Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) – Principle, Composition, Preparation, Uses
Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) is commonly abbreviated as PDA.
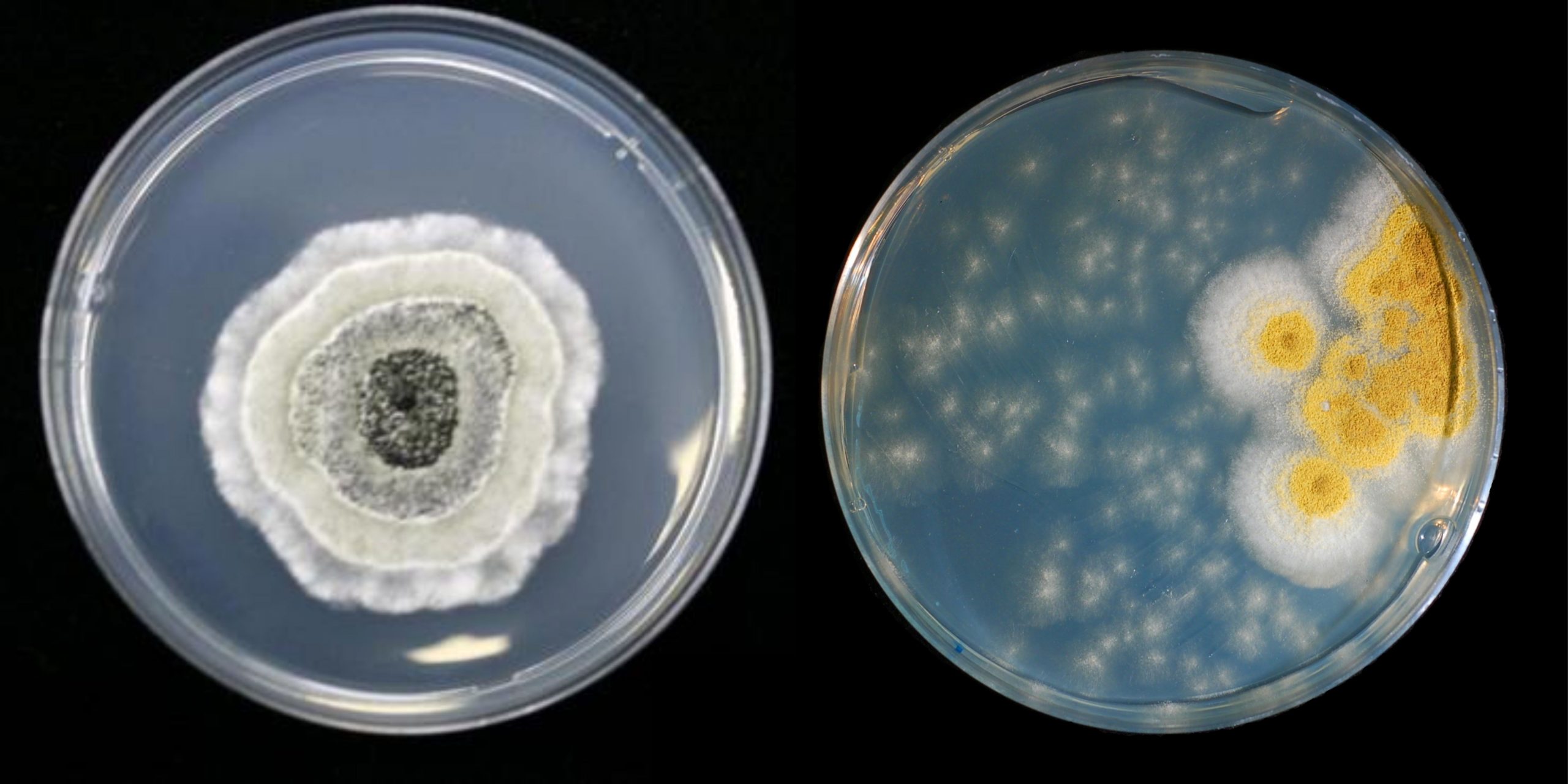
Potato Dextrose Agar has been suggested by APHA and F.D.A.for the count of moulds and yeasts during the testing of food items and dairy products.