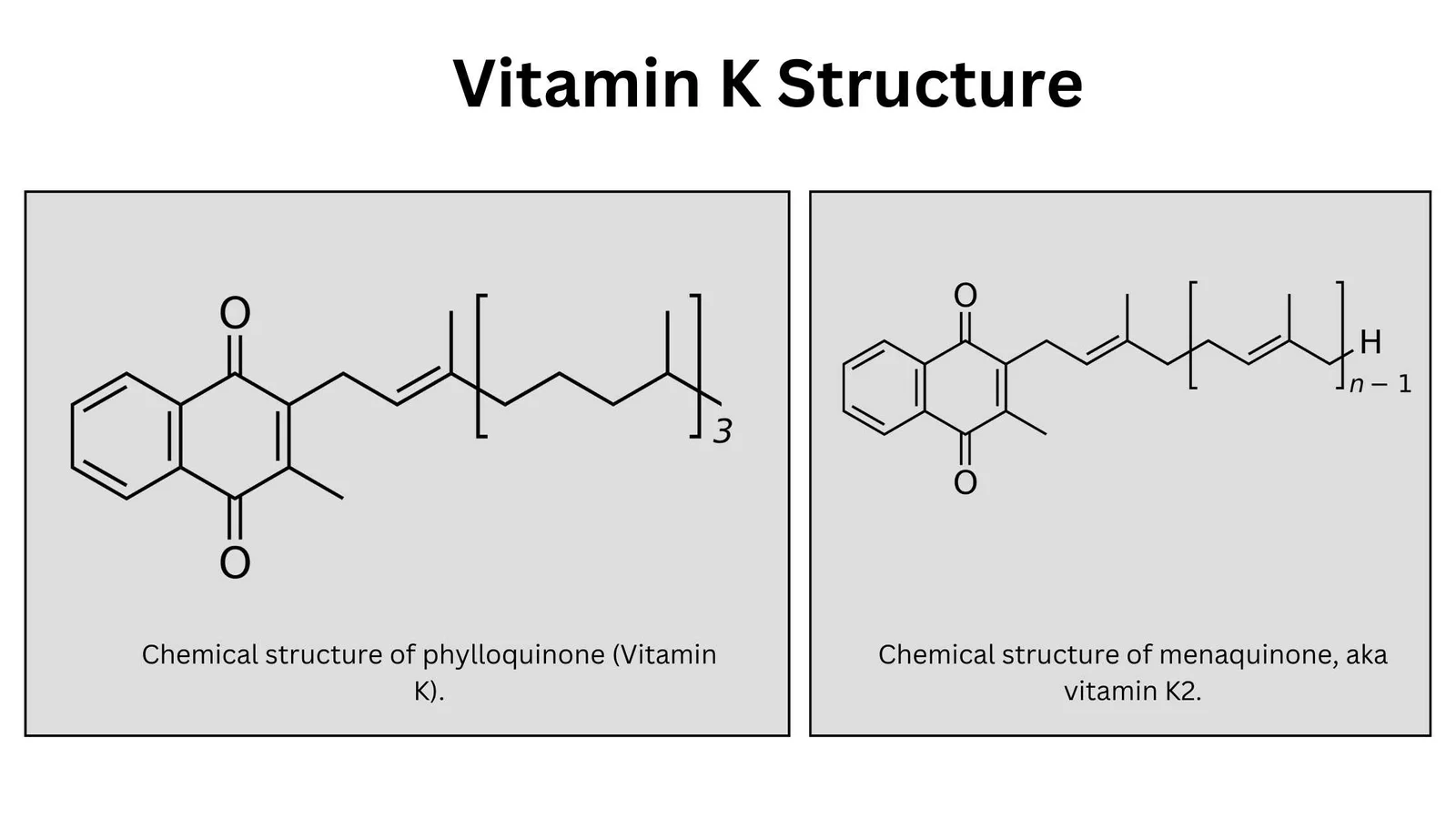
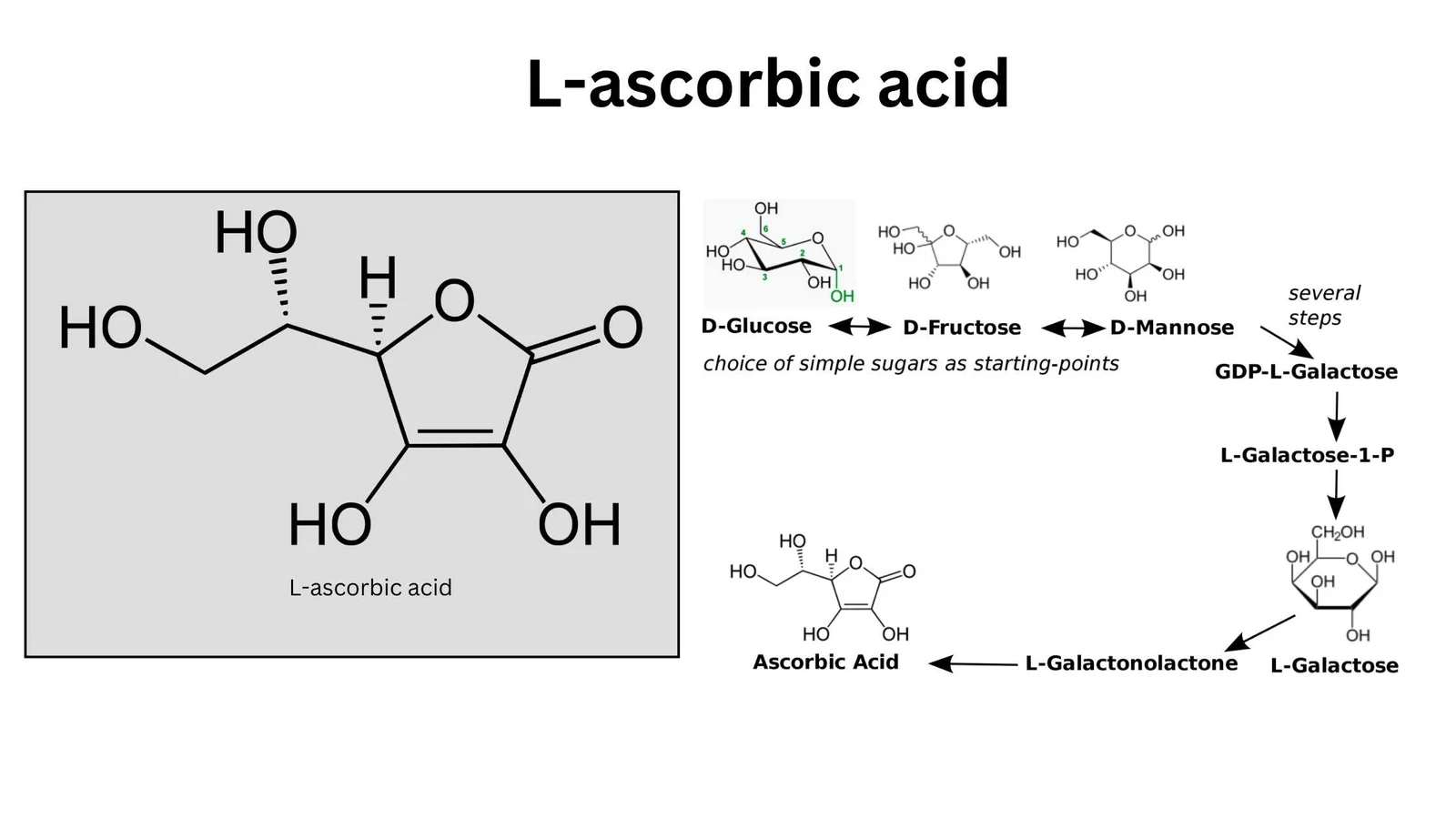
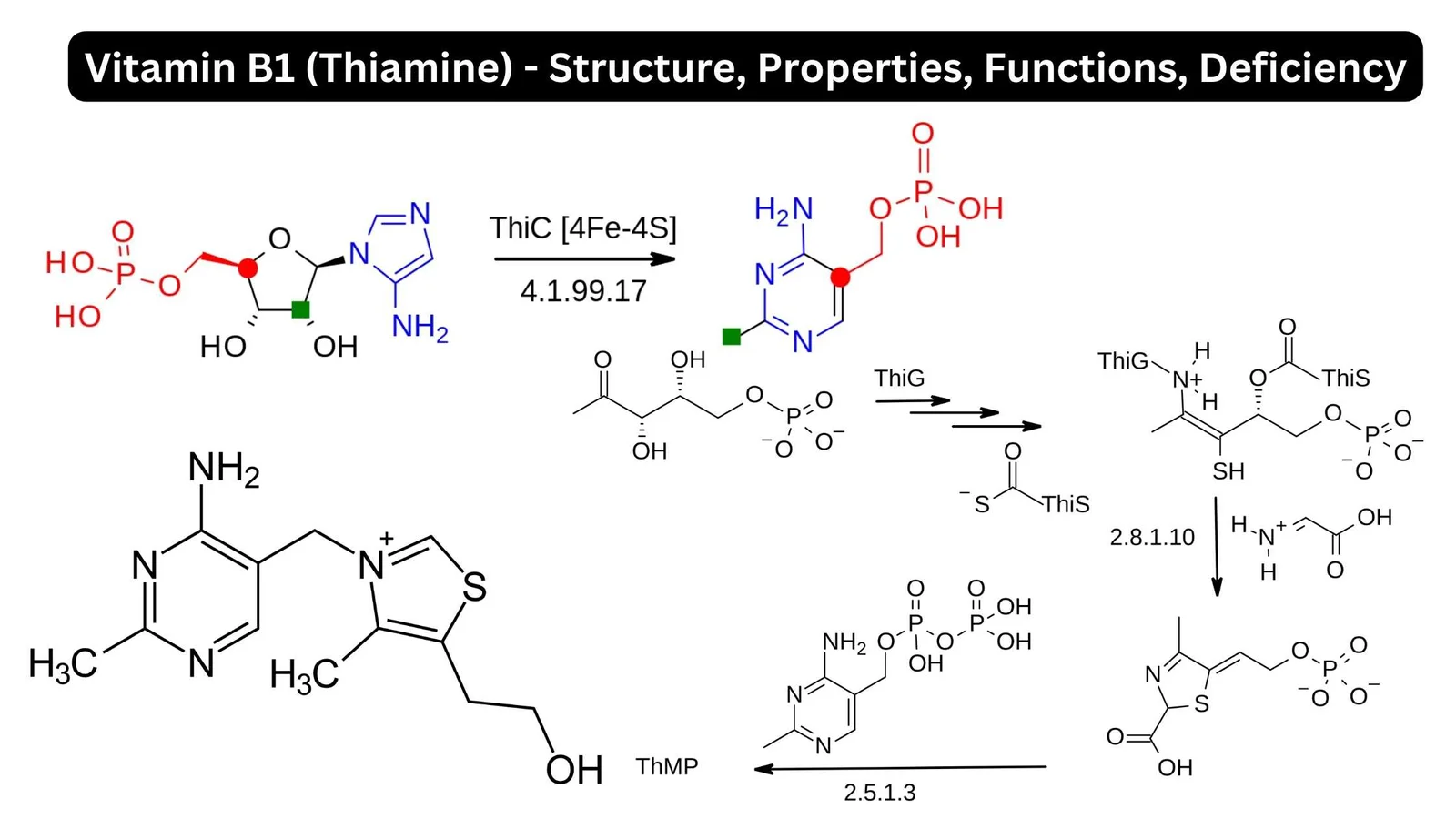
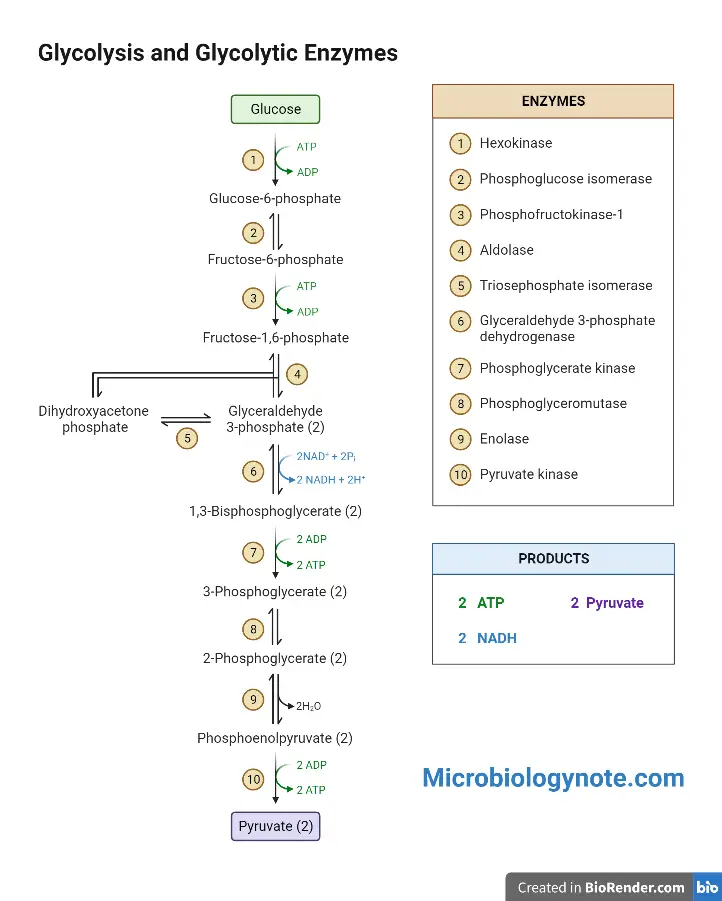
Vitamins – Classification, Source, Importance, Example
What are Vitamins? Definition of Vitamins Vitamins are organic molecules essential in small amounts for an organism’s proper metabolic function, which are typically obtained through the diet as they cannot be synthesized by the organism in sufficient quantities. History and nomenclature of Vitamins The history and nomenclature of vitamins have their roots in the early … Read more