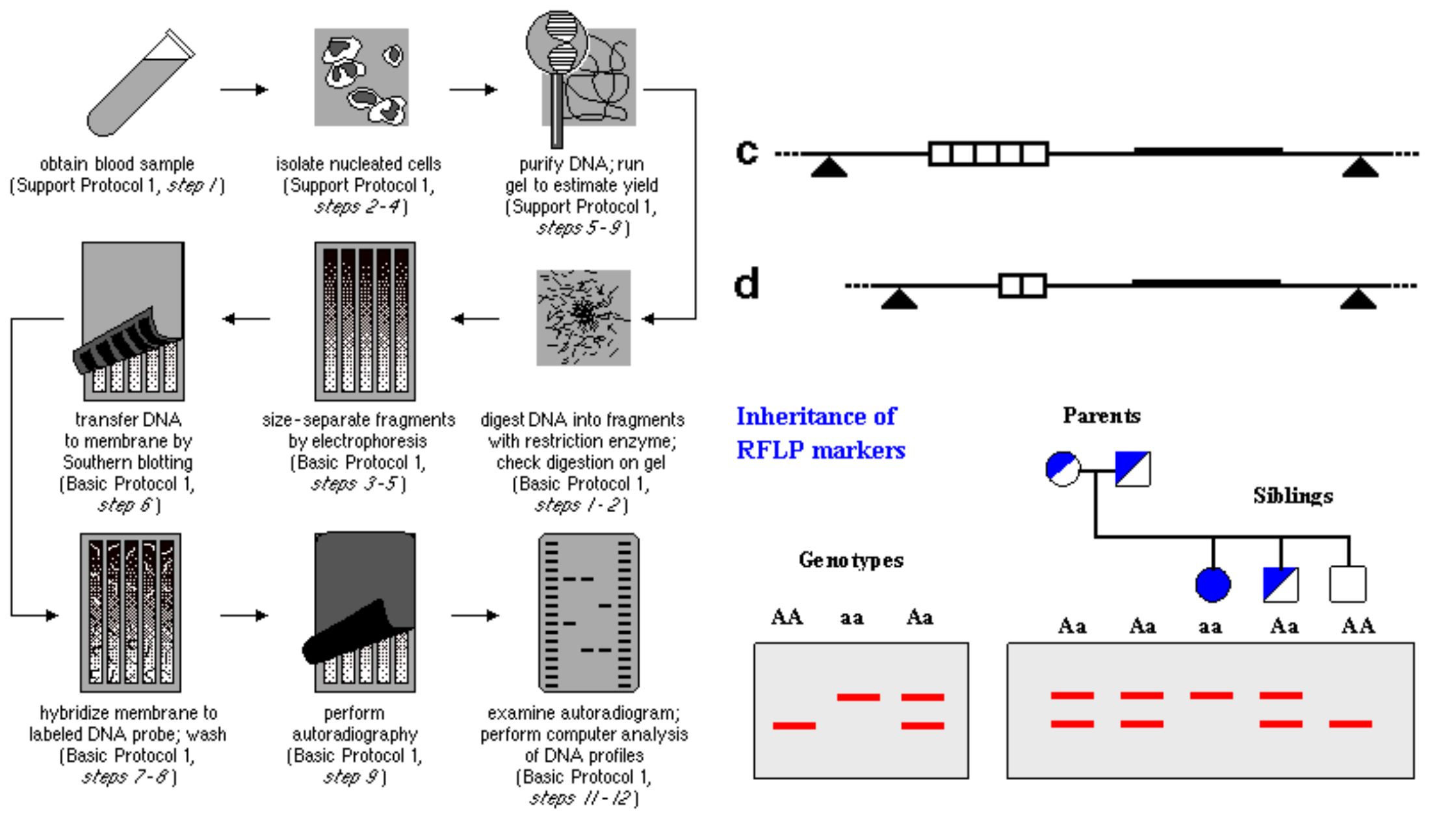
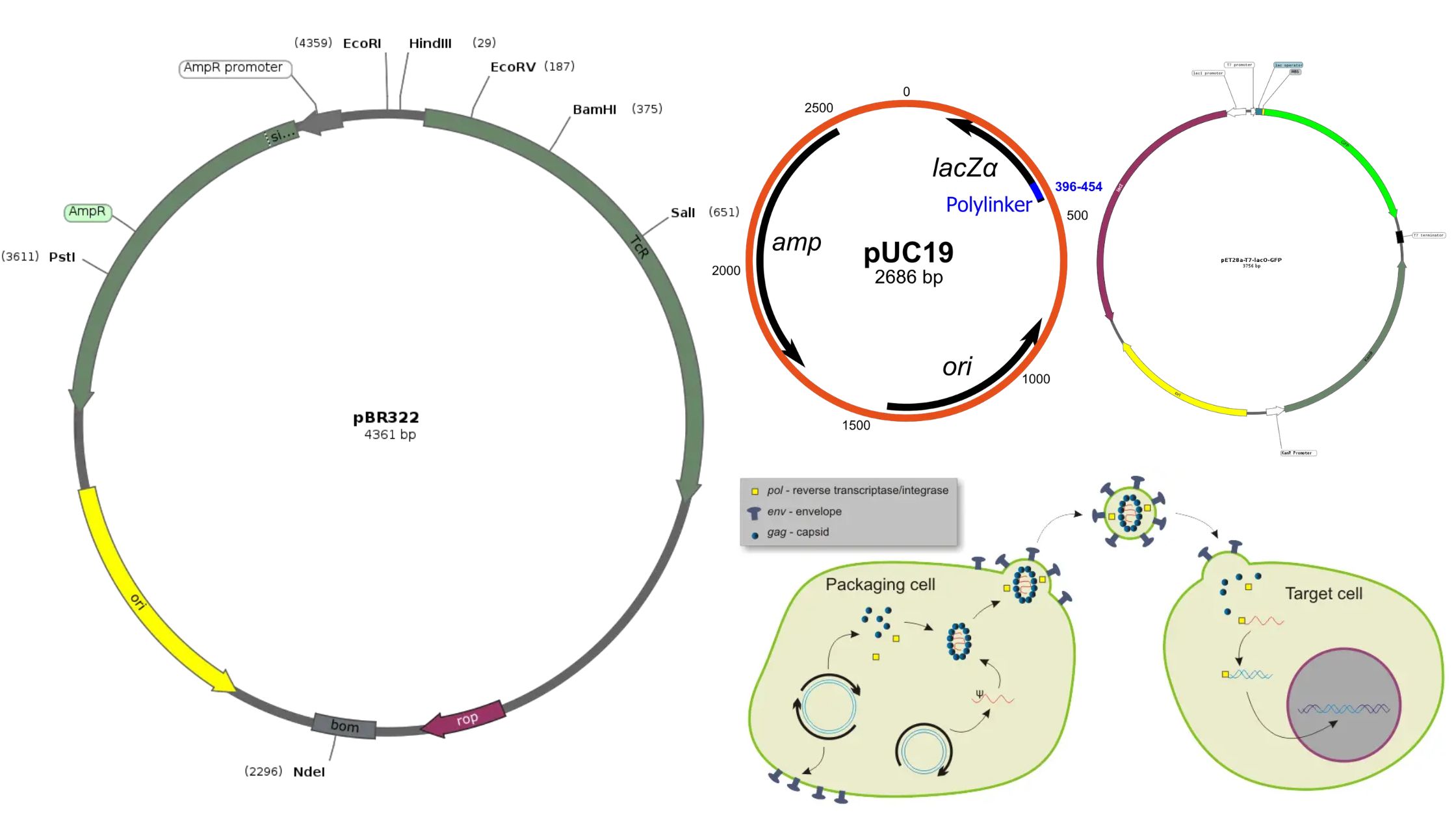
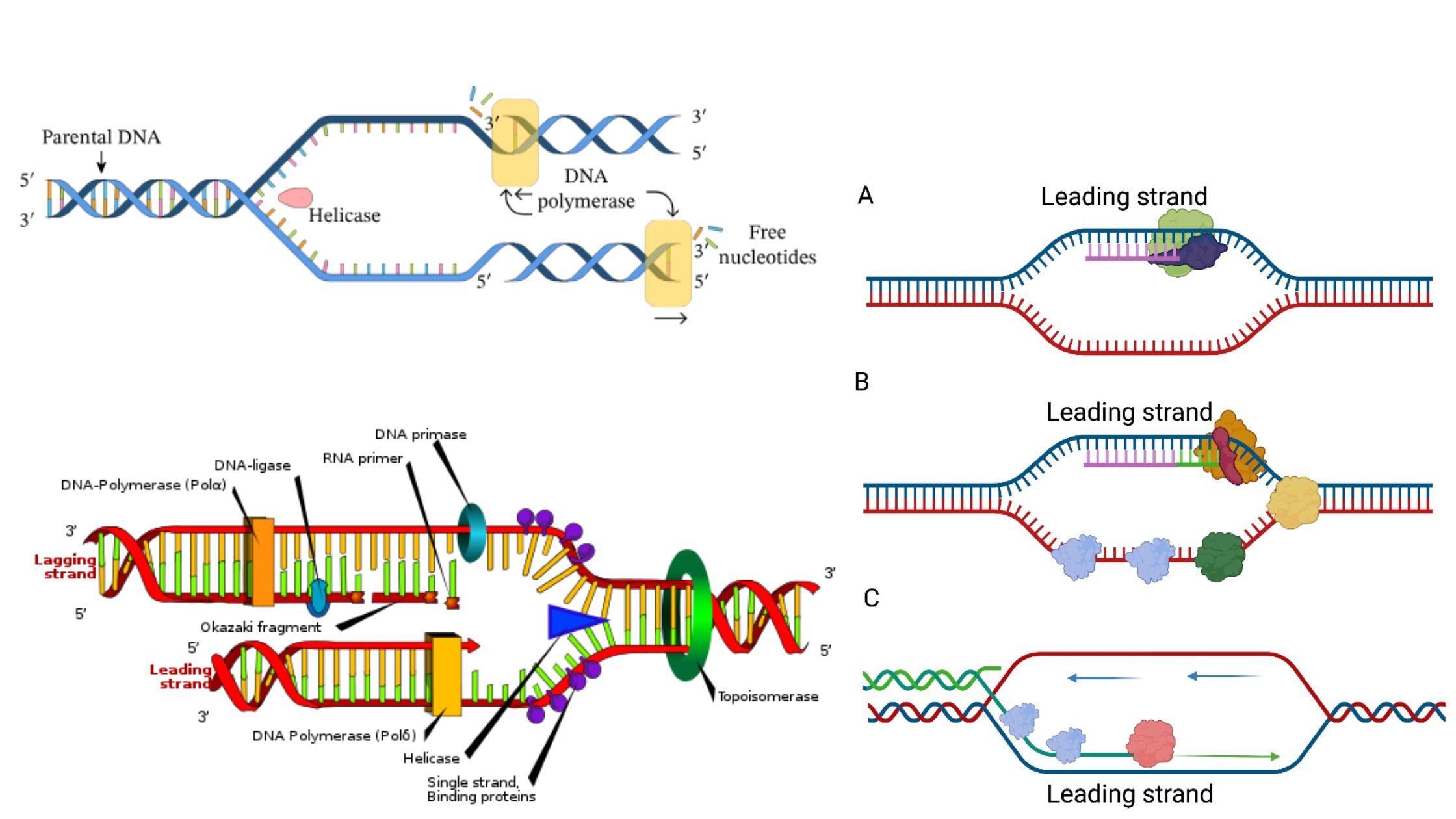
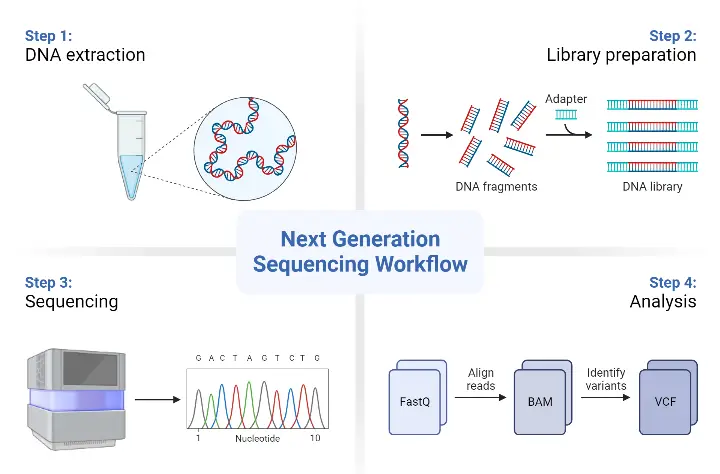
DNA Sequencing – Definition, Principle, Steps, Types, Applications
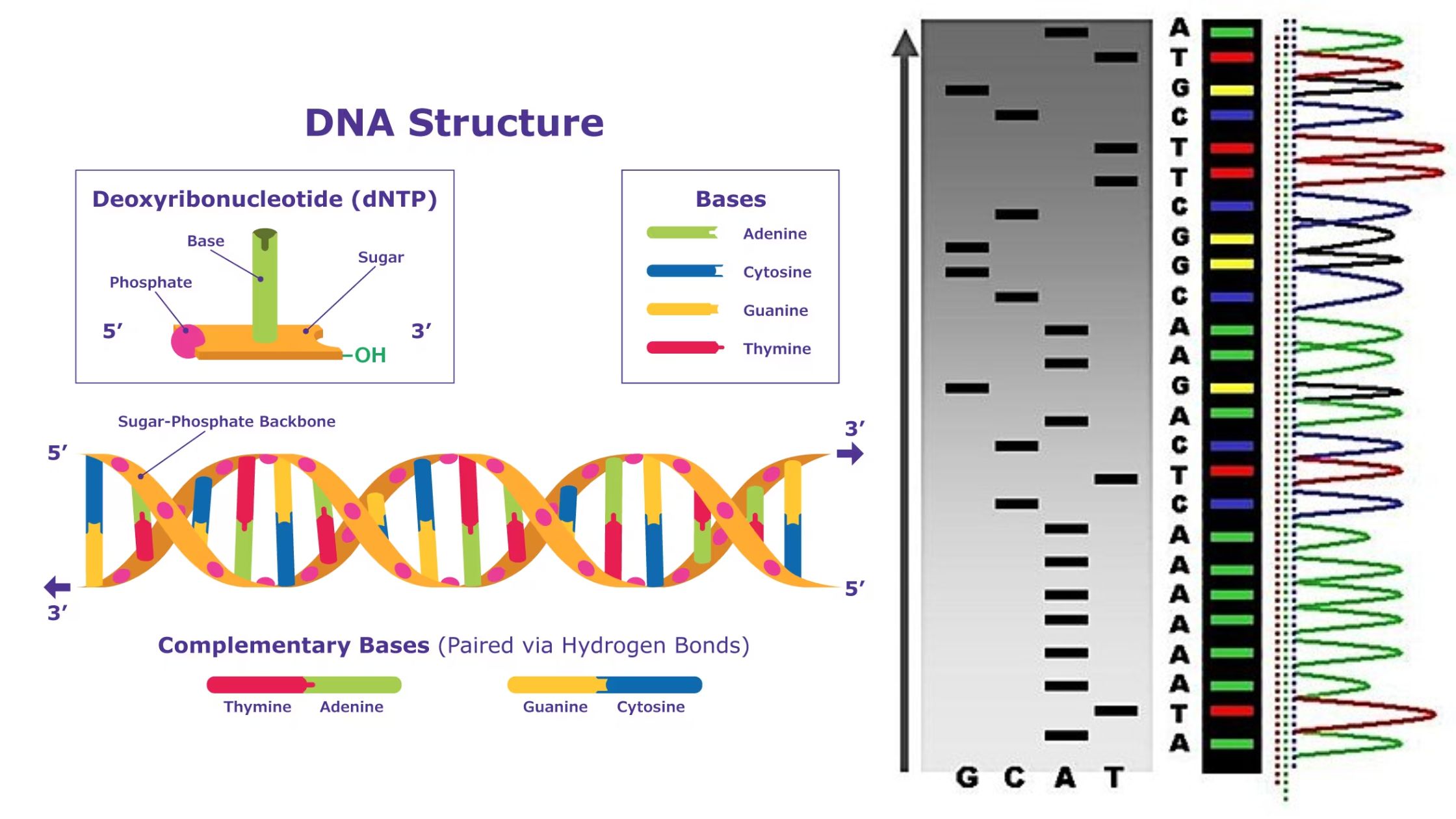
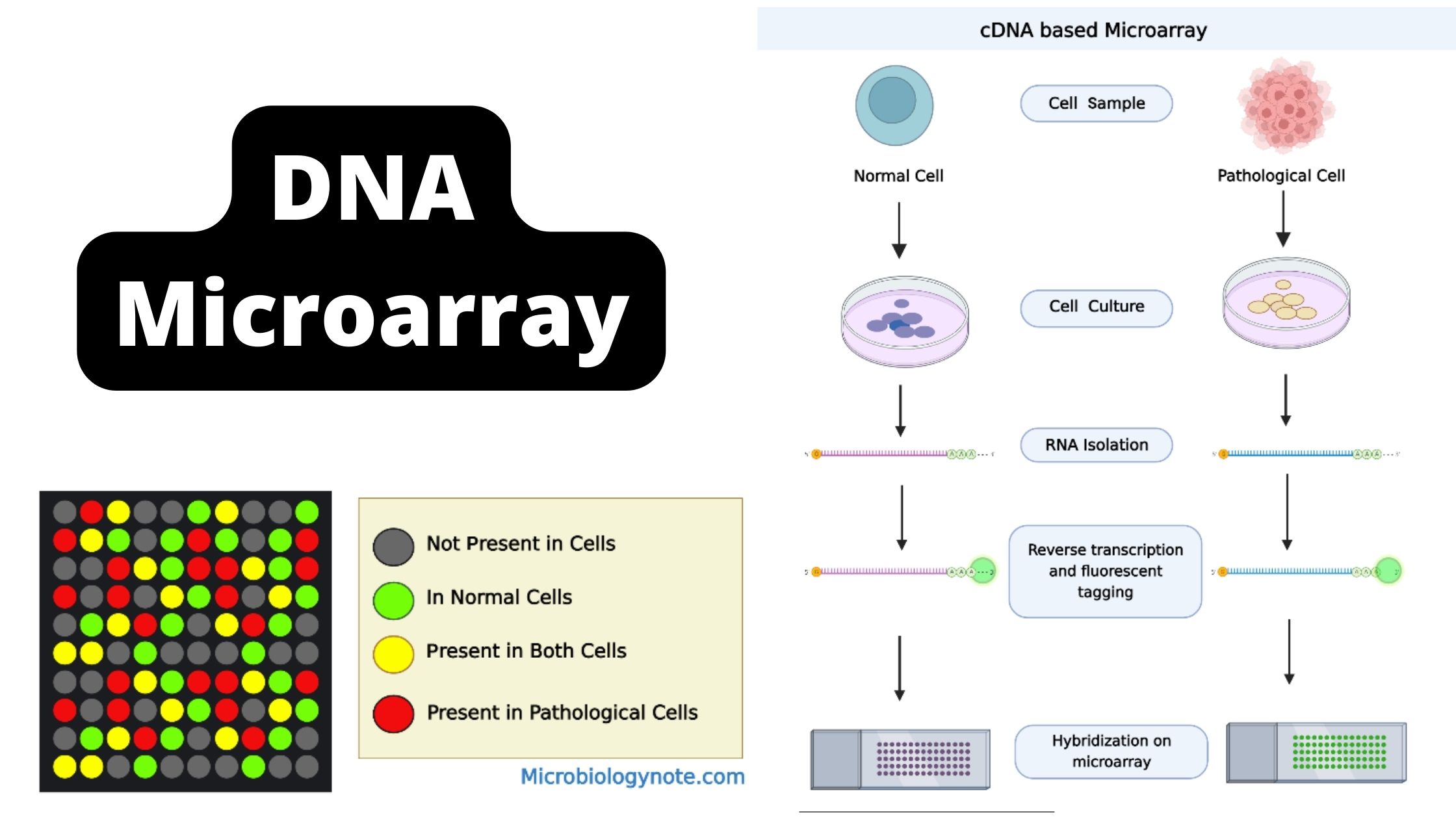
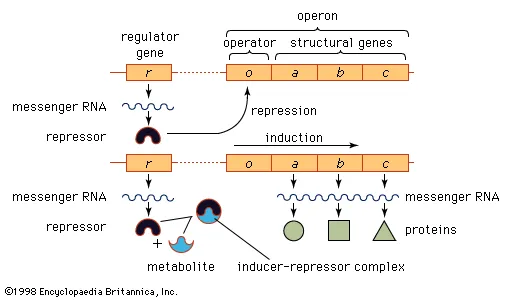
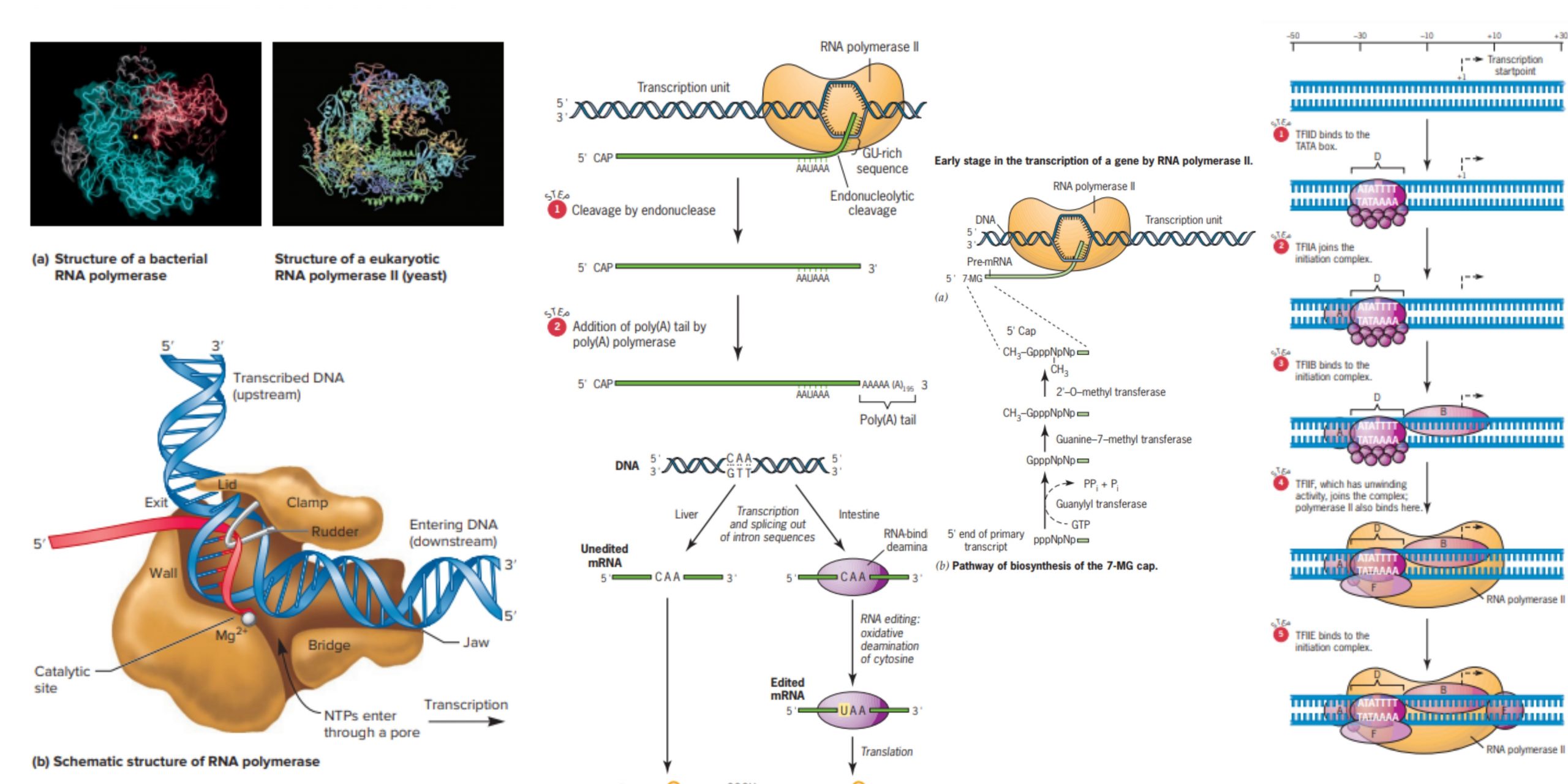
What is DNA Sequencing? Definition of DNA Sequencing DNA sequencing refers to the techniques used to determine the order of the nucleotide bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine within a DNA molecule. Methods of DNA Sequencing DNA sequencing is a crucial technique used in various fields of biological research, allowing scientists to unravel the genetic … Read more