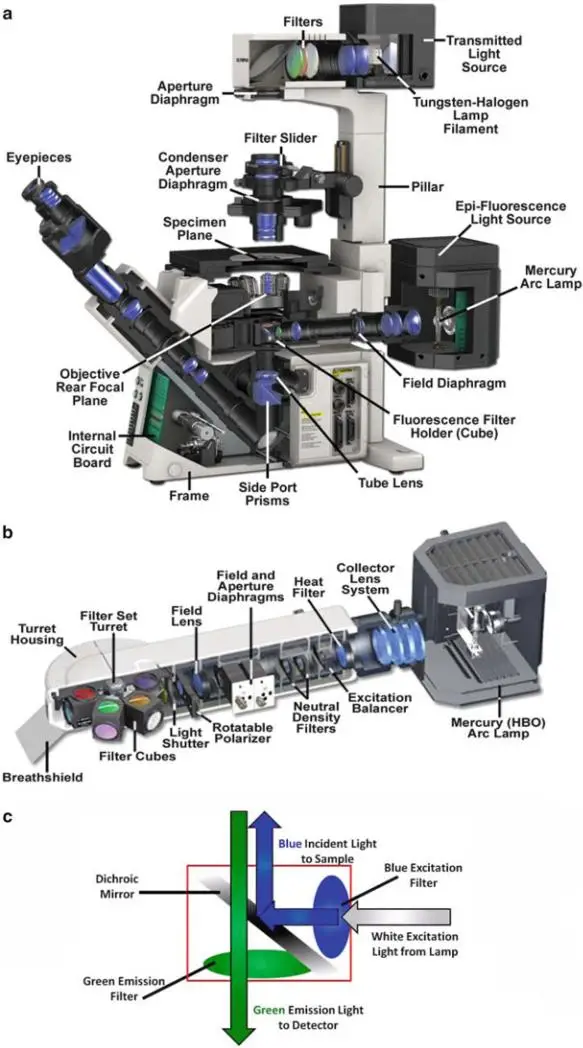
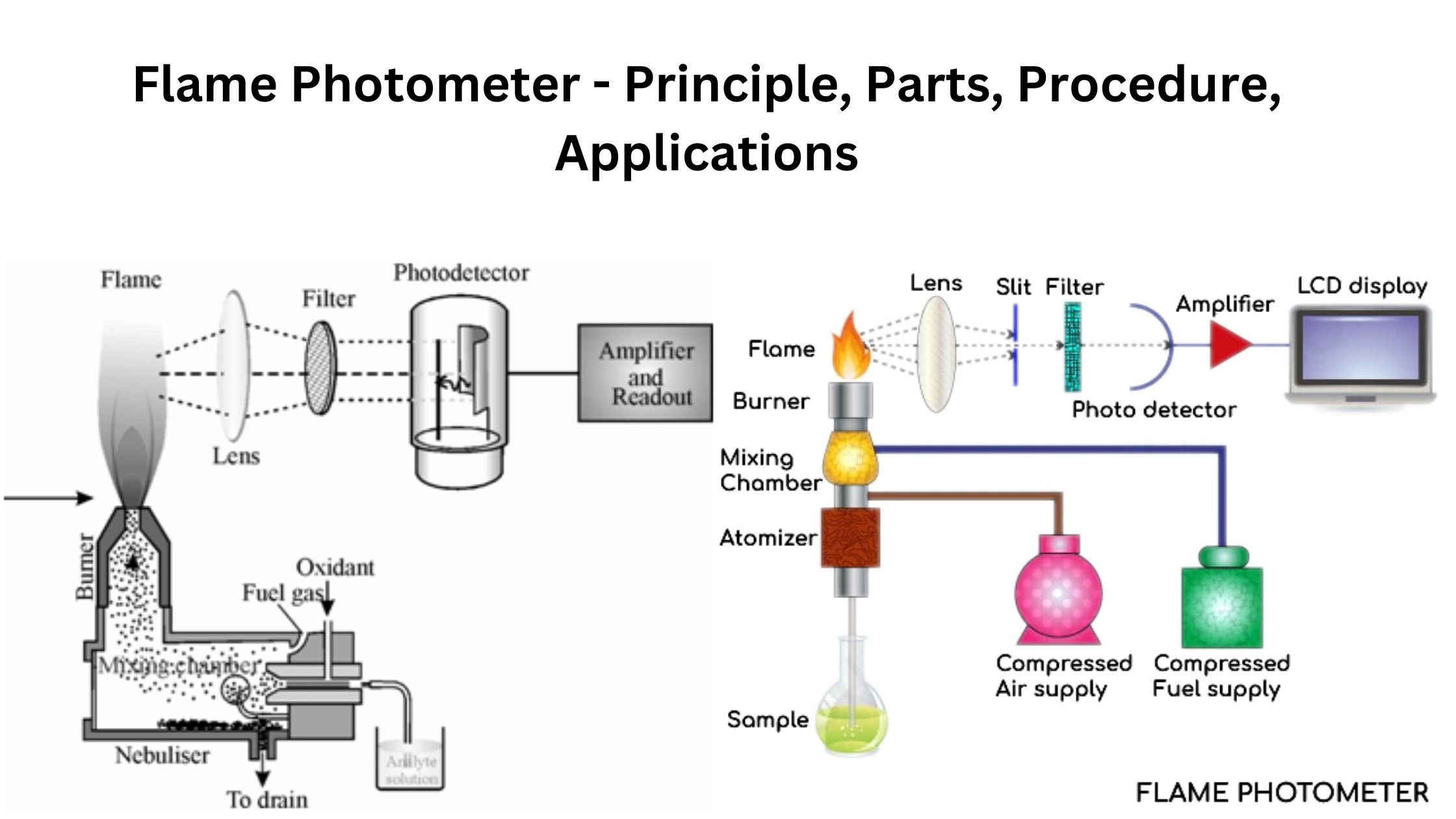
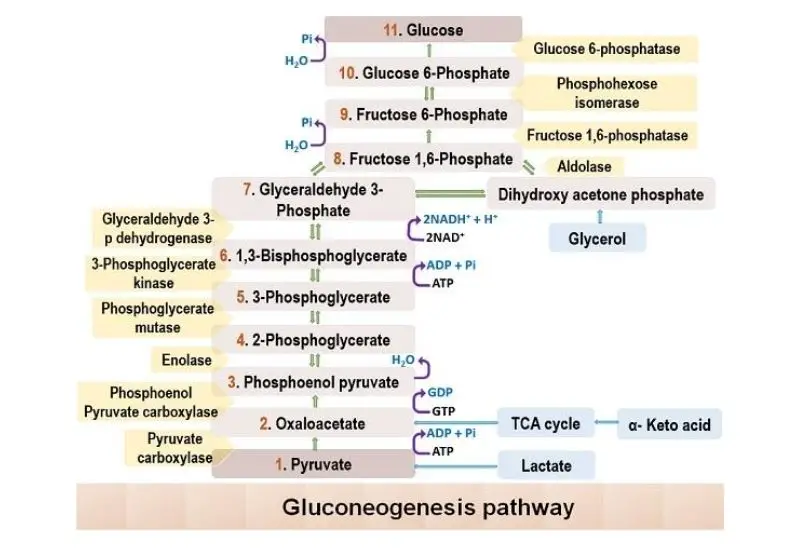
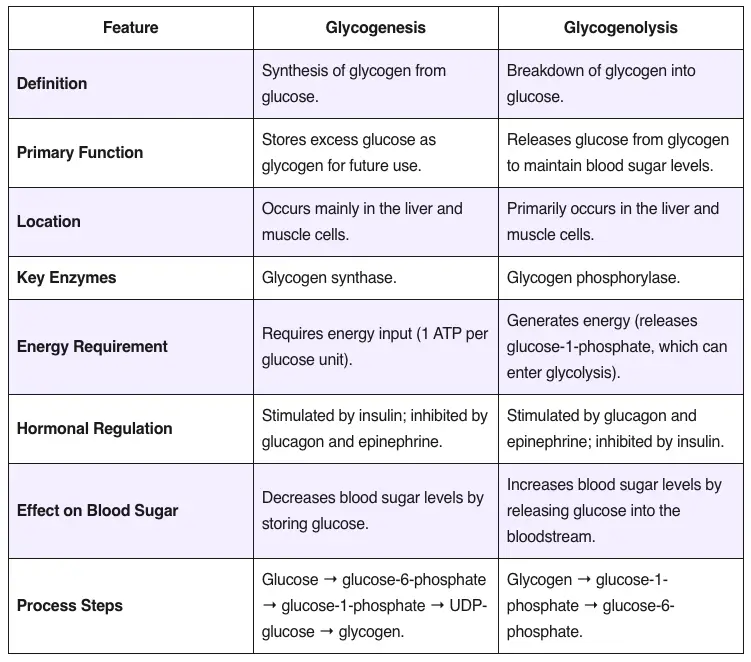
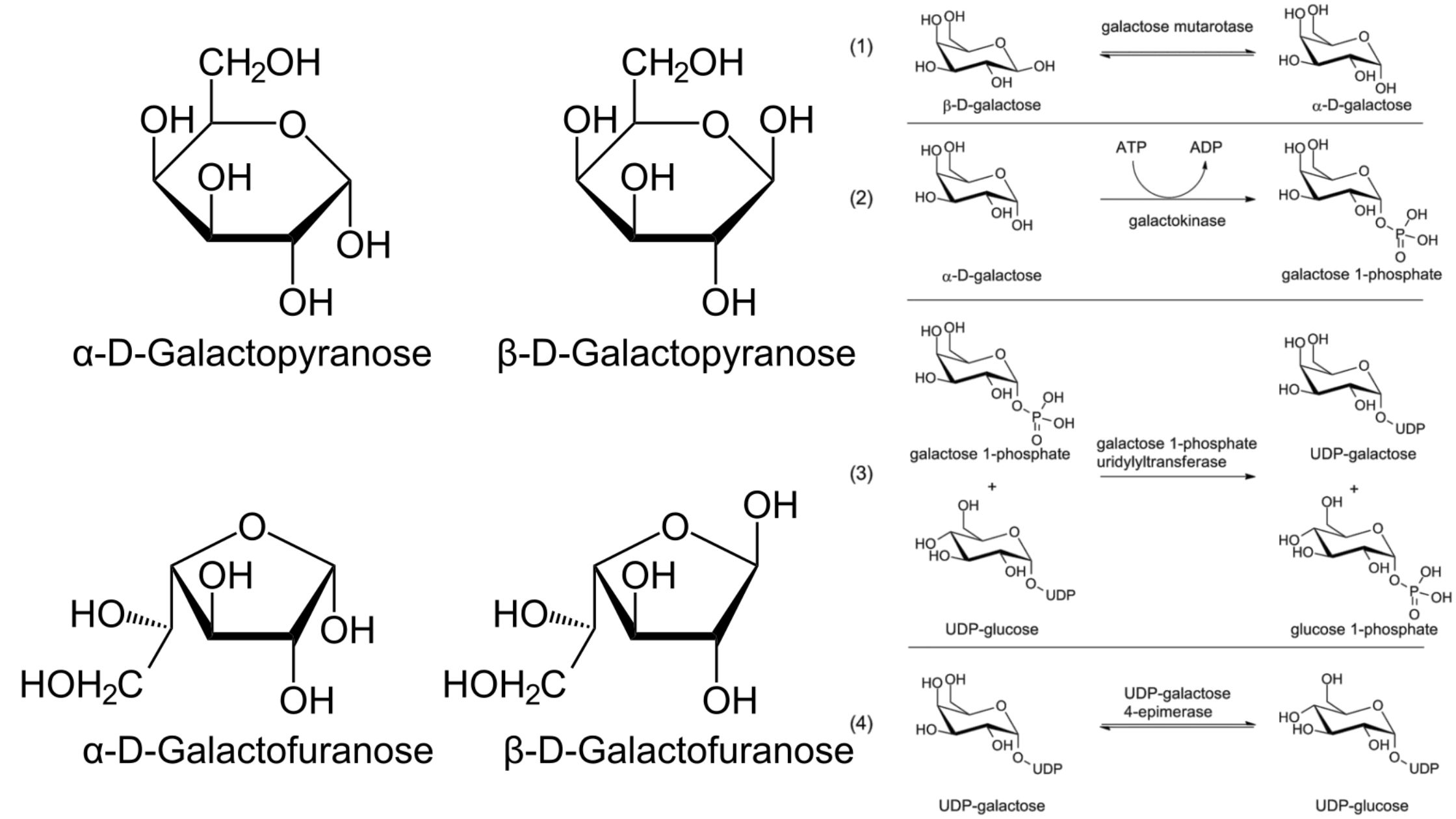
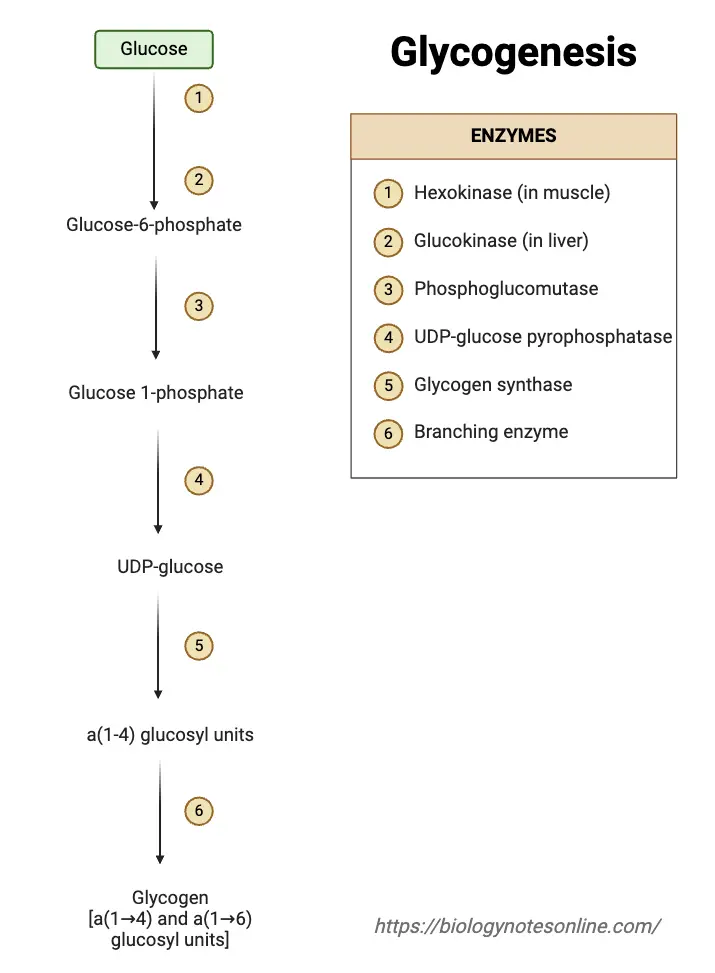
Epi-Fluorescence Microscopy – Principle, Parts, Steps, Uses
Epi-Fluorescence Microscopy is defined as an optical imaging method, which is employed in laboratories for visualization of fluorescent-labeled samples. The technique is widely described as an essential approach, and it has been repeatedly applied in cell studies, tissue examinations, and even in material analysis. In this method, illumination is delivered from the same side / … Read more