Cyanobacteria – Definition, Characteristics, Structure, Functions, Examples
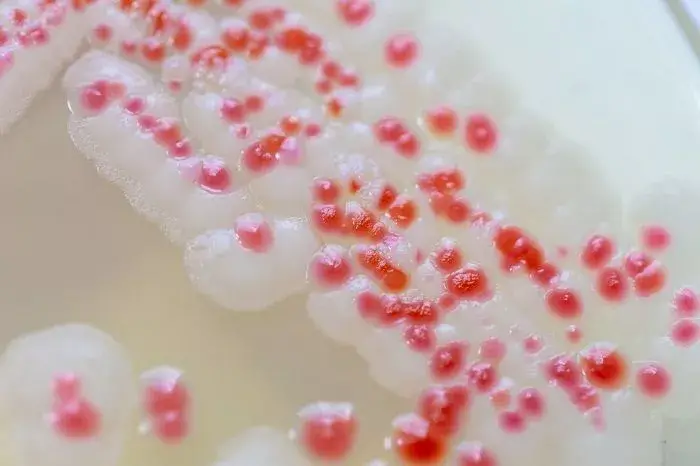
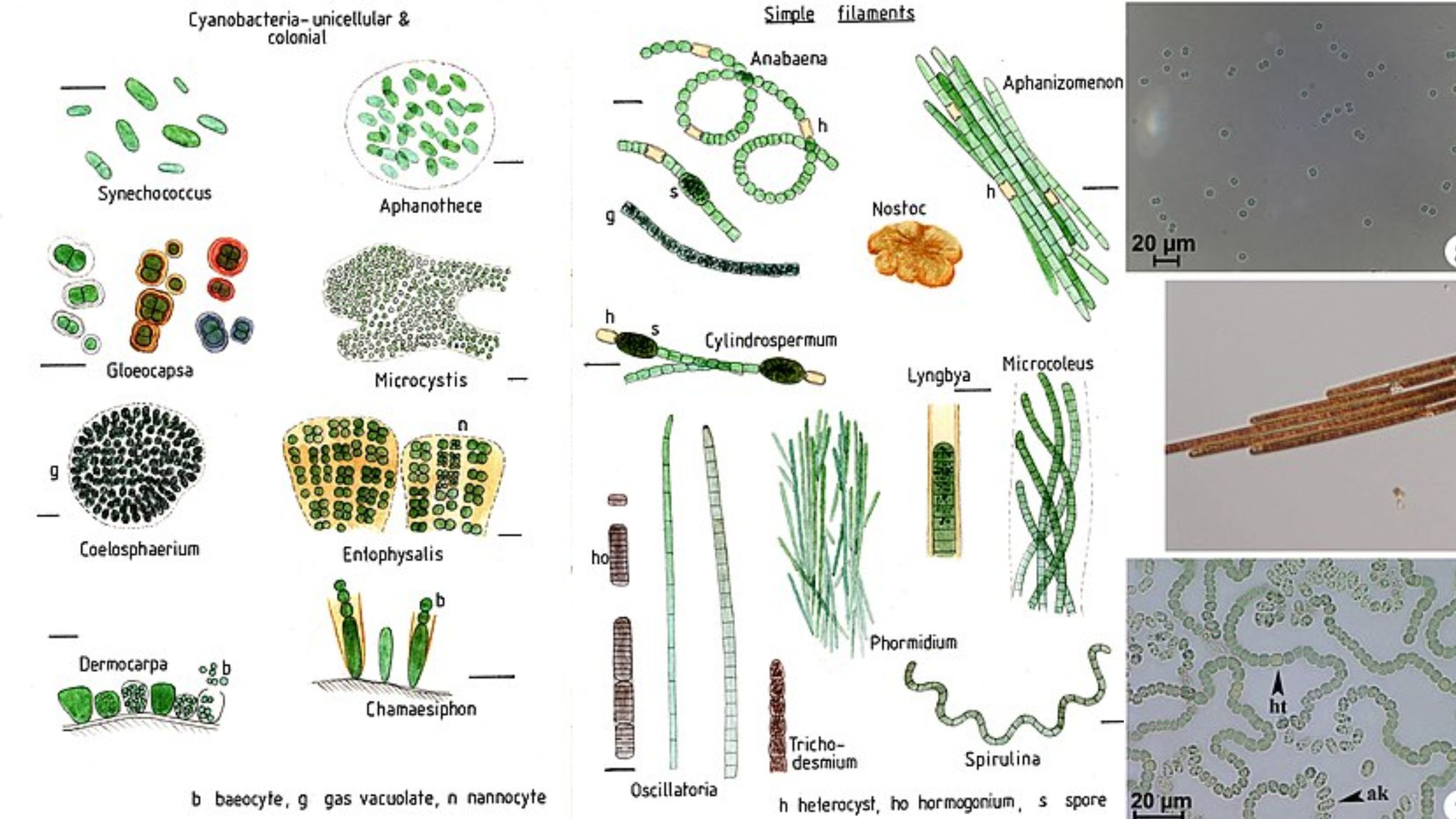
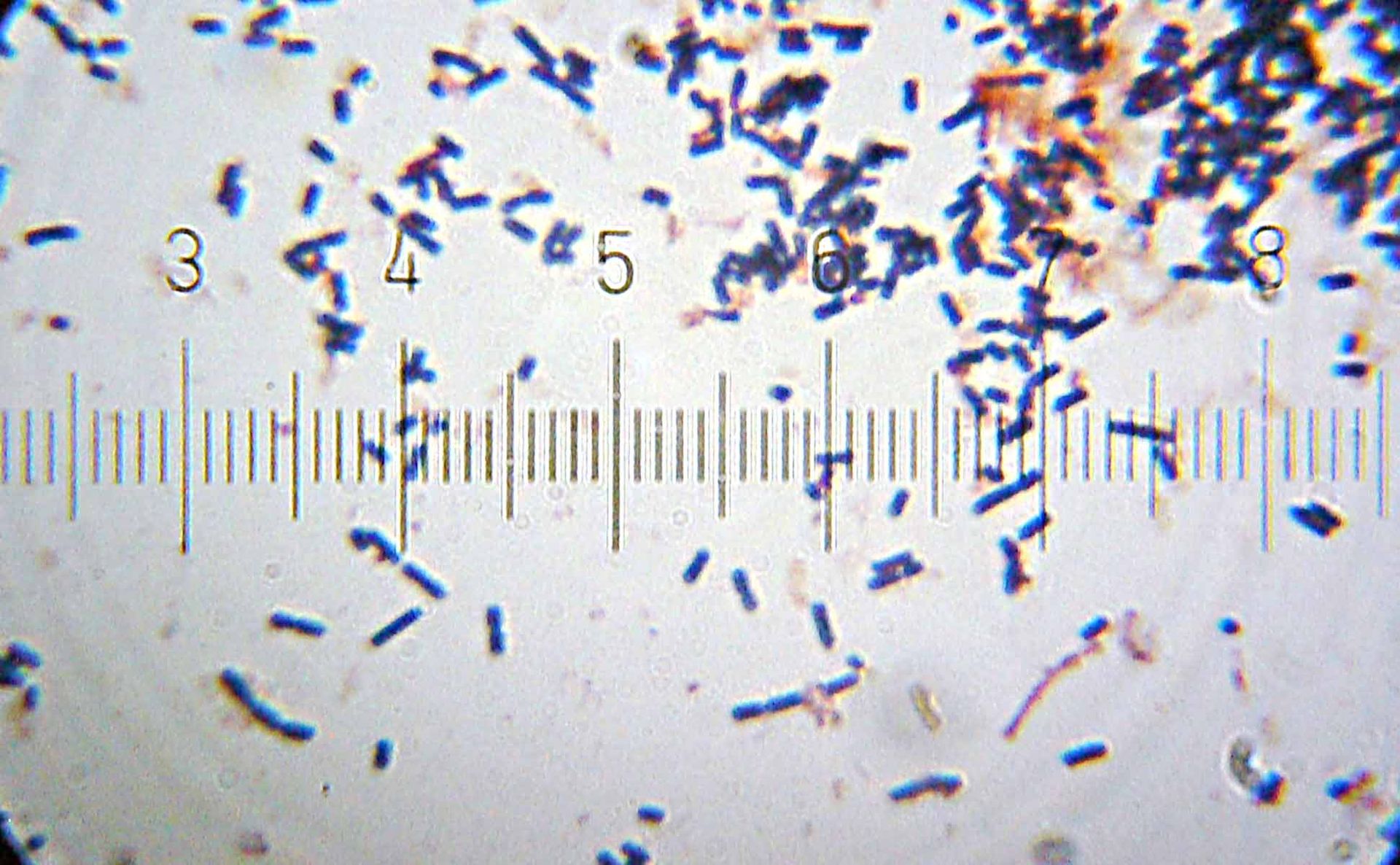
What is Cyanobacteria? Definition of Cyanobacteria/Cyanobacteria definition Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic bacteria that obtain energy through photosynthesis. They are often referred to as blue-green algae, although they are not classified as true algae. Cyanobacteria played a crucial role in the production of oxygen and the shaping of Earth’s atmosphere. They can be found in various aquatic … Read more