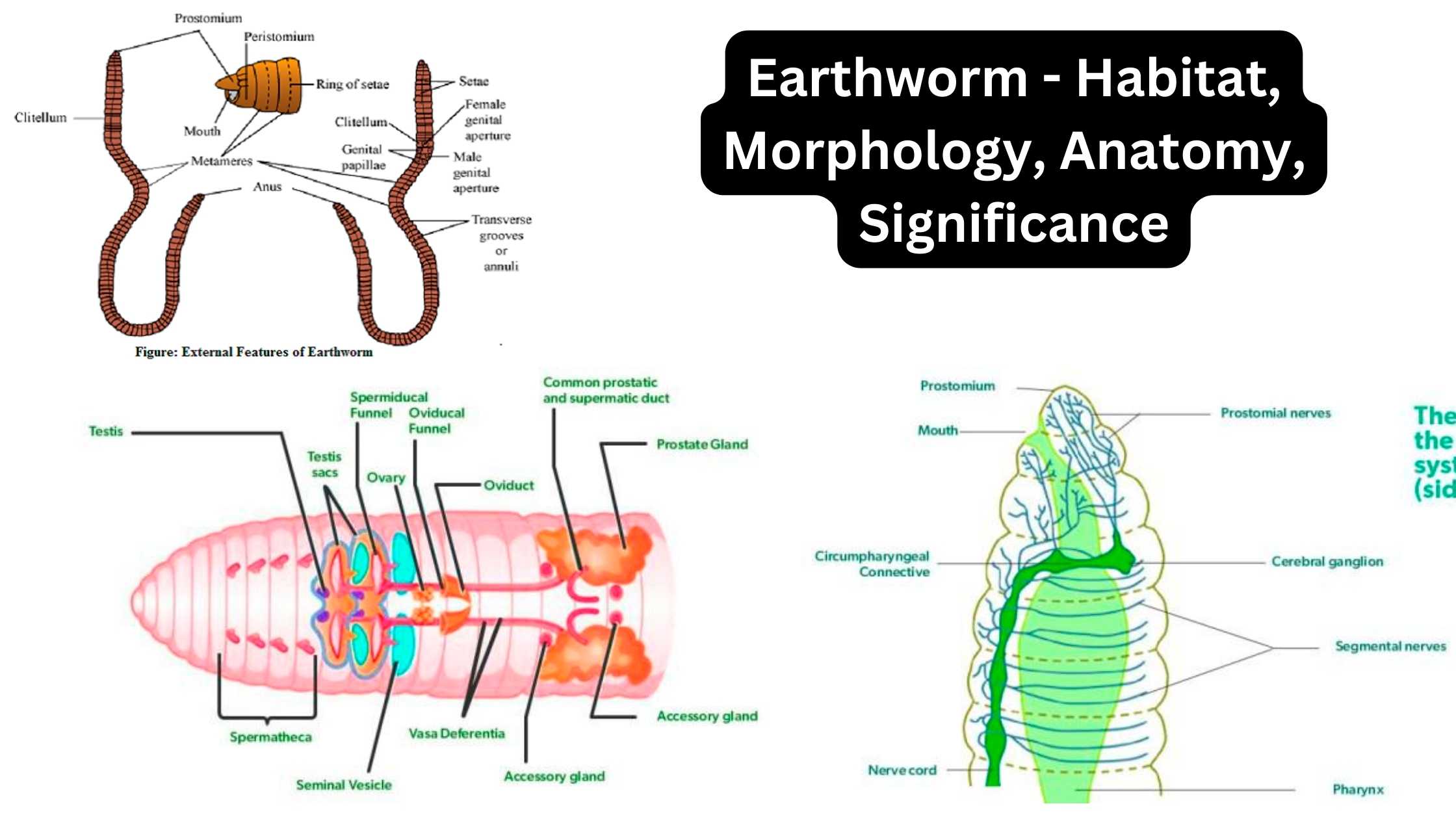
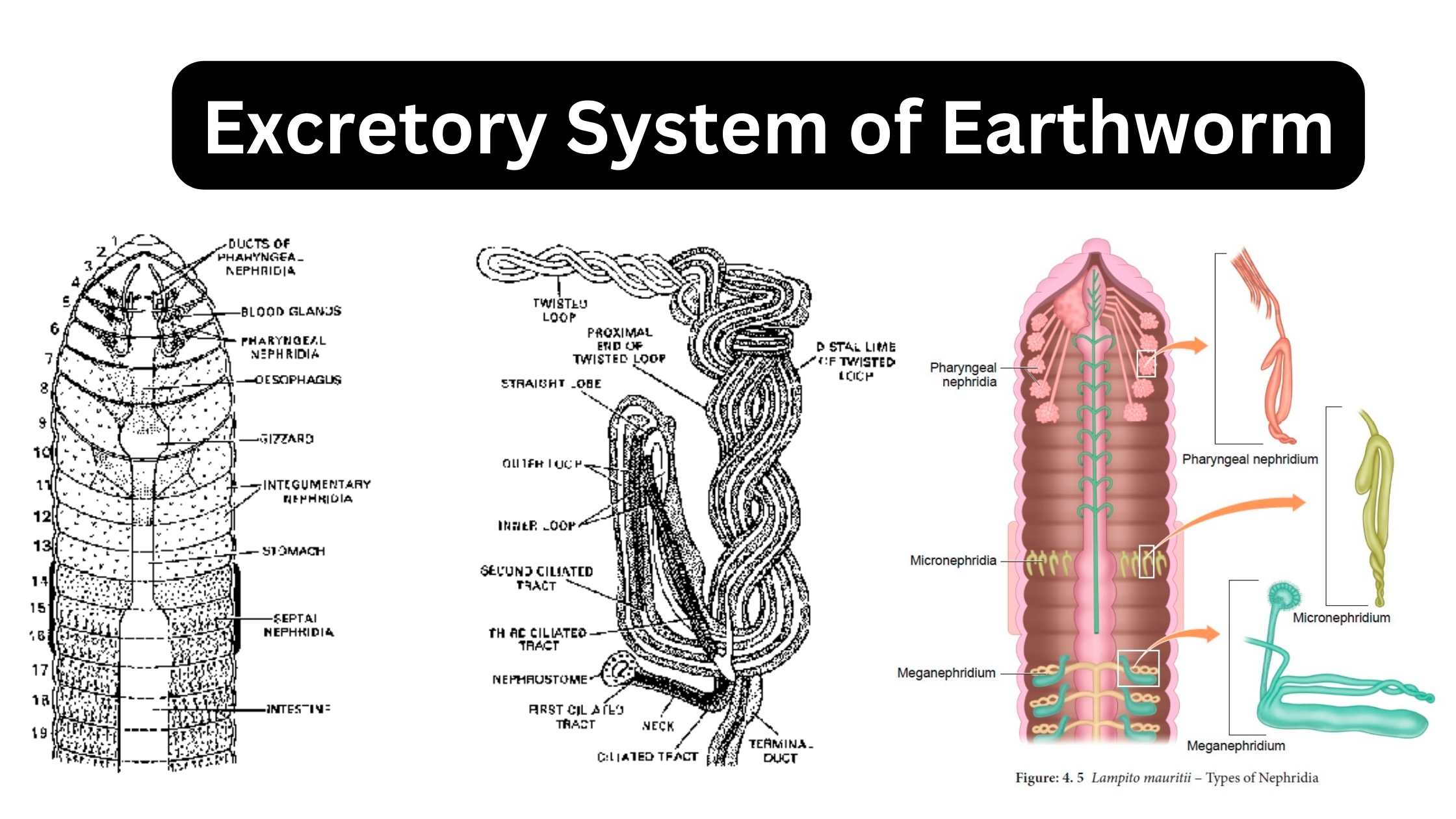
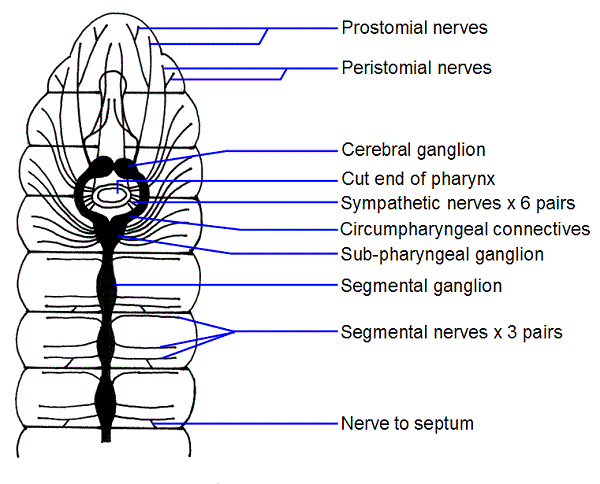
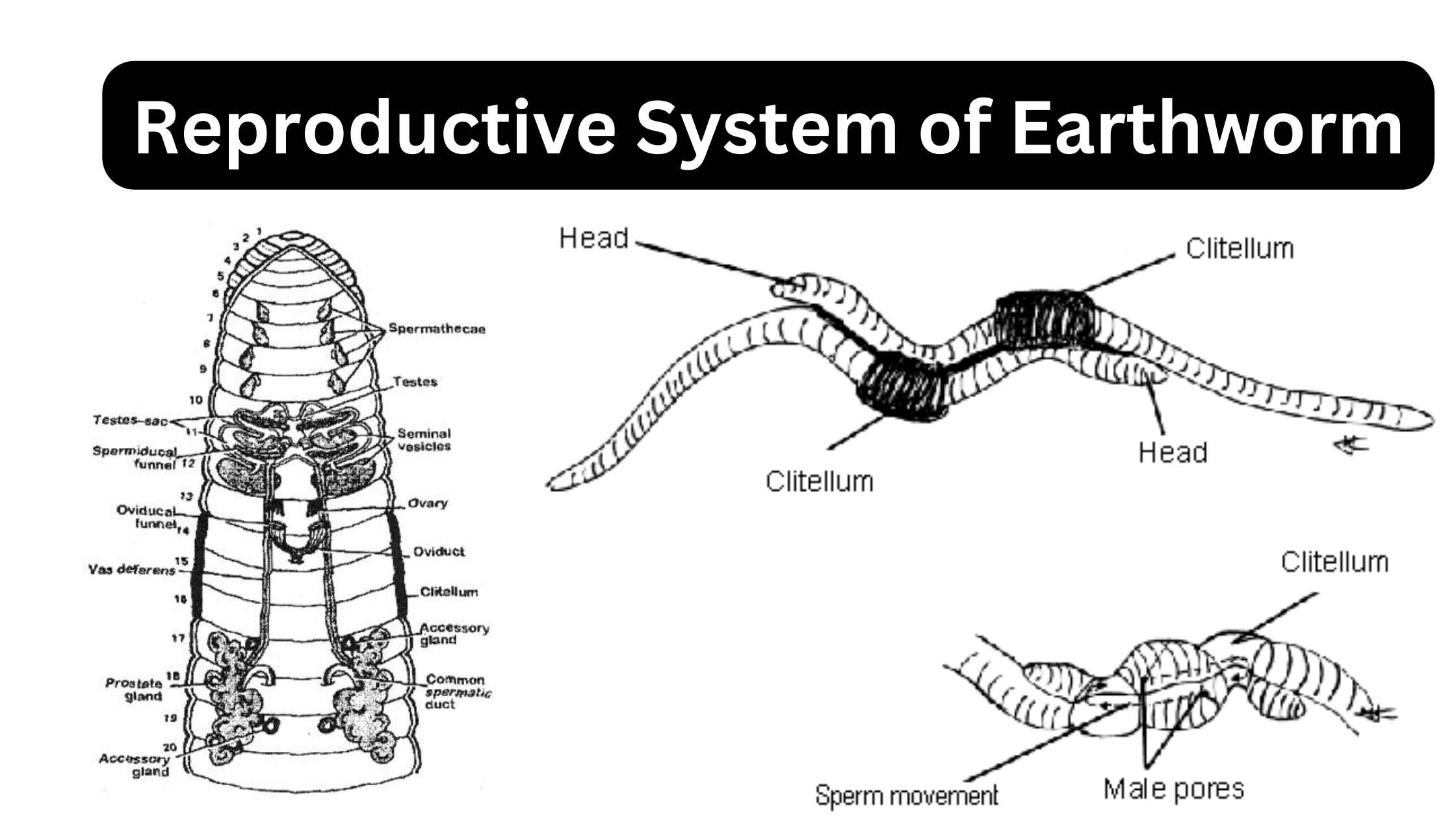
Earthworm – Habitat, Morphology, Anatomy, Significance
What is Earthworm? Classifications of Earthworms Earthworms, commonly known as nightcrawlers, are complex organisms that play a vital role in the ecosystem. Their classification within the biological hierarchy is detailed and sequential, providing a comprehensive understanding of their evolutionary lineage and biological significance. Habit and habitat of Earthworm Earthworms are fascinating creatures that play a … Read more