Bial test is a biochemical test which is used for the detection of pentose sugars and to differentiate them from hexose sugars. It is mainly employed for identifying sugars like ribose and xylose and is also useful for the detection of RNA because RNA contains ribose sugar. This test is based on the reaction of pentoses with a specific reagent known as Bial’s reagent which contains orcinol, concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) and ferric chloride (FeCl₃).
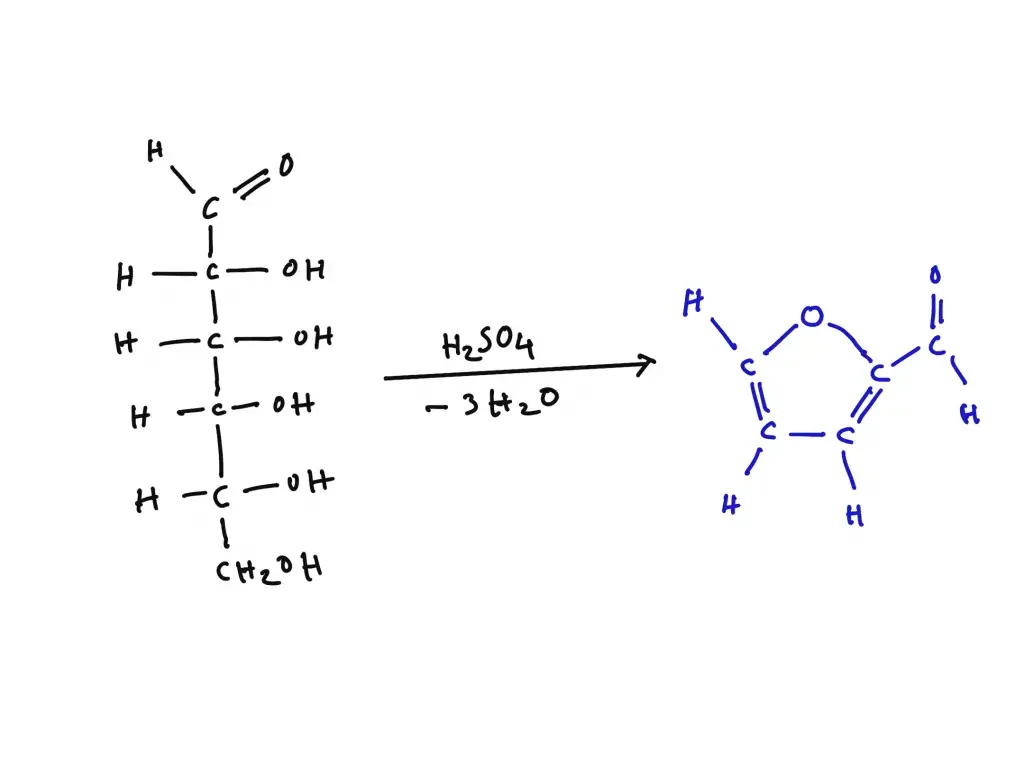
It is the process in which pentose sugars on heating with concentrated acid undergo dehydration and form furfural. This furfural further reacts with orcinol in the presence of ferric ions to produce a blue-green coloured complex. This is referred to as a positive result of Bial test. In contrast hexose sugars also undergo dehydration but they form hydroxymethyl furfural which reacts differently with orcinol and produces a muddy brown or yellow colour. The ferric ion acts as a catalyst and helps in development of characteristic colour.
In this test the sample is mixed with Bial’s reagent and heated for a short duration usually one to three minutes. The appearance of blue or blue-green colour indicates presence of pentoses whereas brown or yellow colour indicates presence of hexoses. Accurate heating time is important because prolonged heating may lead to false results due to degradation of sugars.
Objectives of Bial’s Test
- To detect the presence of pentose sugars in a given sample.
- To distinguish pentoses from hexose sugars based on colour reaction.
- To identify ribose containing compounds such as RNA.
- To detect pentose sugars in urine for diagnosis of pentosuria.
- To estimate concentration of pentoses or RNA by colorimetric method.
- To detect formaldehyde in specific chemical analysis.
Principle of Bial’s test
Bial’s test is based on the principle of dehydration of pentose sugars under strong acidic conditions. When pentoses are heated with Bial’s reagent containing concentrated hydrochloric acid, orcinol and ferric chloride, the pentose sugars is rapidly dehydrated to form furfural. This furfural then condenses with orcinol in presence of ferric ions and produces a characteristic blue-green coloured complex.
Hexose sugars also undergo dehydration under the same conditions but they form 5-hydroxymethyl furfural instead of furfural. This compound reacts slowly with orcinol and produces a muddy brown, yellow or grey colour. Thus the difference in rate of dehydration and colour formation is used to distinguish pentoses from hexoses in Bial’s test.
Requirements for Bial’s Test
- Bial’s reagent (orcinol, concentrated hydrochloric acid and ferric chloride).
- Test solution containing carbohydrate or RNA.
- Positive control solution (pentose sugar such as ribose or xylose).
- Negative control solution (distilled water or hexose sugar).
- Clean and dry test tubes.
- Pipette or dropper for transferring solutions.
- Boiling water bath for heating the reaction mixture.
- Ice bath for rapid cooling after heating.
- Stopwatch or timer to control heating time.
- Spectrophotometer (optional, for quantitative estimation).
- Safety gloves and goggles for handling concentrated acid.
Procedure of Bial’s test
- Take clean and dry test tubes and label them as test sample, positive control and negative control.
- Add 0.5–1 ml of the given test solution into the respective test tube.
- Add equal volume of Bial’s reagent to each test tube.
- Mix the contents of the test tubes gently by shaking.
- Place the test tubes in a boiling water bath and heat for 1–3 minutes.
- Remove the test tubes from the water bath and immediately cool them in cold water or ice bath.
- Observe the colour developed in the test tube and compare it with the control tubes.
Result and Interpretation of Bial’s Test
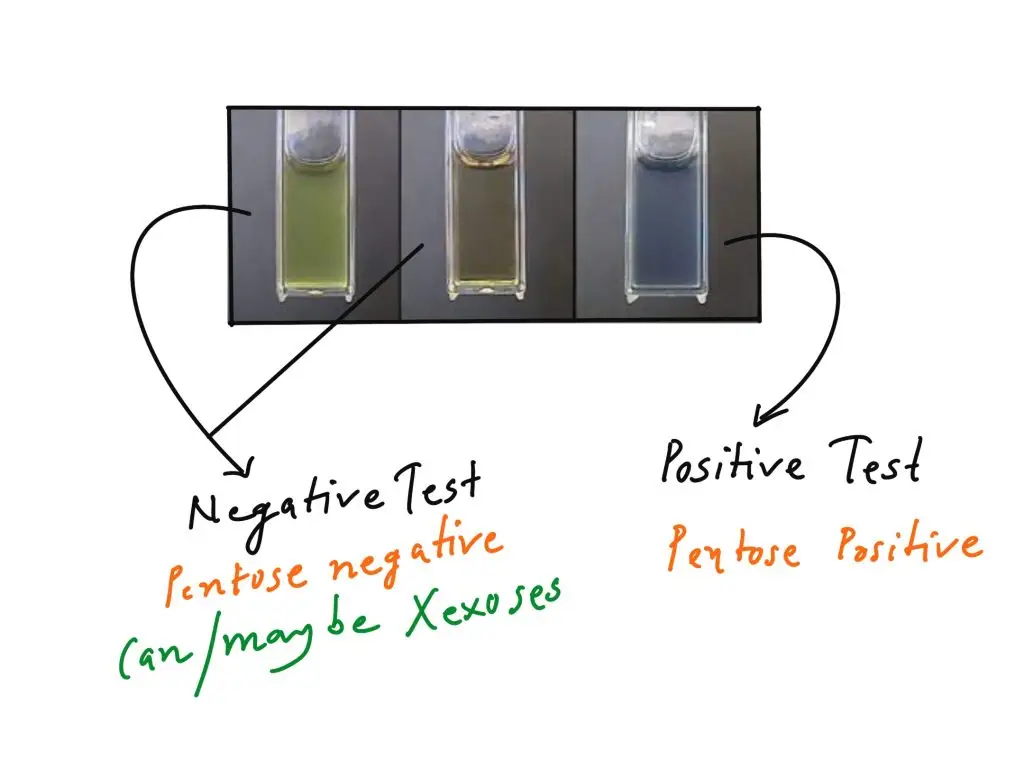
- Blue-green colour (Positive result)– It is observed that formation of blue or blue-green colour indicates presence of pentoses. This colour is due to formation of furfural from pentose sugar which condenses with orcinol. It also shows presence of ribose, xylose, RNA or pentosan type compounds.
- Muddy brown / yellow / grey colour (Negative result for pentoses)– If muddy brown, yellow, grey or reddish-brown colour is produced it indicates presence of hexoses. In this case hexoses form hydroxymethyl furfural which does not give specific blue-green colour. Hence it is considered as negative for pentose detection.
- Blue-purple colour– When large amount of pentose is present the colour formed may appear blue-purple instead of typical blue-green colour. This is due to higher concentration of reaction product.
- No colour change– If no colour change is observed and solution remains colourless it indicates absence of carbohydrates. This is generally seen in negative control such as distilled water.
- False positive results (Interferences)
– Glucuronates may give blue-green colour similar to pentoses leading to false positive result.
– Prolonged heating may hydrolyse complex carbohydrates releasing pentoses which gives positive reaction even if free pentose was absent originally. Excess heating may also cause dark precipitate formation masking actual result.
Uses of Bial’s Test
- It is used for detection of pentoses such as ribose, xylose and arabinose in the given sample.
- It is useful in distinguishing pentoses from hexoses. Pentoses give blue-green colour while hexoses produce muddy brown or grey colour.
- It is applied in analysis of RNA as RNA contains pentose sugar ribose. The modified Bial’s orcinol test is used for detection or estimation of RNA.
- It was earlier used in diagnosis of pentosuria in which pentose sugars are excreted through urine.
- It helps in detection of pentosans which are pentose derived compounds like hemicellulose. These compounds are degraded to pentoses during the test.
- It can be used for quantitative estimation of pentoses or RNA when absorbance is measured using spectrophotometer at about 620 nm.
- It is also adapted for detection and estimation of formaldehyde in aqueous solutions, helping in identification of contamination.
Limitations of Bial’s Test
- Heating time must be strictly controlled. Prolonged heating may hydrolyse disaccharides or polysaccharides into pentoses leading to false positive result.
- Glucuronates may interfere with the reaction. On excess heating these compounds may produce blue-green colour similar to pentoses.
- Hexoses may interfere when present in high concentration or when heated for long time. They may form greenish or reddish-brown products which may confuse the result.
- Colour variation may occur. Different pentoses may give slightly different shades and very high concentration of pentose may produce blue-purple colour instead of blue-green.
- The test has limited accuracy for quantitative analysis. At higher sugar concentration colour intensity may not be directly proportional to concentration.
- Precipitate formation may occur during quantitative estimation. This interferes with spectrophotometric absorbance reading due to light scattering.
- The reaction mixture may bump during heating if proper care is not taken. This may cause spilling of corrosive acid mixture and creates safety hazard.

FAQ
What is Bial’s Test?
Bial’s test is a chemical test used for detection of pentoses in a given sample. It is mainly applied to identify five carbon sugars.
What is the principle of Bial’s Test?
It is based on dehydration of pentoses by concentrated acid to form furfural. The furfural then condenses with orcinol to produce a coloured compound.
What is Bial’s reagent composed of?
Bial’s reagent is composed of orcinol dissolved in concentrated hydrochloric acid with traces of ferric chloride.
What is the procedure for Bial’s Test?
The sample solution is mixed with Bial’s reagent and heated carefully in a boiling water bath. The colour developed is observed after heating.
What are the uses of Bial’s Test?
It is used for detection of pentoses, differentiation of pentoses from hexoses and for analysis of RNA containing ribose sugar.
What color indicates a positive result in Bial’s Test?
Blue-green colour indicates a positive result for pentoses.
How does Bial’s Test differentiate between pentoses and hexoses?
Pentoses produce blue-green colour while hexoses produce muddy brown or grey colour due to formation of different dehydration products.
What is the significance of the blue-green color in Bial’s Test?
The blue-green colour confirms formation of furfural from pentose which reacts with orcinol.
What is the role of orcinol in Bial’s Test?
Orcinol condenses with furfural formed from pentoses to produce the characteristic blue-green coloured complex.
What is the role of hydrochloric acid (HCl) in Bial’s Test?
Hydrochloric acid acts as dehydrating agent and helps in conversion of pentoses into furfural.
Who developed Bial’s Test?
Bial’s test was developed by the scientist Bial.
Can Bial’s Test be used to detect RNA?
Yes it can be used to detect RNA because RNA contains ribose which is a pentose sugar.
What is the expected result for hexoses in Bial’s Test?
Hexoses give muddy brown, grey or yellowish colour and are considered negative for pentoses.
What are the common examples of pentoses detected by Bial’s Test?
Ribose, xylose and arabinose are common pentoses detected by this test.
Are there any false positives in Bial’s Test?
Yes false positive results may occur due to glucuronates or prolonged heating which may release pentoses from complex carbohydrates.
- Al-Mustaqbal University College. (n.d.). Lecture 3: Qualitative analysis of carbohydrate – Bial’s test [Lecture notes]. Department of Medical Physics.
- Azer Scientific. (n.d.). Bial’s reagent.
- Collop, D. [Professor Drew Collop]. (n.d.). Bial’s test for pentoses 2.0 [Video]. YouTube.
- Exp.10 Assay of carbohydrate (part II). (n.d.). [Laboratory manual].
- Harper College. (n.d.). Carbohydrates – Bial’s test. Department of Chemistry.
- Mustansiriyah University. (2020). Practical biochemistry: Section one [Lecture notes].
- Omran, A. P., & Coughlin, C. B. (2020). Bial’s test, a simple method for formaldehyde detection. Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research, 27(3), 20635-20639. https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2020.27.004515
- Proprep. (n.d.). Explain the use of Bial’s reagent in carbohydrate testing.
- Sapkota, A. (2022, September 5). Bial’s test- definition, principle, procedure, result, uses. Microbe Notes.
- Shrestha, A. (n.d.). Bial’s test: Principle, procedure, and application. Microbe Online.
- The Bial test for pentoses: An advanced analytical evaluation of principle, optimized procedure, and spectrophotometric quantification. (n.d.).
- Wikipedia contributors. (n.d.). Bial’s test. Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia.
- Text Highlighting: Select any text in the post content to highlight it
- Text Annotation: Select text and add comments with annotations
- Comment Management: Edit or delete your own comments
- Highlight Management: Remove your own highlights
How to use: Simply select any text in the post content above, and you'll see annotation options. Login here or create an account to get started.