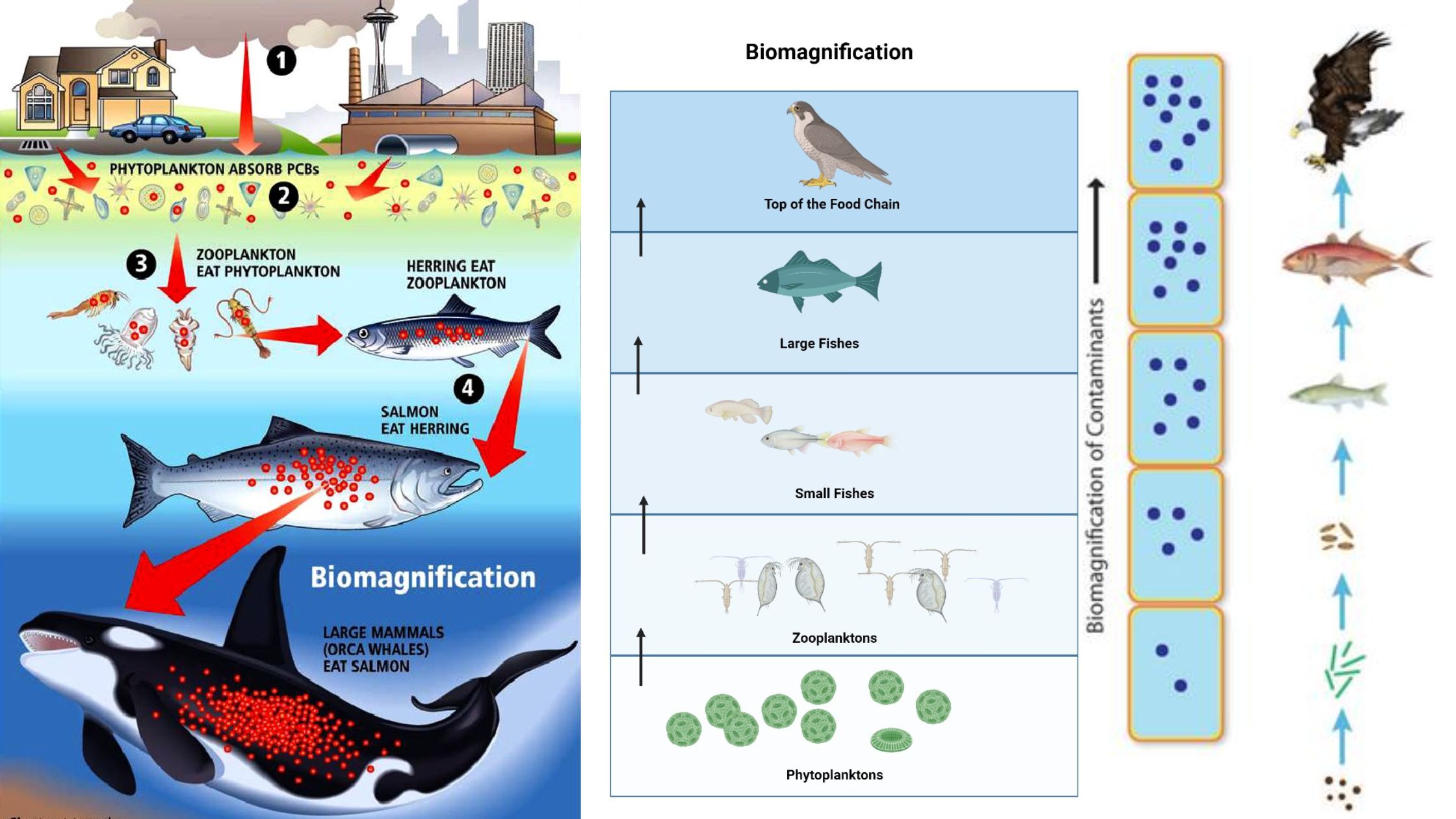
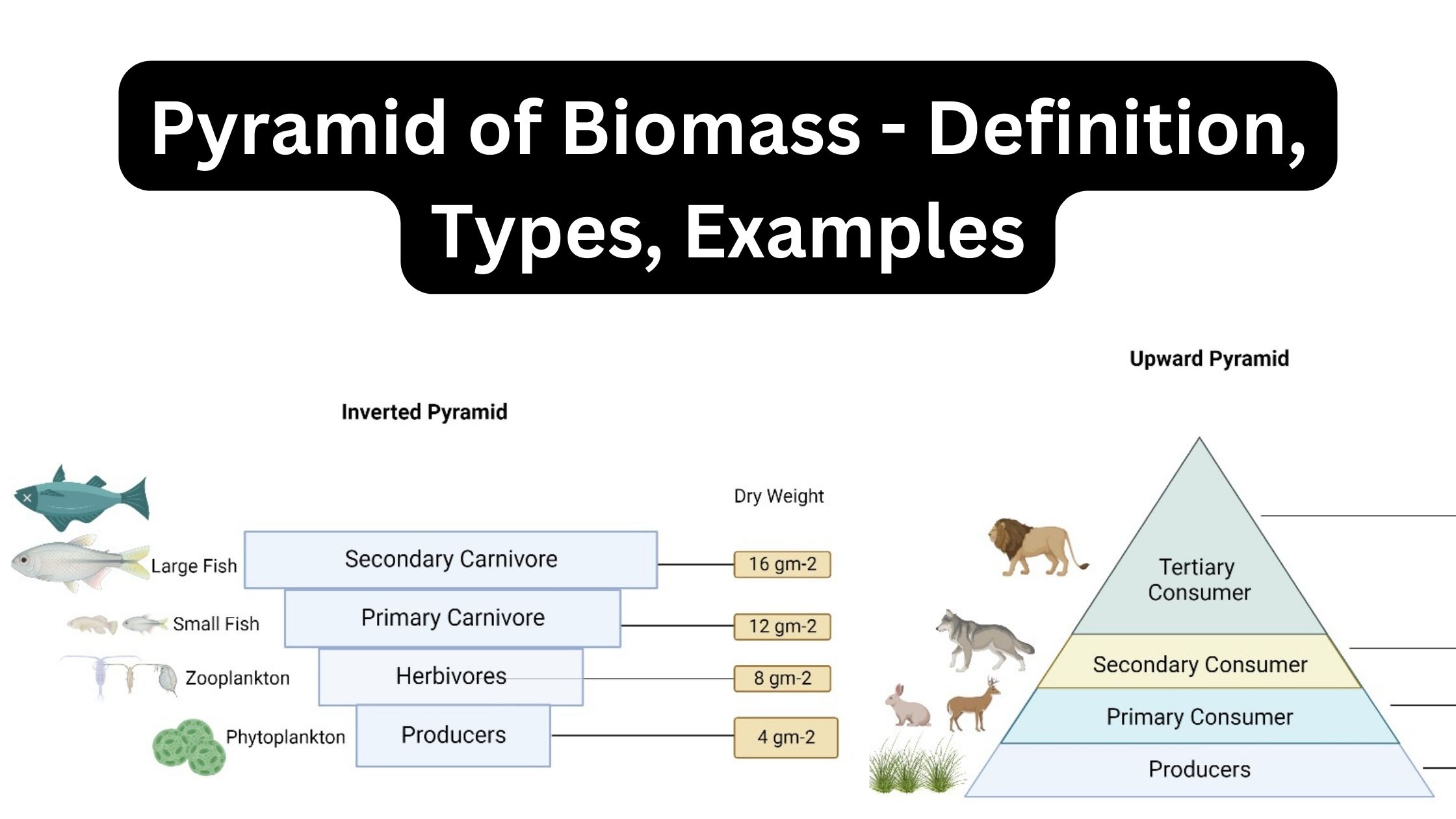
Zonation – Definition, Types, Importance, Example
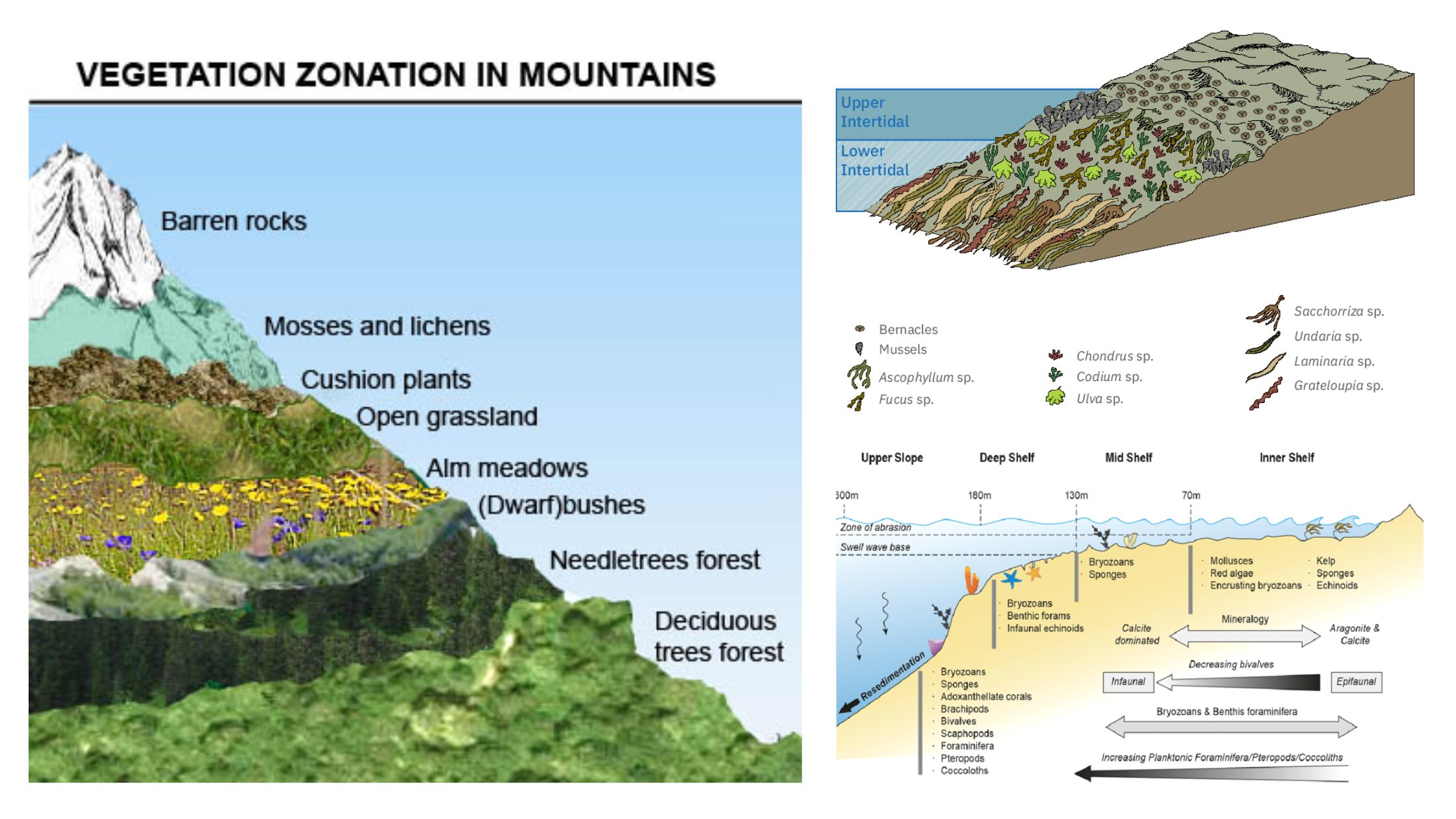
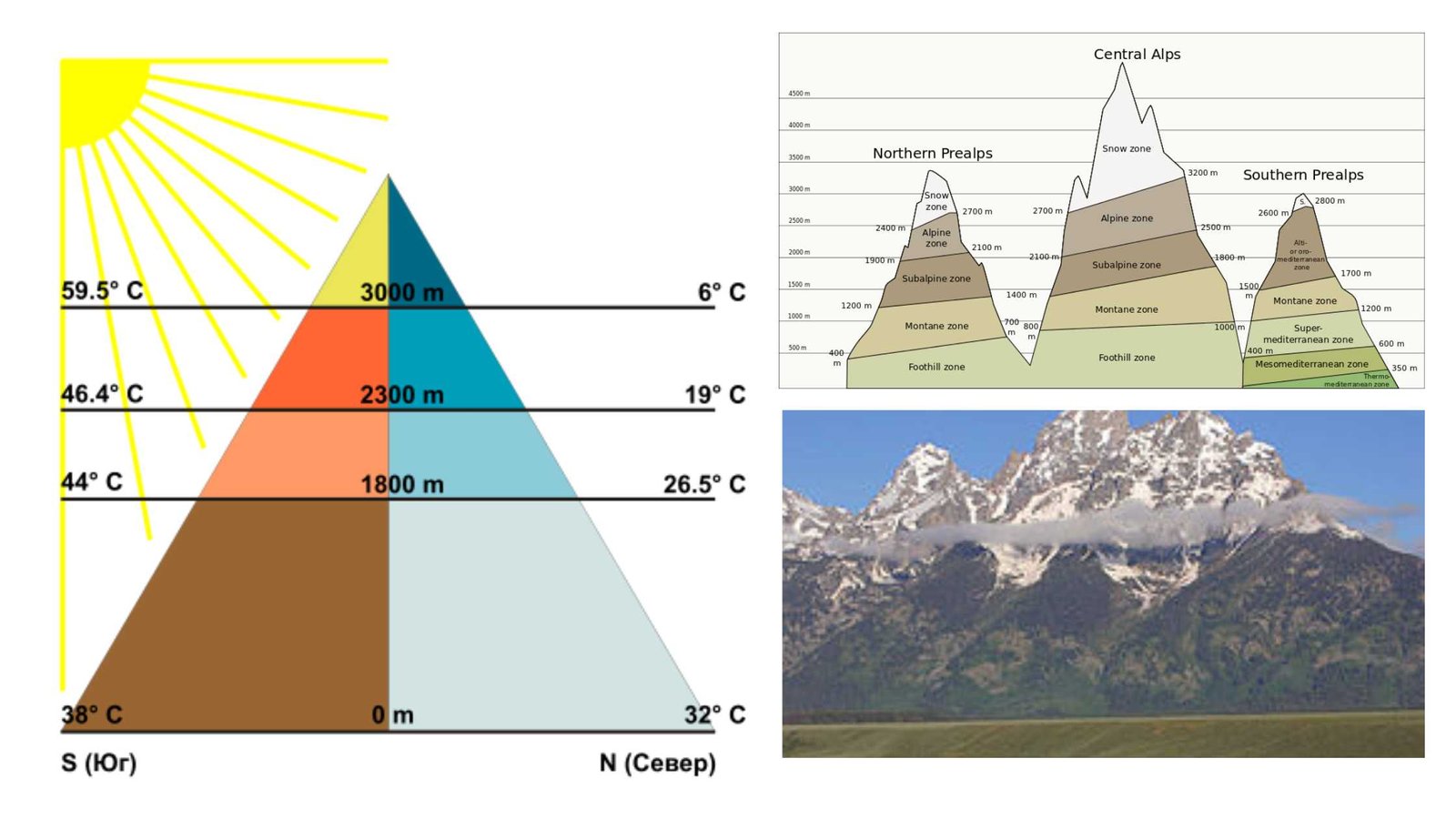
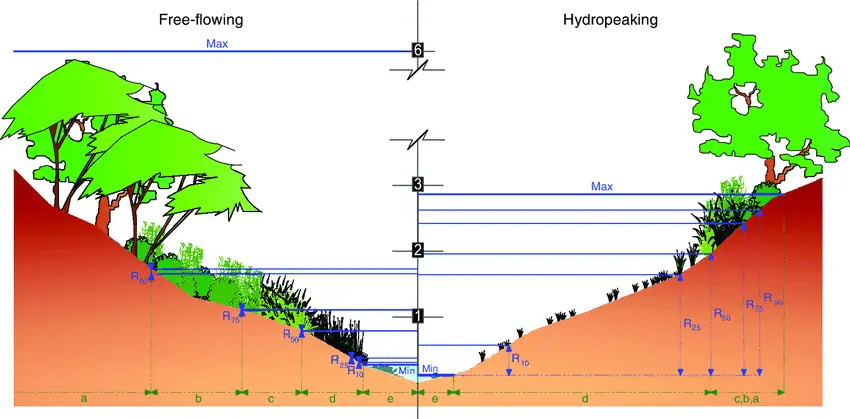
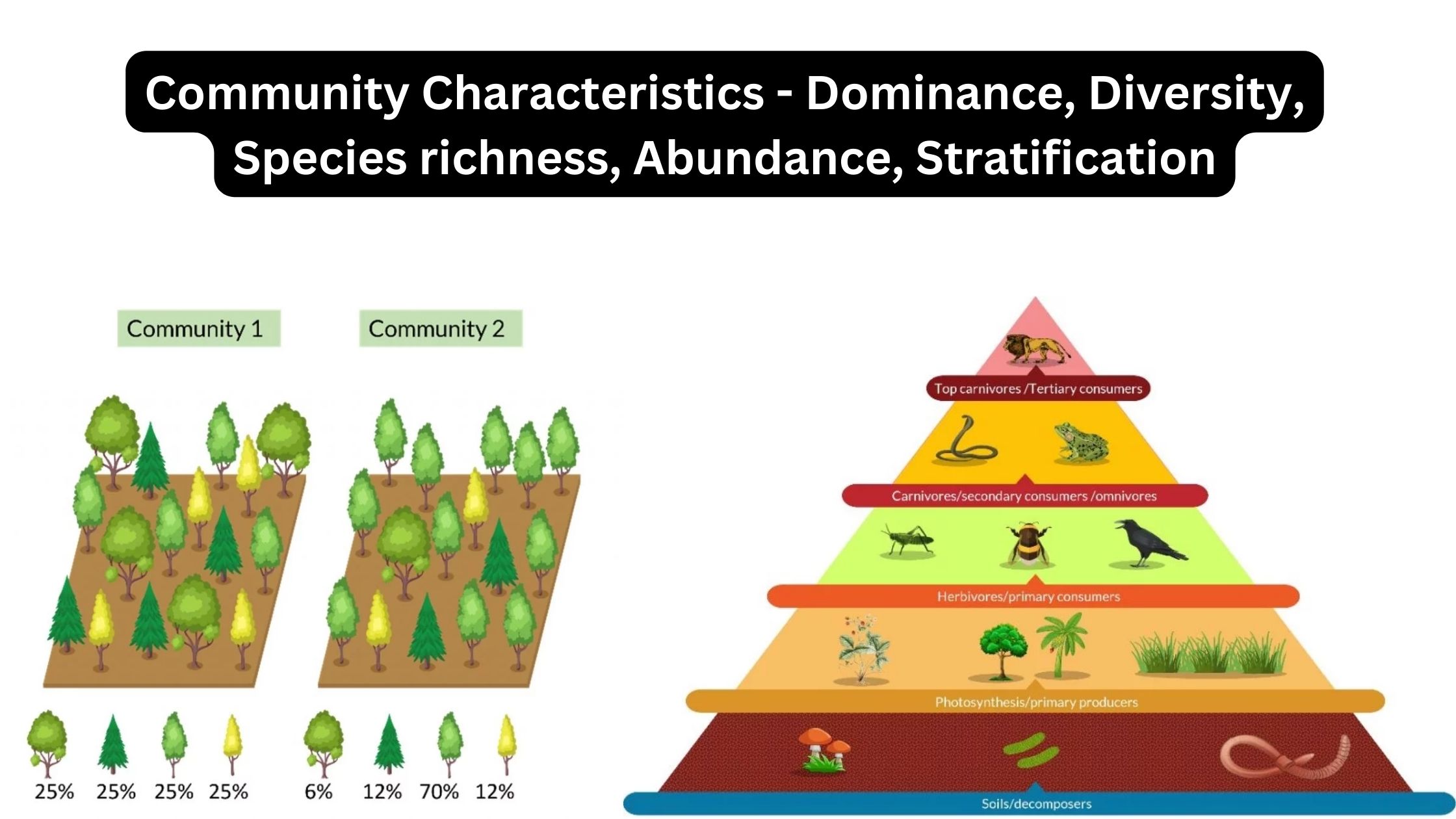
What is Zonation? Definition of Zonation Zonation is the spatial arrangement of distinct ecological communities based on predominant flora and fauna across a gradient, influenced by both biotic and abiotic factors. How Does Zonation Works? Zonation in ecological contexts refers to the distinct stratification or partitioning of habitats or ecosystems into zones, each characterized by … Read more