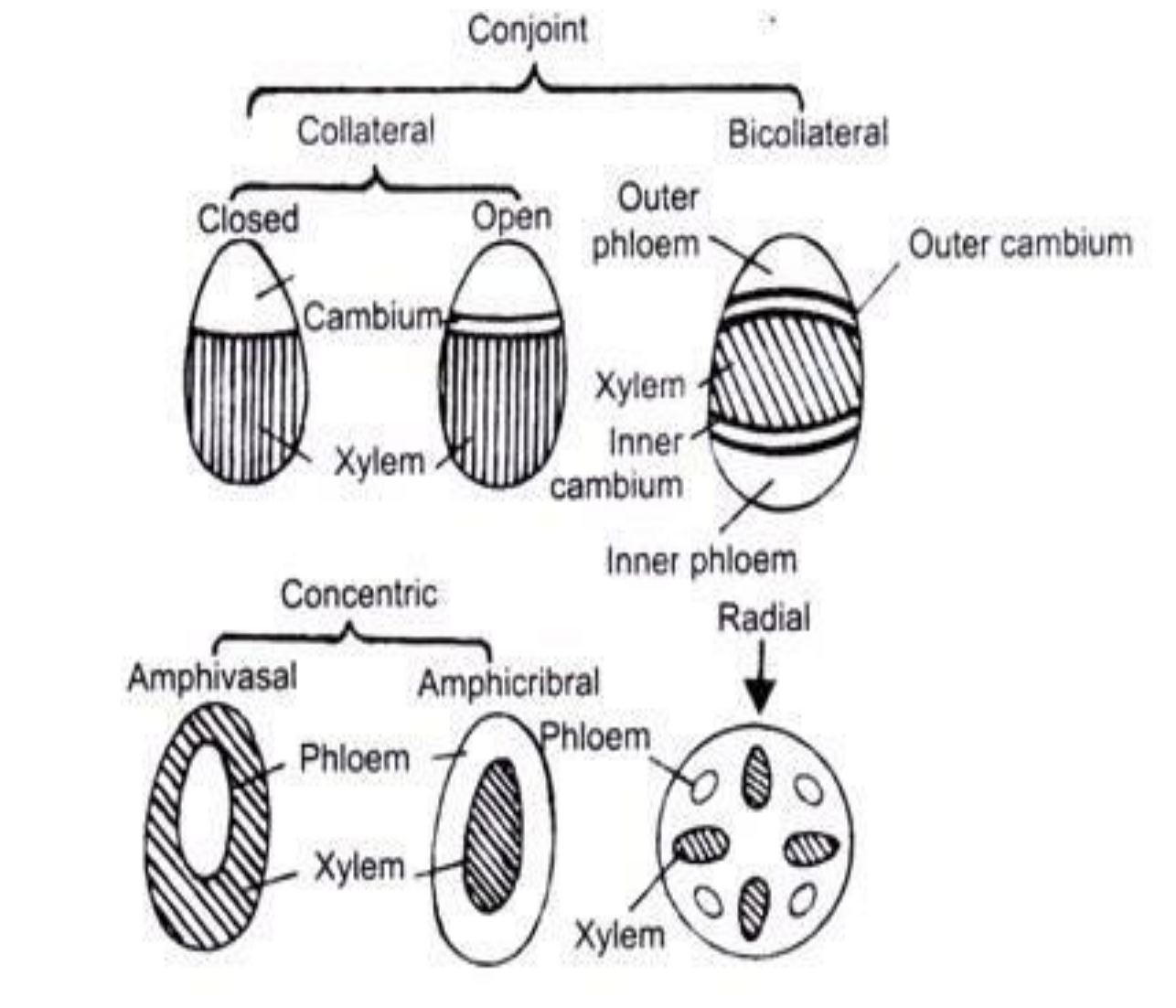
Vascular Bundles – Definition, Structure, Types, Functions
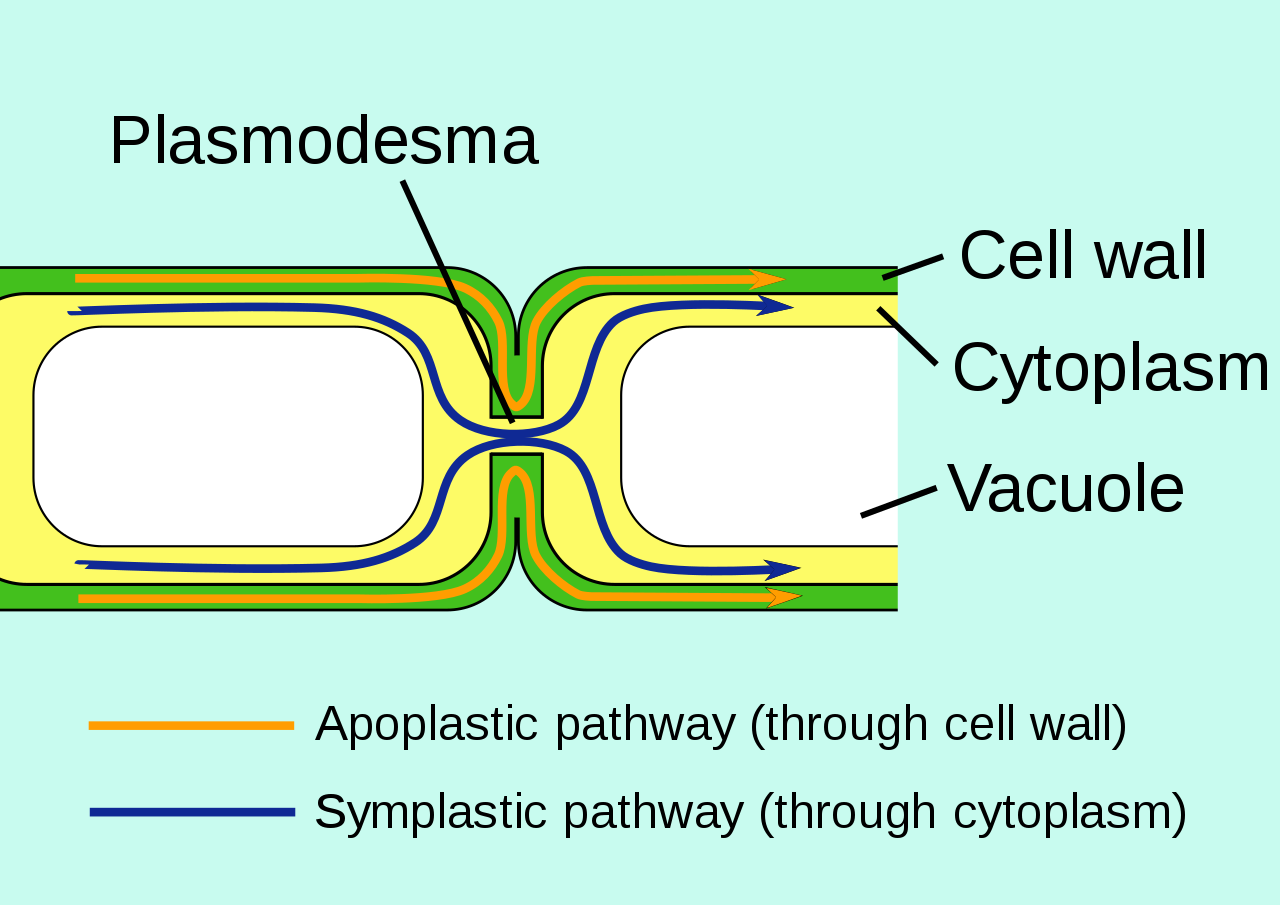
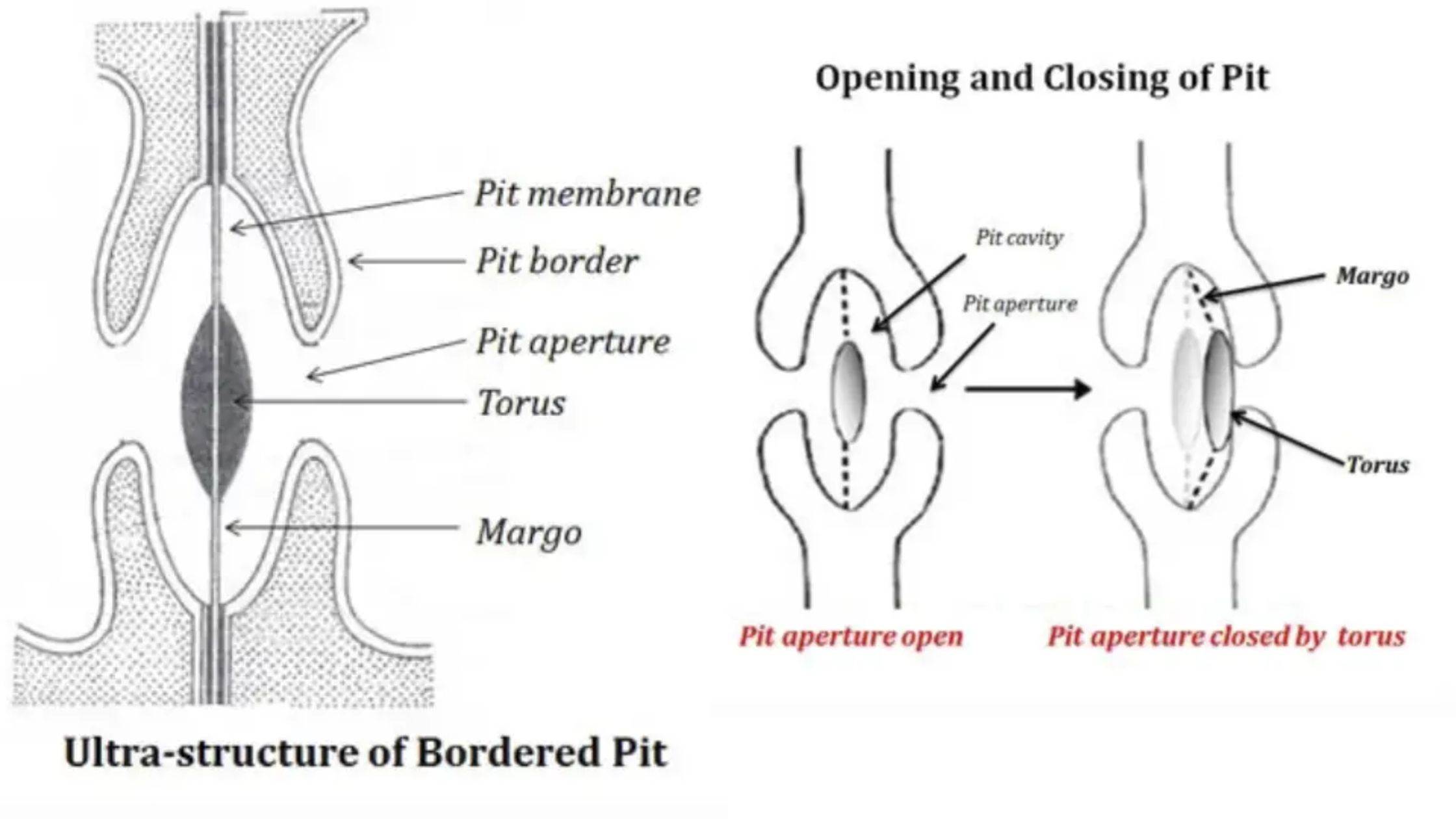
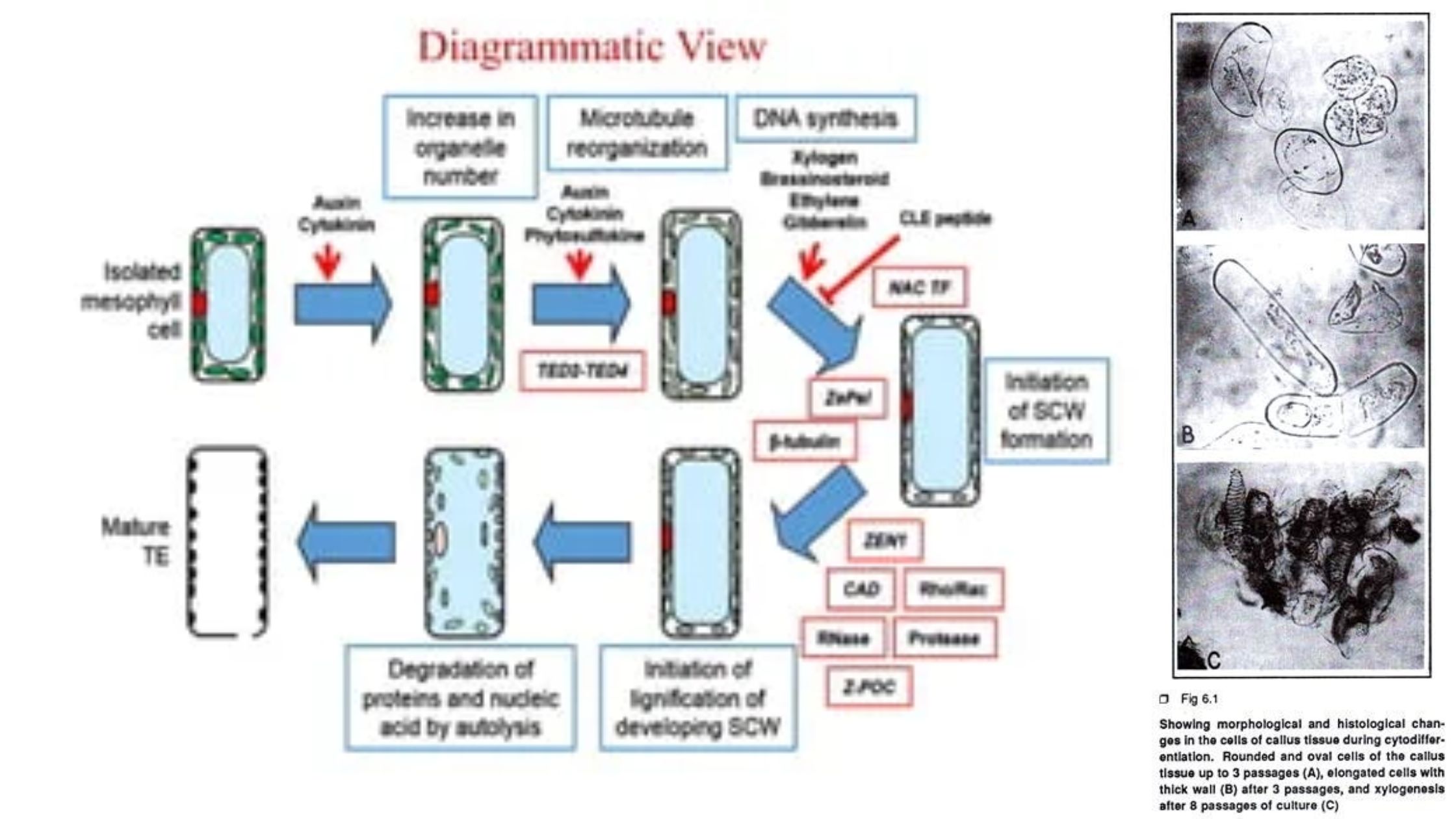
What are Vascular Bundles? Components of vascular bundles Vascular bundles are fundamental structures in vascular plants, comprising two primary components: xylem and phloem. These components play essential roles in the transportation of water, minerals, and nutrients throughout the plant. Both xylem and phloem are classified as complex tissues, meaning they are made up of various … Read more