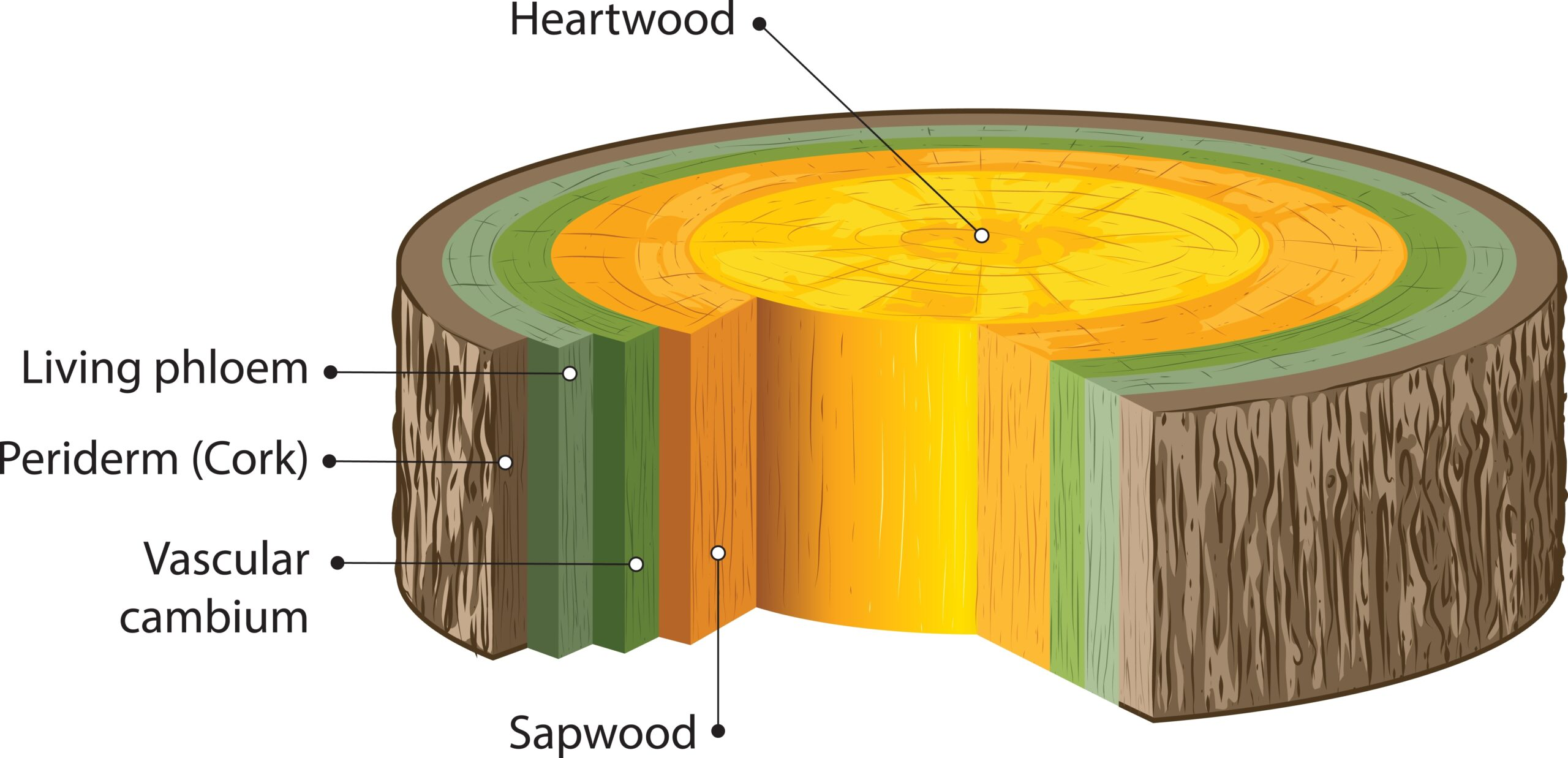
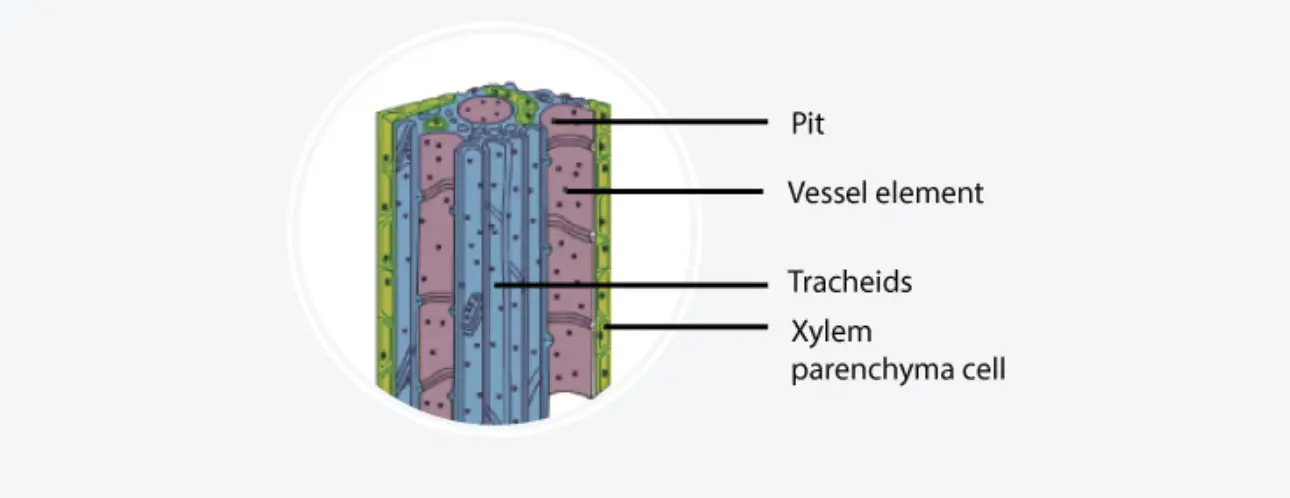
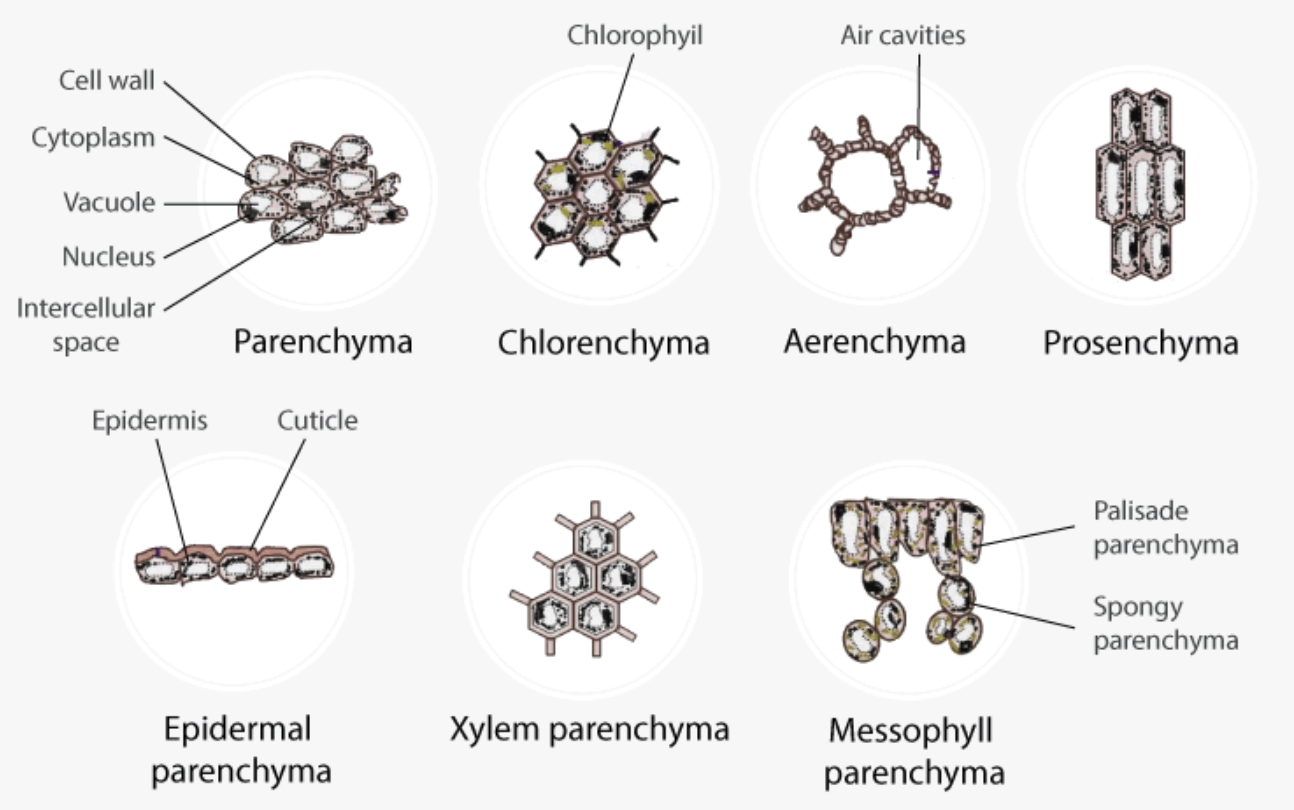
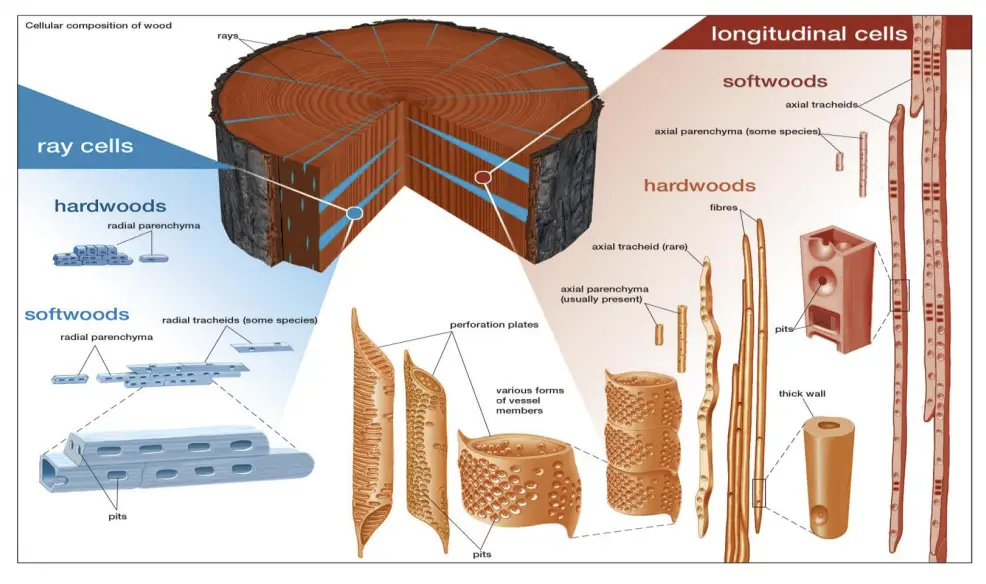
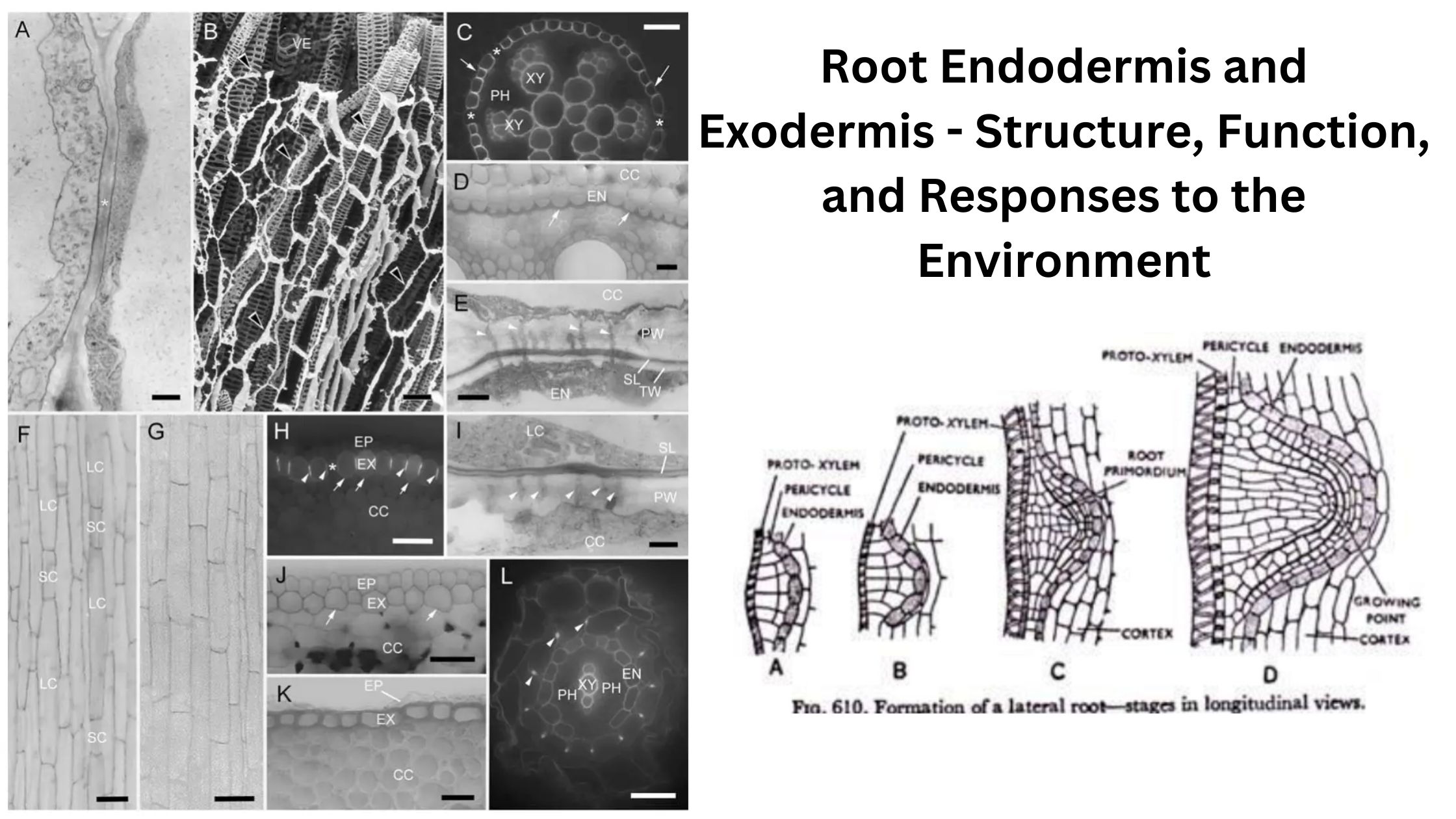
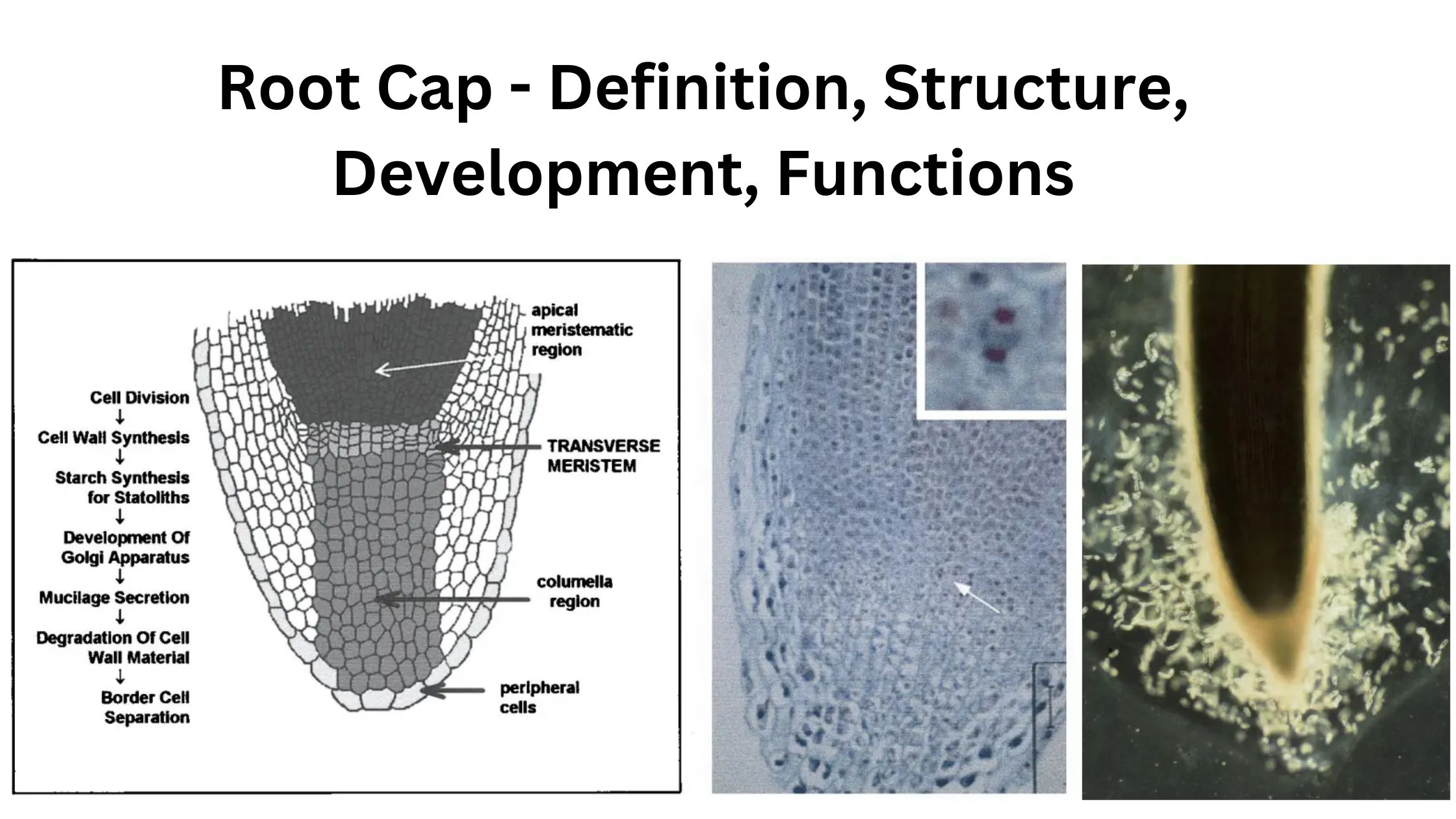
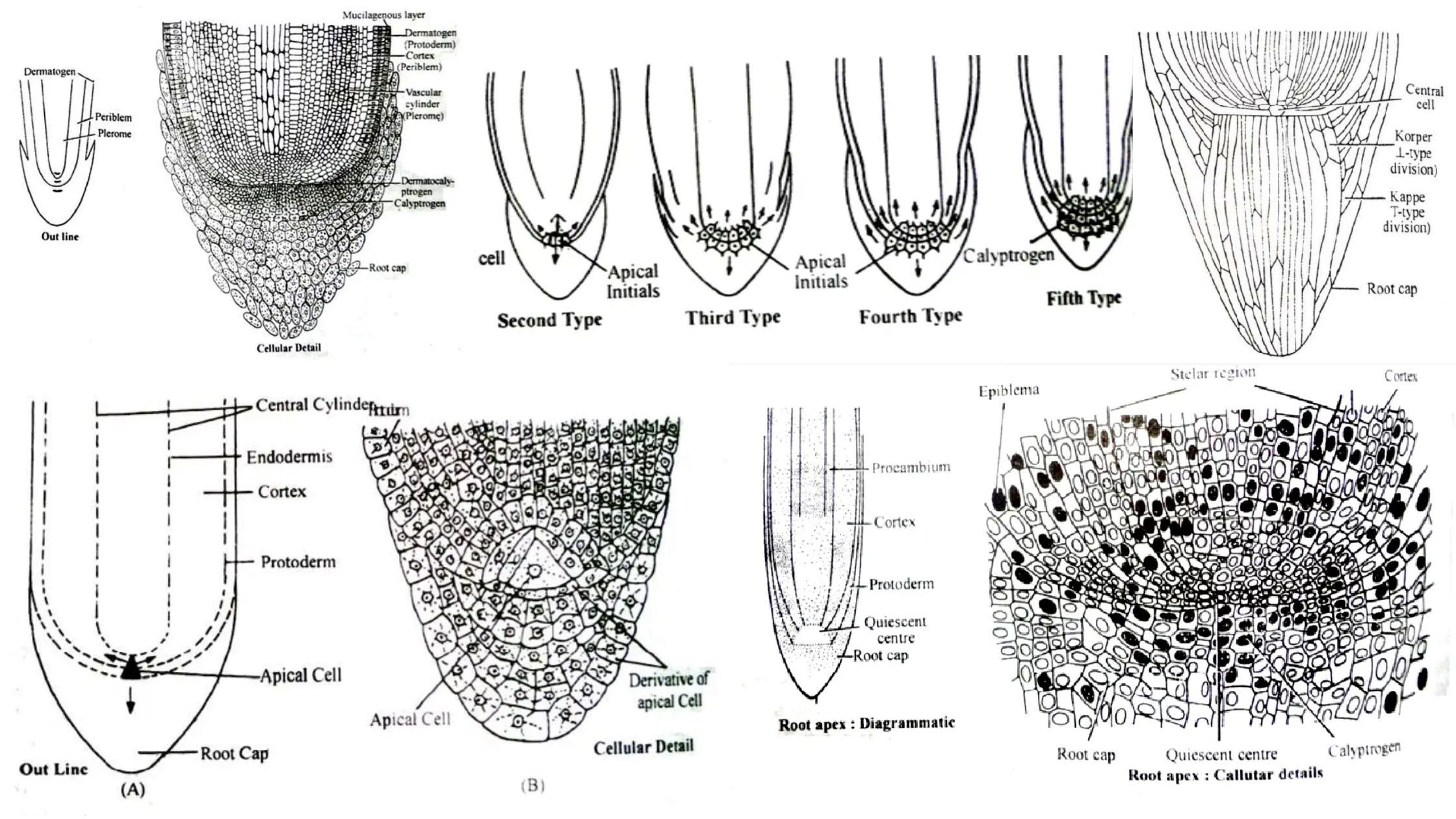
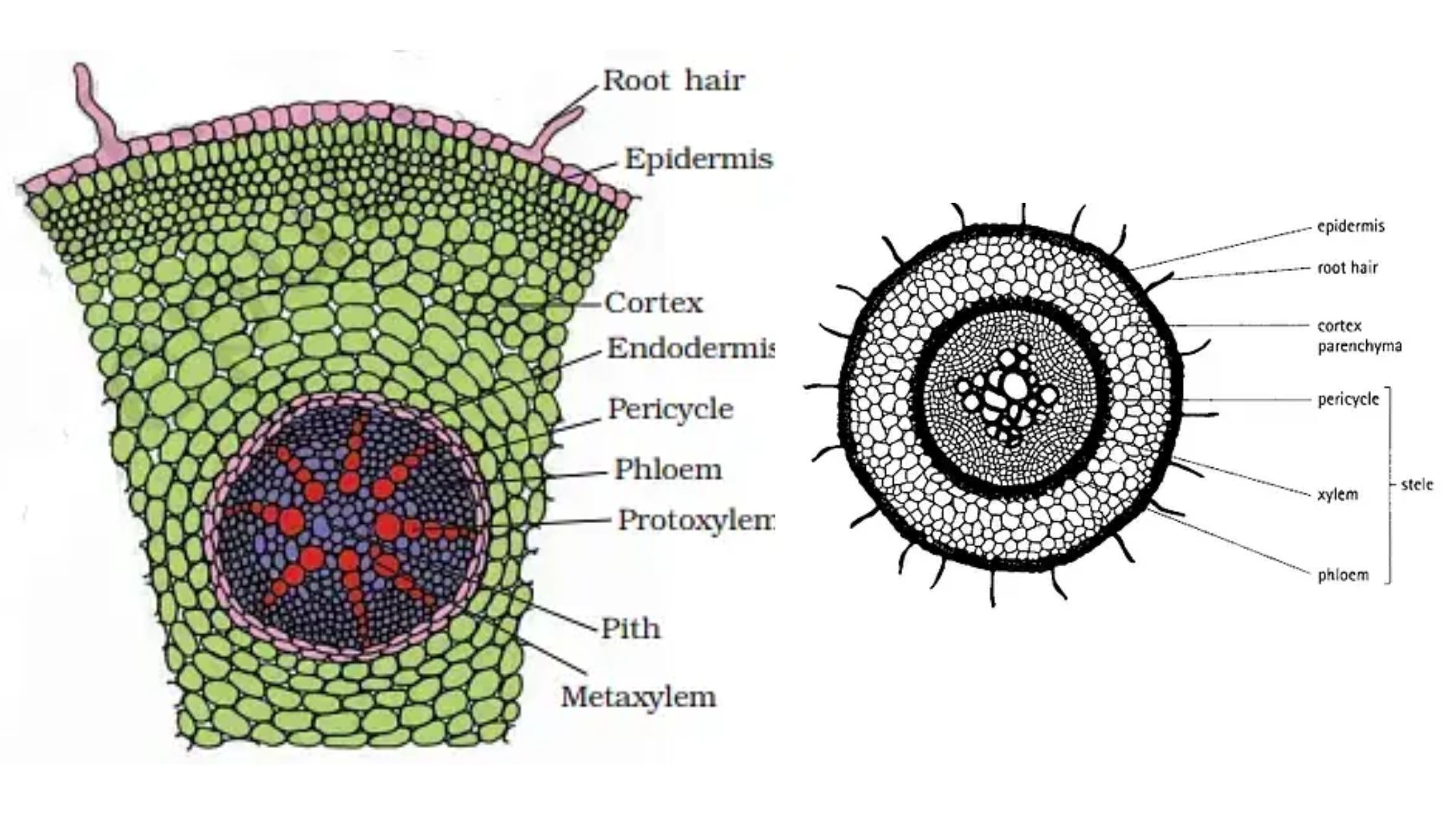
Sapwood and Heartwood – Definition, Structure, Functions
What are Sapwood and Heartwood? Sapwood and heartwood represent two distinct yet essential components of a tree’s structure, playing crucial roles in the overall functionality and durability of wood. Understanding these components is fundamental for students and educators studying plant biology, botany, or forestry. Structure and Development of Sapwood and Heartwood The structure and development … Read more