L-form bacteria – Definition, Size and shape, Culturing , Applications
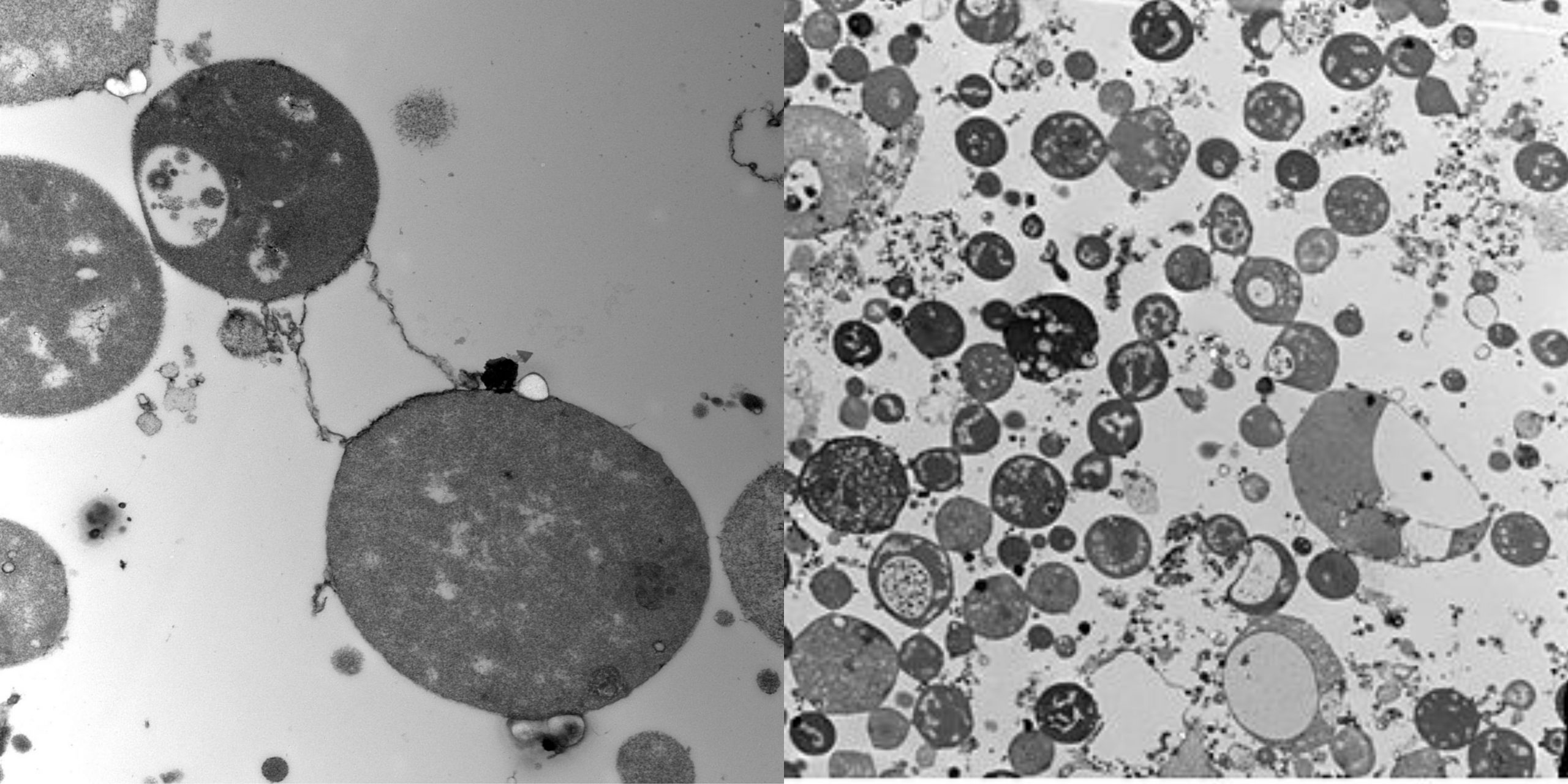
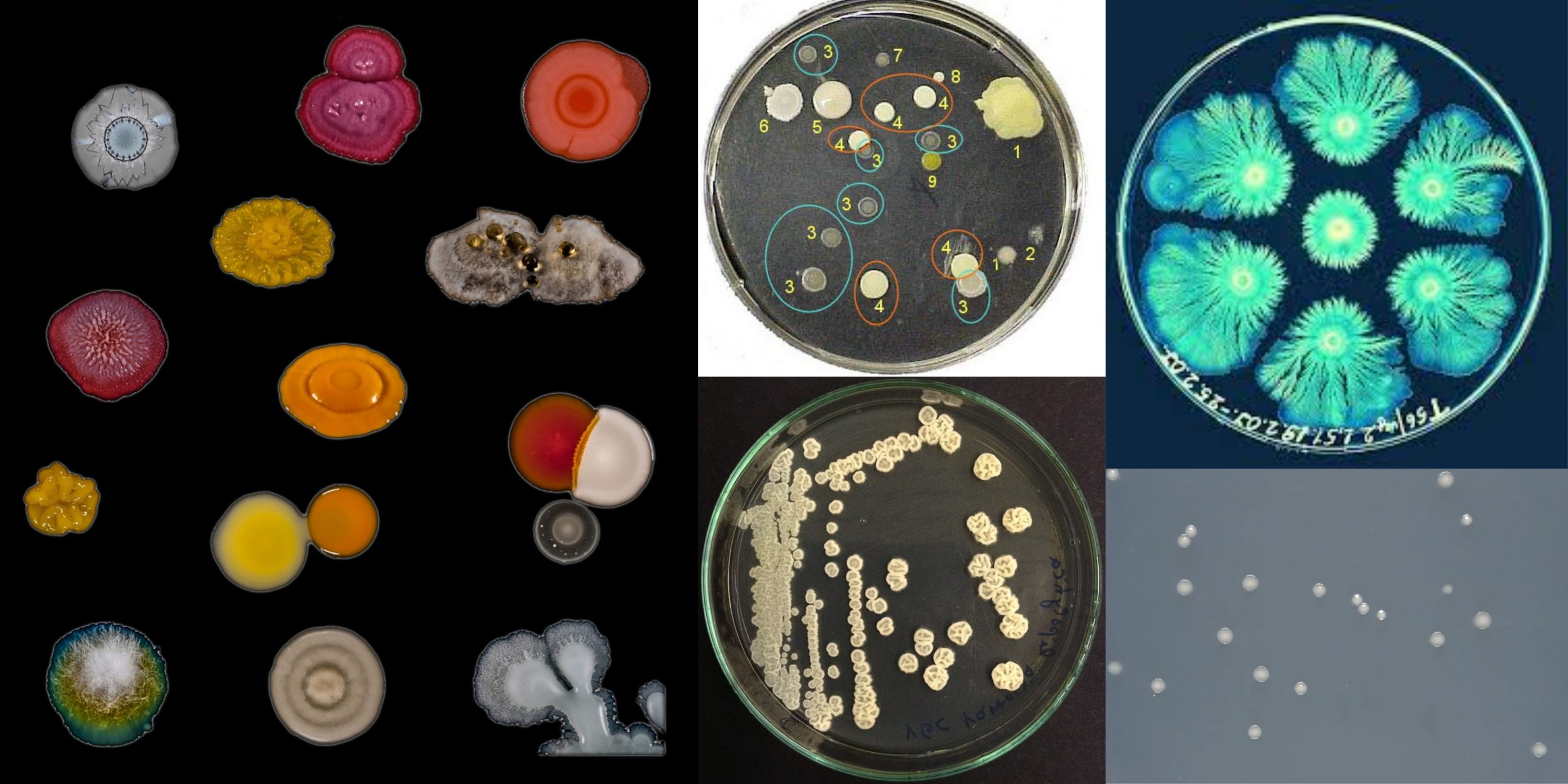
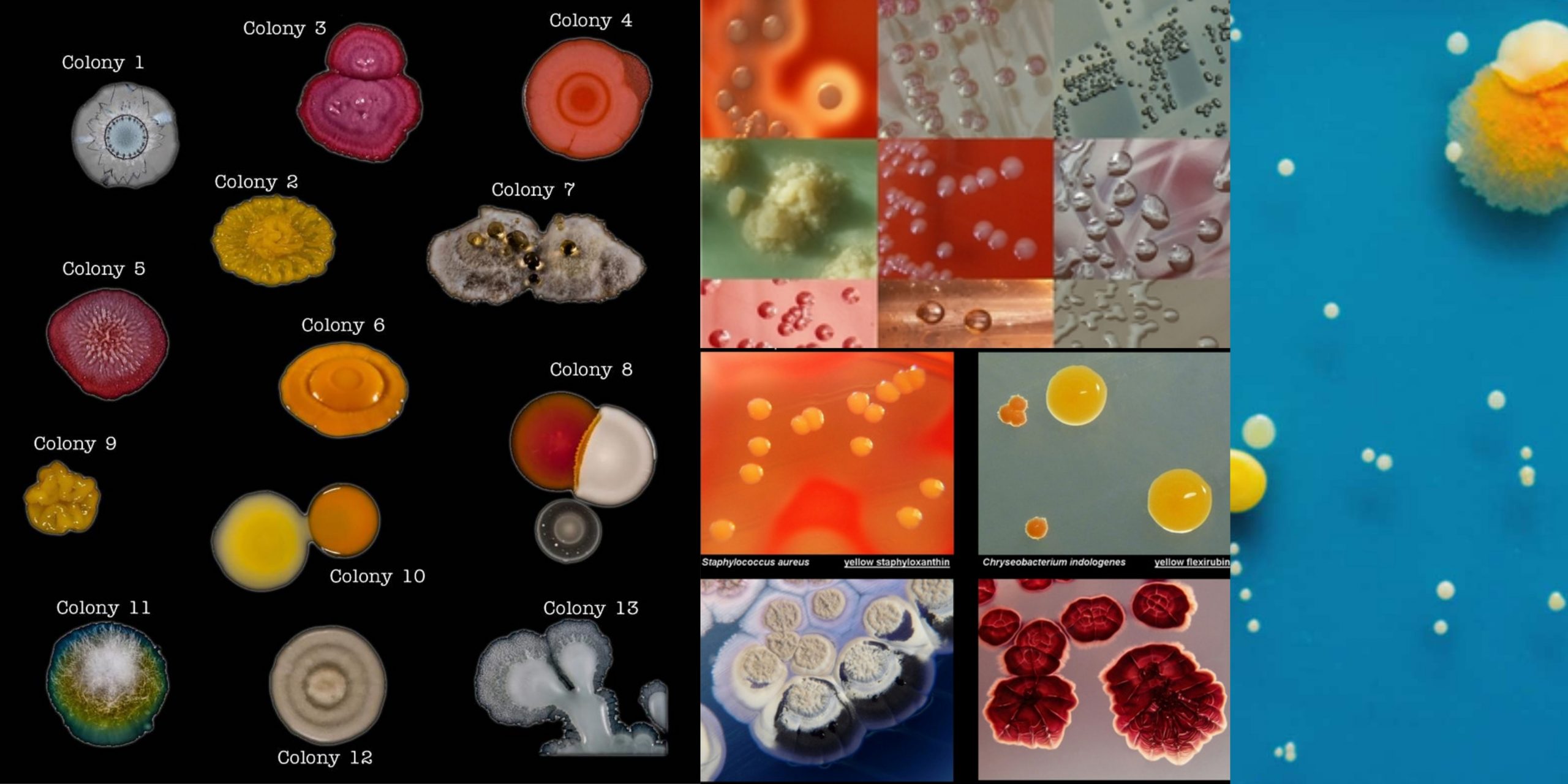
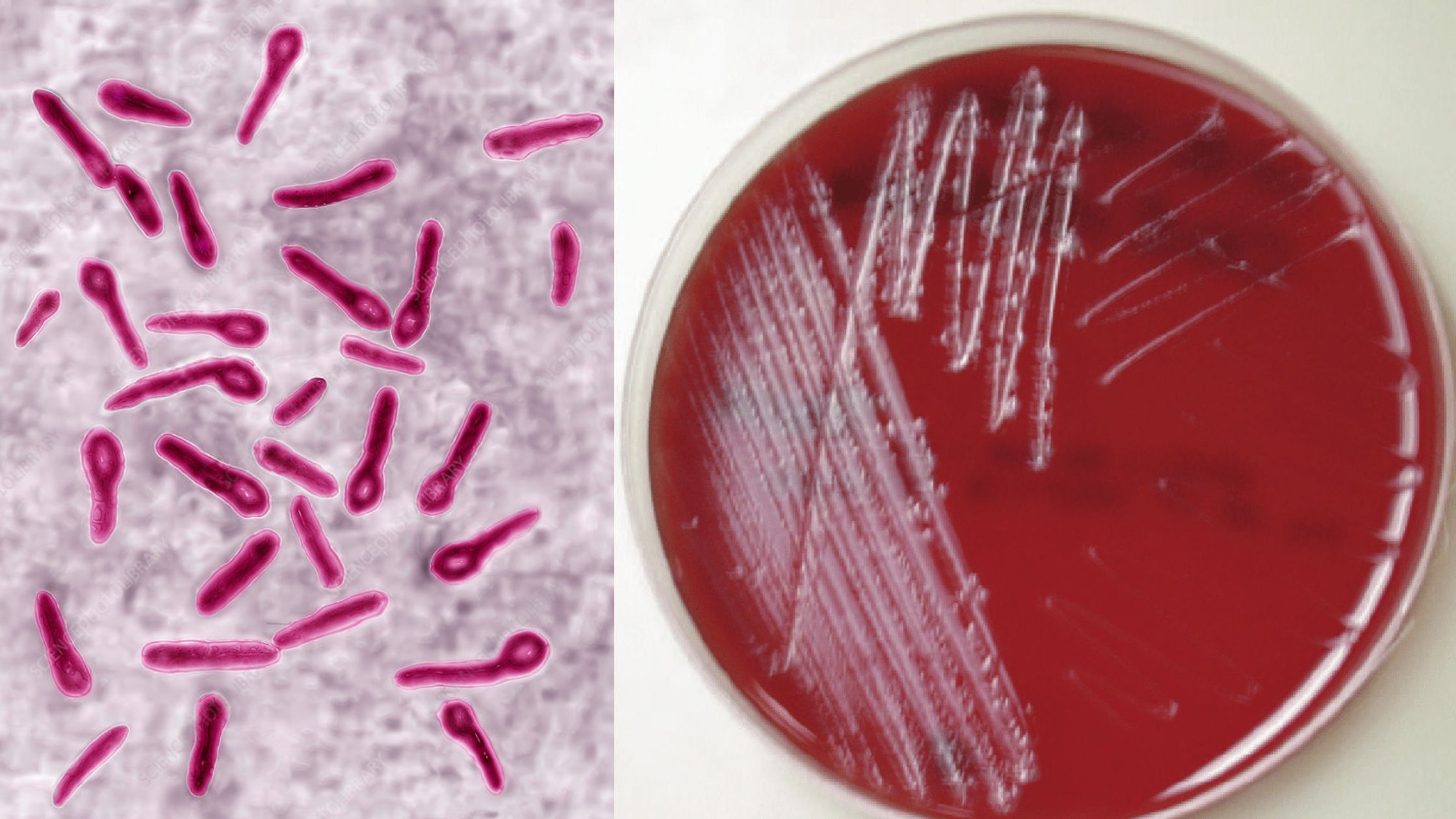
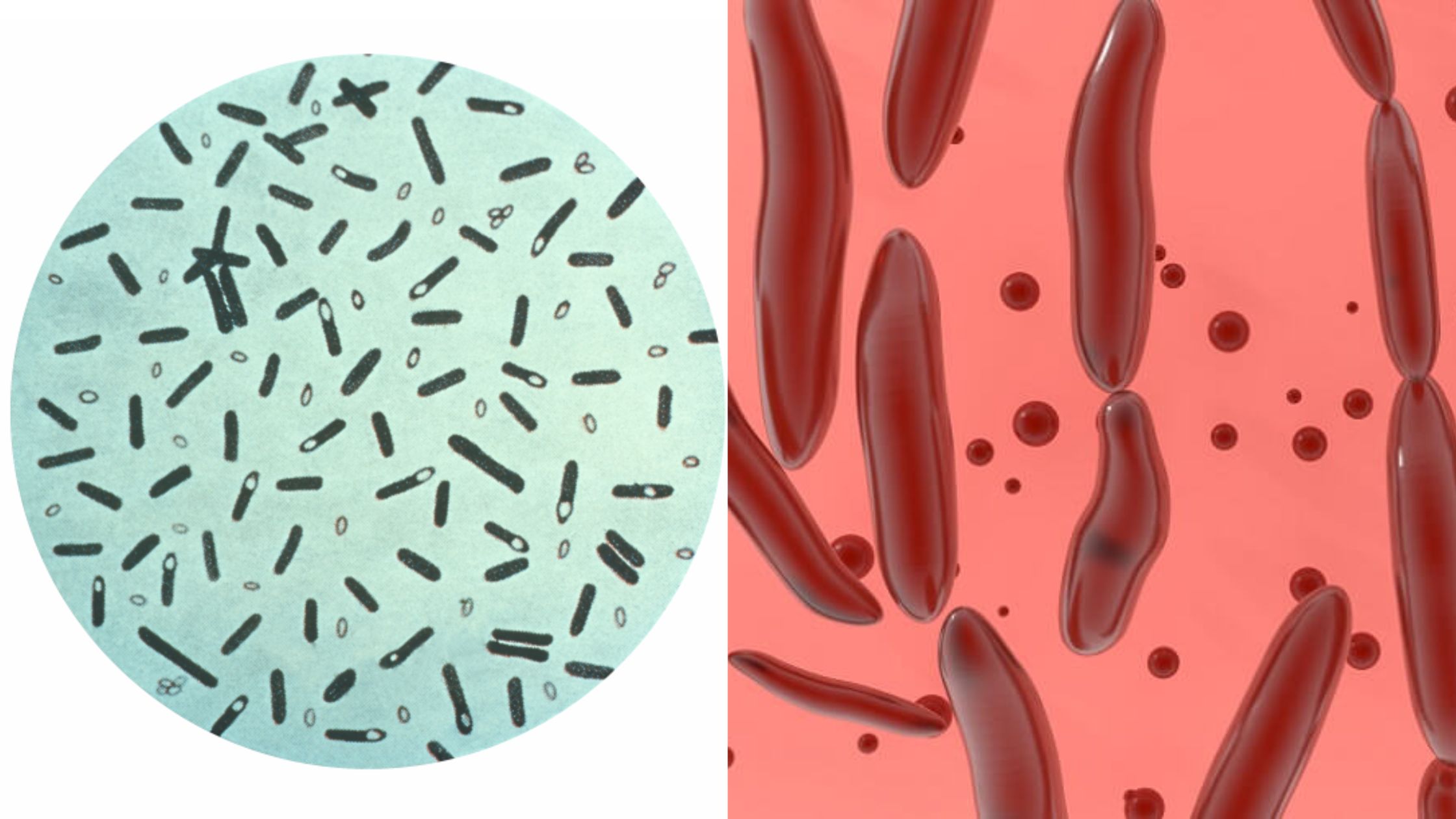
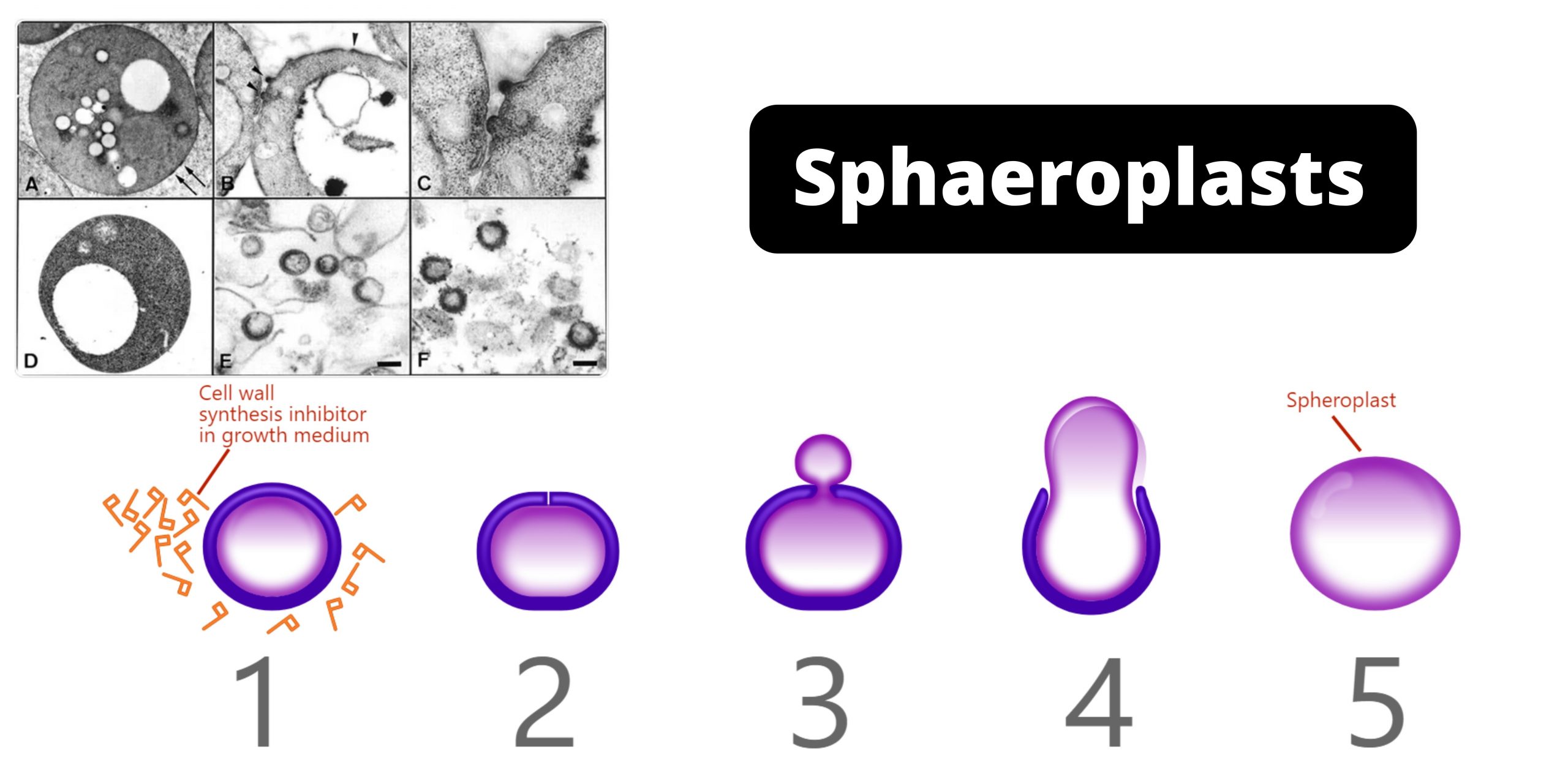
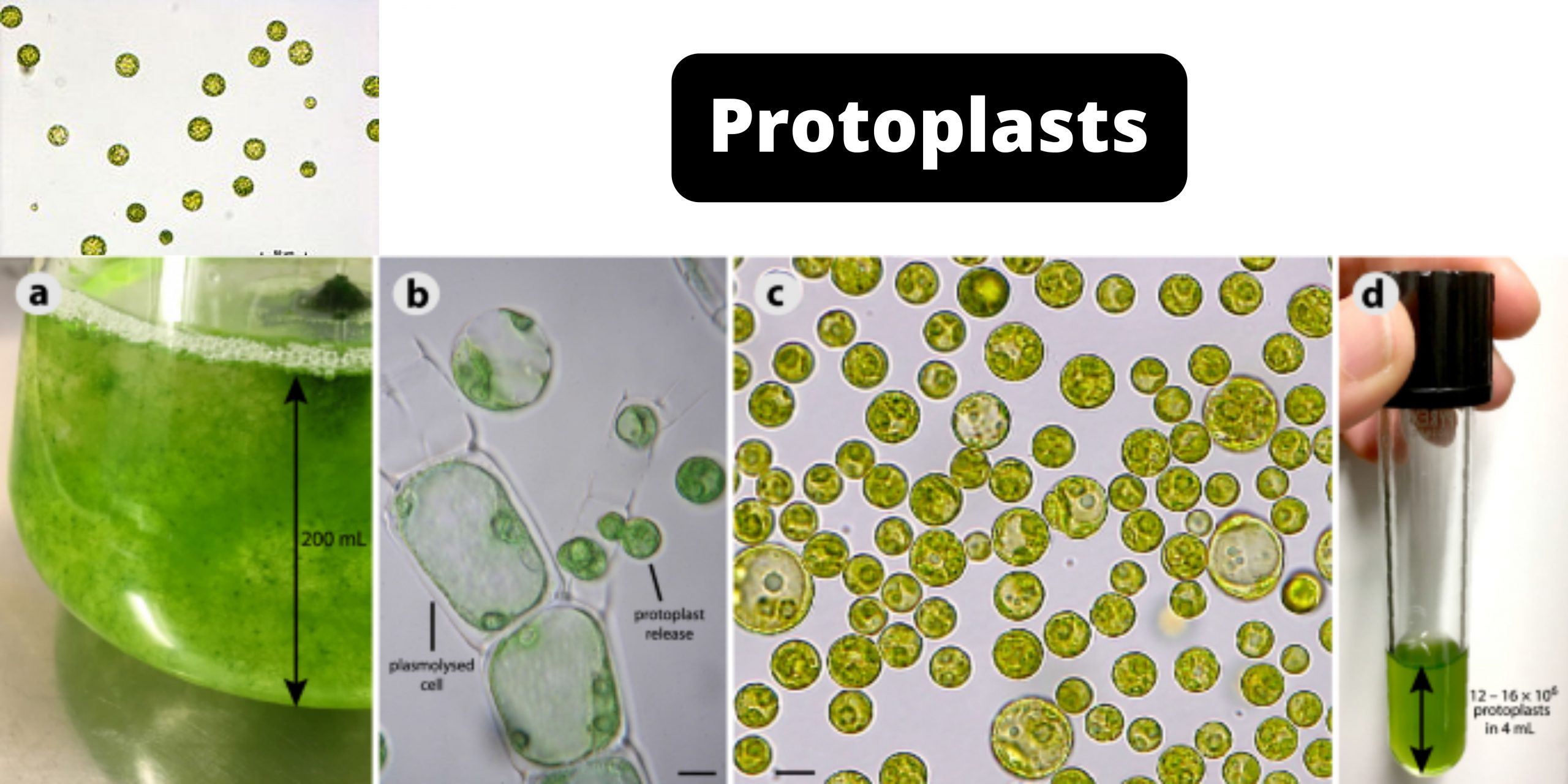
L-form bacteria Definition “L-form” bacteria are also referred to as L-phase bacteria or L-phase variants, and cell wall deficient (CWD) bacteria are bacteria with no cell walls. They were first identified around 1935, by the scientist Emmy Klieneberger Nobel who identified them as “L-forms” after the Lister Institute in London which she was working at. … Read more