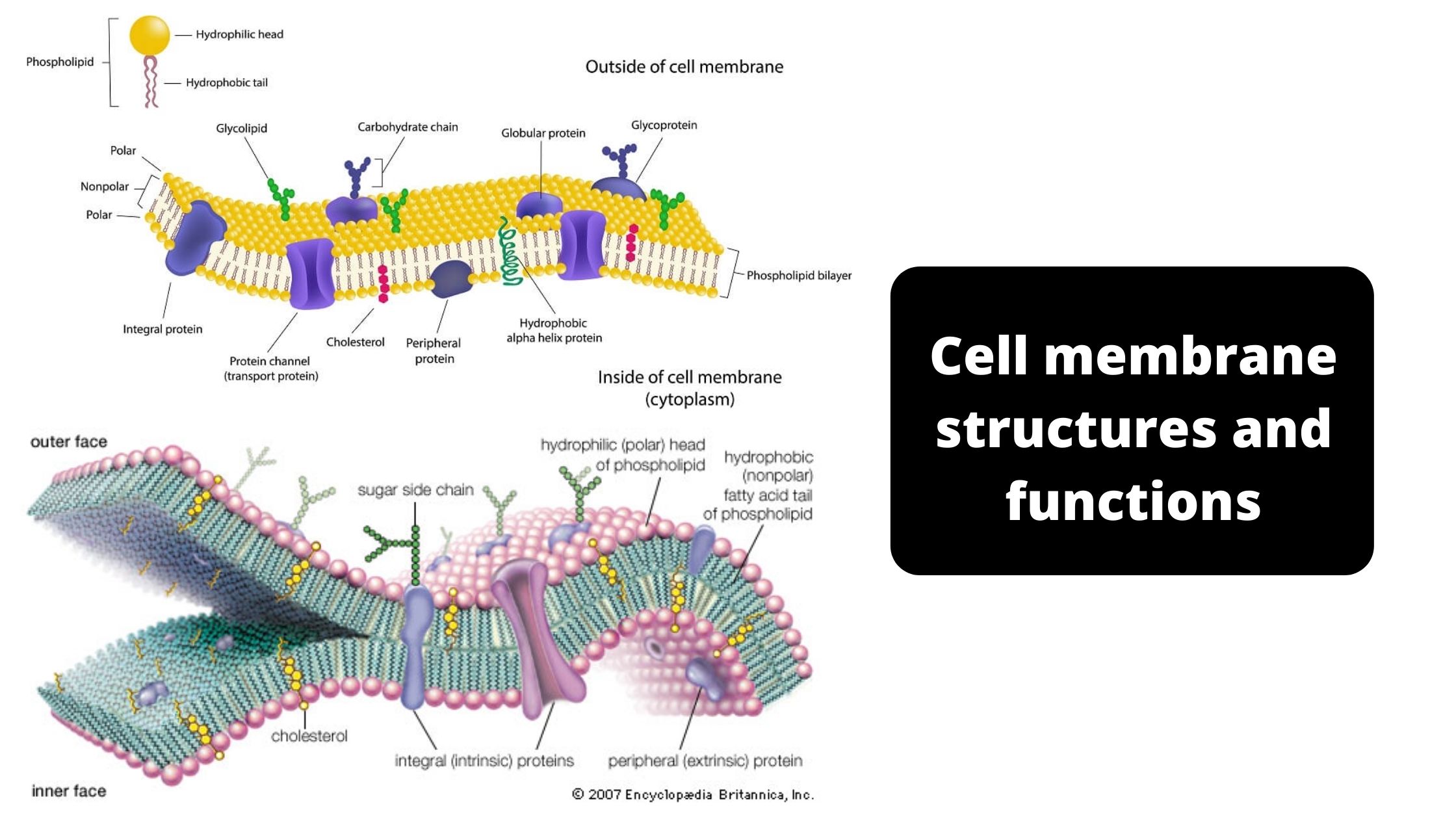
Cell membrane (Plasma Membrane) Structures and Functions
What is Cell membrane or Plasma Membrane? Definition of Cell membrane or Plasma Membrane The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a semi-permeable biological barrier that surrounds and protects the cell’s interior from the external environment, regulating the passage of molecules in and out of the cell. Cell Membrane Composition The cell … Read more