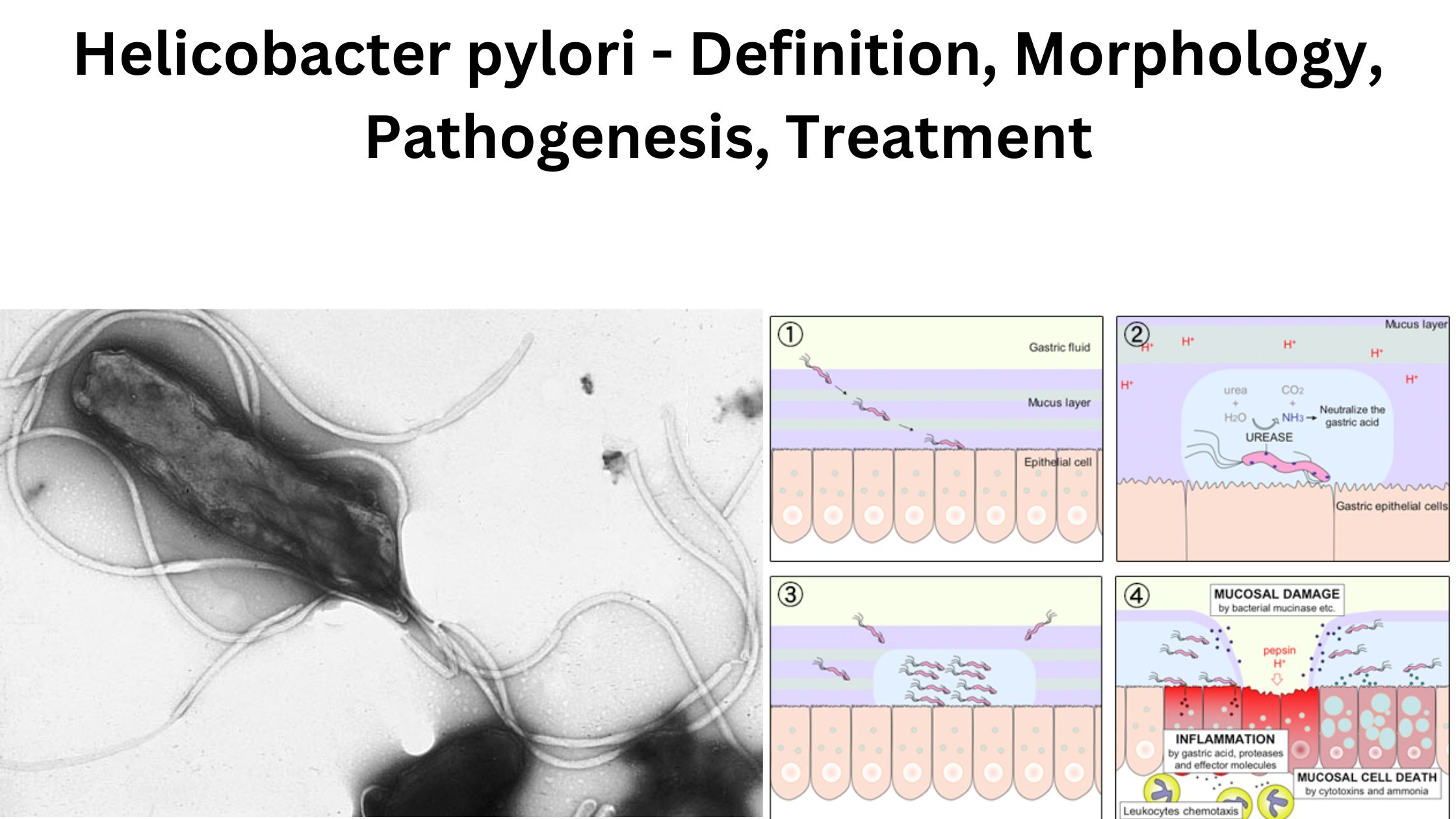
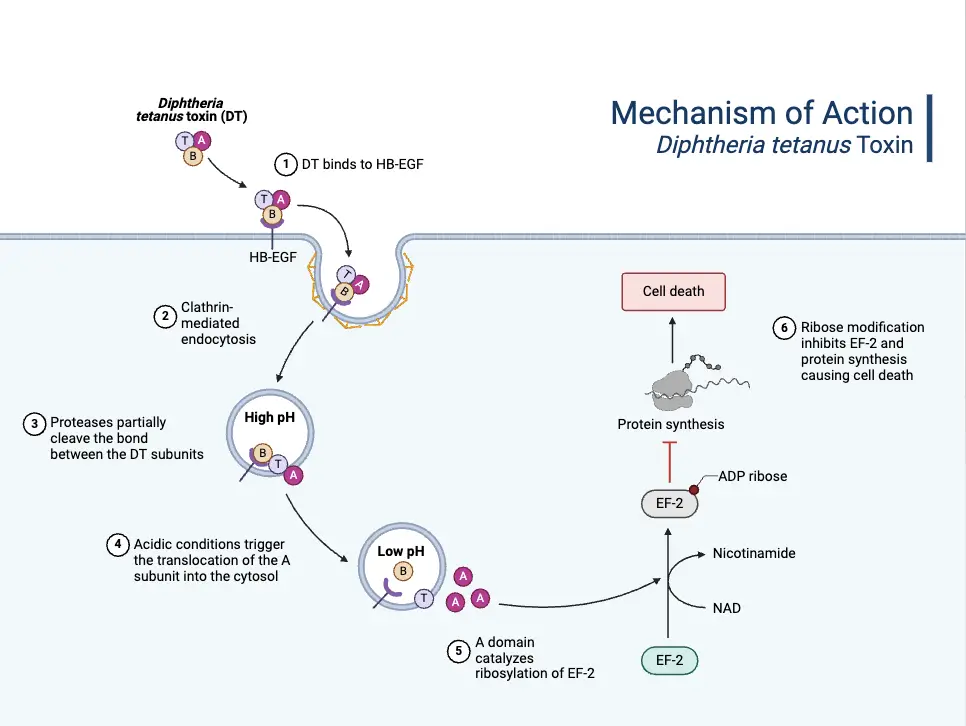
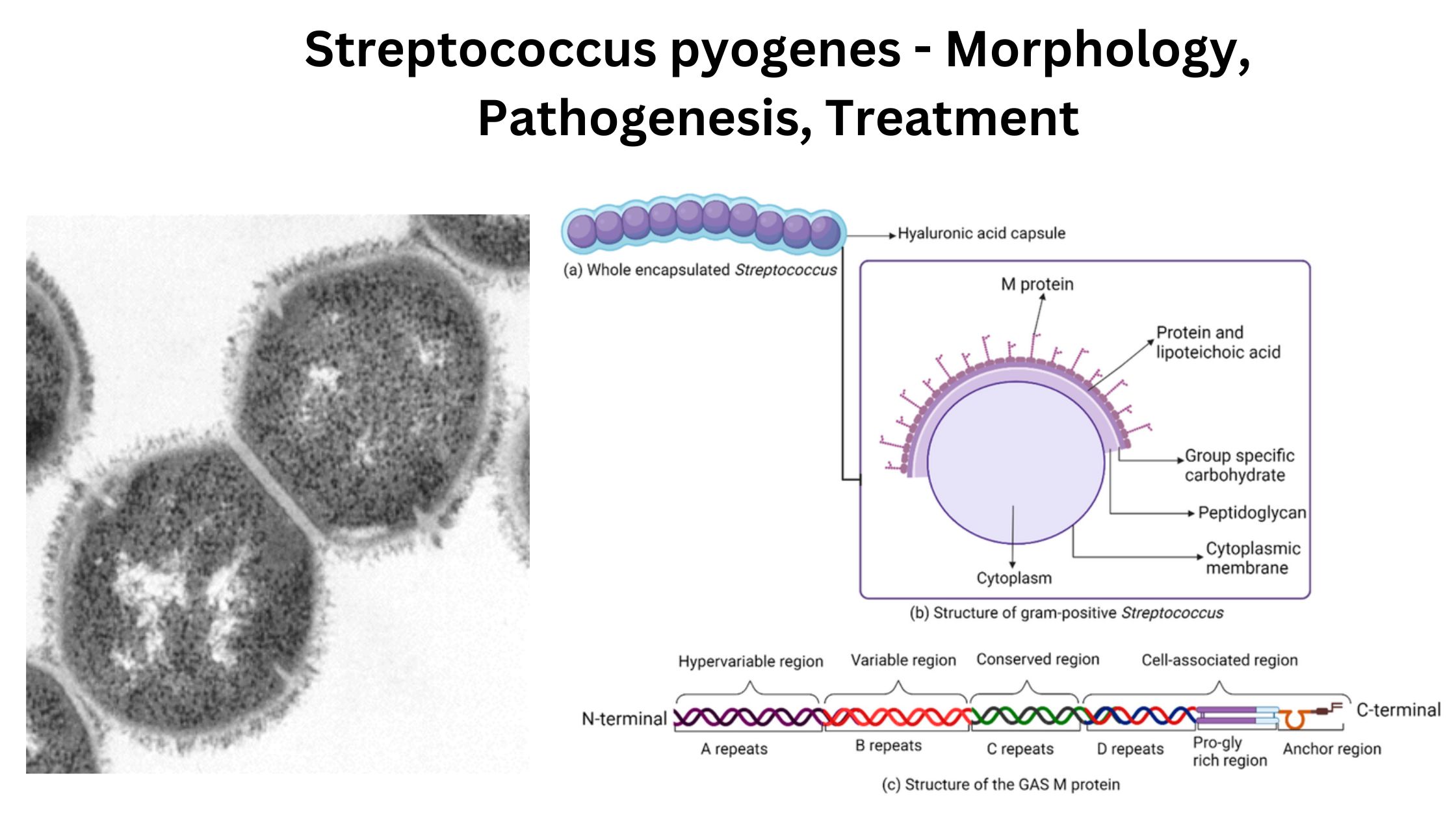
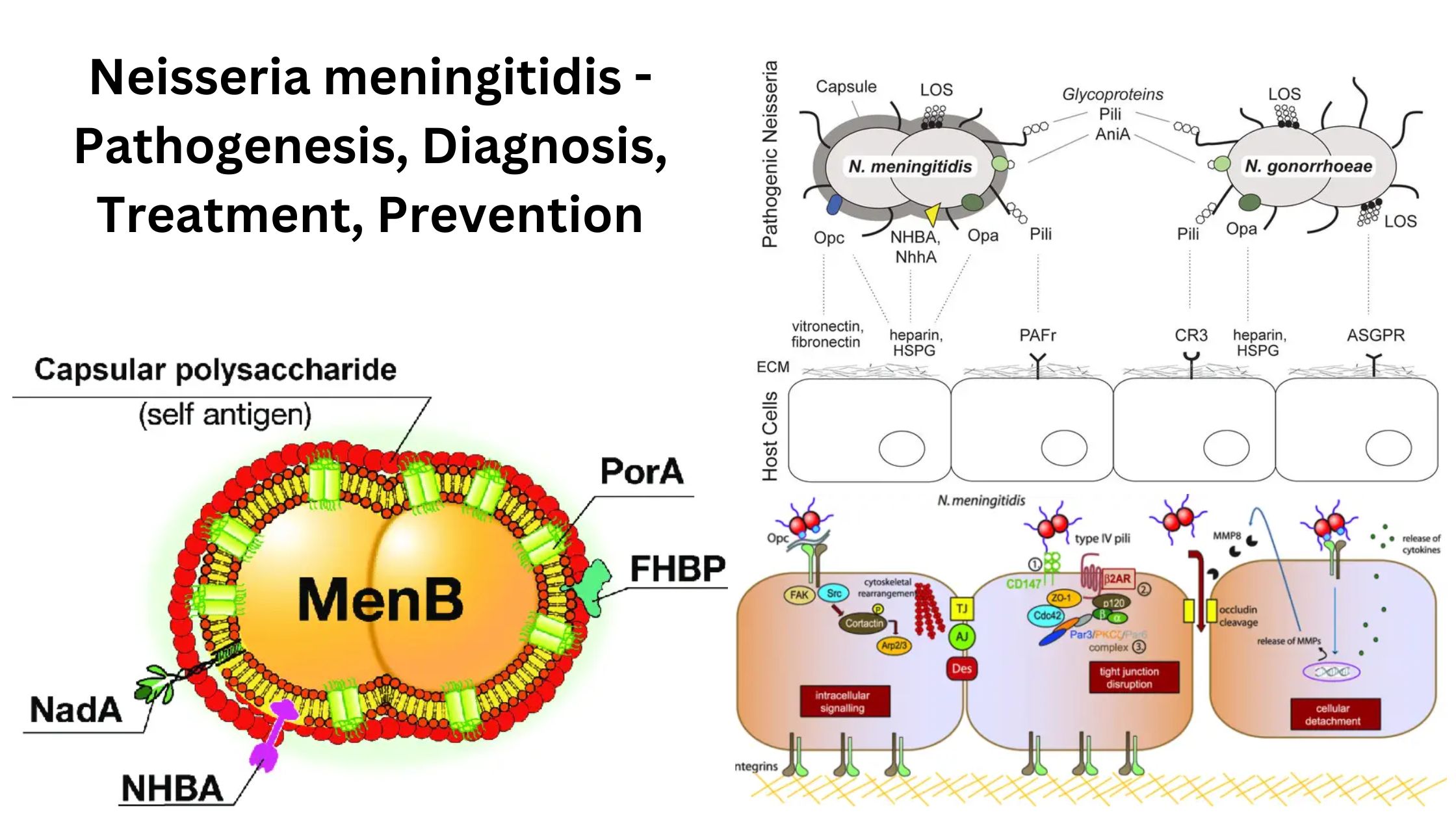
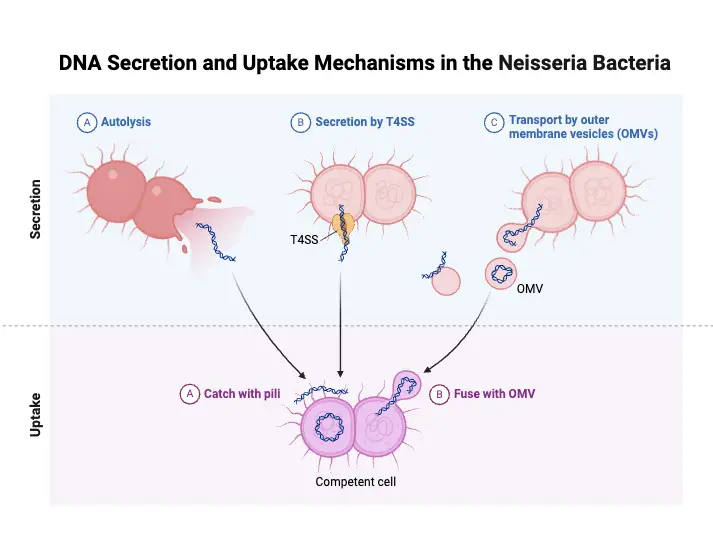
Helicobacter pylori – Definition, Morphology, Pathogenesis, Treatment
What is Helicobacter pylori? Scientific classification of Helicobacter pylori Domain: Bacteria Phylum: Campylobacterota Class: “Campylobacteria” Order: Campylobacterales Family: Helicobacteraceae Genus: Helicobacter Species: H. pylori Morphology of Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori is a Gram-negative bacterium with distinctive features that make it highly adapted to its environment. Its unique structure plays a critical role in its mobility and … Read more