OF (Oxidation-Fermentation)Test – Principle, Purpose, Procedure
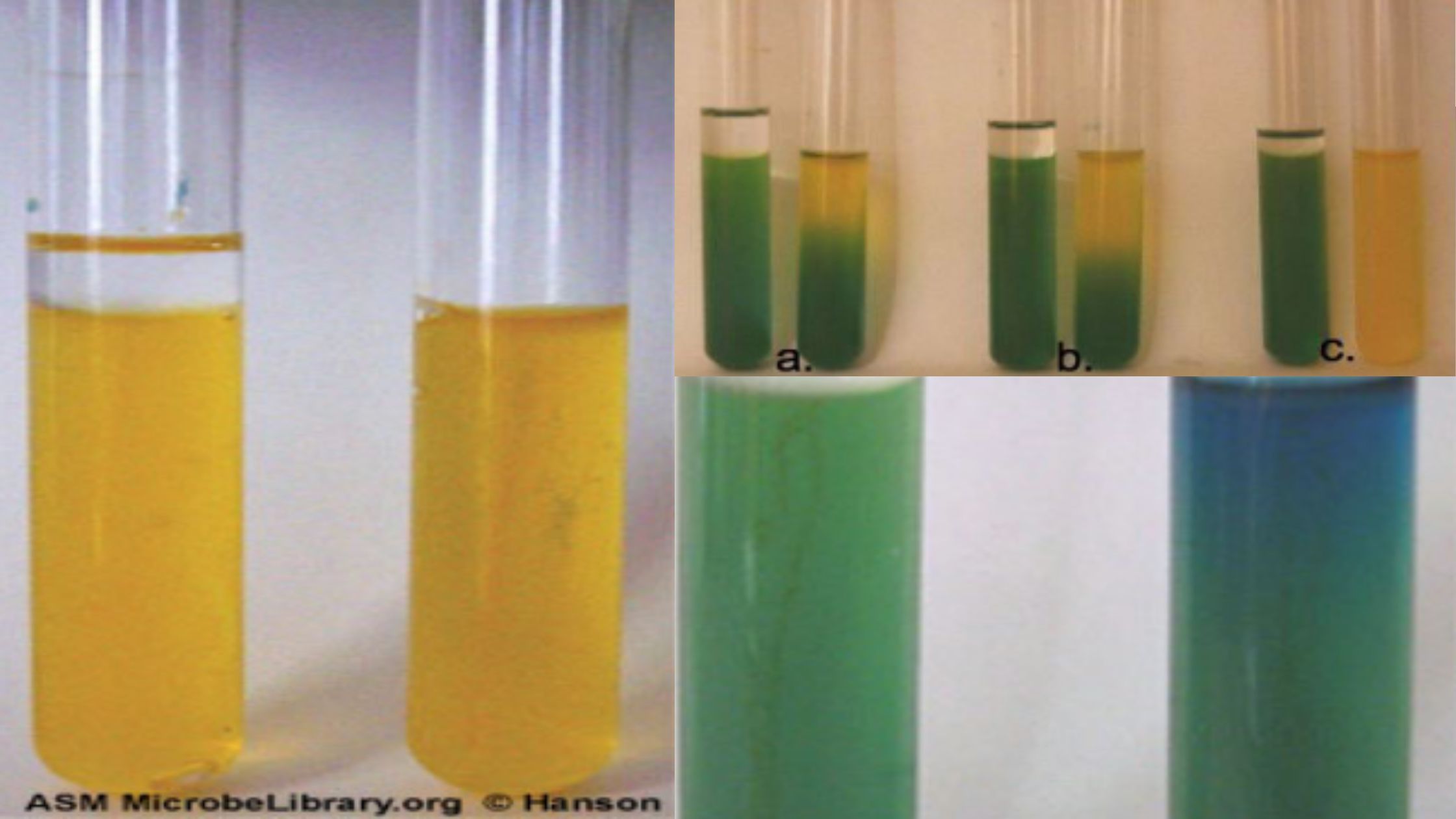
The Oxidation–Fermentation (OF) test is a biochemical test that is used to differentiate bacteria on the basis of their ability to metabolize carbohydrates by oxidative or fermentative pathways. It is the process that helps in identifying whether the organism utilizes carbohydrate in the presence of oxygen or in the absence of oxygen. This test was … Read more