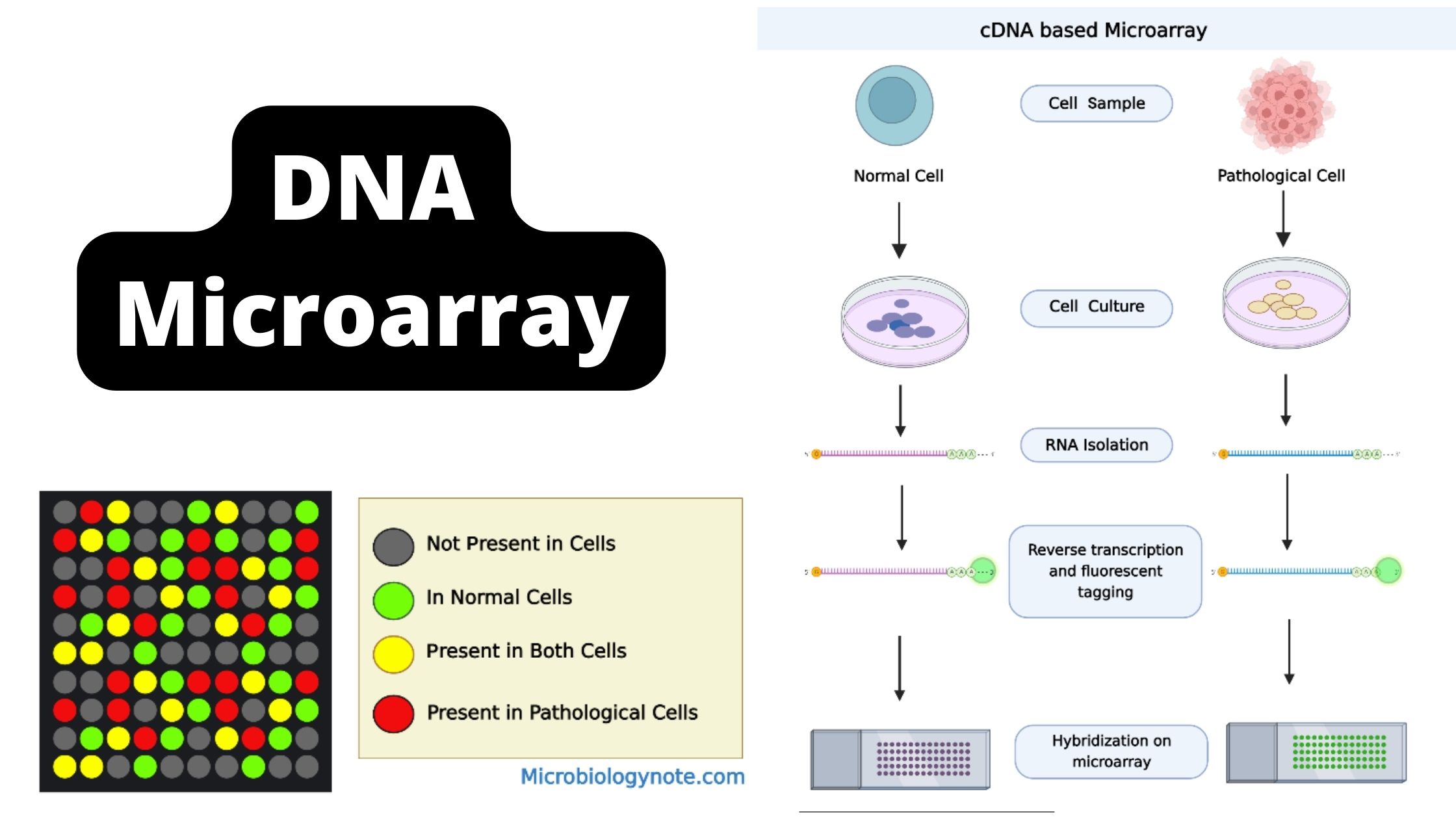
cDNA Cloning – Definition, Principle, Steps, Applications
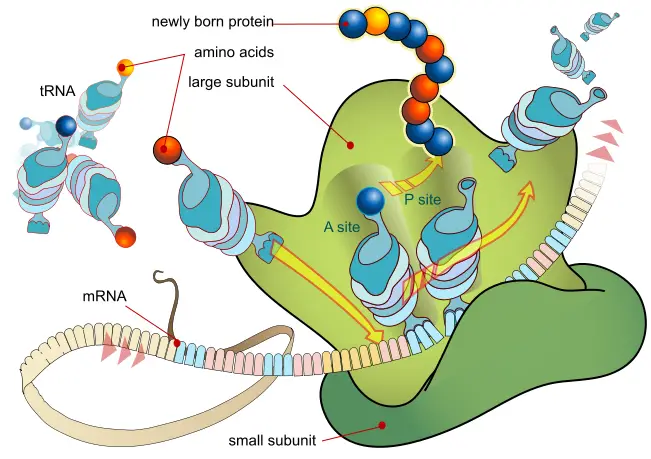
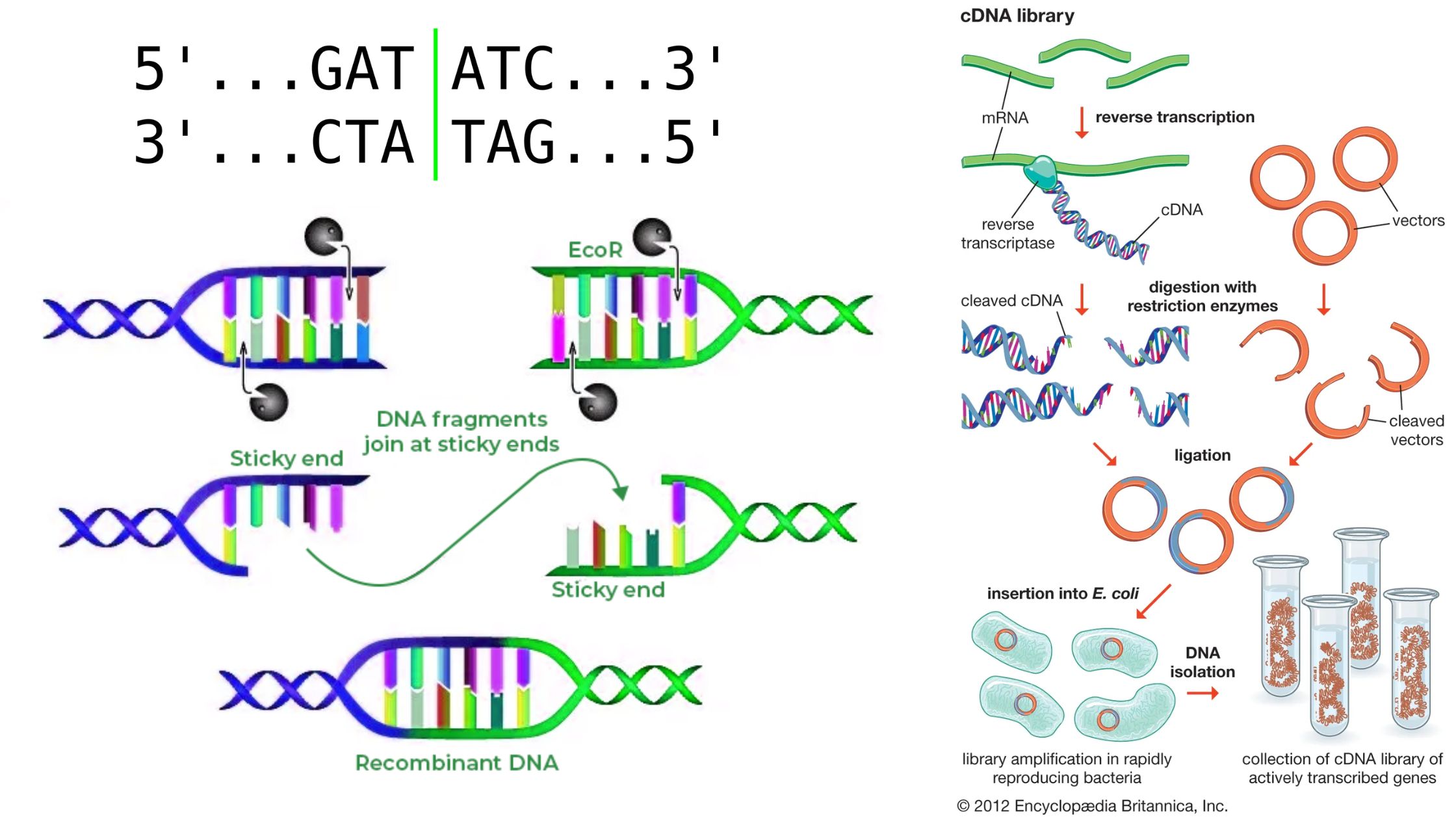
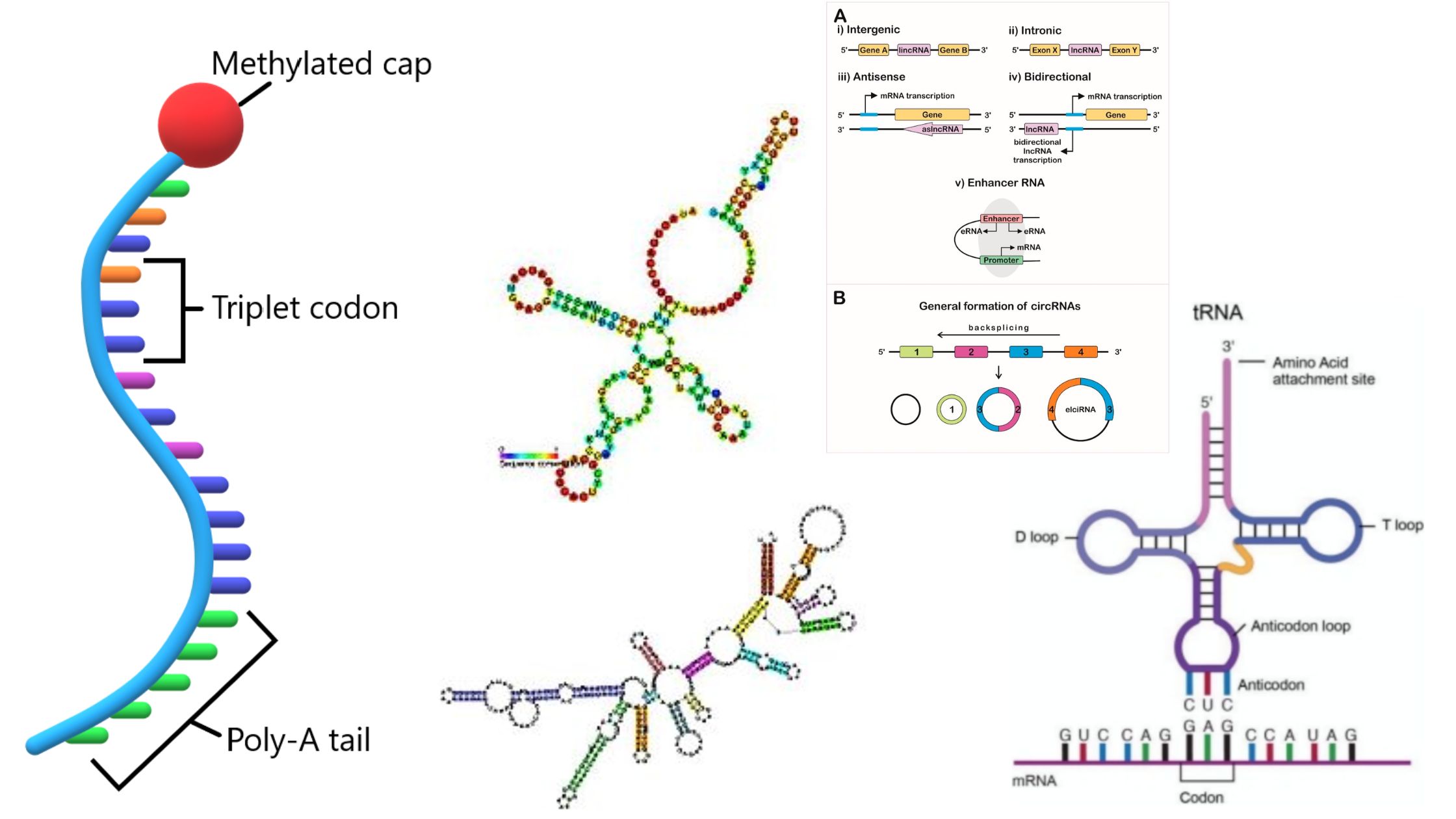
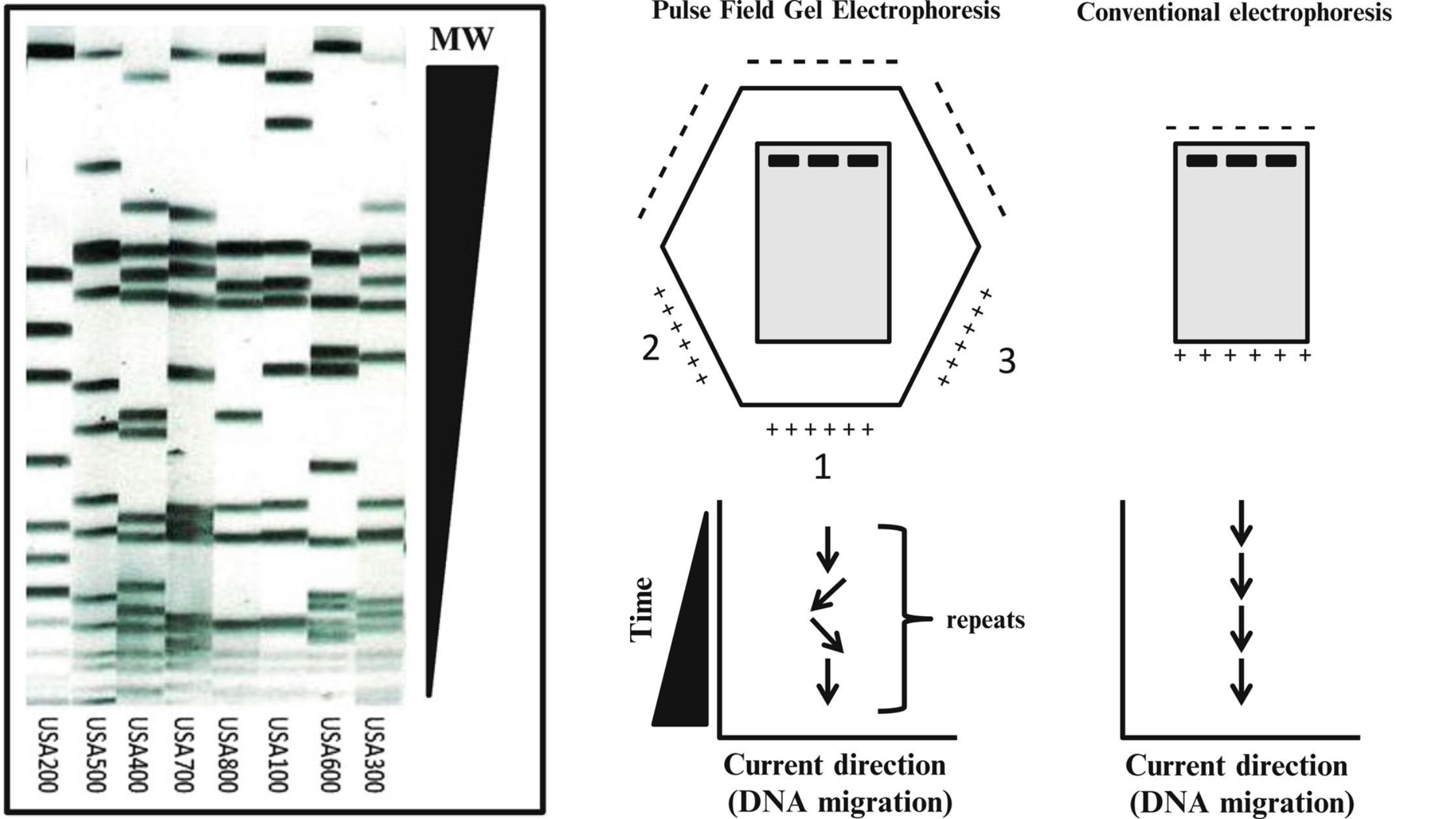
What is cDNA cloning? Definition of Complementary DNA or cDNA Complementary DNA (cDNA) is a form of DNA synthesized from a messenger RNA (mRNA) template through the action of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. It represents the coding sequence of genes and is commonly used in gene cloning and expression studies. cDNA Cloning Definition cDNA cloning … Read more